Chapter 9: Articulations
1/285
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
286 Terms
The place where a bone meets another bone, cartilage, or teeth is known as what?
joint or articulation
What is the study of joints called?
arthrology
Articulations are classified into categories based on what?
joint structure
mobility
more mobility=?
less stability (& vice versa)
Rank the following in order from least stability to most stability/most mobility to immobile: elbow joint, suture, hip joint, glenohumeral joint, intervertebral joints
glenohumeral joint (shoulder), hip joint, elbow joint, intervertebral joints, suture
What are the different classifications by structure?
fibrous joint
cartilaginous joint
synovial joint
What are the different classifications by function?
synarthrosis
amphiarthrosis
diathrosis
fibrous joints are bones held together by?
dense regular CT
cartilaginous joints are bones are joined by?
cartilage
synovial joints are bones separated by?
fluid-filled cavities (synovial fluid)
synarthrosis
immobile joint
amphiarthrosis
slightly mobile joint
diarthrosis
freely moveable joint
What are the different types of fibrous joints?
gomphoses
sutures
syndesmoses
gomphoses are what kinds of joints and found where?
fibrous joints
between teeth and maxilla and mandible
what kind of mobility do gomphoses joints have?
synarthroses
each tooth is held in socket by ?
periodontal ligament
sutures are what kinds of joints and found where?
fibrous joints
between skull bones
what kind of mobility do sutures have?
synarthroses
Sutures may eventually ossify to become what?
synostoses
Syndesmoses are what kinds of joints and found where?
fibrous joints
between parallel bones in forearm and leg (tibia/fibula, ulna/radius)
What kind of mobility do syndesmoses joints have?
amphiarthrosis
__________________ connect radius to ulna and tibia to fibula
interosseous membranes
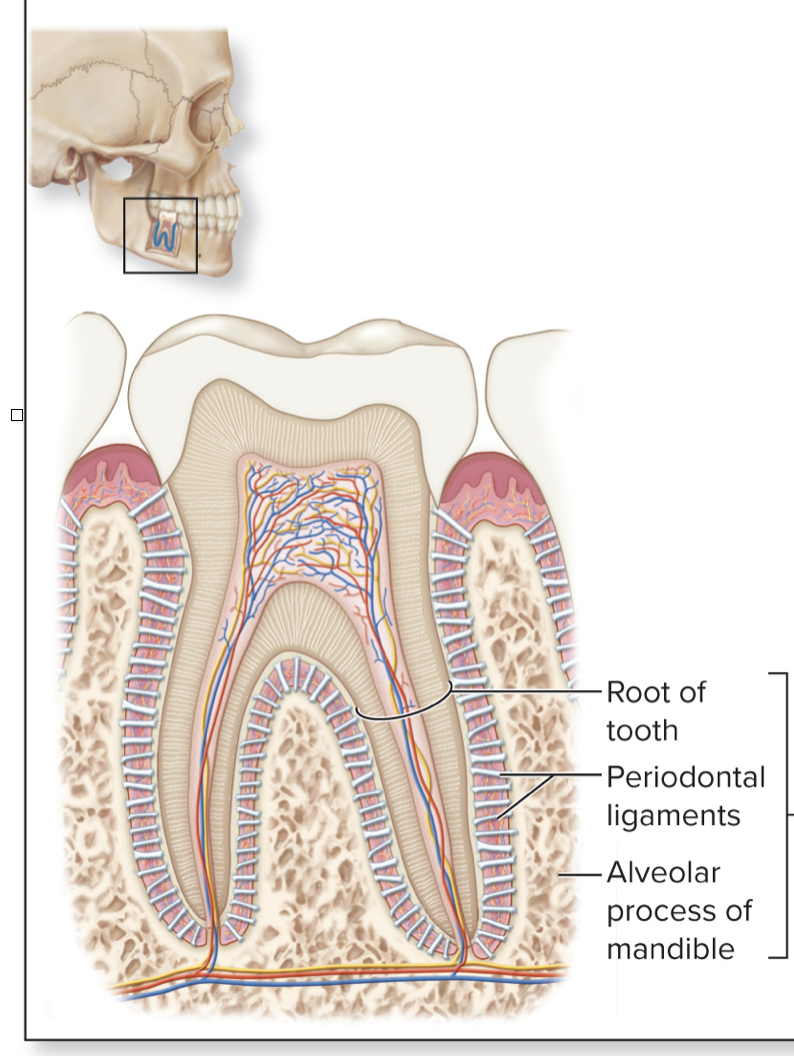
What kind of joint can be found in this image?
gomphosis
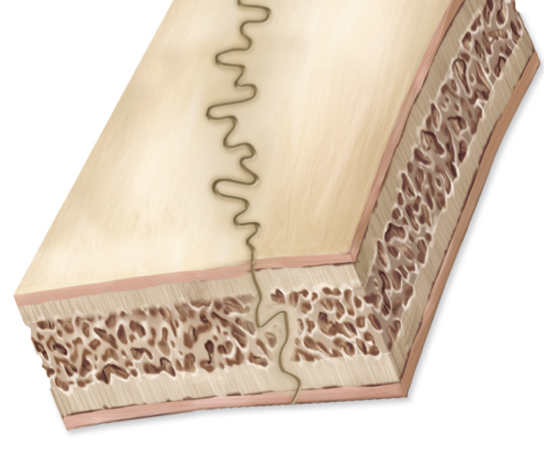

What kind of joint can be found in this image?
sutures
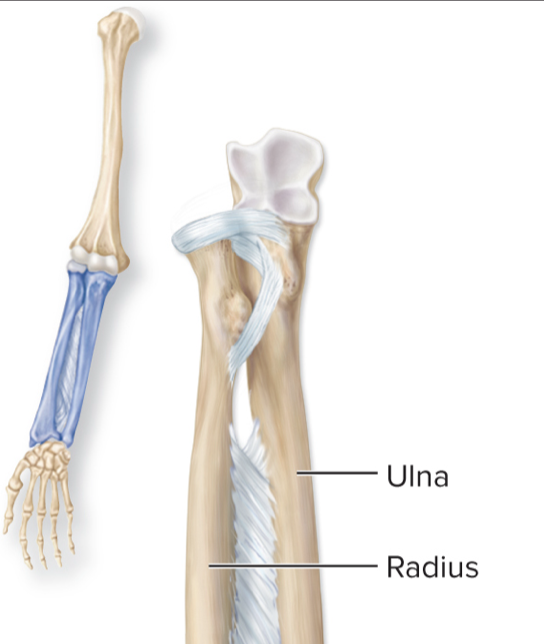
What kind of joint can be found in this image?
syndesmosis
What are the different cartilaginous joints?
synchondroses
symphyses
synchondroses are what kinds of joints and joined by what?
cartilaginous joints
joined by hyaline cartilage
What kind of mobility do synchondroses joints have?
synarthroses
What are examples of synchondroses joints?
epiphyseal plate, costochondral joints
symphyses are what kinds of joints and joined by what?
cartilaginous joints
joined by pad of fibrocartilage
What kind of movement do symphyses joints have?
