Gardner's Art Through The Ages: Chapter 1 - 5
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
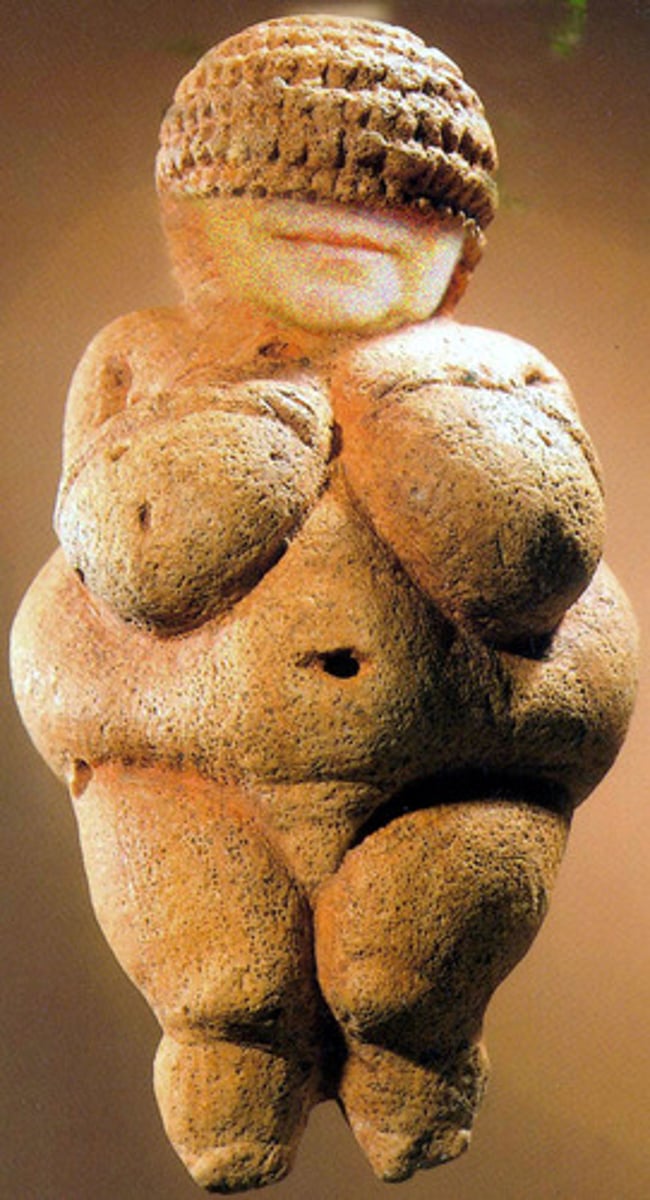
Venus of Willendorf
Symbol of fertility, exaggerated female body parts. As hunter-gatherers, women would not have had this body shape.

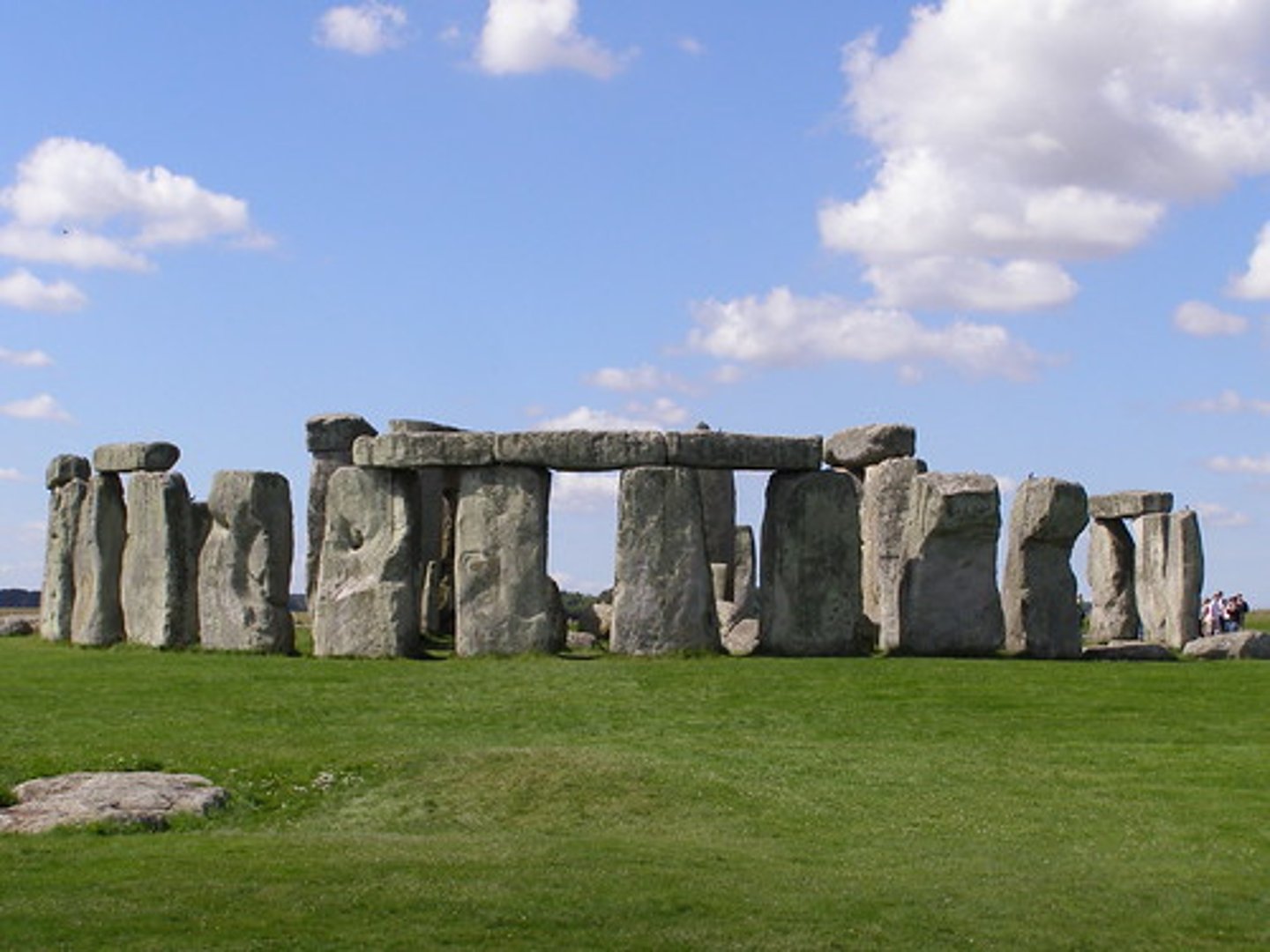
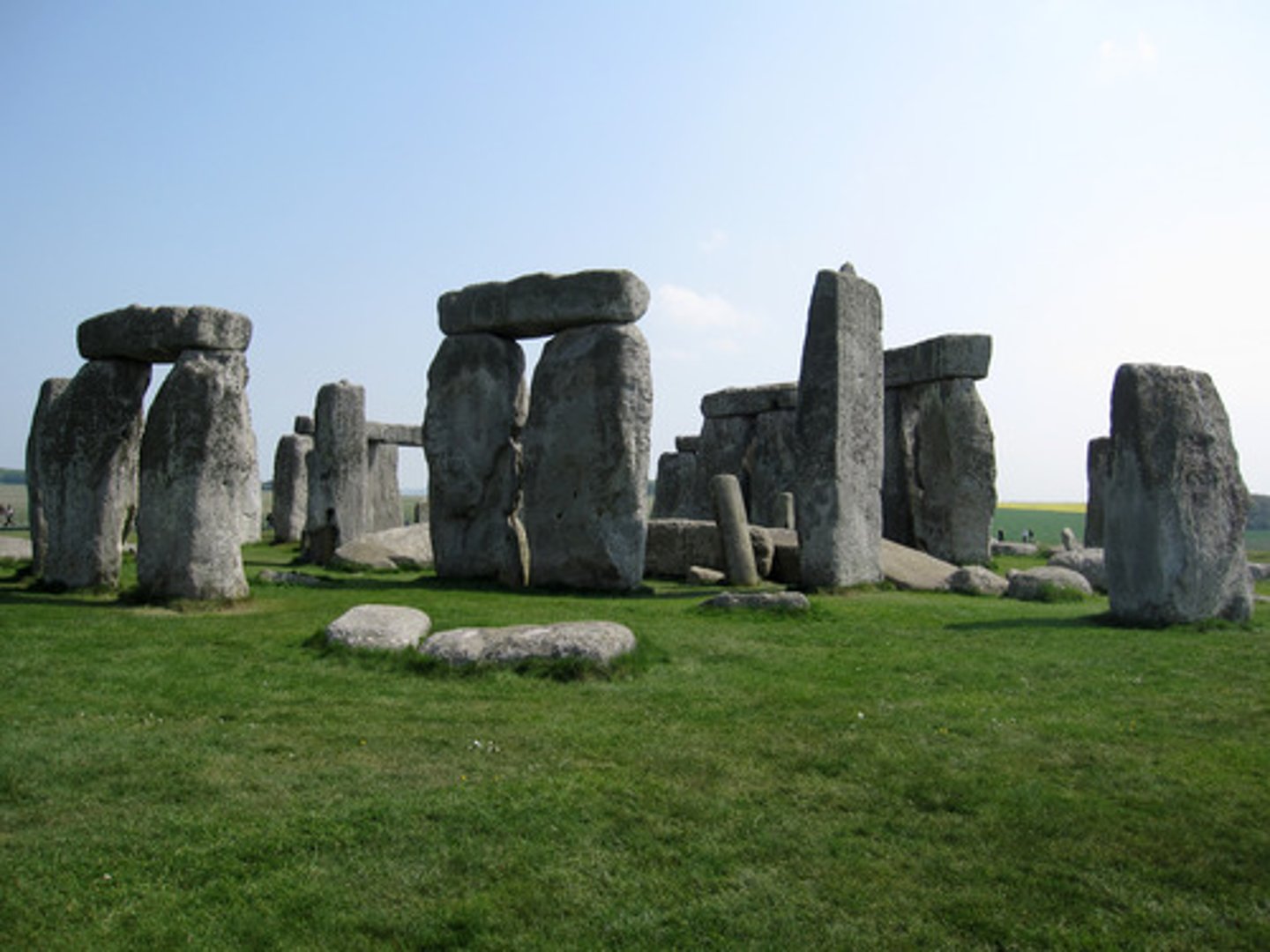
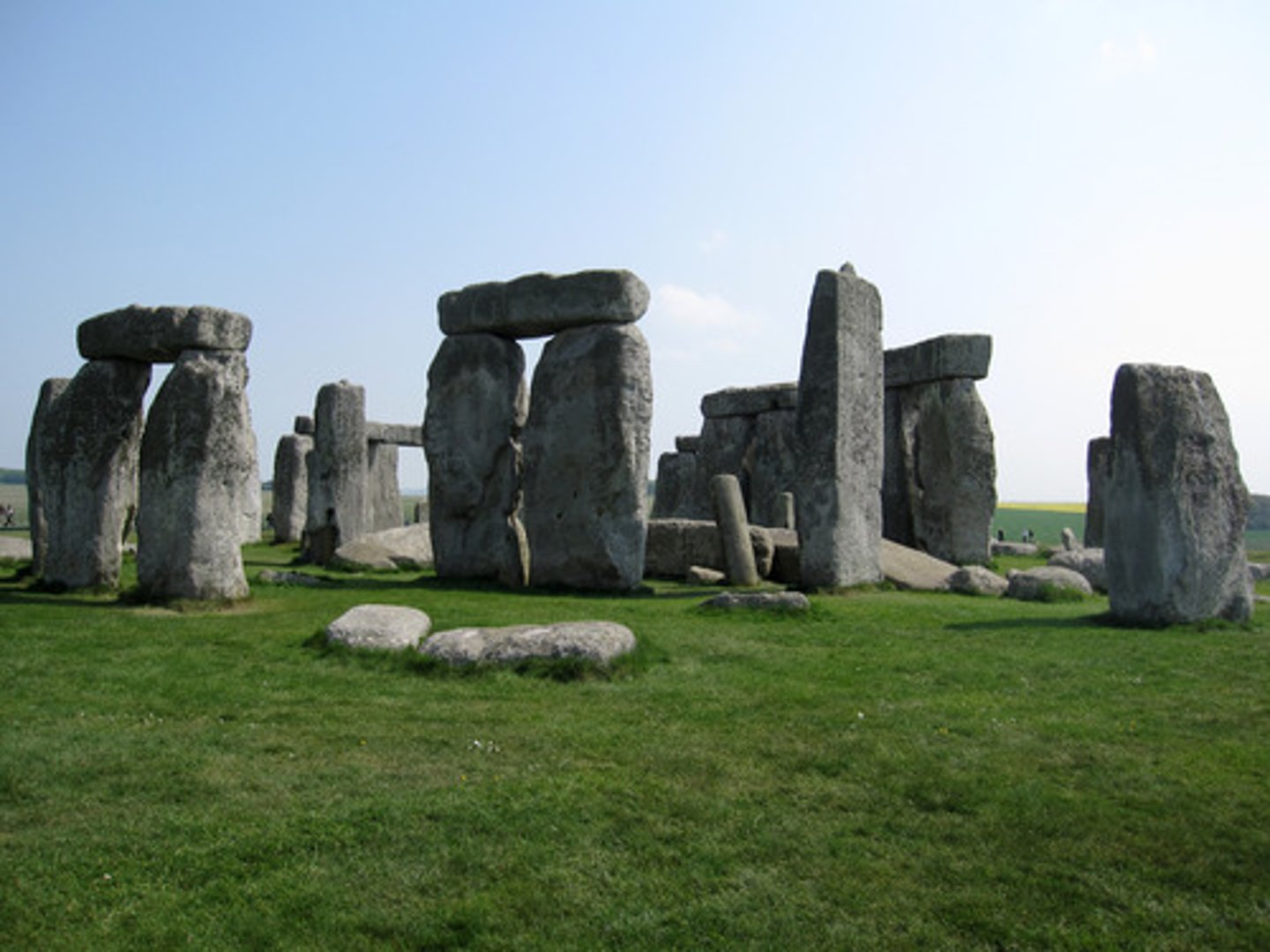
Stonehenge, England
Marks passage of time with the sun, stars, and moon. Religious complex, built over generations. Center of religious complex people would visit once a year. Stones were not native to the area. used to be a ditch, center stone used to match with summer solstice.

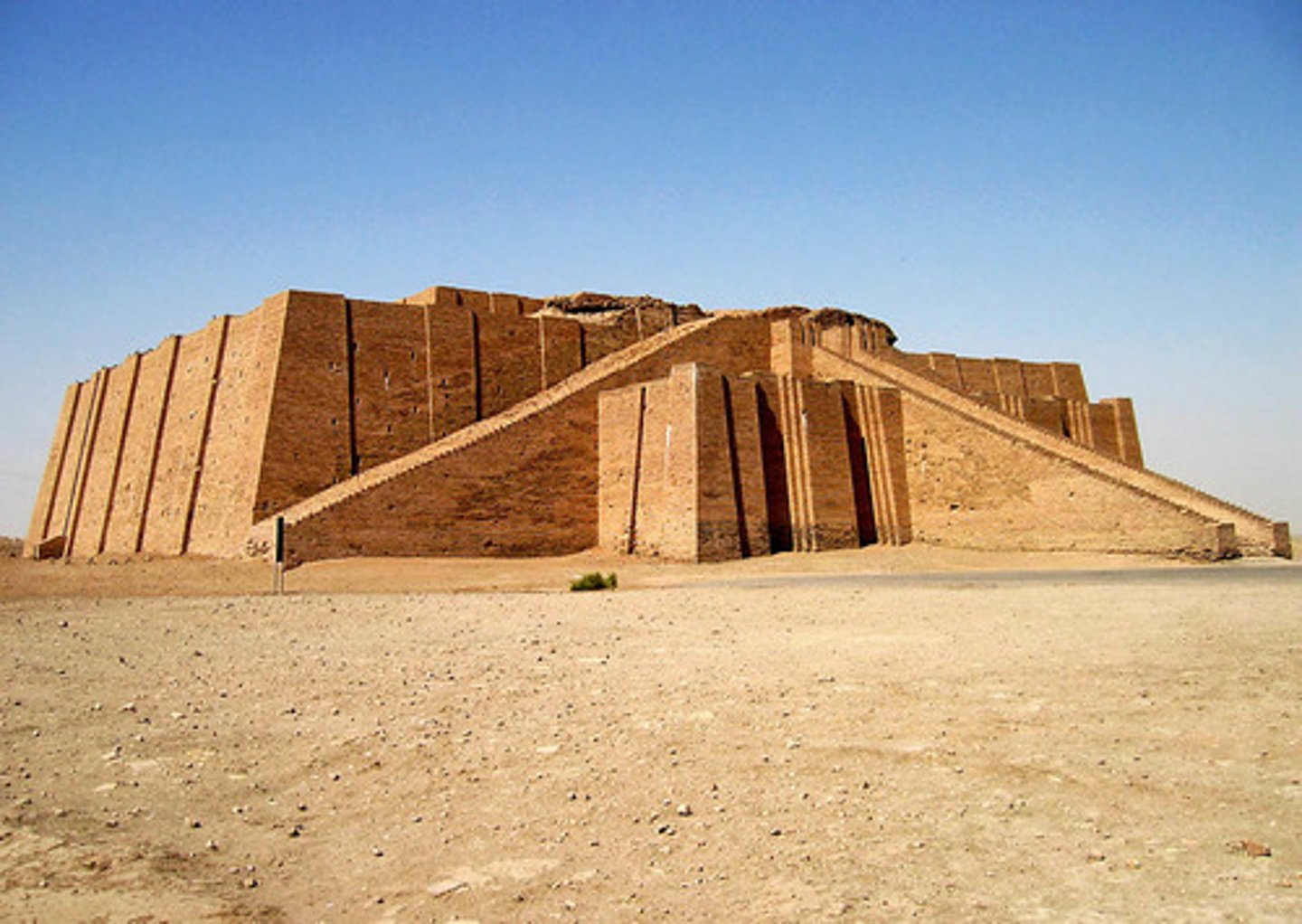
Ziggurat at Ur, Summerian,
One of the largest Ziggurats. Each city state was ruled by a specific god and the priest or priestess was the most important person. At the top of the Ziggurat was the waiting room to converse with the gods. It is also where the priest would make offerings to the god. Artificial mountain.