amphiarthroses
What are examples of symphyses joints?
pubic symphysis, intervertebral joints
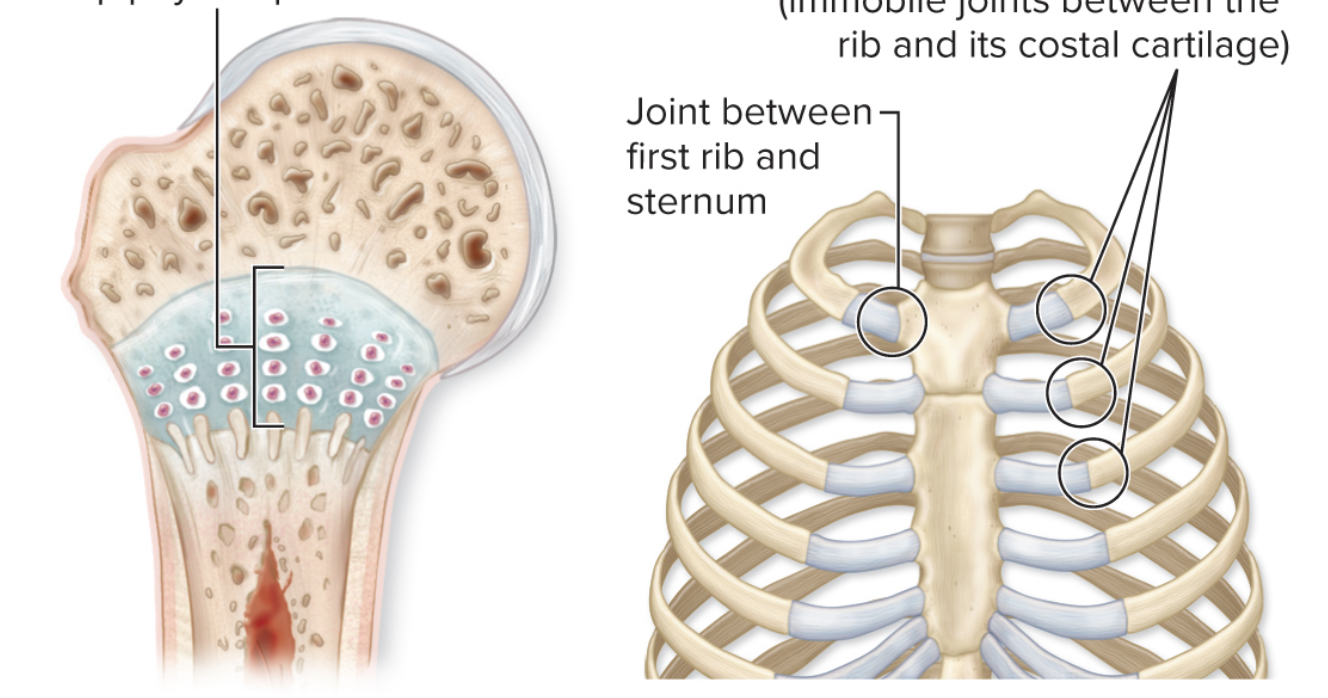
What kind of joints can be found in this image?
synchondroses
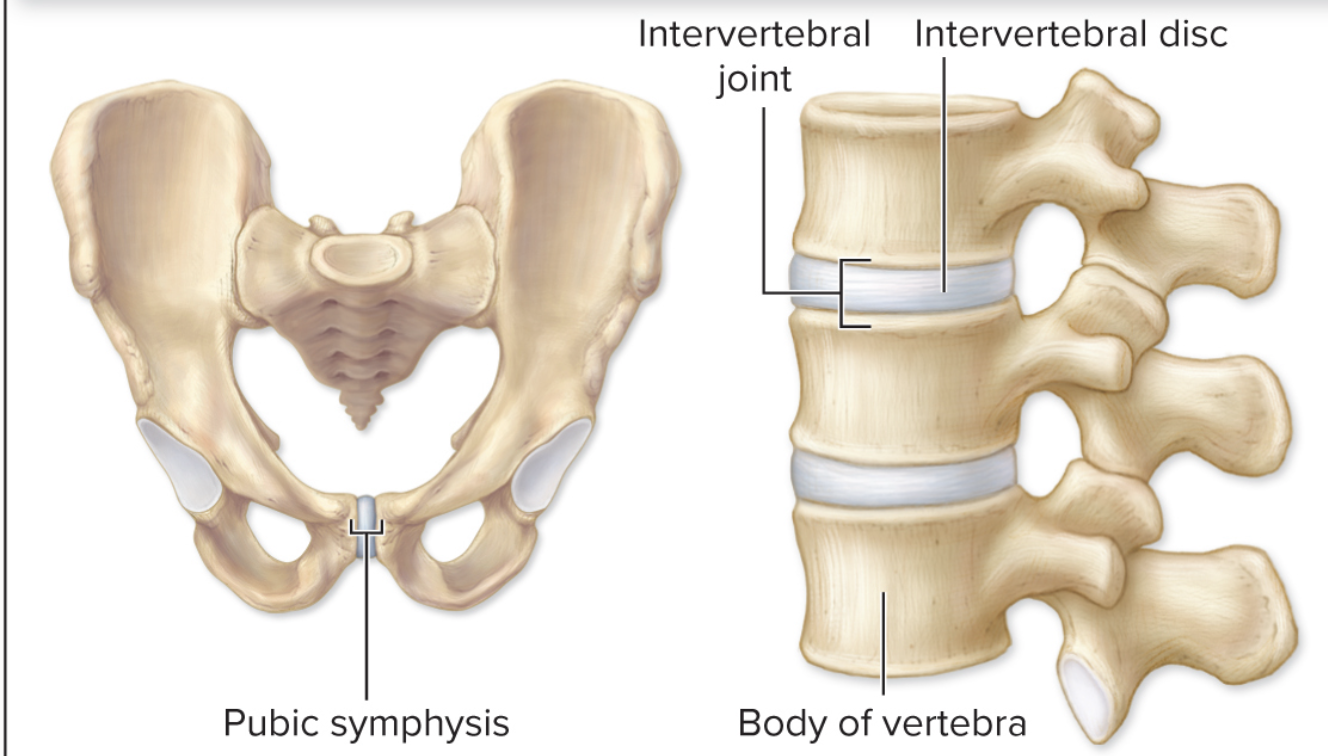
What kind of joints can be found in this image?
symphyses
all synovial joints share several structural features
articular capsule contains two layers
contains articular cartilage
articular capsule contains two layers which are?
outer fibrous layer
inner synovial membrane
What is the outer fibrous layer of articular capsule composed of and what is its function?
dense regular CT
strengthens joint
What is the function of inner synovial membrane of the articular capsule?
secretes lubricating synovial fluid (lubricates the joint)
What is the function of articular cartilage of articular capsule?
reduces friction and acts as shock absorber
What is the articular cartilage of articular capsule made up of?
hyaline cartilage that covers articulating surfaces
What is the space between articulating bones called?
joint cavity
joint cavity contains small amounts of ?
synovial fluid
What is the function of synovial fluid?
lubricates articular cartilages, nourishes chonrocytes of articular cartilage and absorbs shock during compression of the joint
ligaments connect?
bone to bone
ligaments are?
dense regular CT that strengthens, reinforces joint capsule
Where are extrinsic ligaments located?
outside capsule
What are intrinsic ligament?
thickenings of capsule
sensory nerves detect?
pain and stretch
blood vessels nourish?
the joint
what are articulating bones separated by a joint cavity called?
synovial joints
what kind of movement do synovial joints have?
diarthroses
What are examples of synovial joints?
joints of the shoulder, elbow, and knee
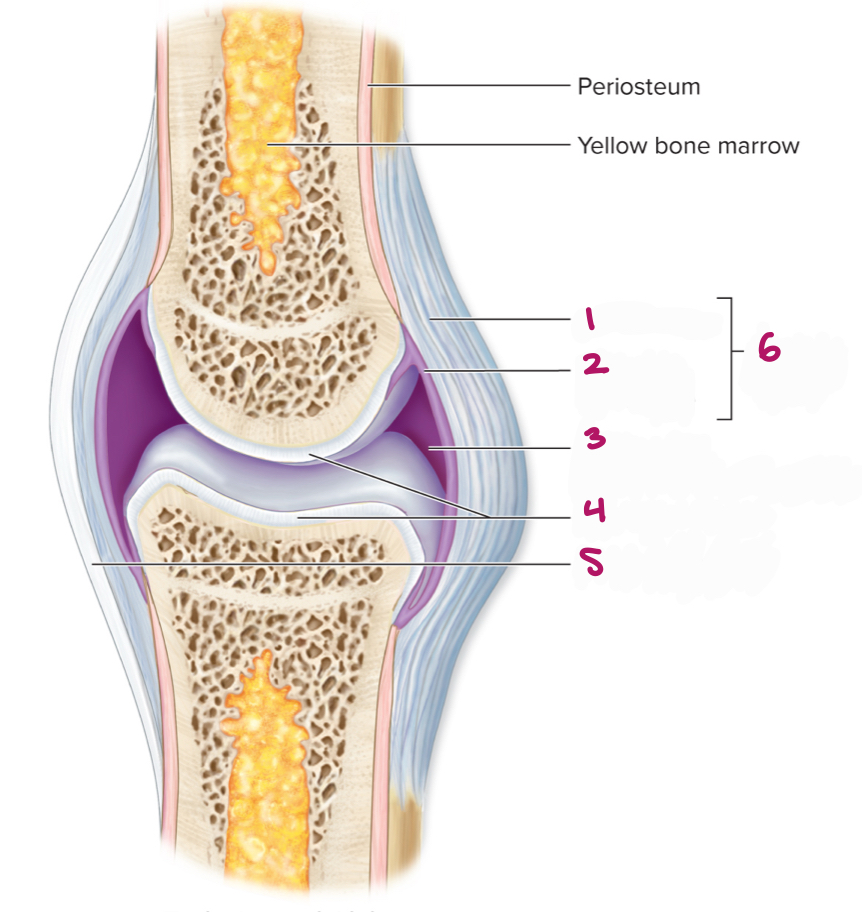
Label figure 1.
fibrous layer
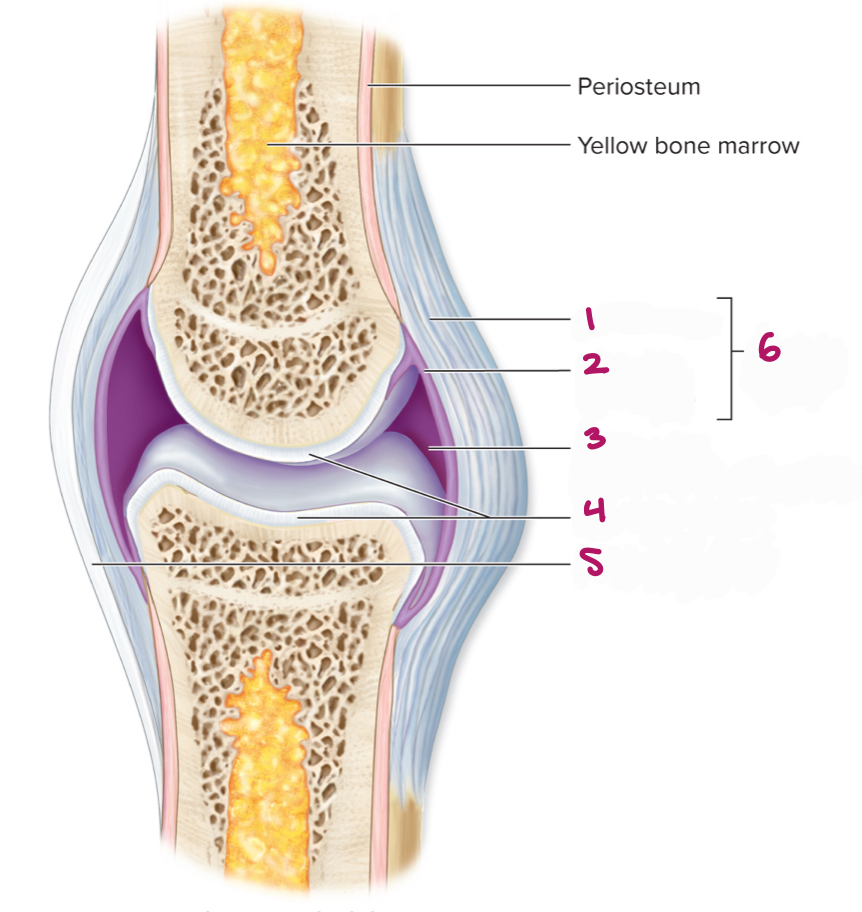
Label figure 2.