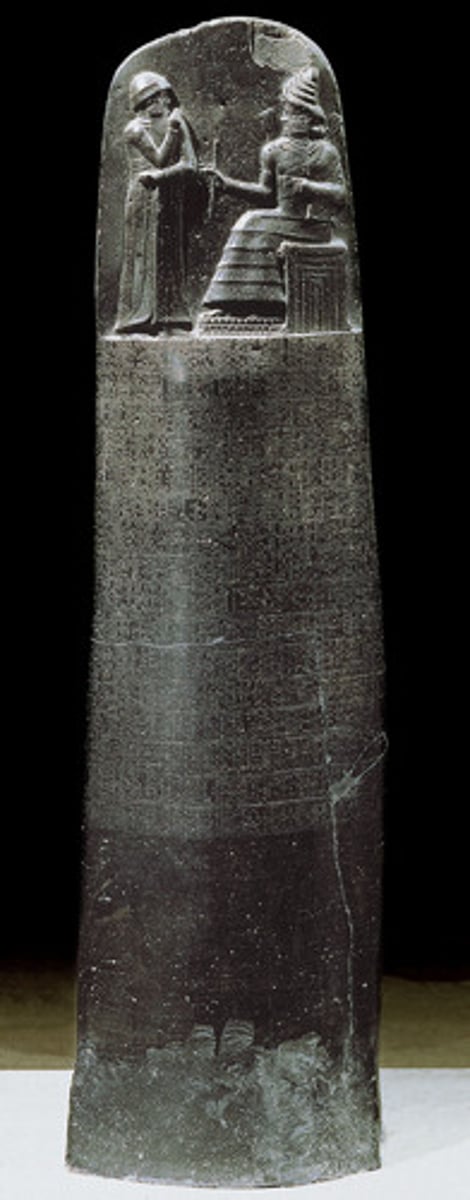
Law Stele of Hammurabi, Babylonian,
First law code, important because laws are not at the whim of the ruler, given to Hammurabi by Shamash, god of justice. The image at the top pioneered the technique of foreshortening.

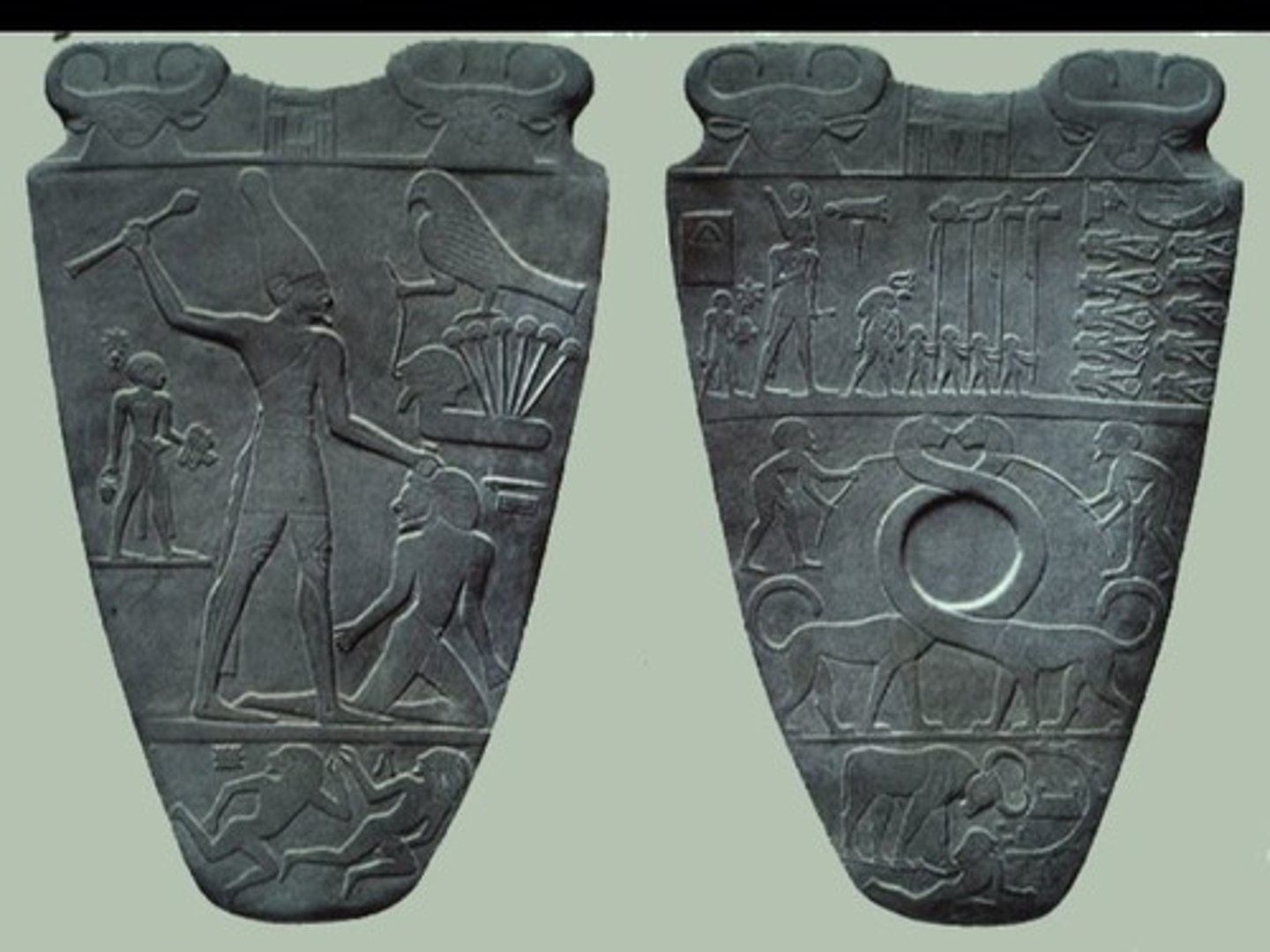
Front and back of Palette of King Narmer, Egypt
King of upper smiting lower, falcon is Horus protecting pharoh. The intertwined neck of the two felines shows the combining of upper and lower Egypt. 2 sided, this is for decoration palette usually used for eye make up. The King defeats enemies alone to show that he is powerful and a god. Egyptians loved balance and afterlife, king considered a god
relief sculpture, depicts unification of upper and lower Egypt, hiearchy of scale, used to prepare eye make-up, intertwining necks of the animals, OLD KINGDOM

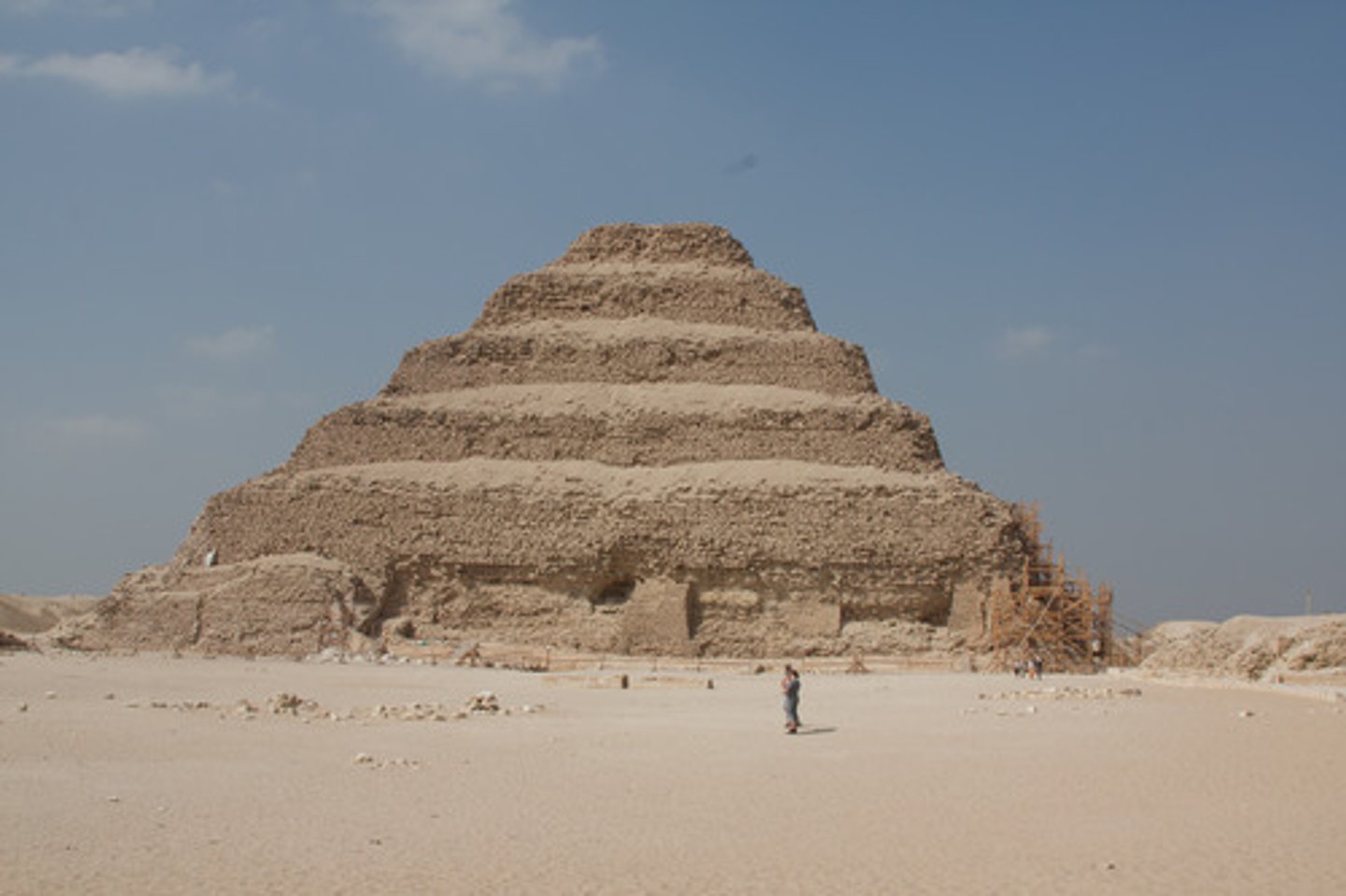
Imhotep, Stepped Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara, Eygpt
history's first recorded artist, supervised art, creation of the Stepped Pyramid
mhotep, first complex, six unequal steps, appears stack of mastabas, OLD KINGDOM

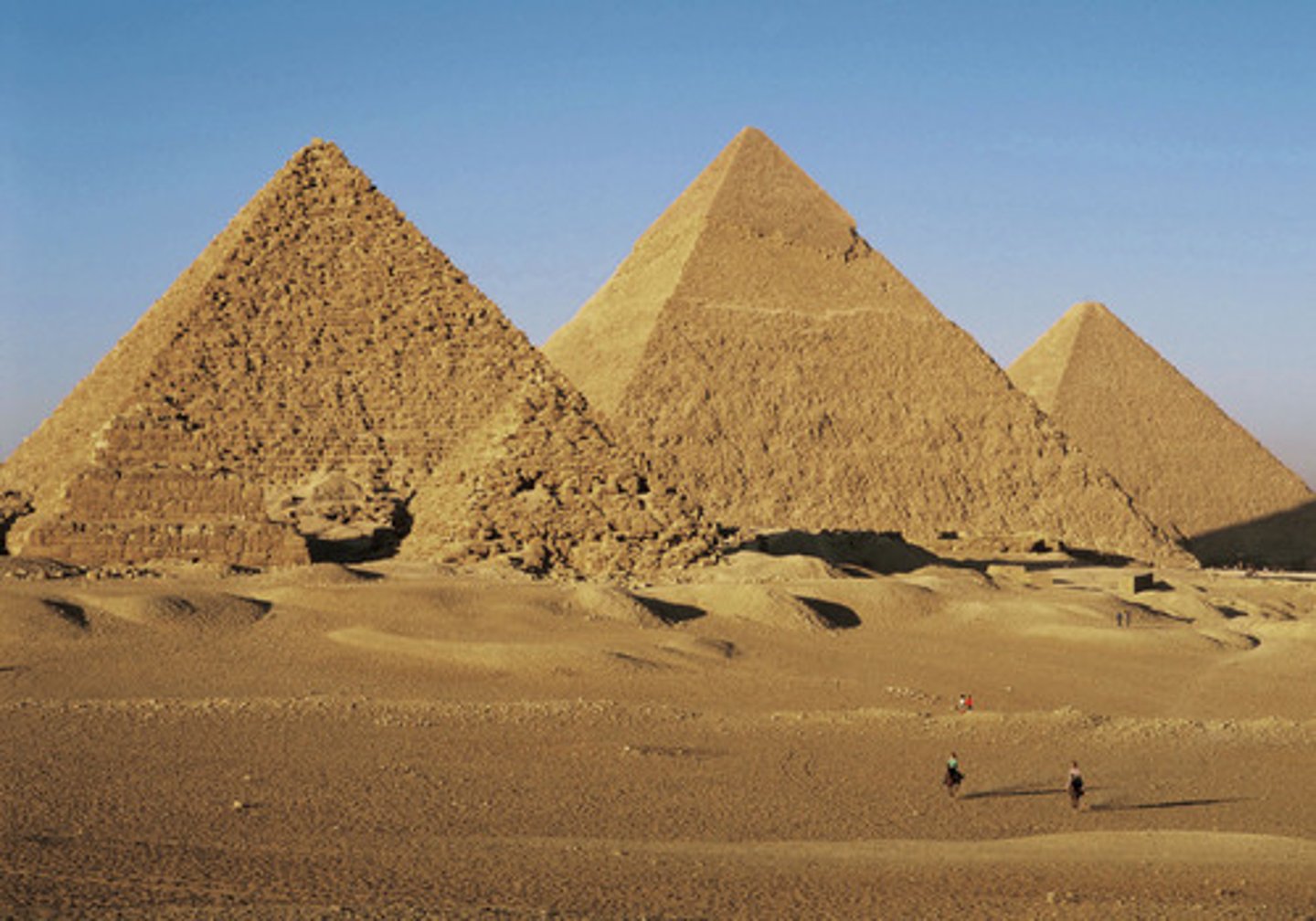
Pyramids at Gizeh, Egypt,
This complex of ancient monuments includes the three pyramid complexes known as the Great Pyramids, the massive sculpture known as the Great Sphinx, several cemeteries, a workers' village and an industrial complex.

Iktinos and Kallikrates, the Parthenon
Doric style temple
Sculptor & Project overseer: Pheidias. Architects: Iktinos and Kallicrates
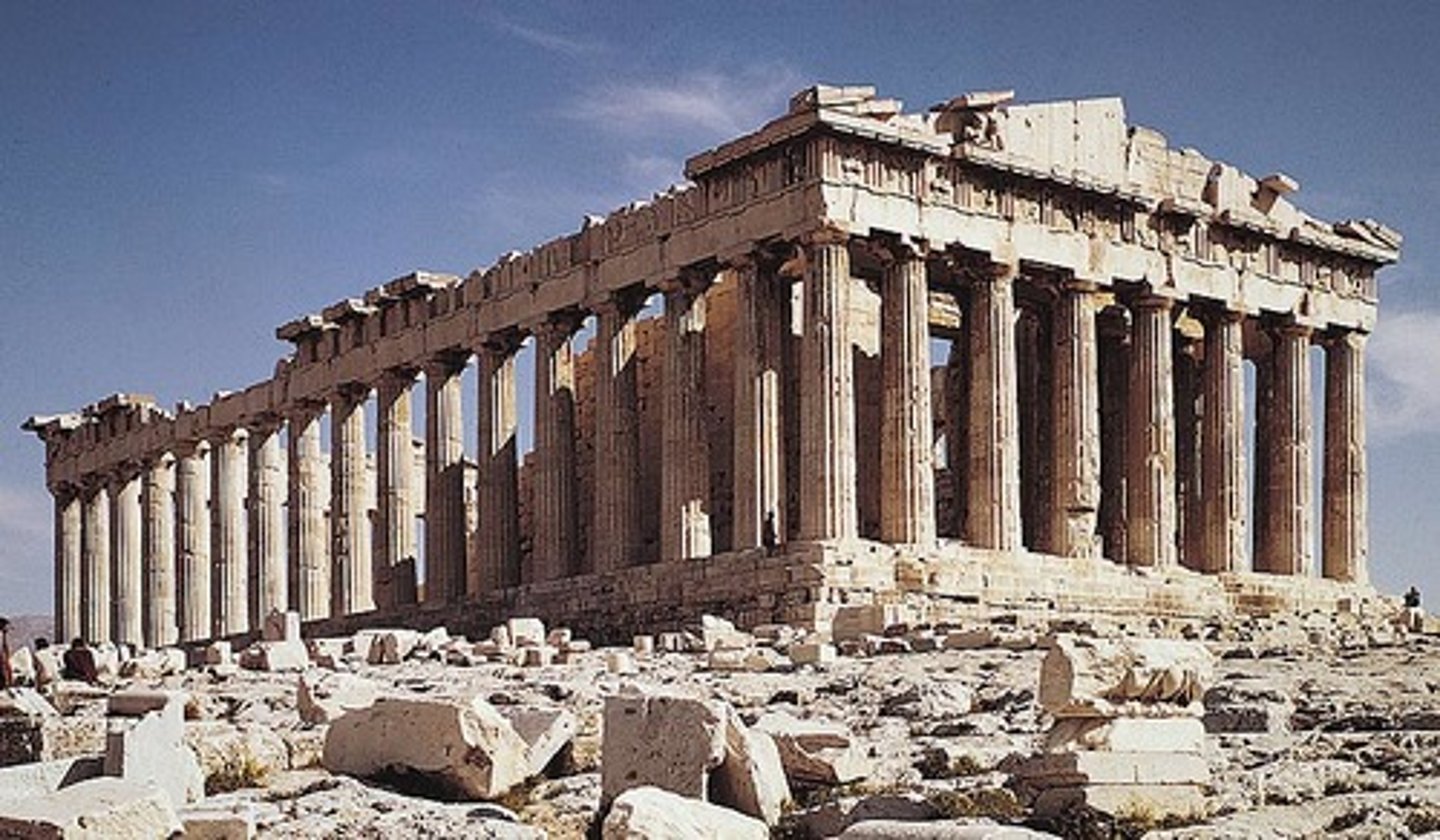