synovial membrane
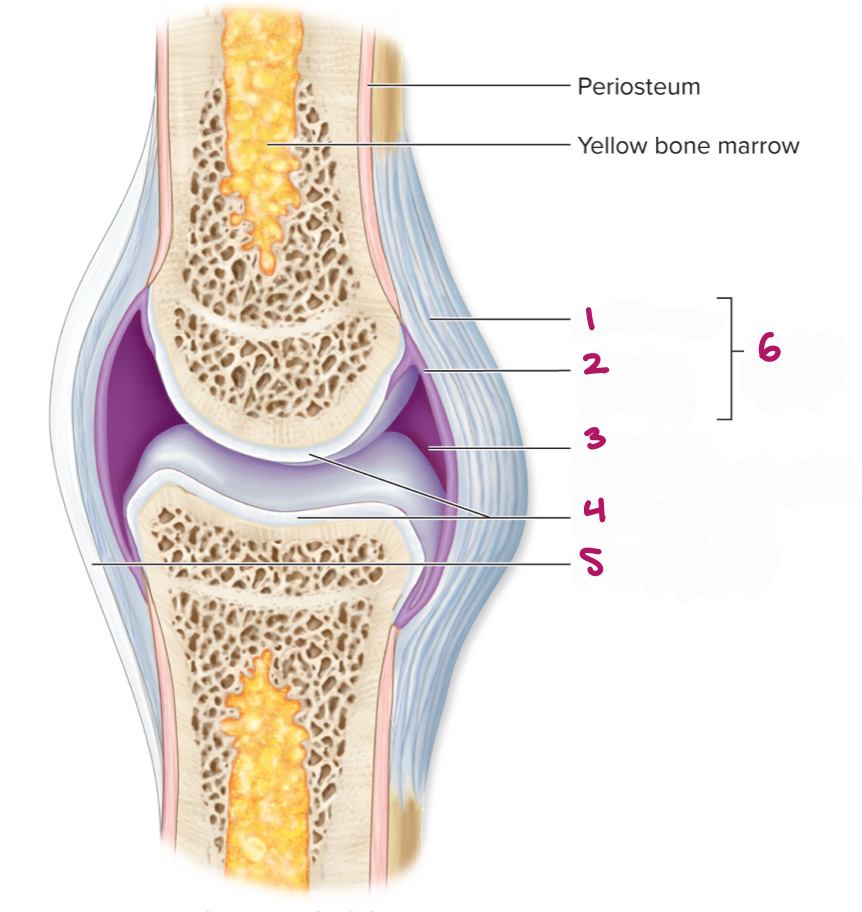
Label figure 3.
joint cavity (containing synovial fluid)
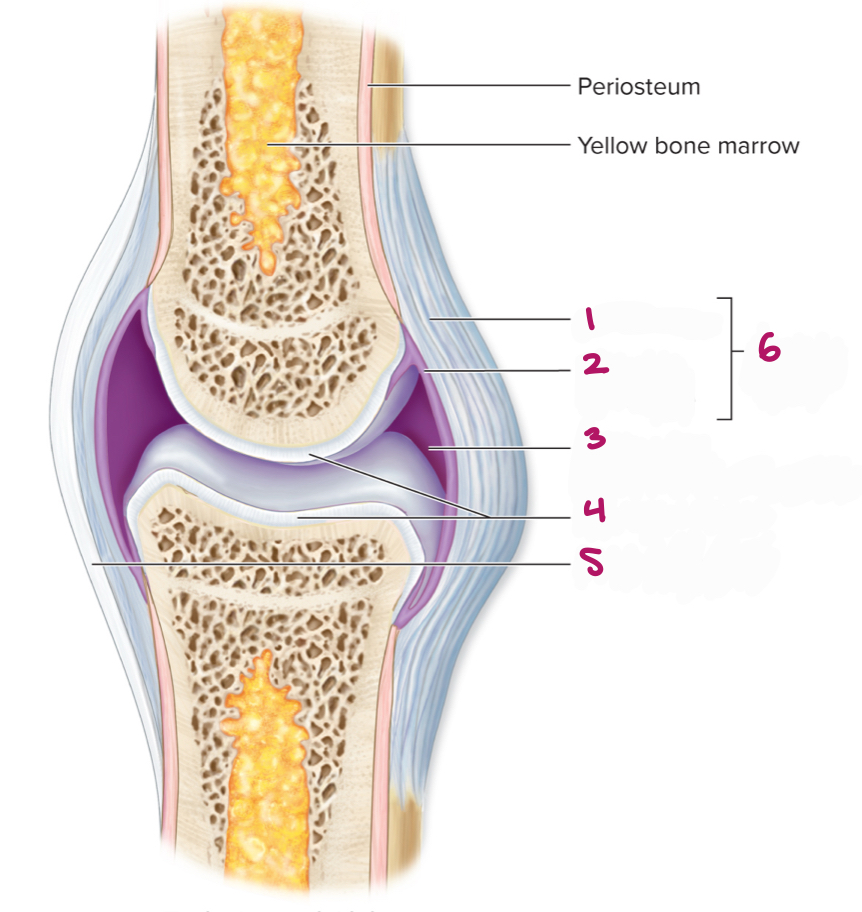
Label figure 4.
articular cartilage
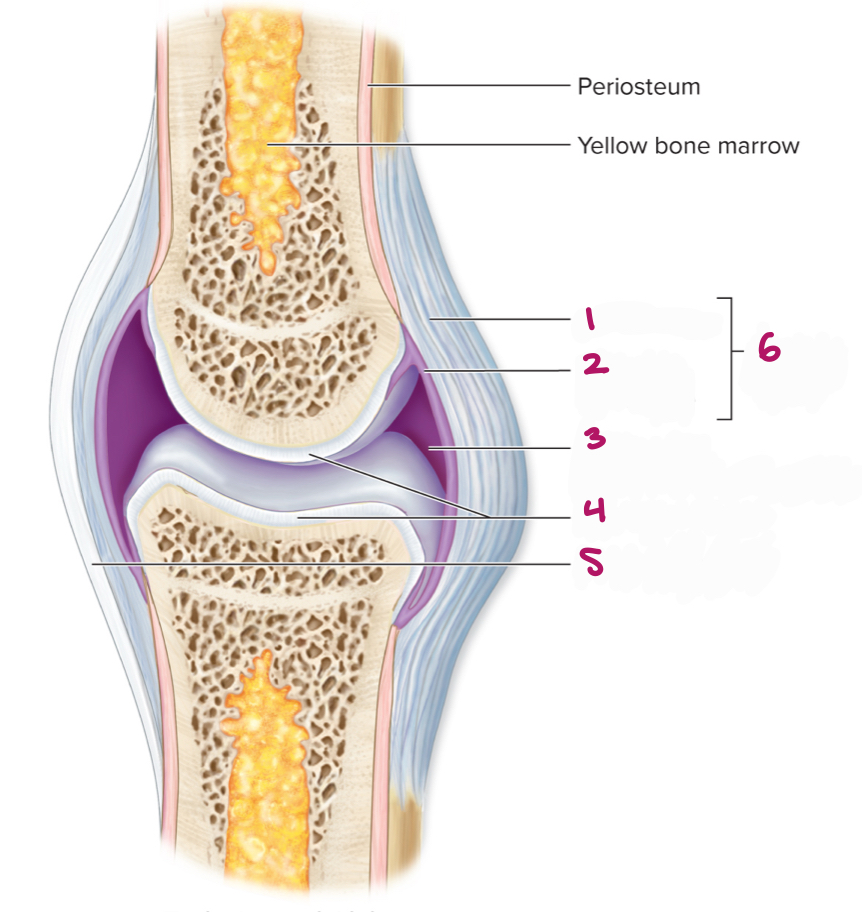
Label figure 5.