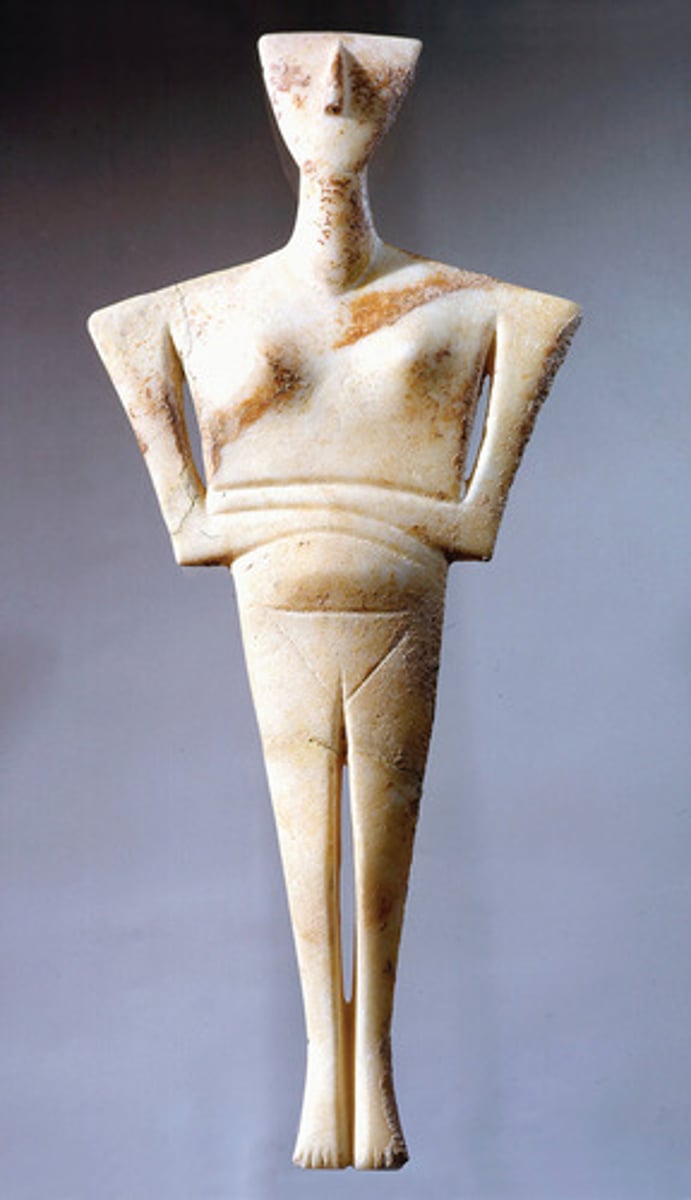
Cycladic figurine.
Marble statuettes are the major surviving artworks of the Cycladic Islands during the third millennium BCE, but little is known about their function. Many of the Cycladic figurines were buried in graves and may represent the deceased, but others, for example, musicians, almost certainly do not. Whatever their meaning, these statuettes mark the beginning of the long history of marble sculpture in Greece.

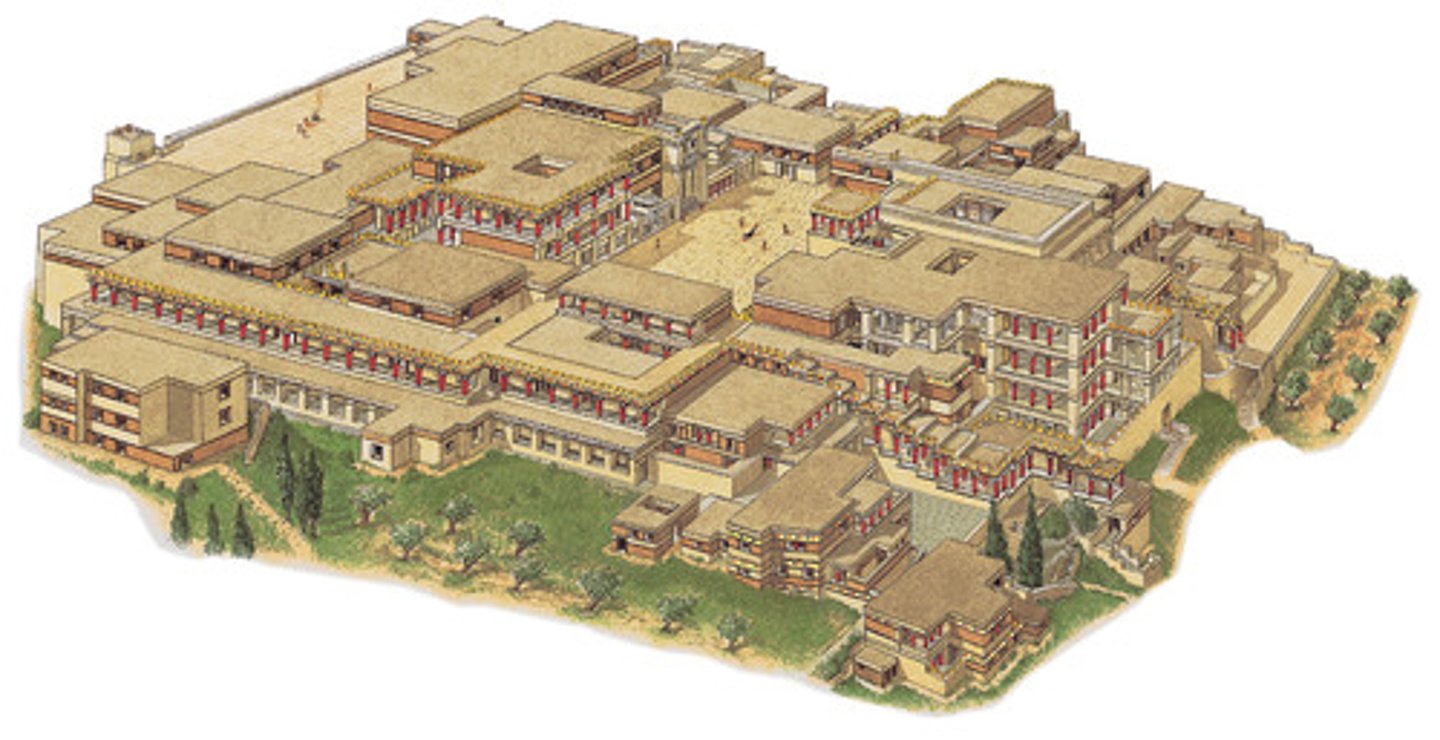
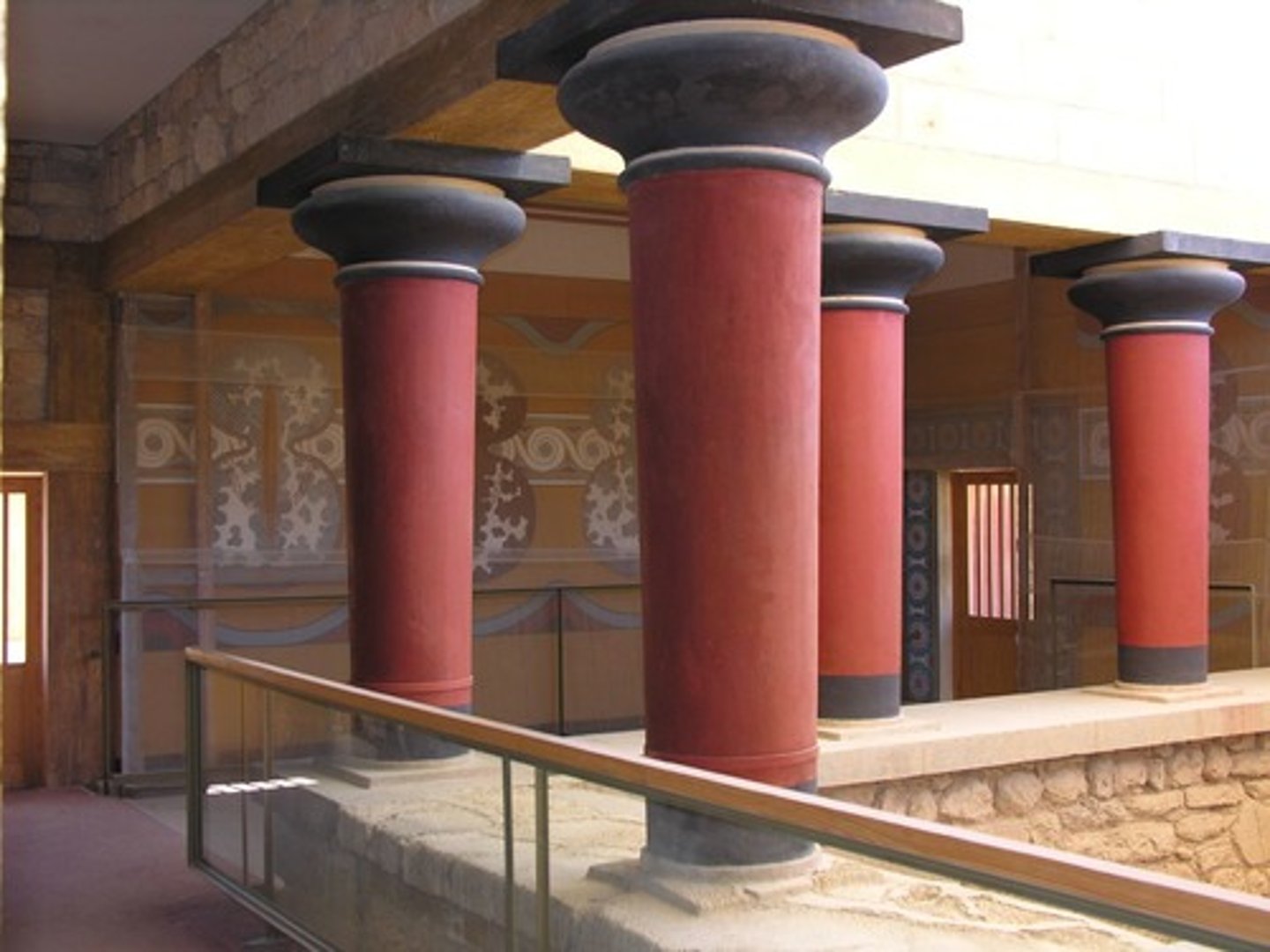
Restored view of Palace at Knossos
central courtyard with flanking rooms, open-air chambers, labyrinthine ground plan, columns painted, capitals painted black, MINOAN
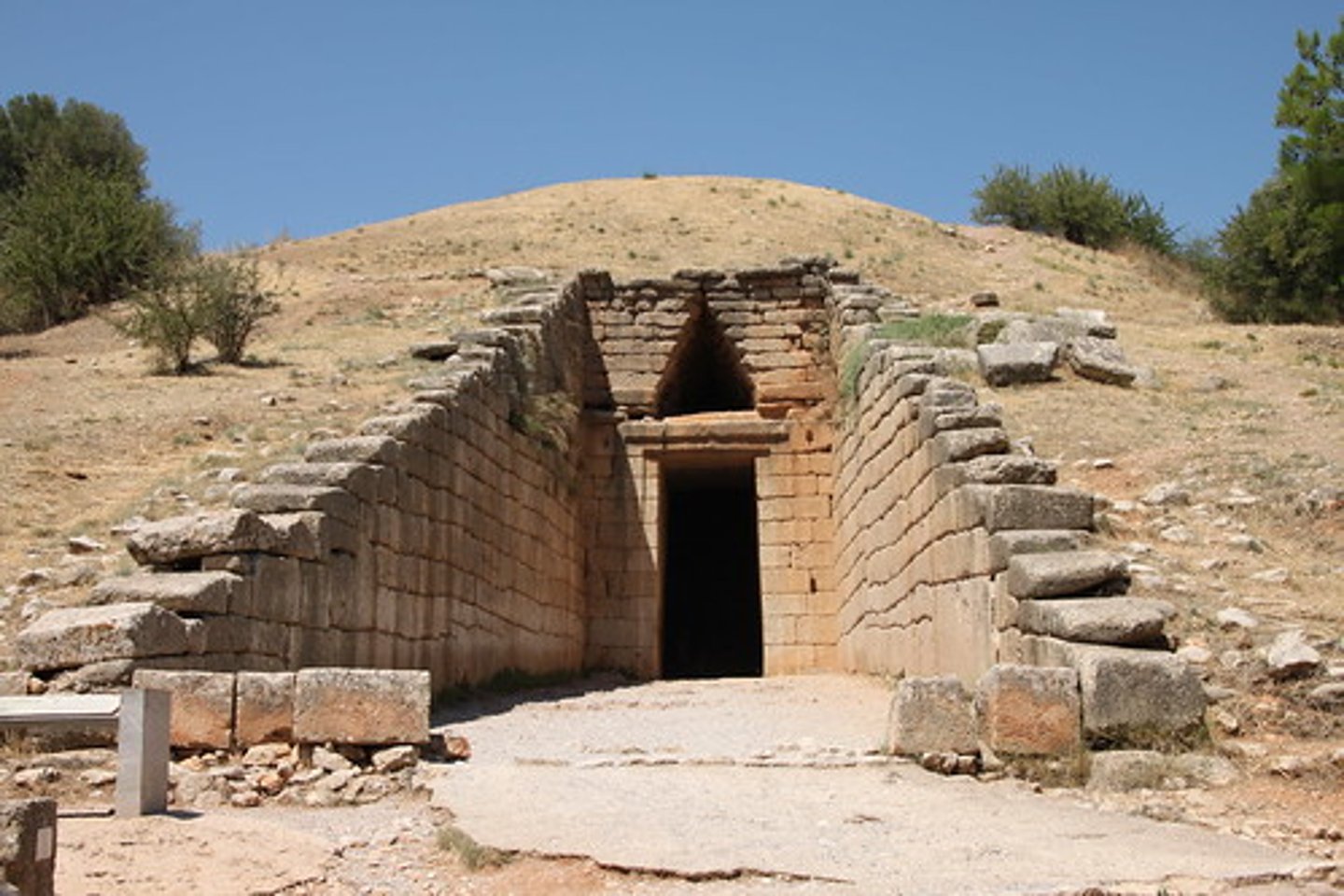
Treasury of Atreus at Mycenae
probably a long-ago tomb, corbel vaulted interior, precise cutting, THOLOS, MYCENAEAN
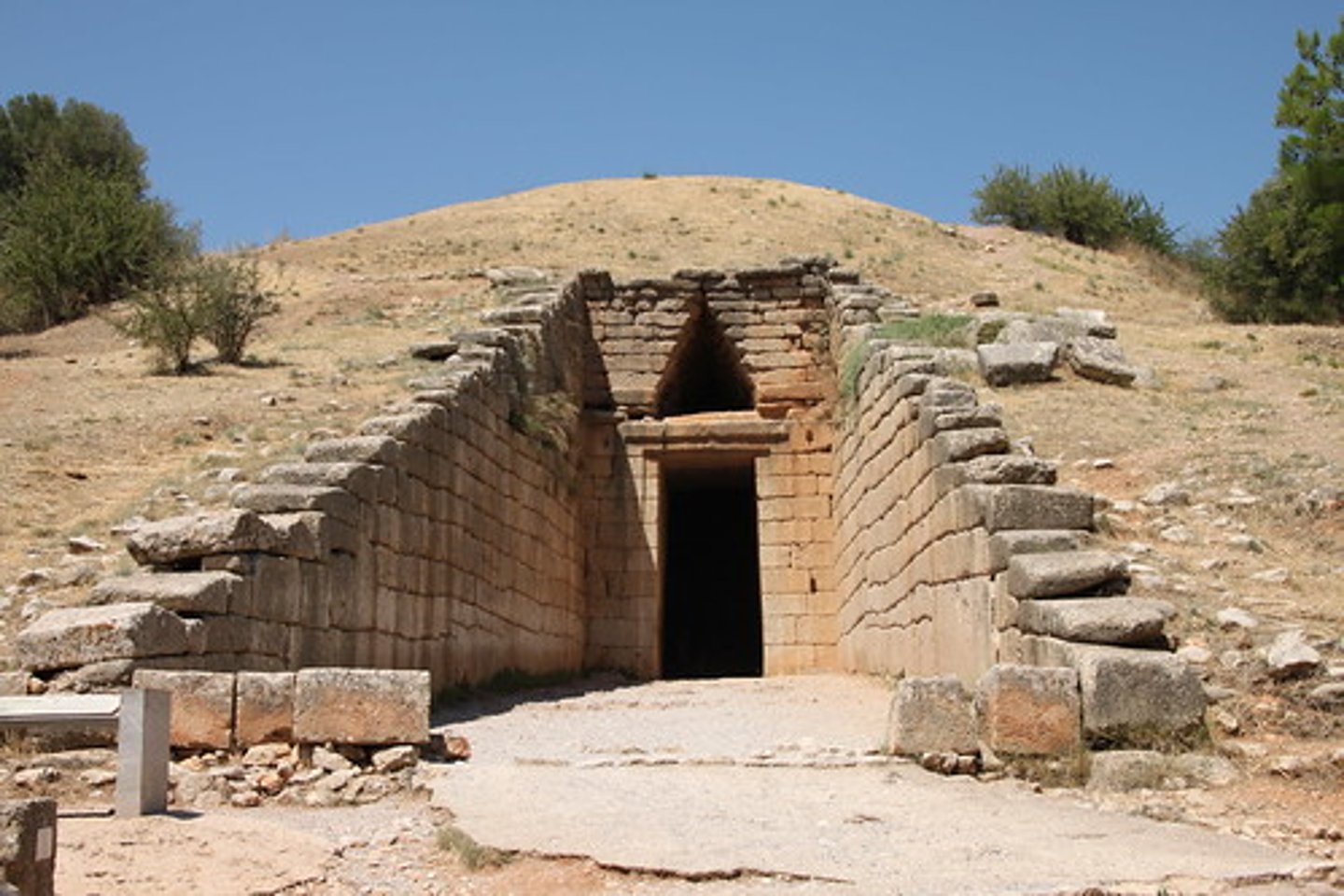