extrinsic ligament
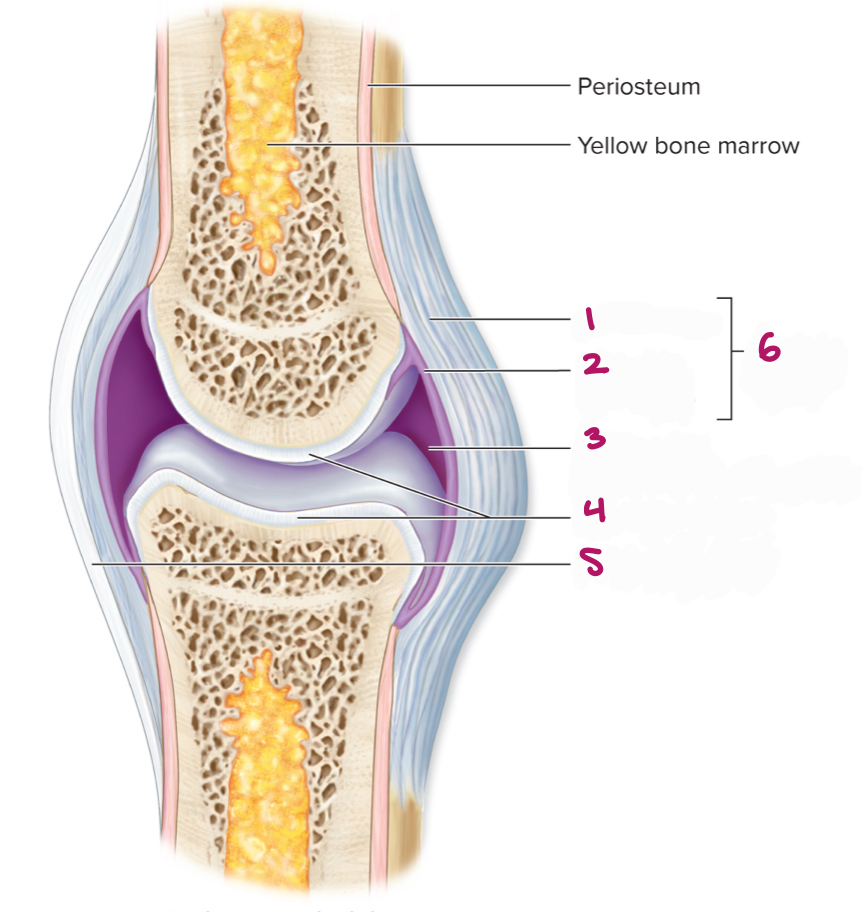
Label figure 6.
articular capsule
What are sacs containing synovial fluid outside most synovial joints where ligaments, muscles and tendons or bones rub?
Bursae
what are elongated bursae along tendons known as?
tendon sheaths
tendons connect what together?
bone to muscle
where are tendon sheaths typically located?
confined areas such as wrist and ankle; area where tendons rub each other
What are fat pads? what is their function?
packing material; provide some protection
synovial joints are classified by what?
shapes of articulating surfaces and amount of movement allowed
what are the types of synovial movement?
uniaxial
biaxial
multiaxial
what kind of movement is described by the joint moving in one plane or axis?
uniaxial
what kind of movement is described by the joint moving in two planes or axes?
biaxial
what kind of movement is described by the joint moving in three planes or axes (in all planes)?
multiaxial
What are the six classifications of synovial joints?
plane joints
hinge joints
pivot joints
condylar joints
saddle joints
ball-and-socket joints
What synovial joint is classified as uniaxial; side to side movement?
plane joint
What synovial joint is classified as uniaxial; like hinge of a door?
hinge joints
What synovial joint is classified as uniaxial; one bone rotates on its longitudinal axis?
pivot joints
What synovial joint is classified as biaxial; oval, concave surface of one bone; convex of the other?
condylar joint
What synovial joint is classified as biaxial; joint surfaces resemble saddle?
saddle joints
What synovial joint is classified as multiaxial; spherical head into cuplike socket?
ball-and-socket joint
what are the four motions that occur at synovial joints?
gliding
angular motion
rotation
special movements (unique to certain joints and don’t fit into other categories)
what kind of motion is defined as articular surfaces sliding back and forth or side to side?
gliding
in gliding motion, does the angle between the bones change?
no
where does gliding motion mainly occur?
in plane joints
what is an example of where gliding motion occurs?
carpals
what are increases or decreases angle between bone?
angular motion
what is the movement in anterior-posterior plane where joint angle is decreased?
flexion
What is movement in anterior-posterior plane where joint angle is increased?
extension
what is extension beyond normal range of motion?
hyperextension
what is body trunk moves laterally in coronal plane?
lateral flexion
what is lateral movement of body part away from midline?
abduction
What is medial movement of body part toward midline?
adduction
what is proximal end of bone stationary while distal end makes a circular (cone) shape?
circumduction
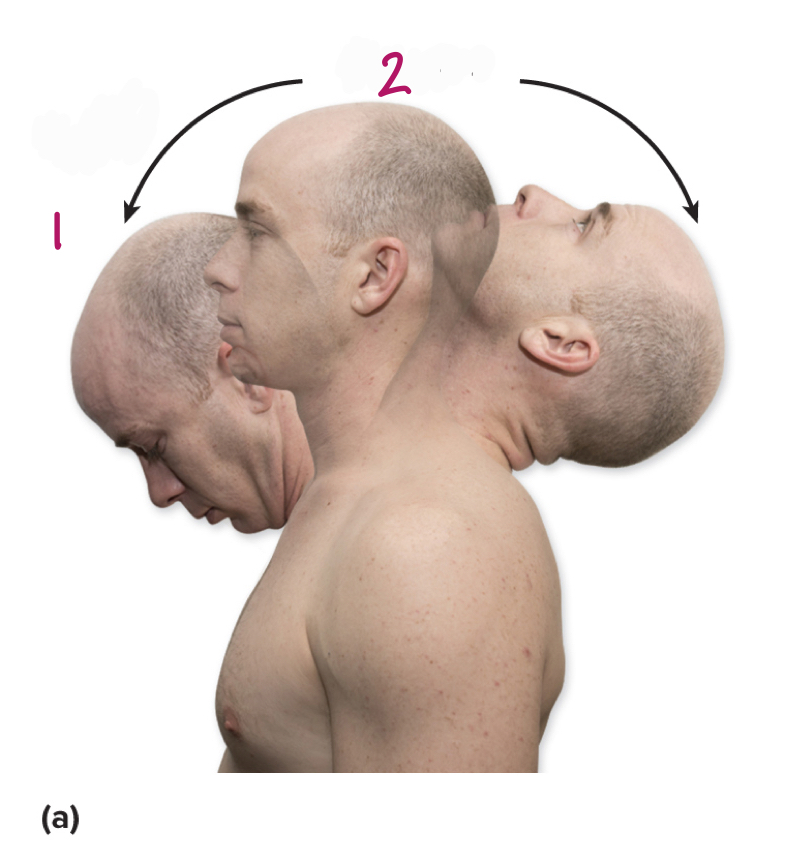
Label figure 1.
flexion
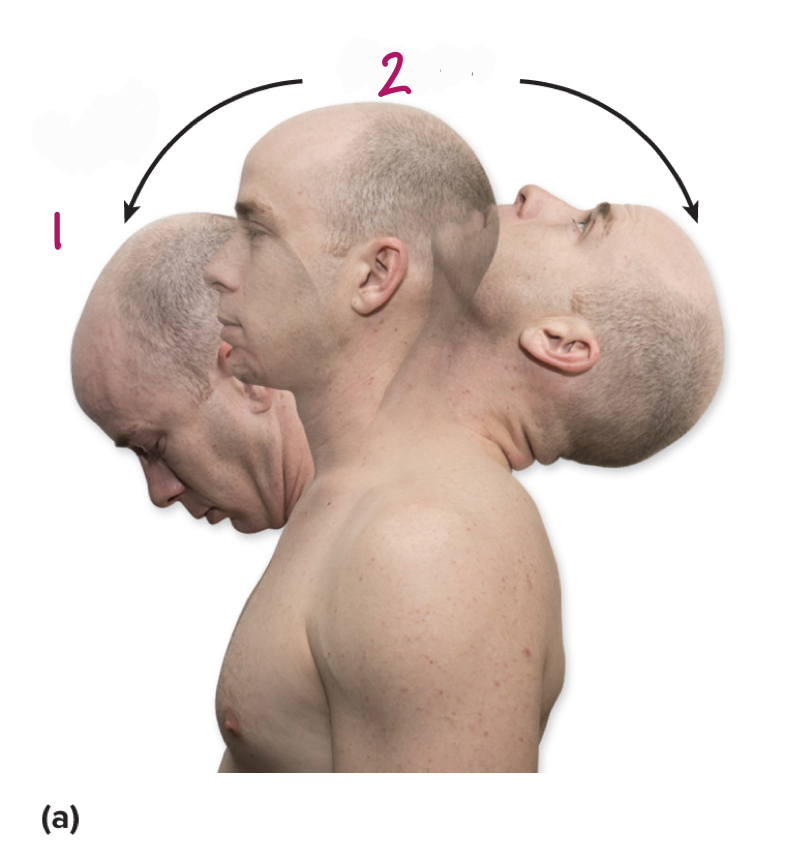
Label figure 2.
extension
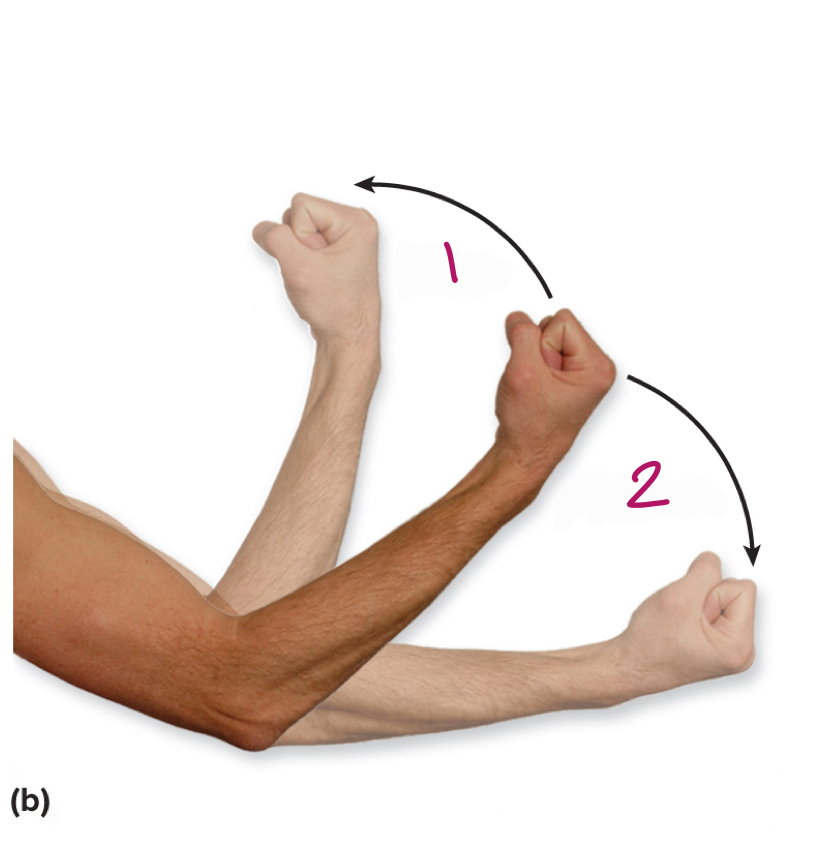
Label figure 1.
flexion
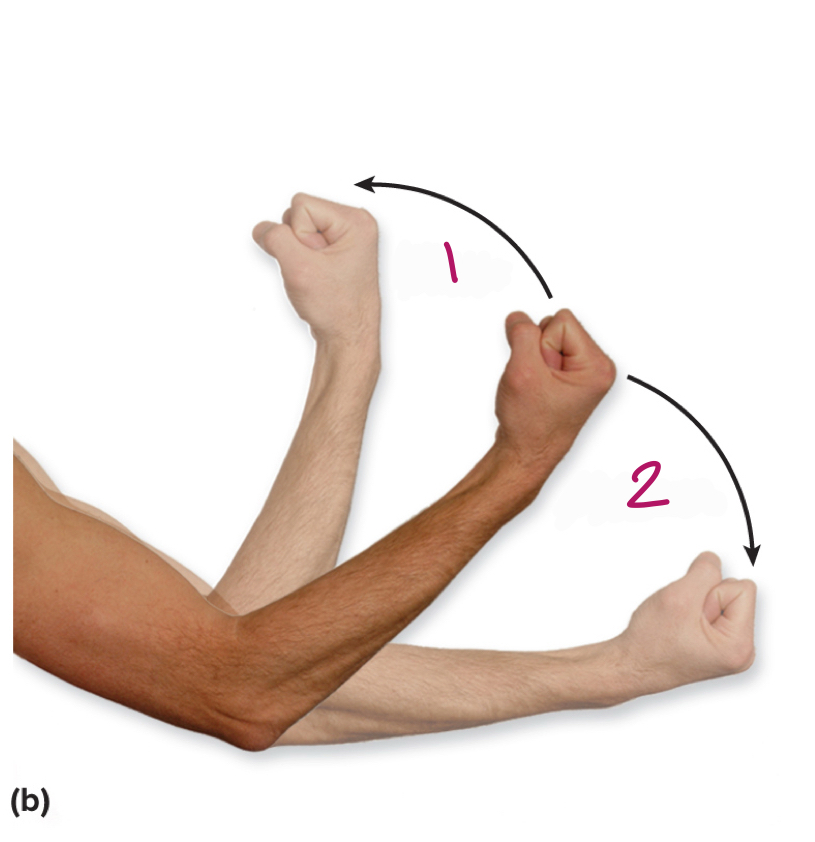
Label figure 2.