New York Kouros.
Archaic Period ca. 600 bce.
Marble. 6.5' high
Could be a votiev offering or a grave marker.
Shown in simmilar manor to pharo.
Freestanding, still looks geometric, stiff, not life-like
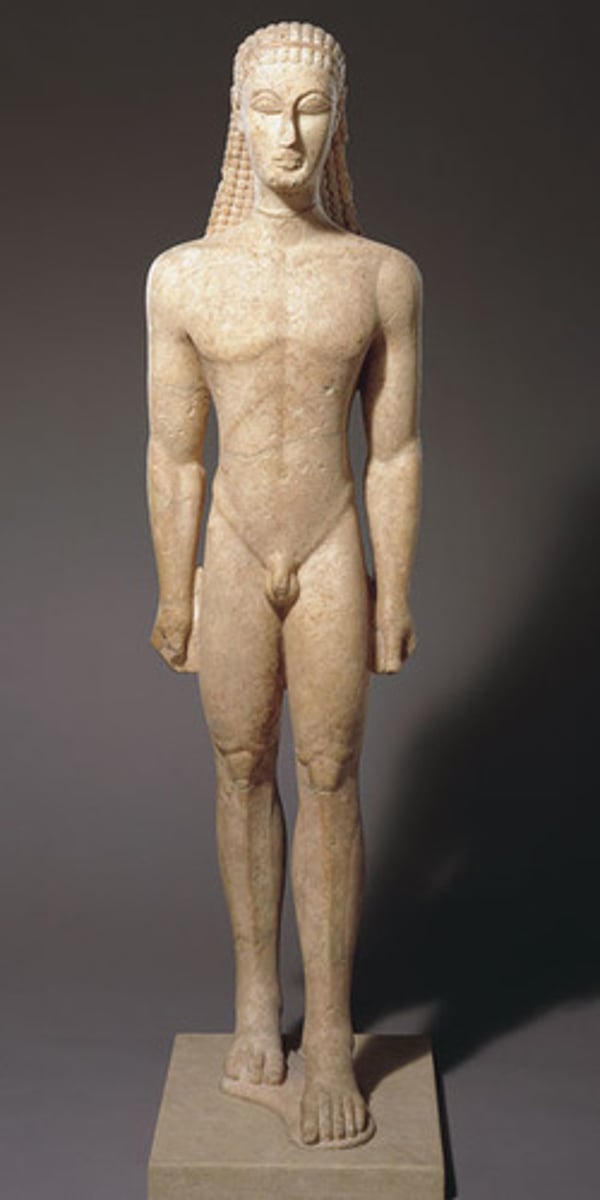

Kritios Boy
TRANSITION FROM LATE ARCHAIC TO EARLY CLASSICAL as it shows naturalistic movement that we see on the frieze and metopes in the Parthenon.
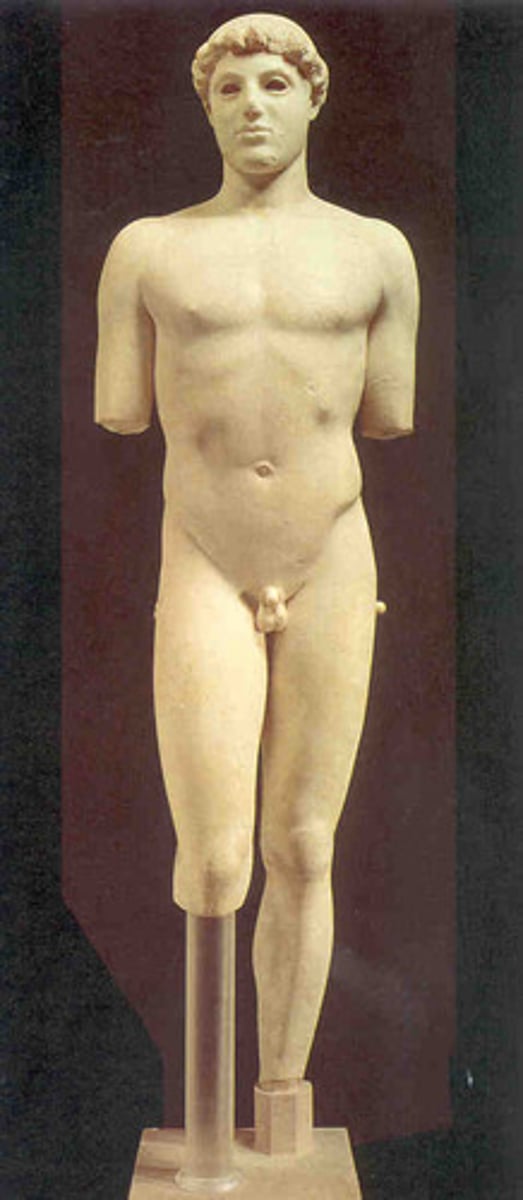

Polykleitos, Doryphorus
Spear Thrower, high classical, 440BC, Polykleitos-artist, copy from bronze original canon proportion 1/7, contrapposto- counterbalanced, weight-shift.
Doryphoros canon. Statue that is recognized because of its embodiment of human beauty b/c of ordered proportions, fine muscle tone and rugged features.
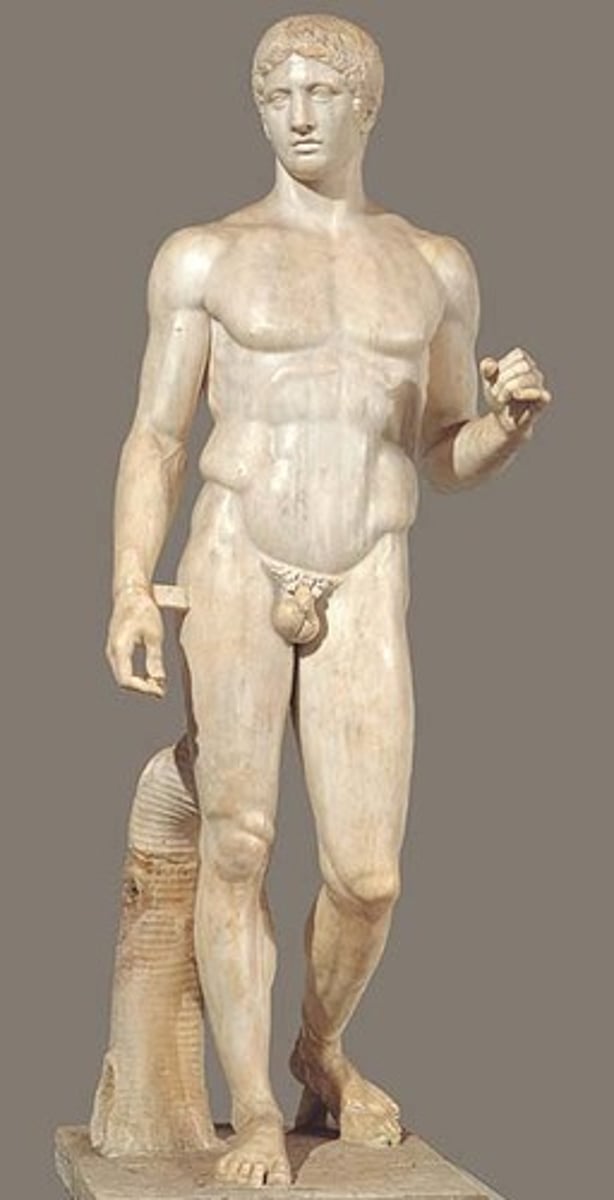

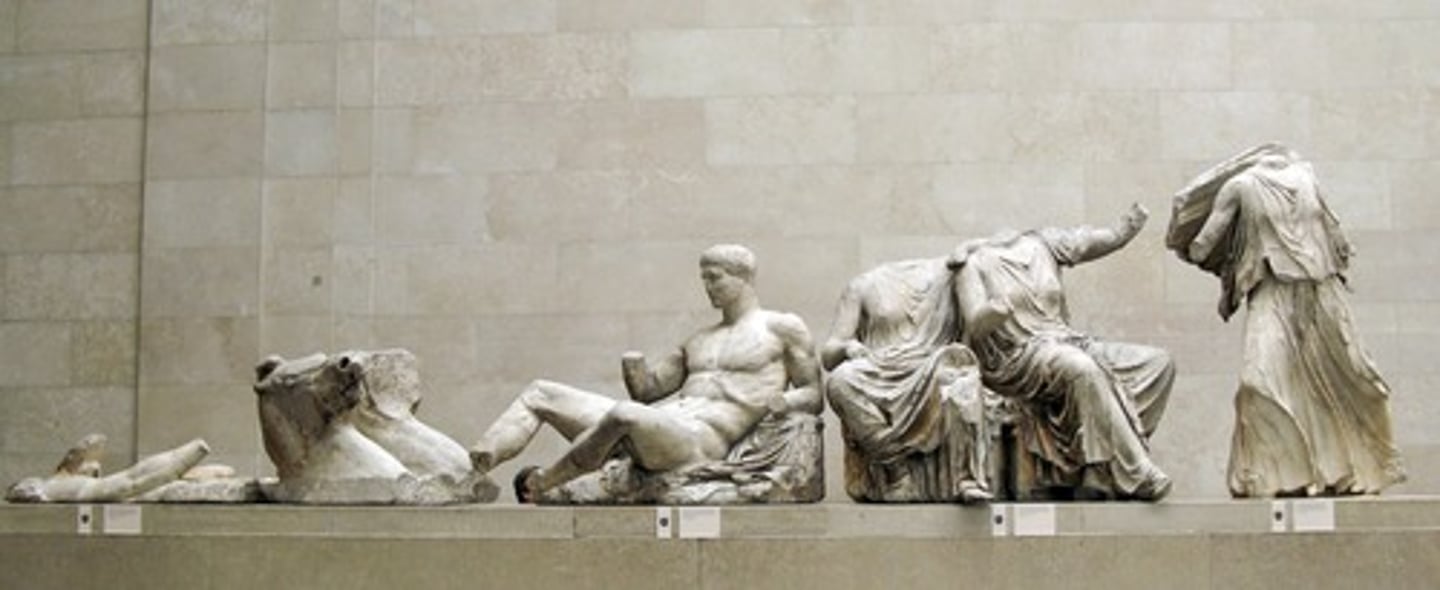
Phidias. Acropolis, Athens, Greece; ca. 438-432 BCE
Three goddesses (from the east pediment of the Parthenon); by Phidias; Probably Hestia, Dione, and Aphrodite. Understanding of human form, muscle and bone mechanics, and clothed forms. Heavy fold of garments reveal and conceal main and lesser body masses...also create interesting light and shade

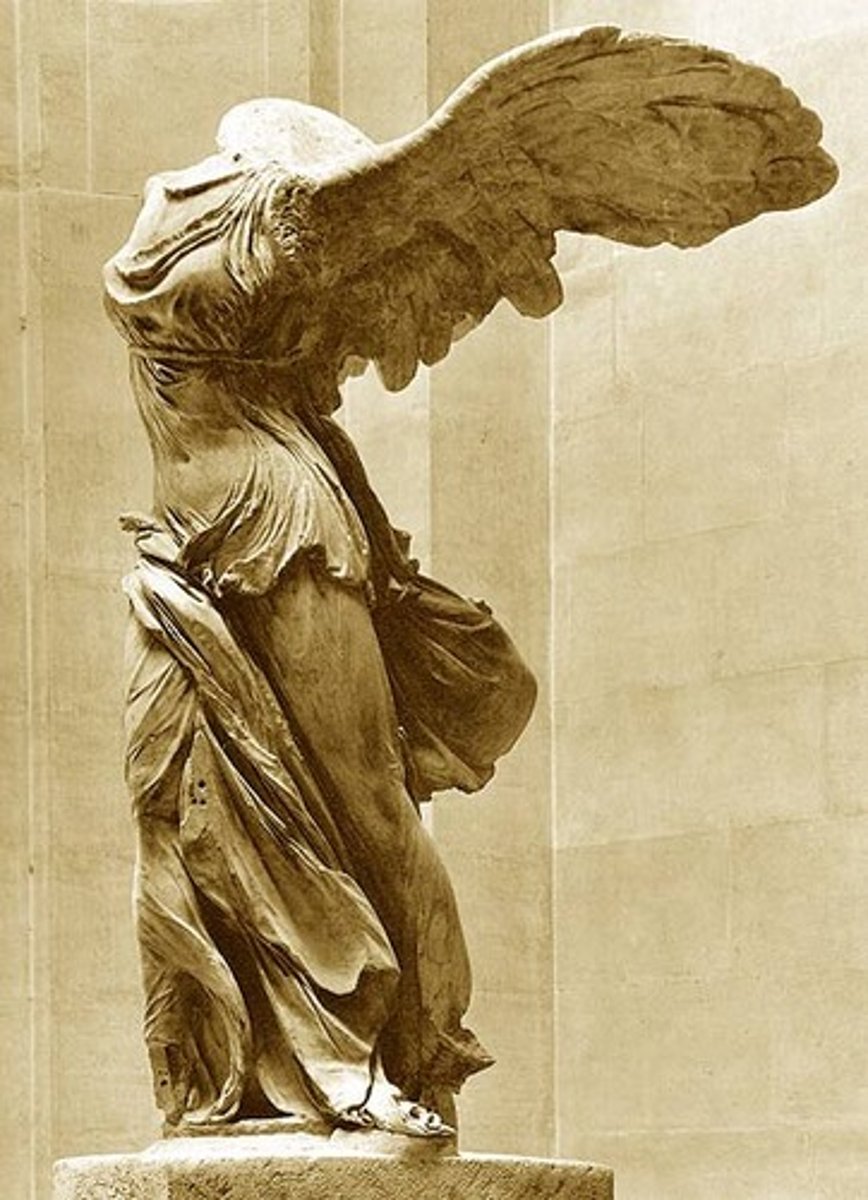
Nike of Samothrace,
Greek, 2nd century BC (190 BC); sculpture; religious; honored Greek-goddess Nike and a sea battle, symbol of Winged Victory, the space around her become important parts of the sculpture itself because of the way it was created

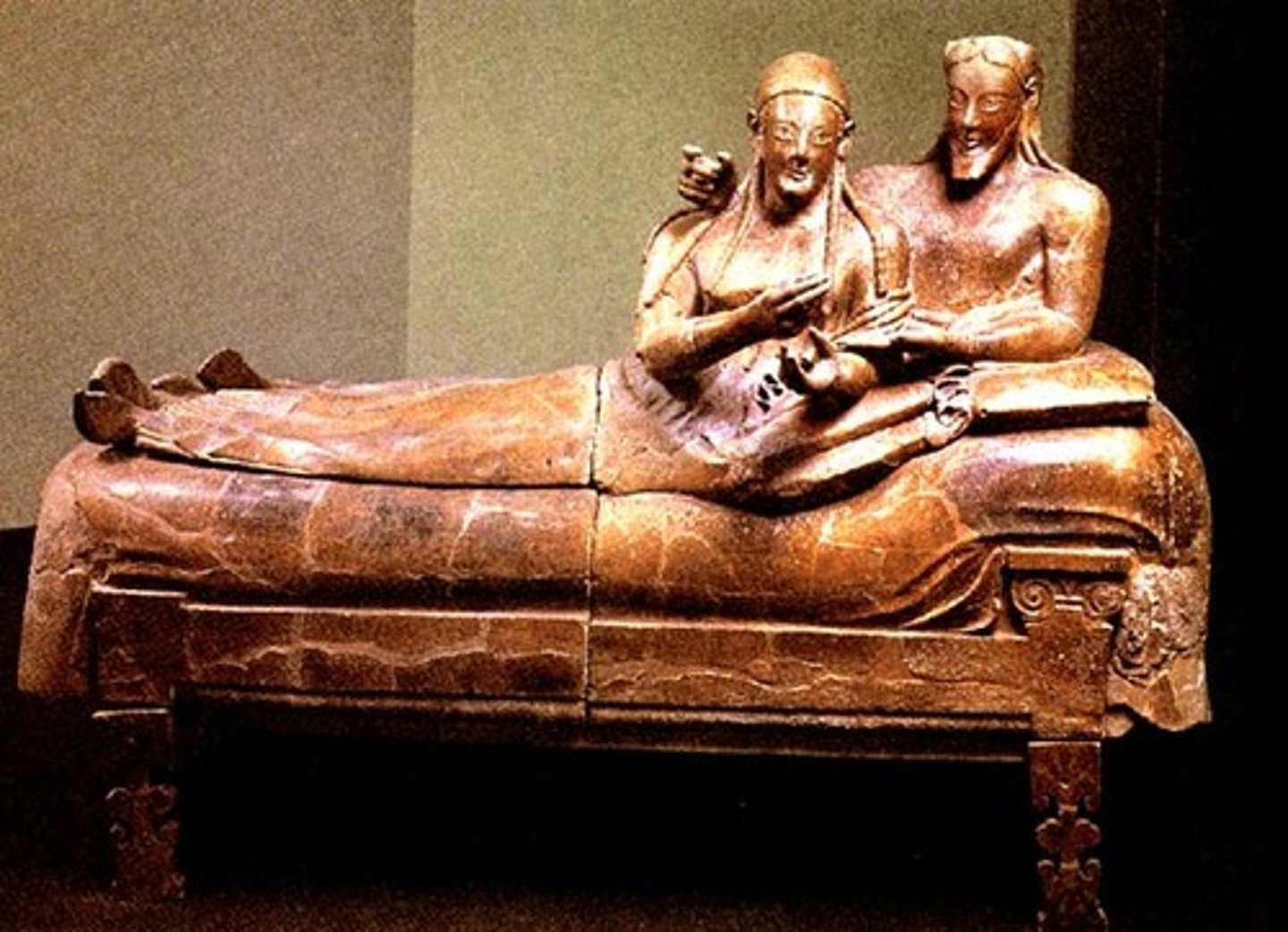
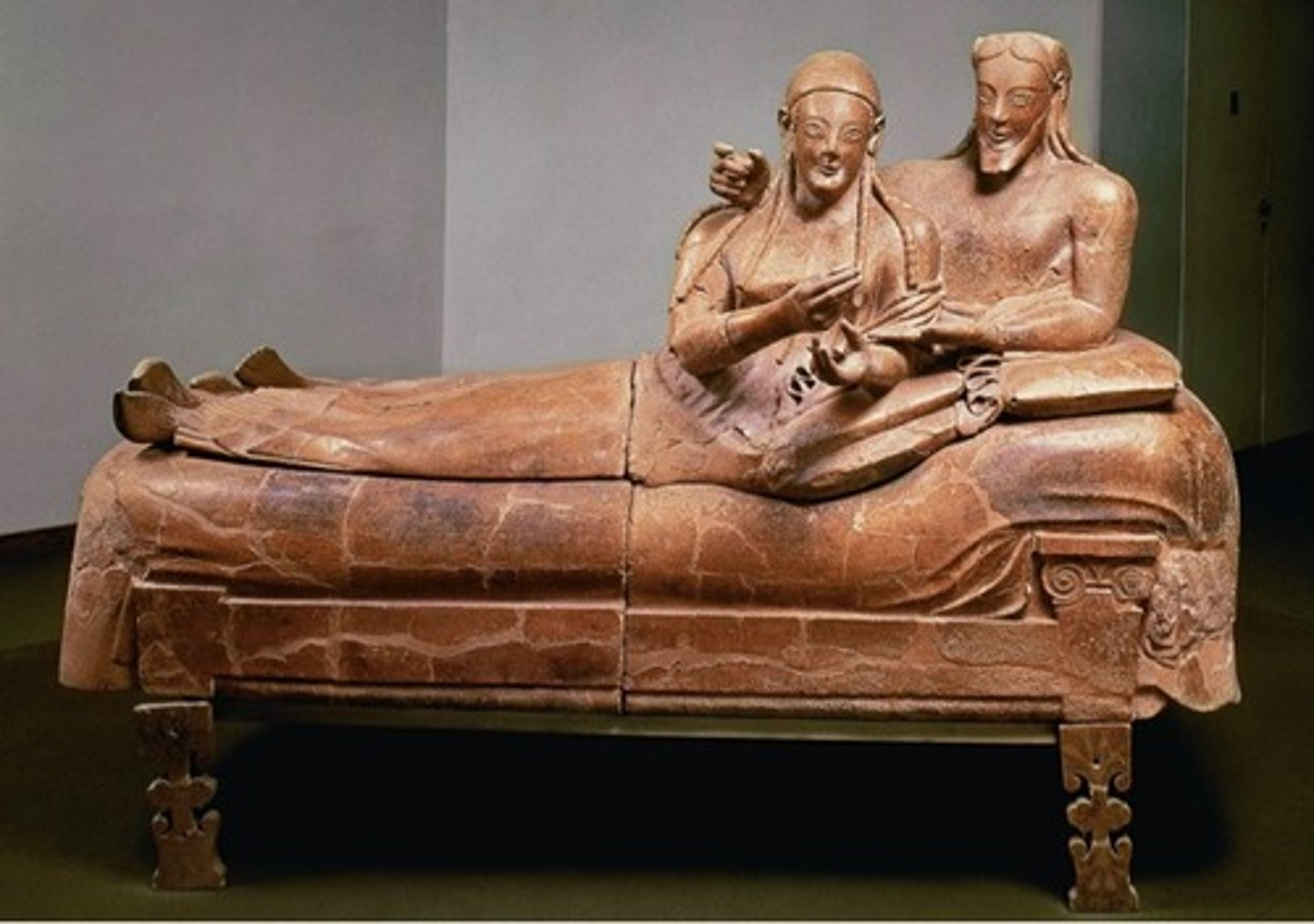
Etruscan sarchophagus,

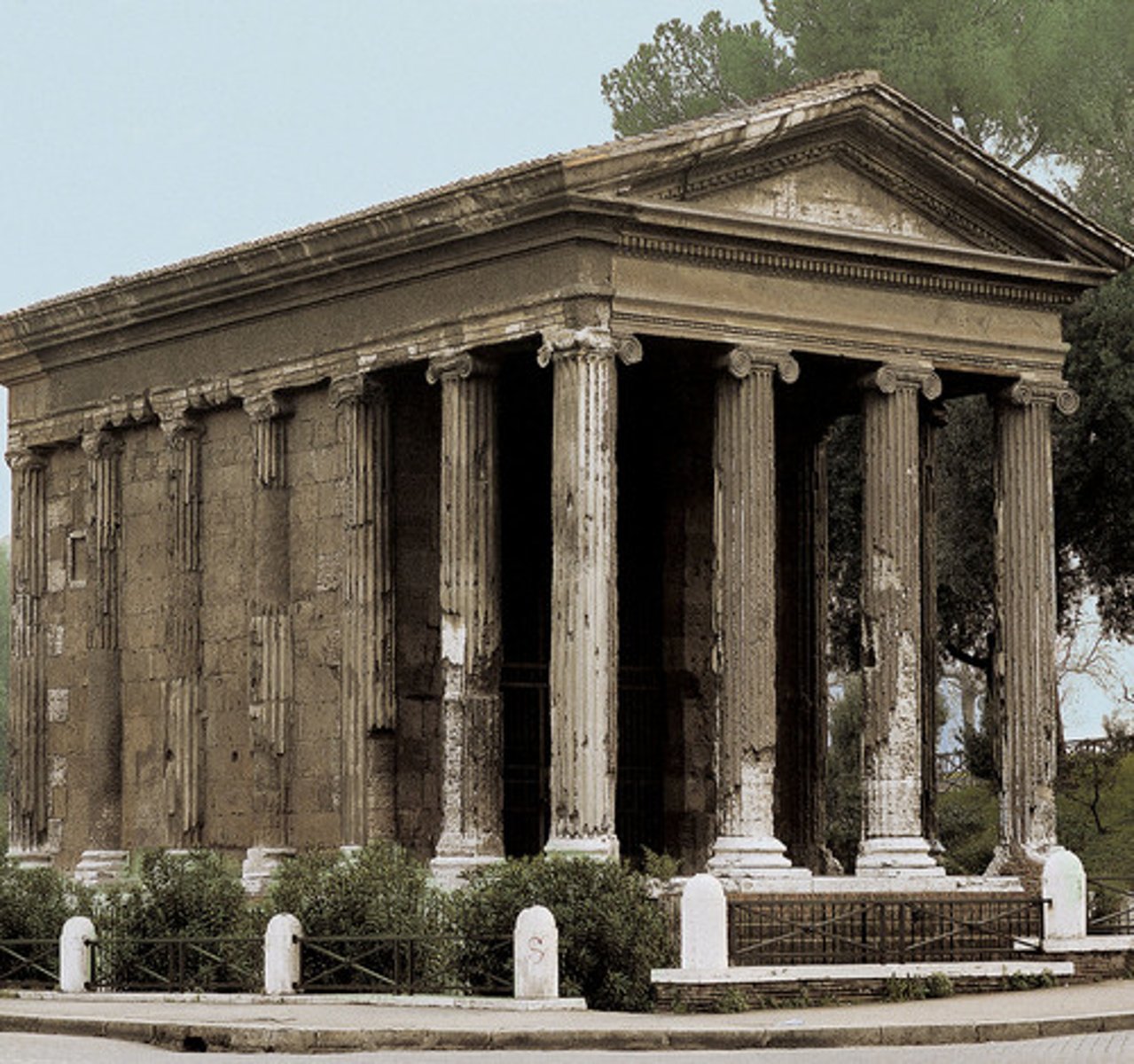
Temple of Portunus,

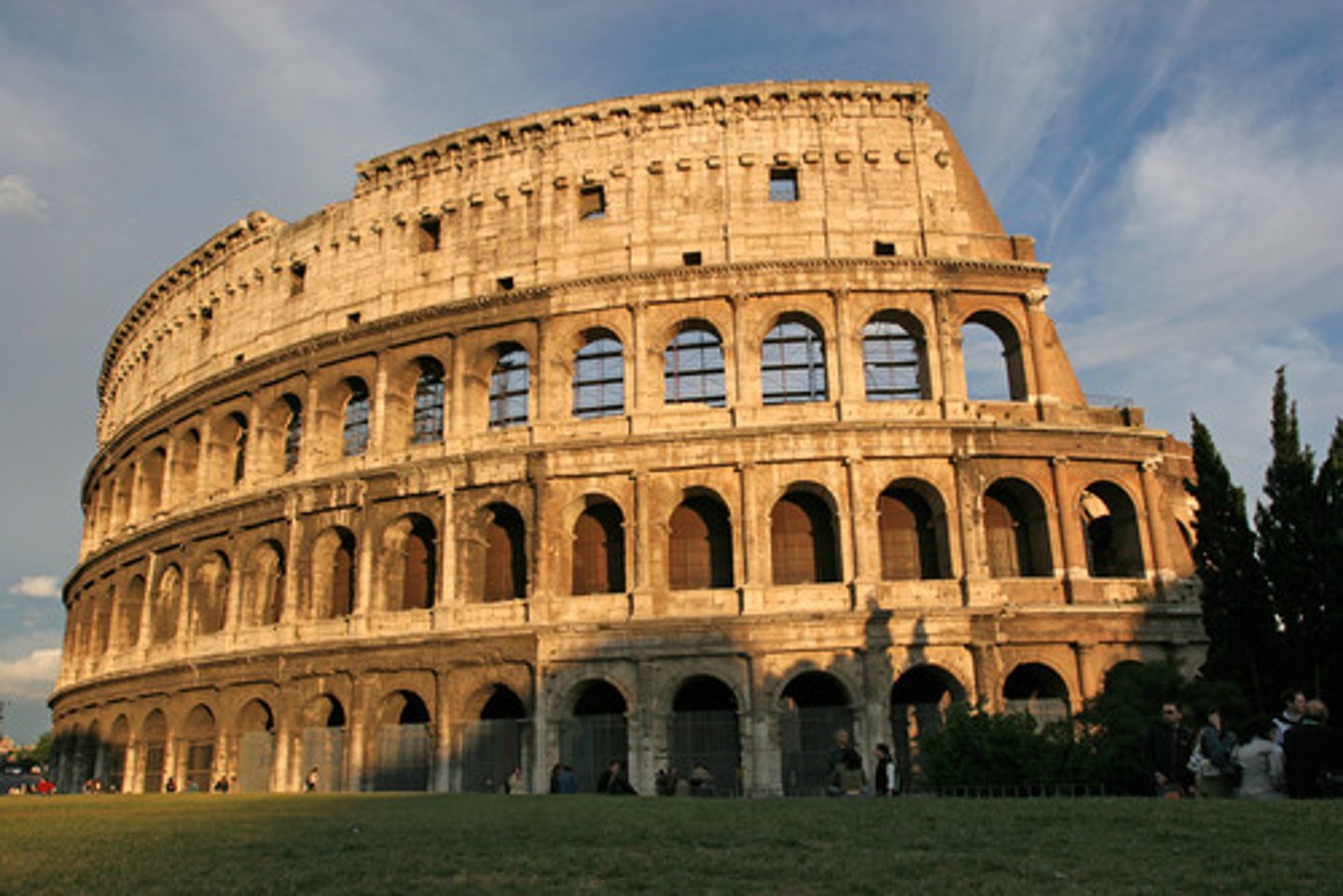
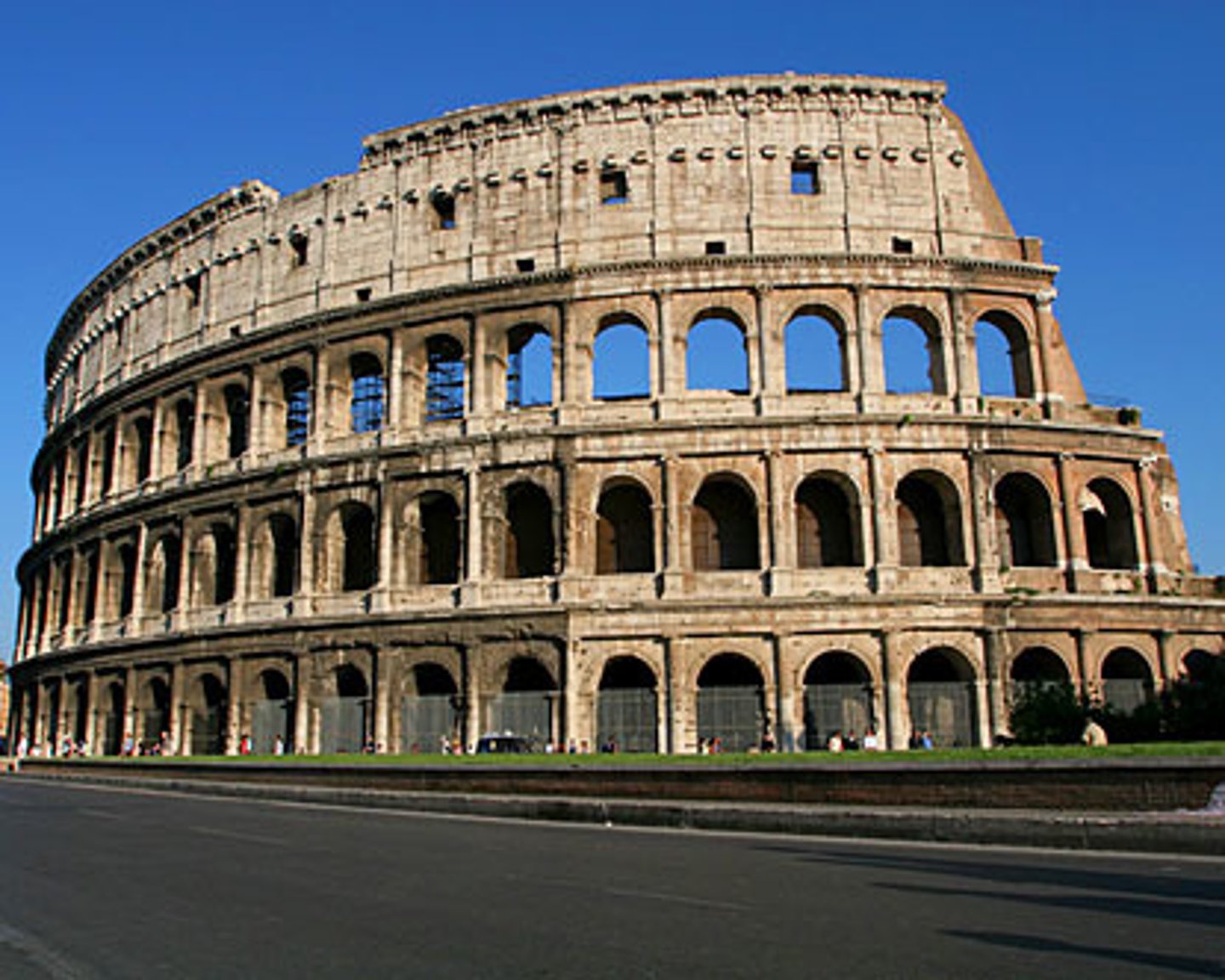
Colosseum