extension
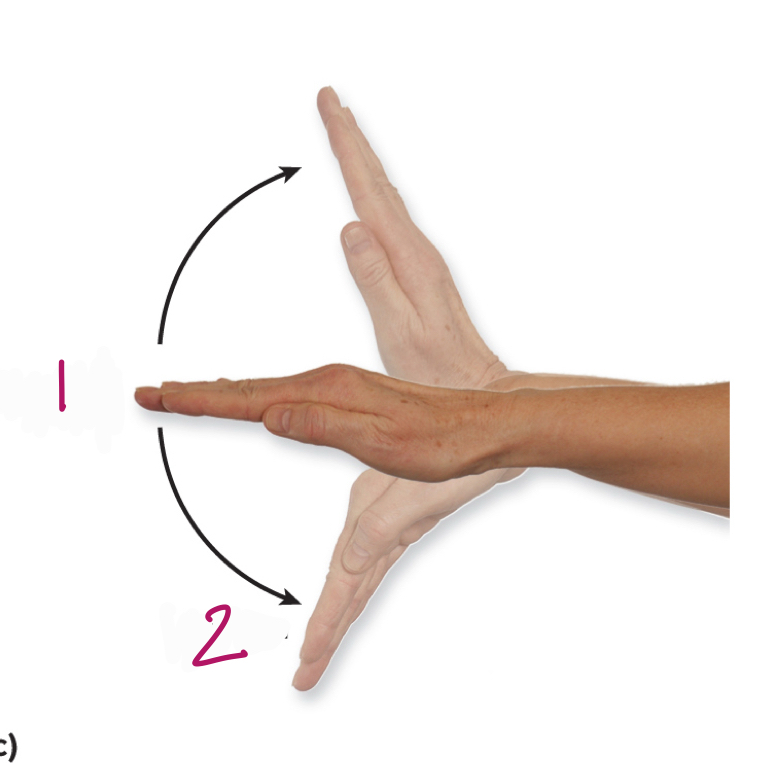
Label figure 1.
extension
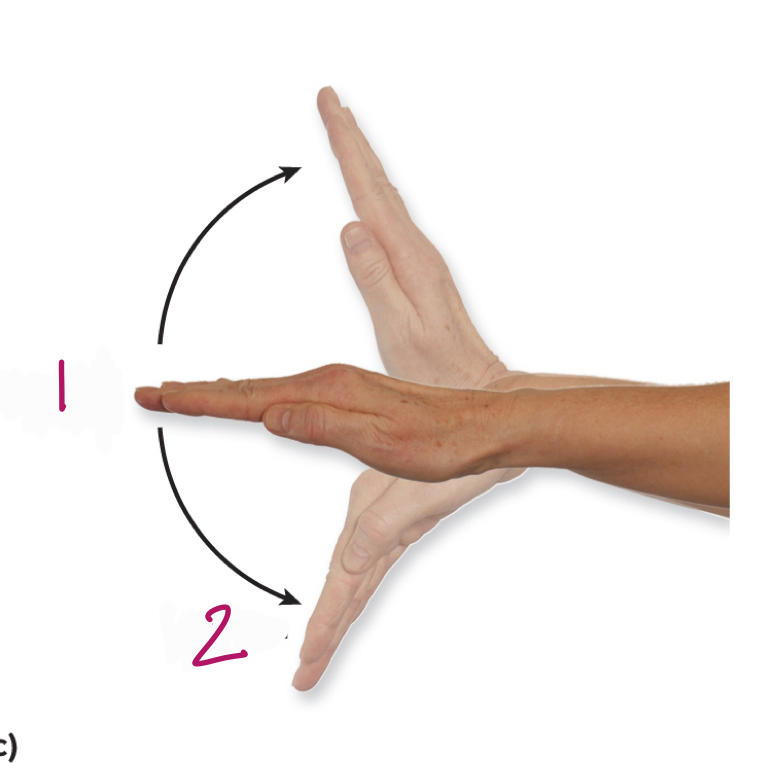
Label figure 2.
flexion
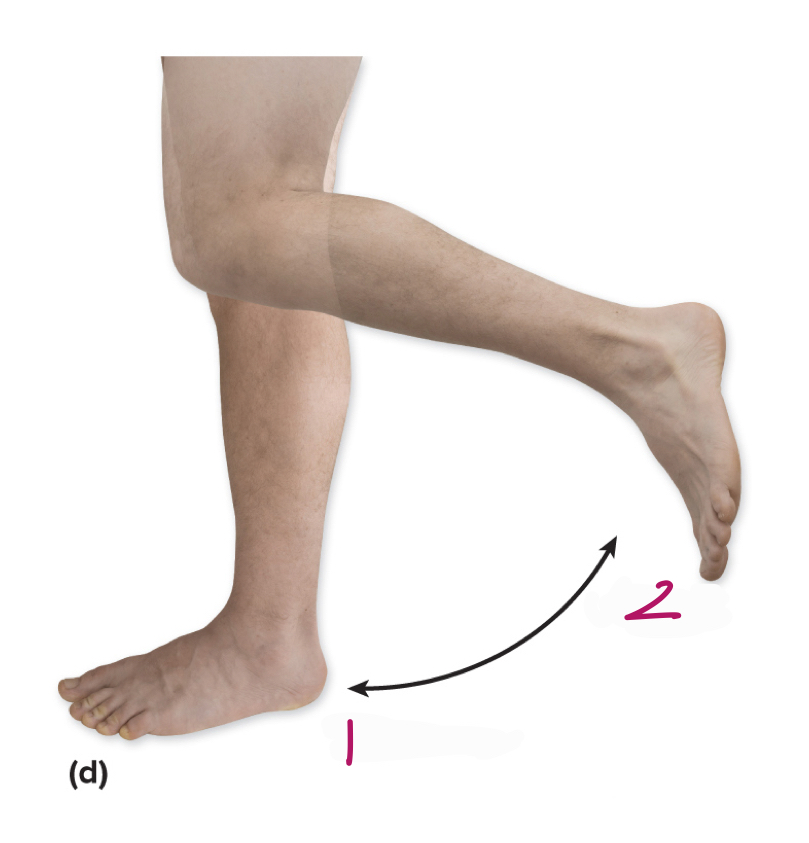
Label figure 1.