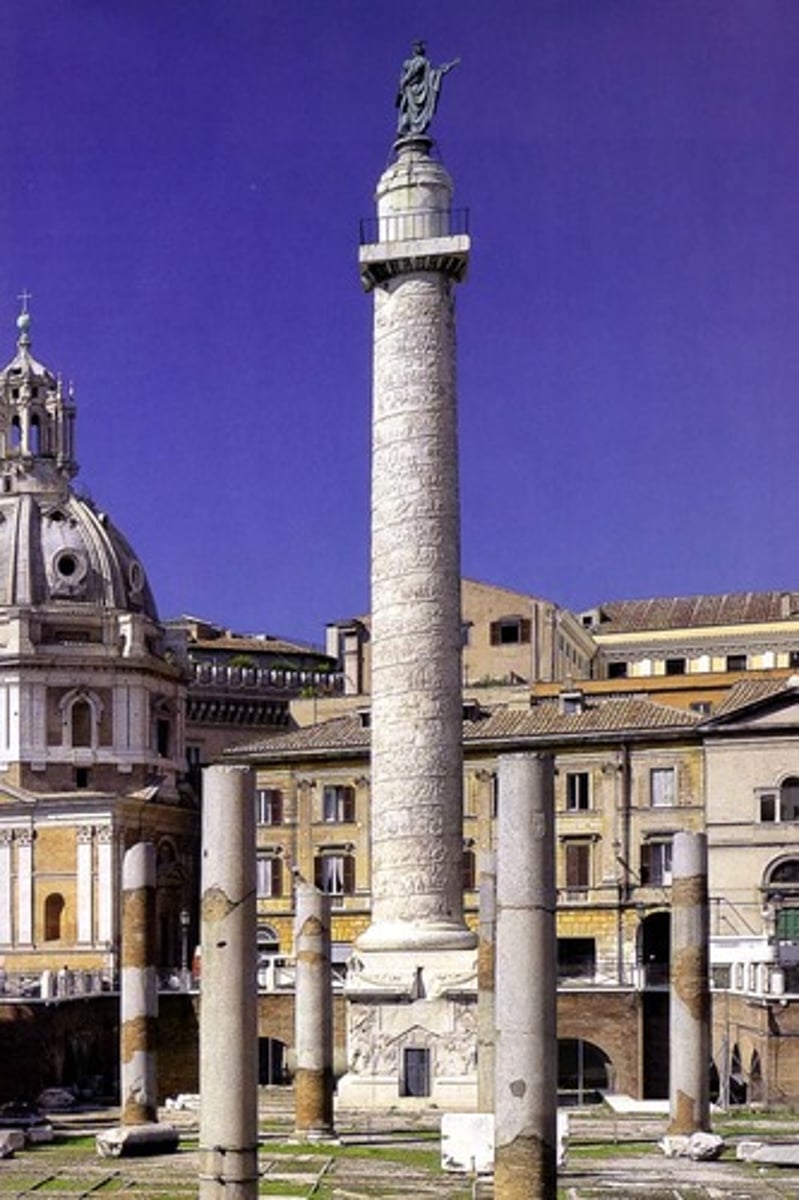
Trajan's Column,

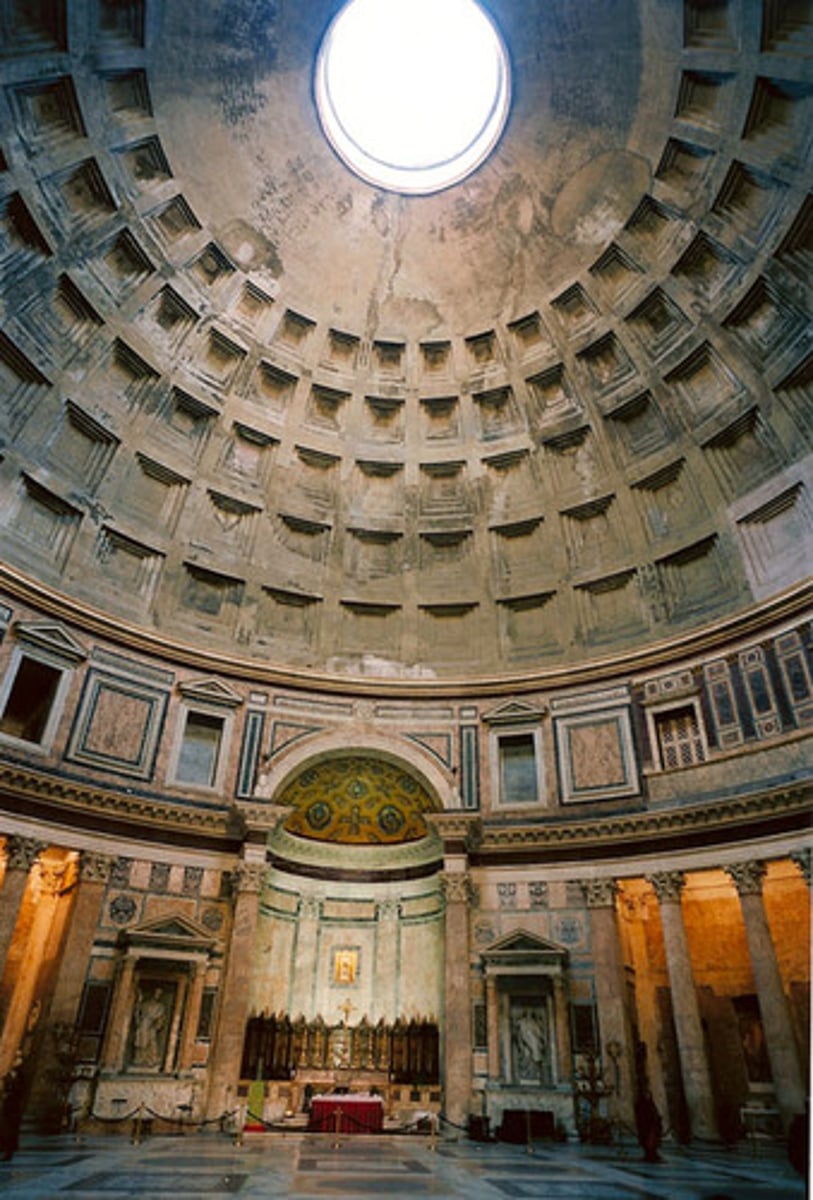
Interior of the Pantheon,

Portrait of Constantine,

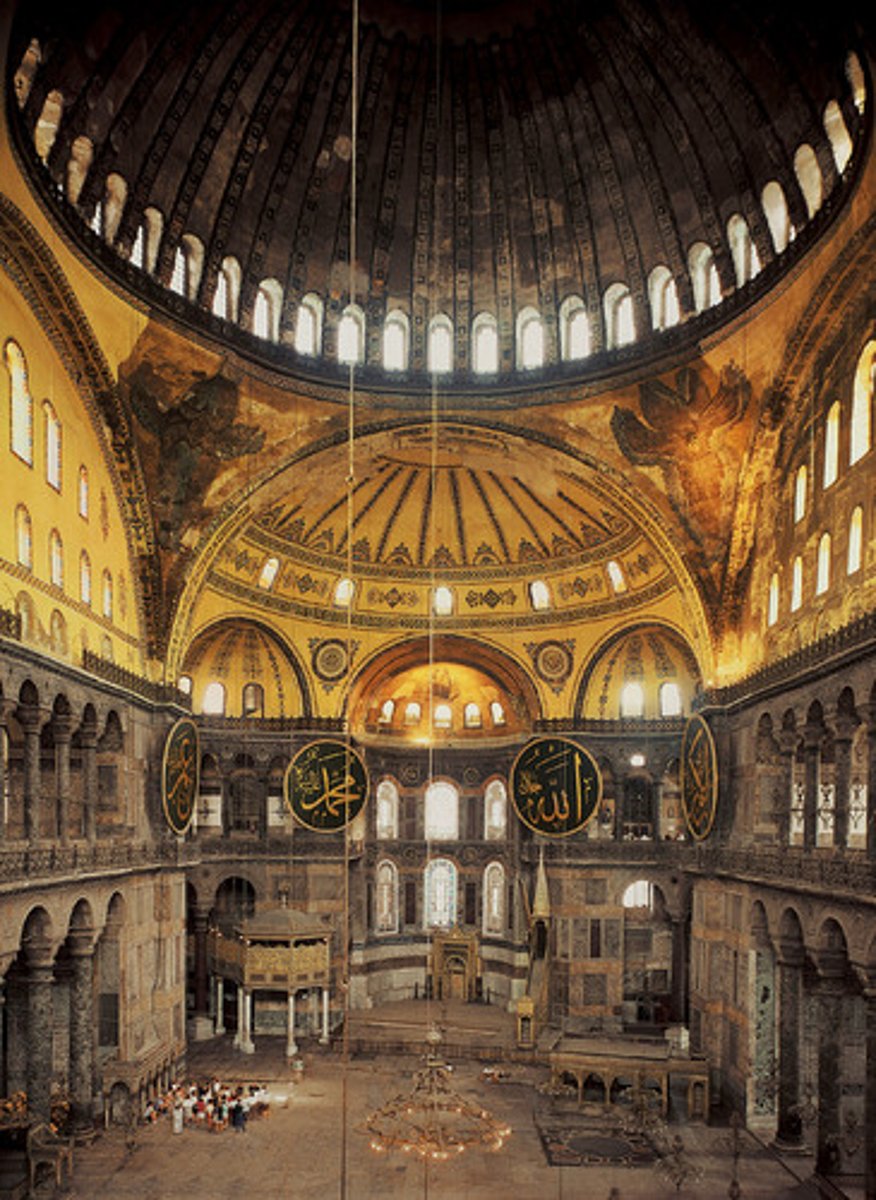
Hagia Sophia, interior

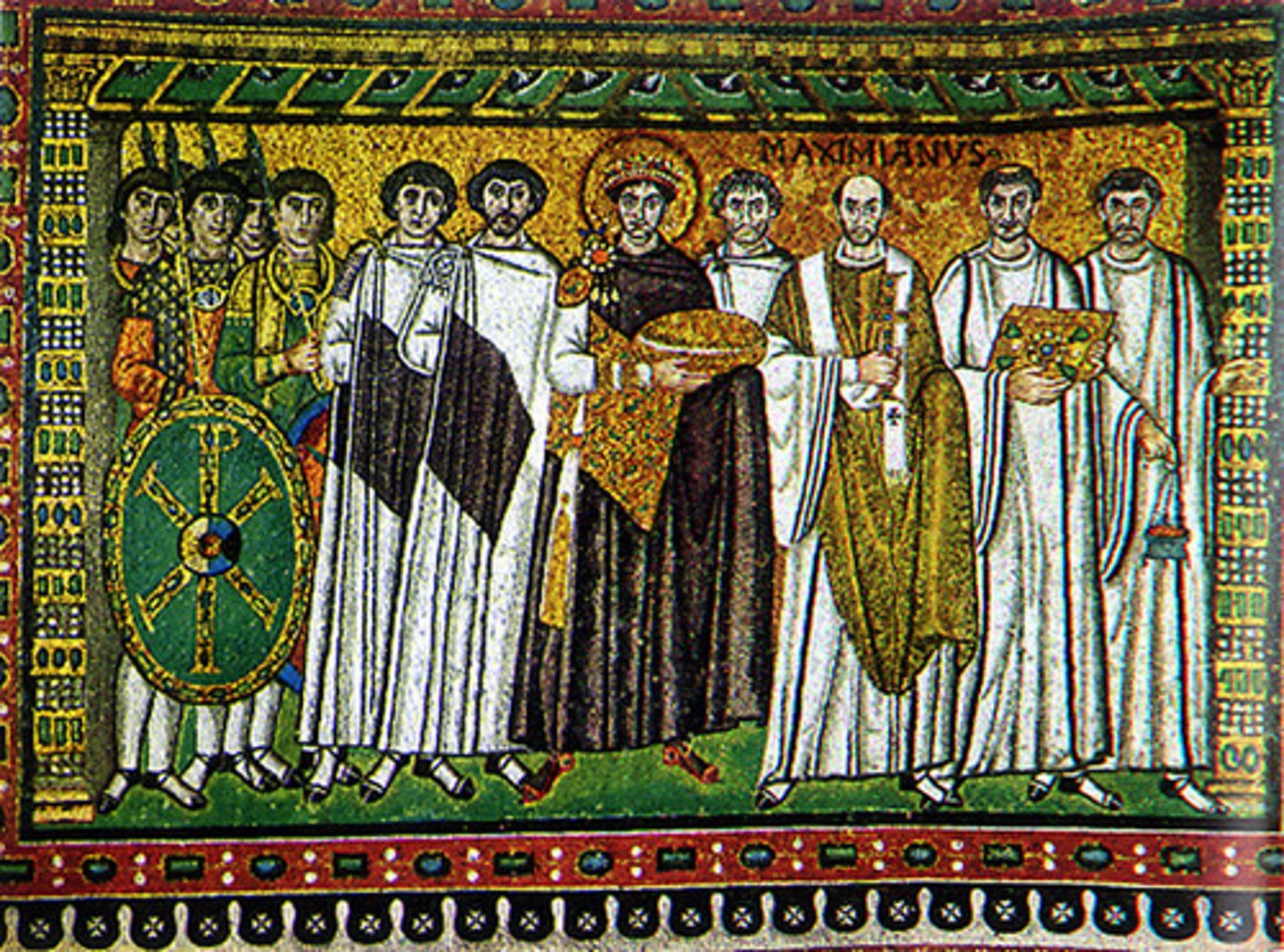
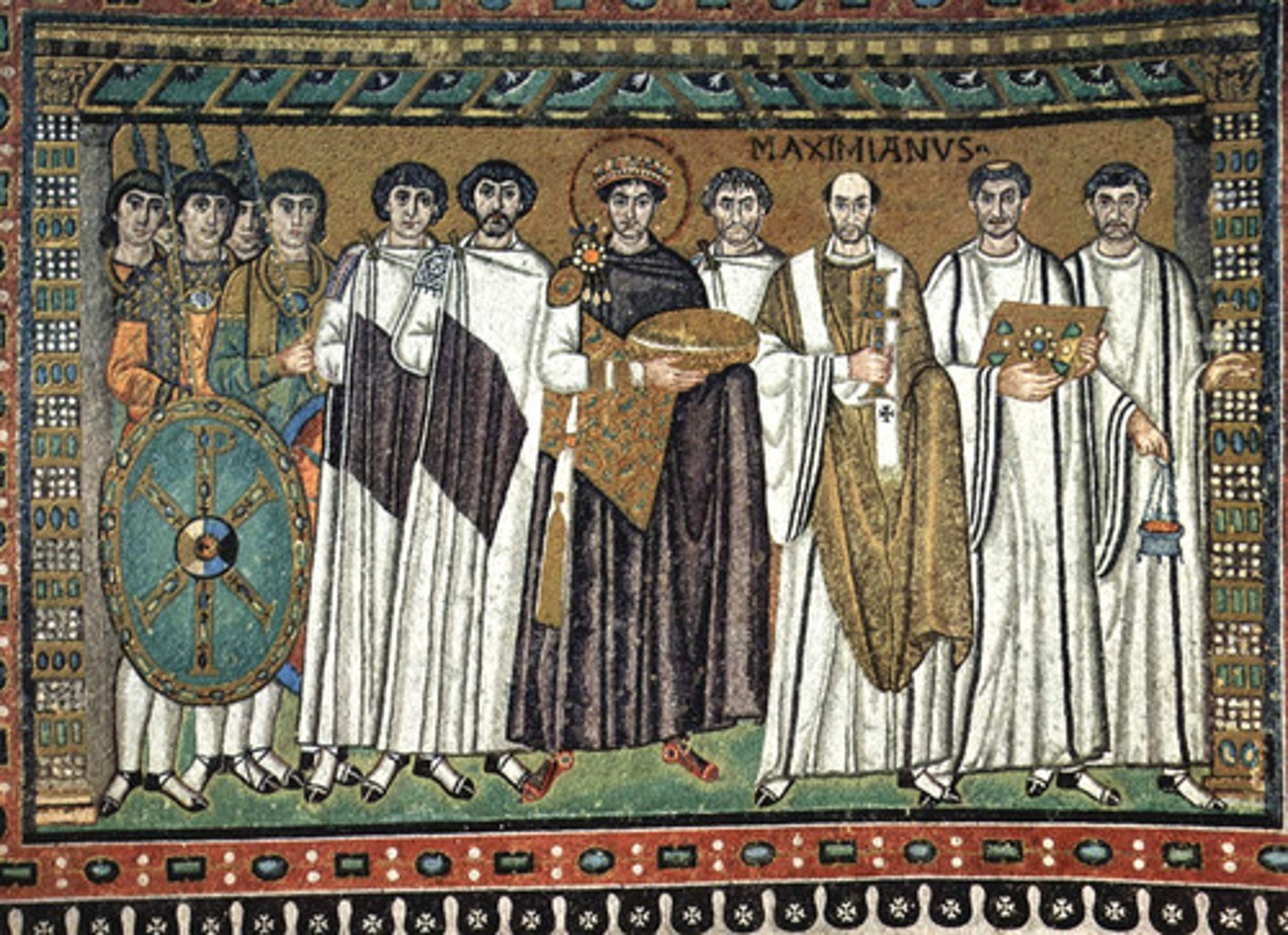
Mosaic with Emperor Justinian from San Vitale at Ravenna,

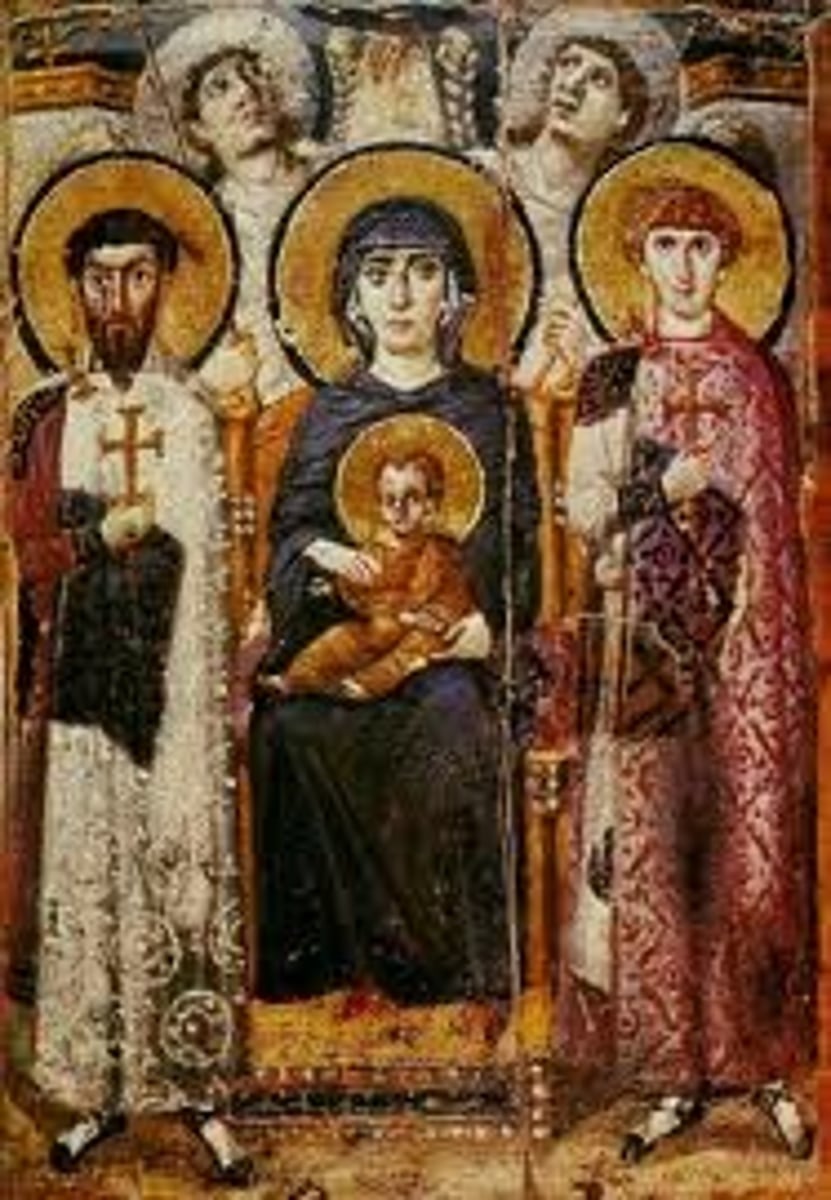
Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George, icon