extension
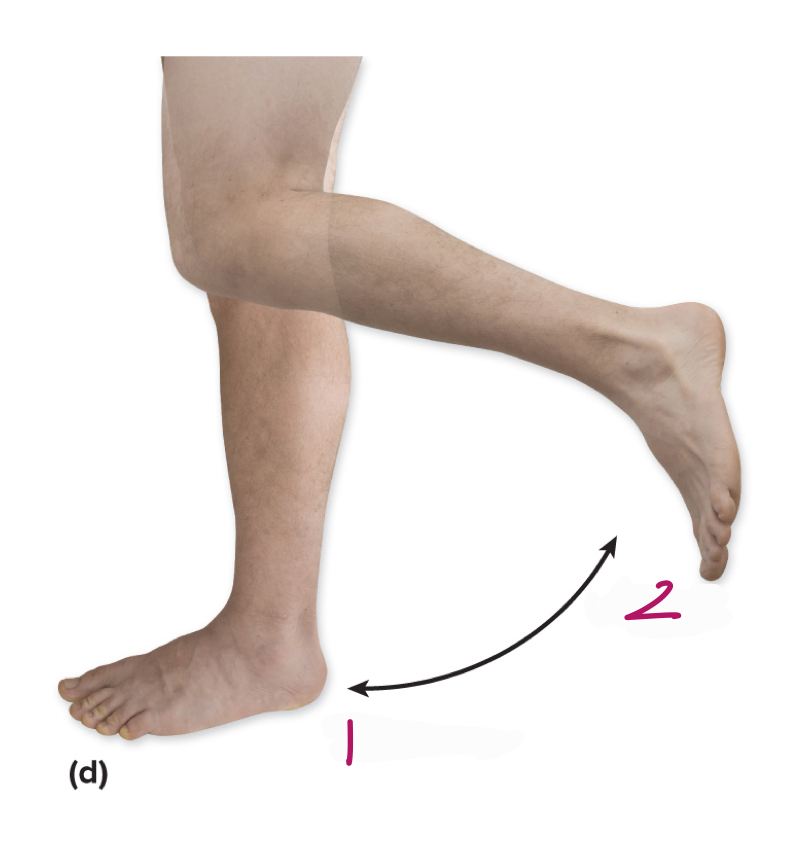
Label figure 2.
flexion
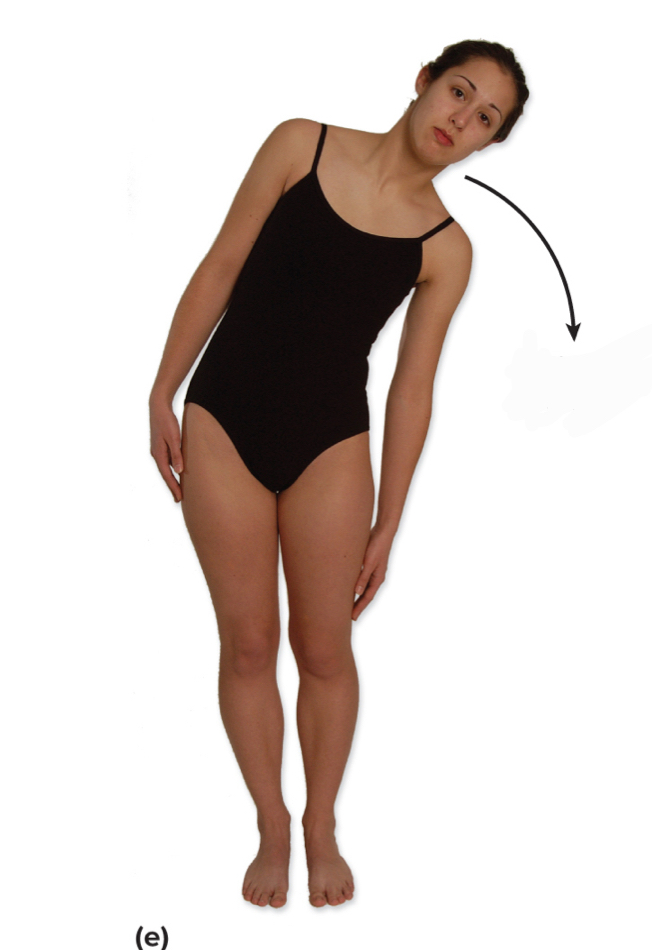

what kind of movement is this?
lateral flexion
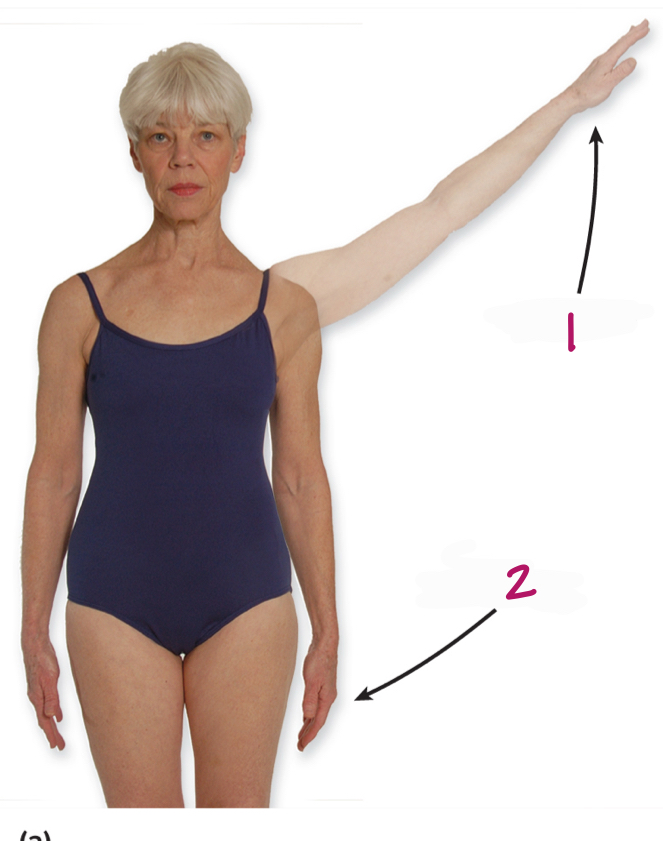

Label figure 1.
abduction
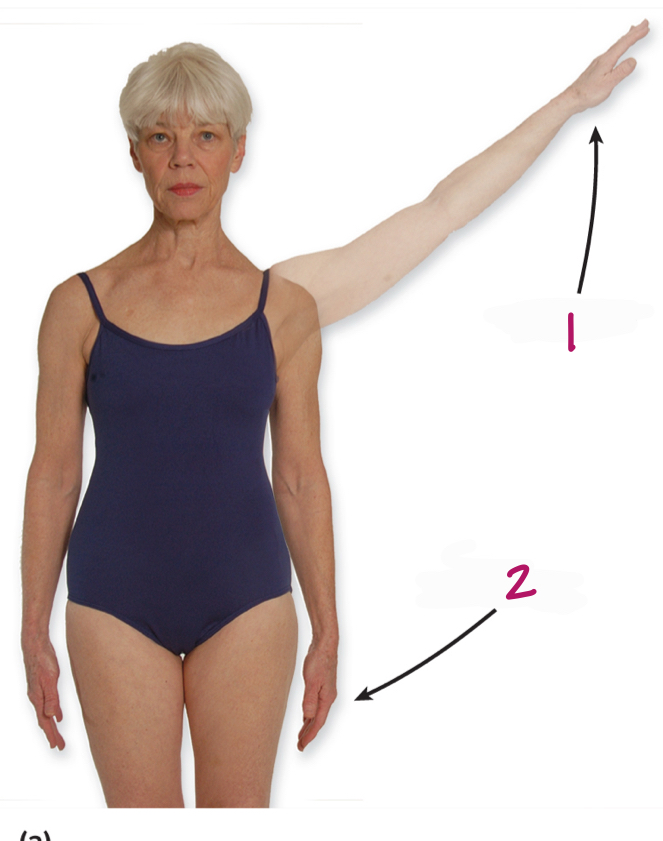

Label figure 2.
adduction