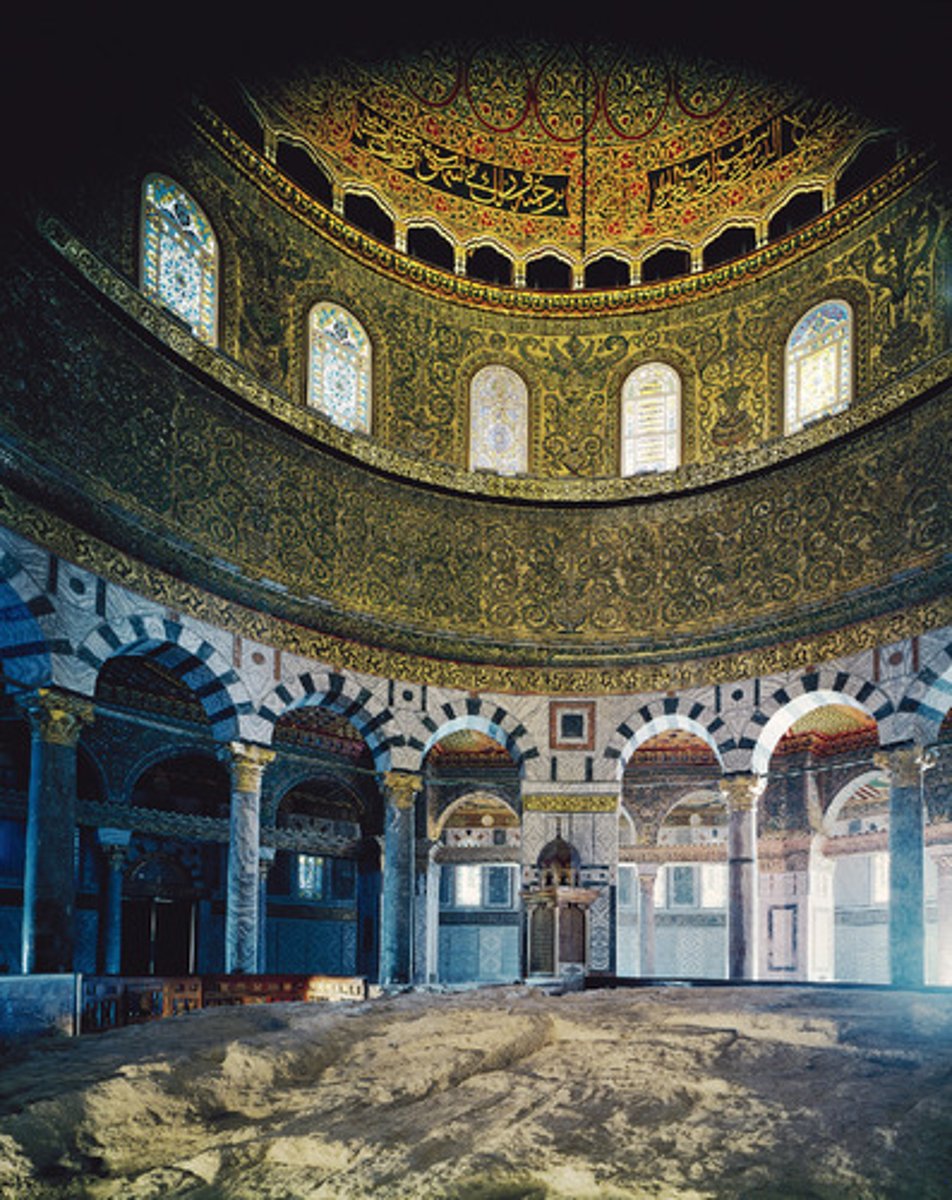
Dome of the Rock, interior

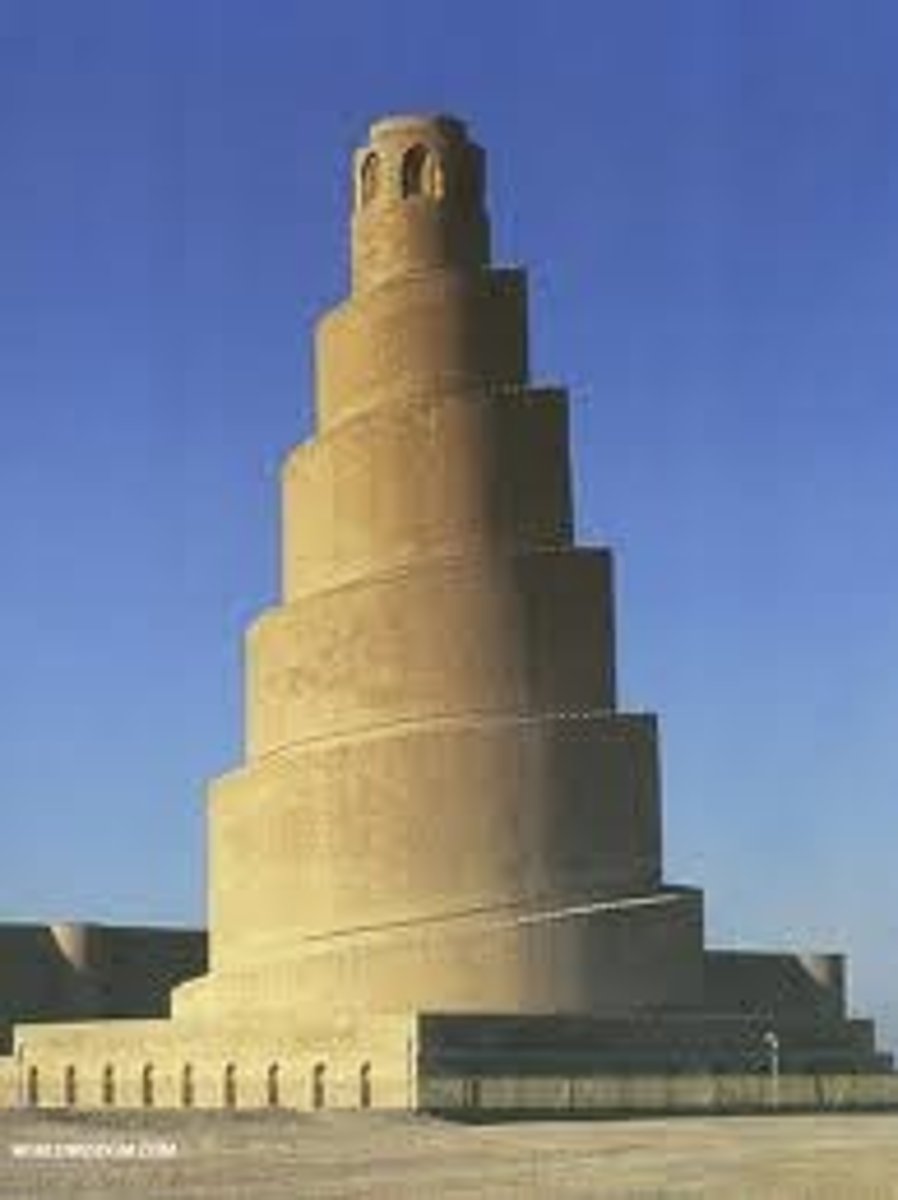
Malwiya Minaret from the Great Mosque at Samarra

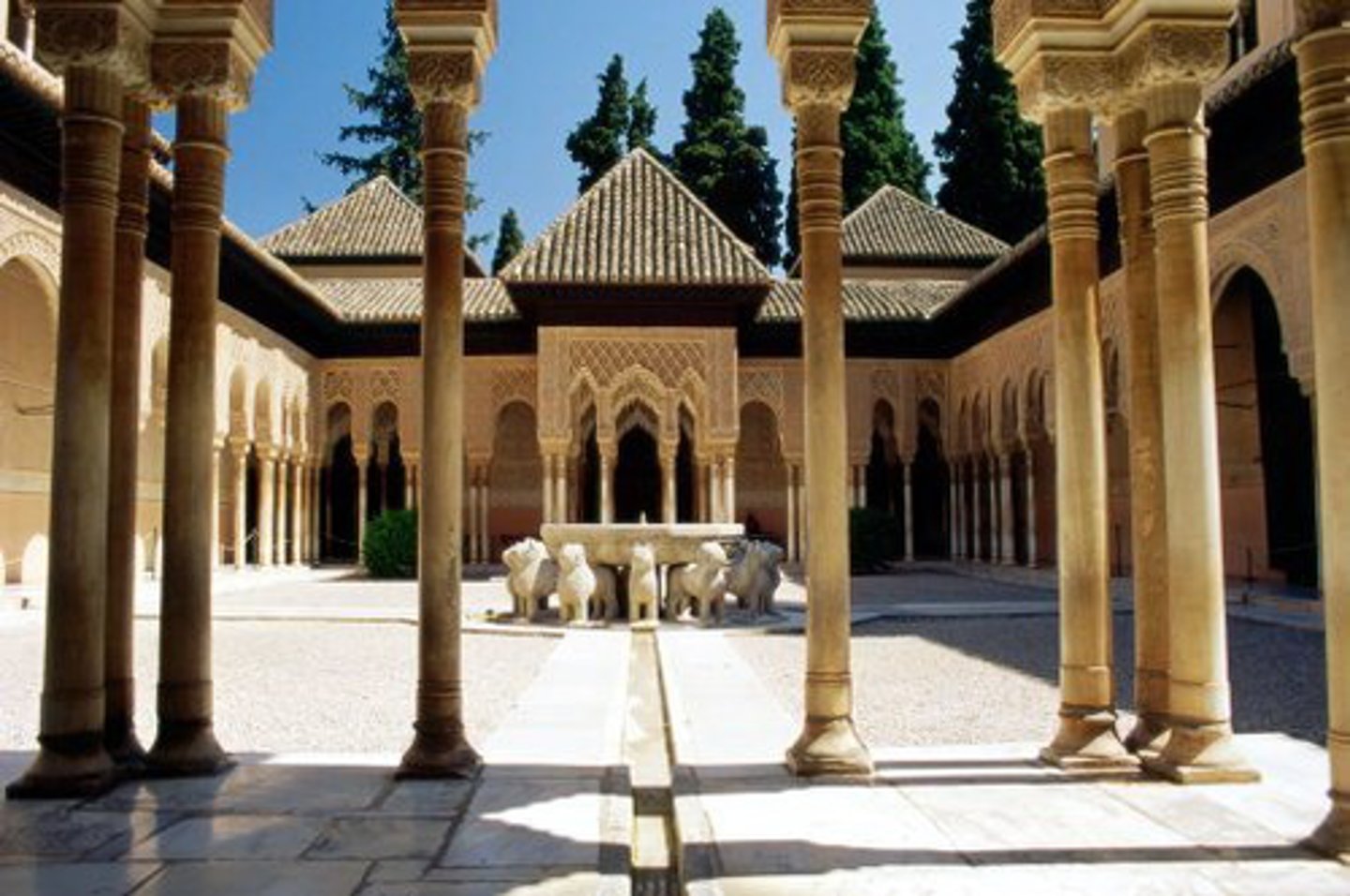
Courtyard of the Lions from the Alhambra, Spain

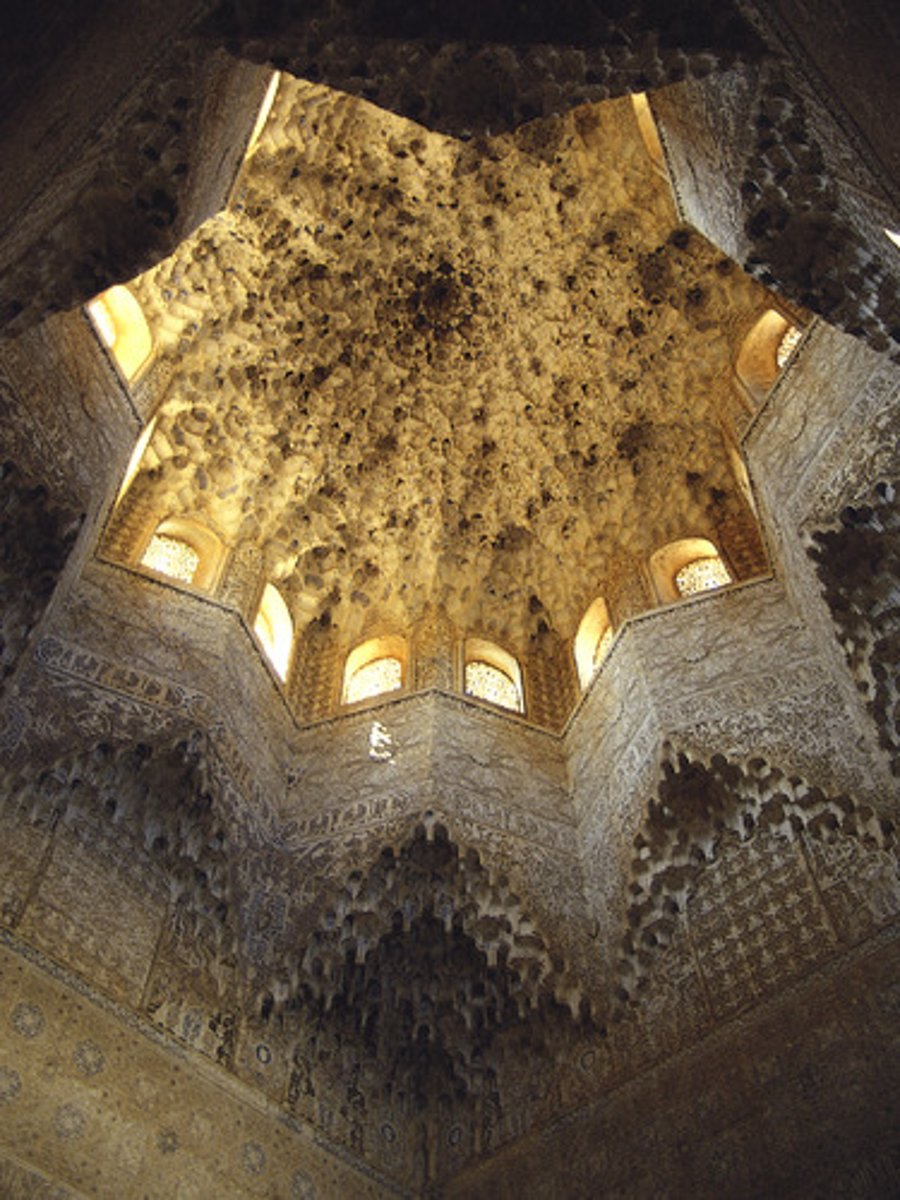
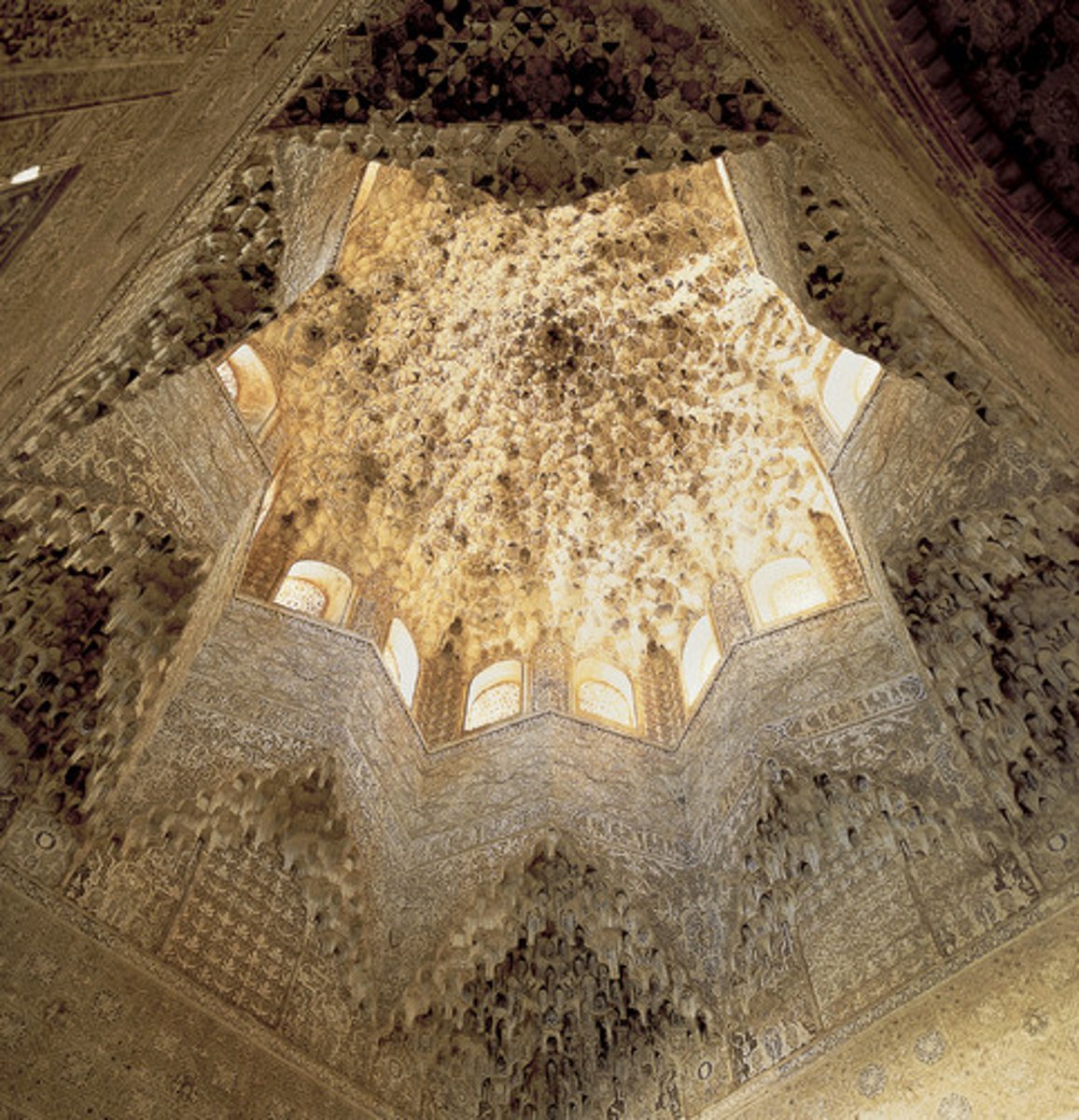
Muqarnas dome from the Hall of the Abencerrajes, Alhambra,

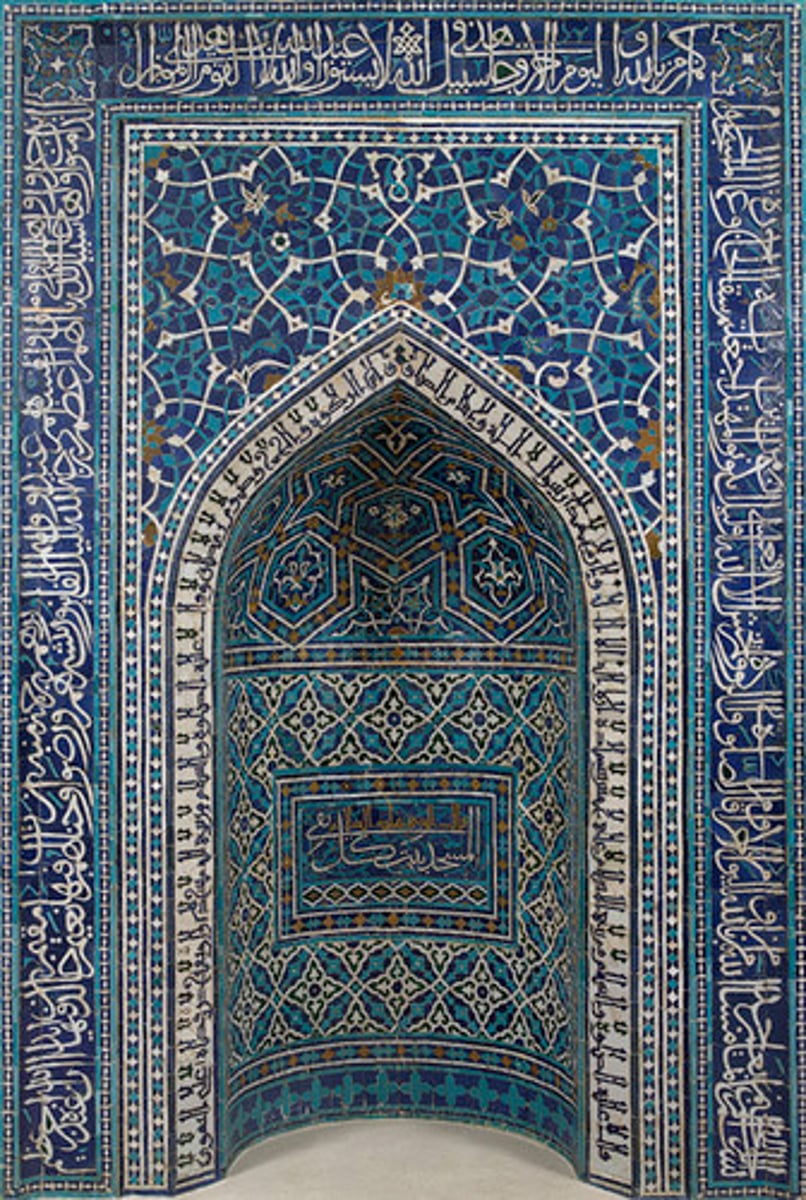
Mihrab from the Madrasa Imami at Isfahan

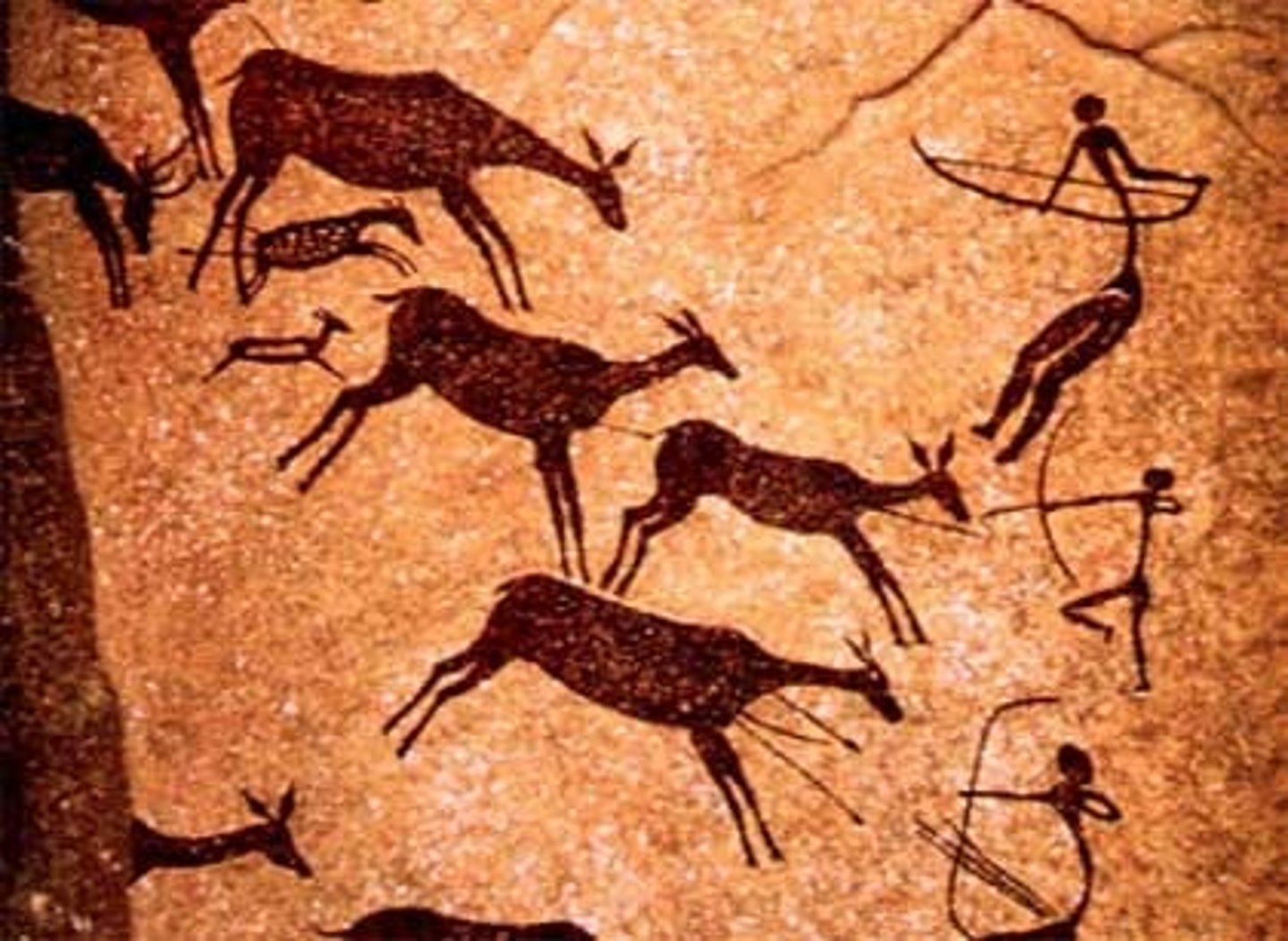
Prehistoric Art
mostly in caves, scattered, animals are three-dimensional, humans are stick-figures, handprints are present, a lot, attempt at a signature

Megalithic
menhirs cut into rectangular shapes and used to construct monuments

Post-and-lintel system
two uprights were used to support a horizontal beam

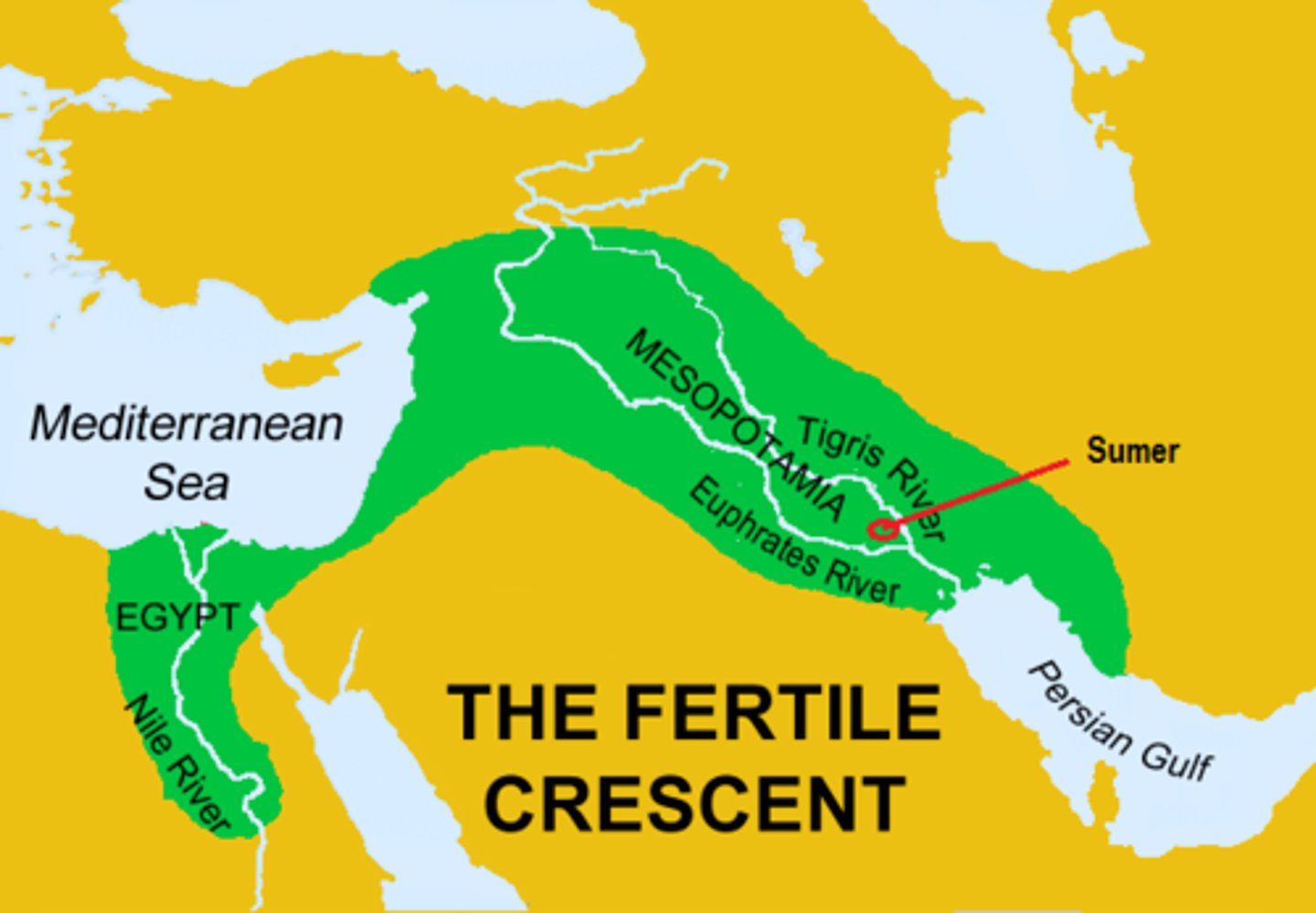
Mesopotamia
Core of a region called "the fertile crescent" gave birth to worlds great modern faiths - judaism, christinaity, and islam. an ancient region in W Asia between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers: now part of Iraq.
sarcophagus
a stone coffin, especially one with a carving or inscription on it

Cycladic art
The pre-Greek art of the Cycladic Islands, most statuettes made from marble, women, but some men doing service activities

Minoan art
The pre-Greek art of Crete, named after the legendary King Minos of Knossos, potter's wheel was made during the middle period, Kamares vase, Marine style octopus car, snake godess, young God out of a hippopotomus tusk, no monumental structures or temples

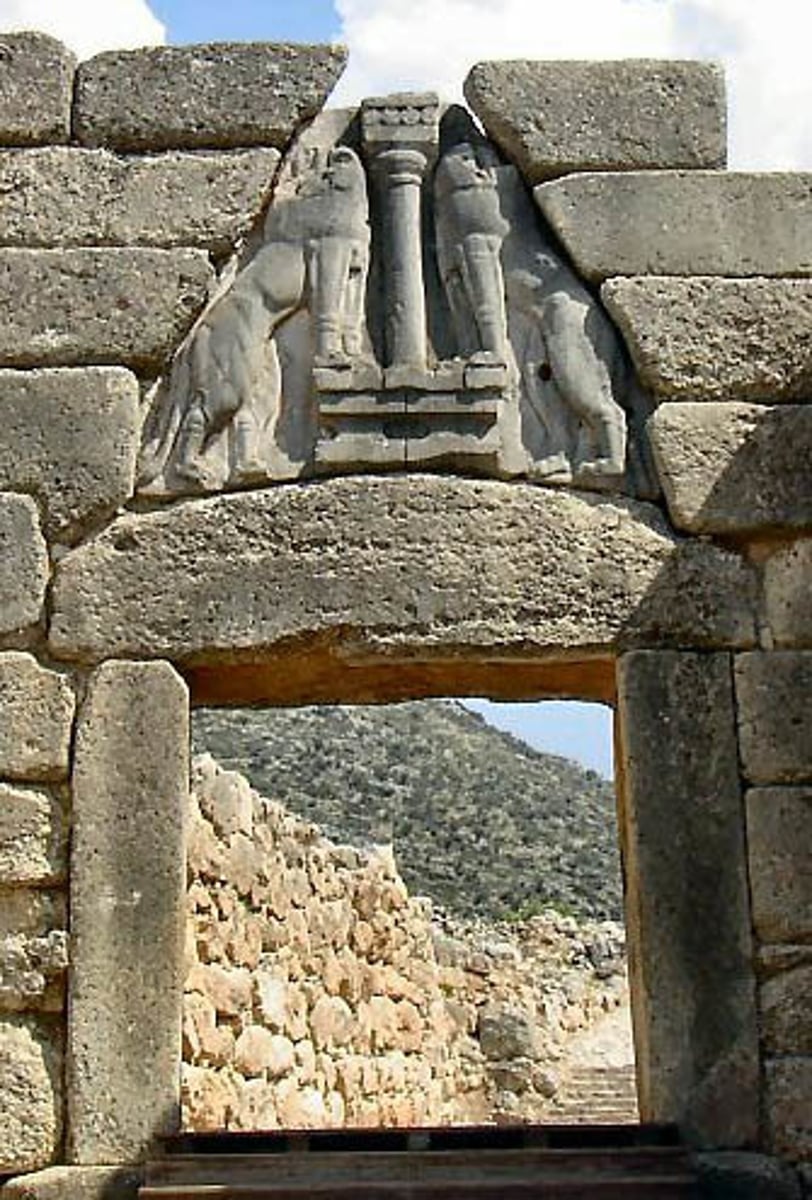
Mycenaean art
from the greek mainland, the late phase of Helladic art, named after the site of Mycenae, lion's gate with relieving triangle (corbeled arch), largest sculpture

tholos
beehive shaped dome that housed a tomb, covered by enormous earthen mounds

Three basic periods of Greek art Archaic,
Characterized by the use of the composite view for painted and relief figures and of Egyptian stances for statues
characterized in part by the use of the composite view for painted and relief figures and of Egyptian stances for statues. (3 areas changes: development of orders, standardized pottery and black and red figure paiting, and sculpture changes in Kourus, developed 1st canon of proportion moved in space, weight shift (contropasto)

Three basic periods of Greek art Classical
the art and culture of ancient greece when written lowercase it refers more generally to Greco-Roman art and culture

Three basic periods of Greek art Hellenistic
relating to the blend of Greek, Persian, Egyptian, and Indian culture that lasted from the death of Alexander the Great. A combining of the ideas, beliefs and arts of the East and West

contrapposto
("counterbalance") It is the graceful arrangement of the body based on tilted shoulders and hips, one bent knee, and all the weight of the body placed on the "engaged" leg. Alternating parts of the body flexed and relaxed. It is a method developed by the Greeks to represent freedom of movement.

stylobate
the uppermost course of the platform of a classical temple, which supports the columns.
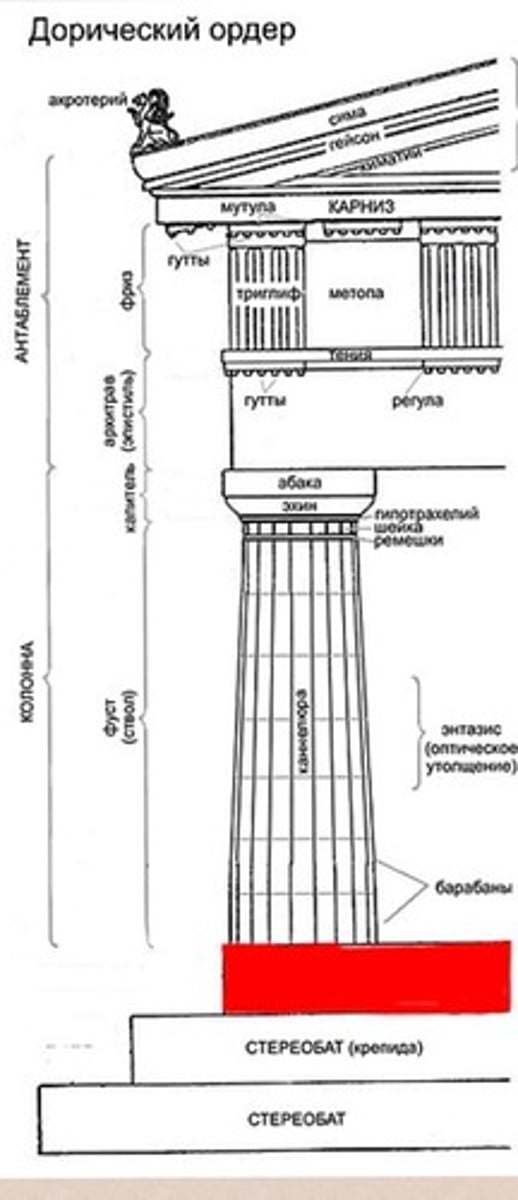
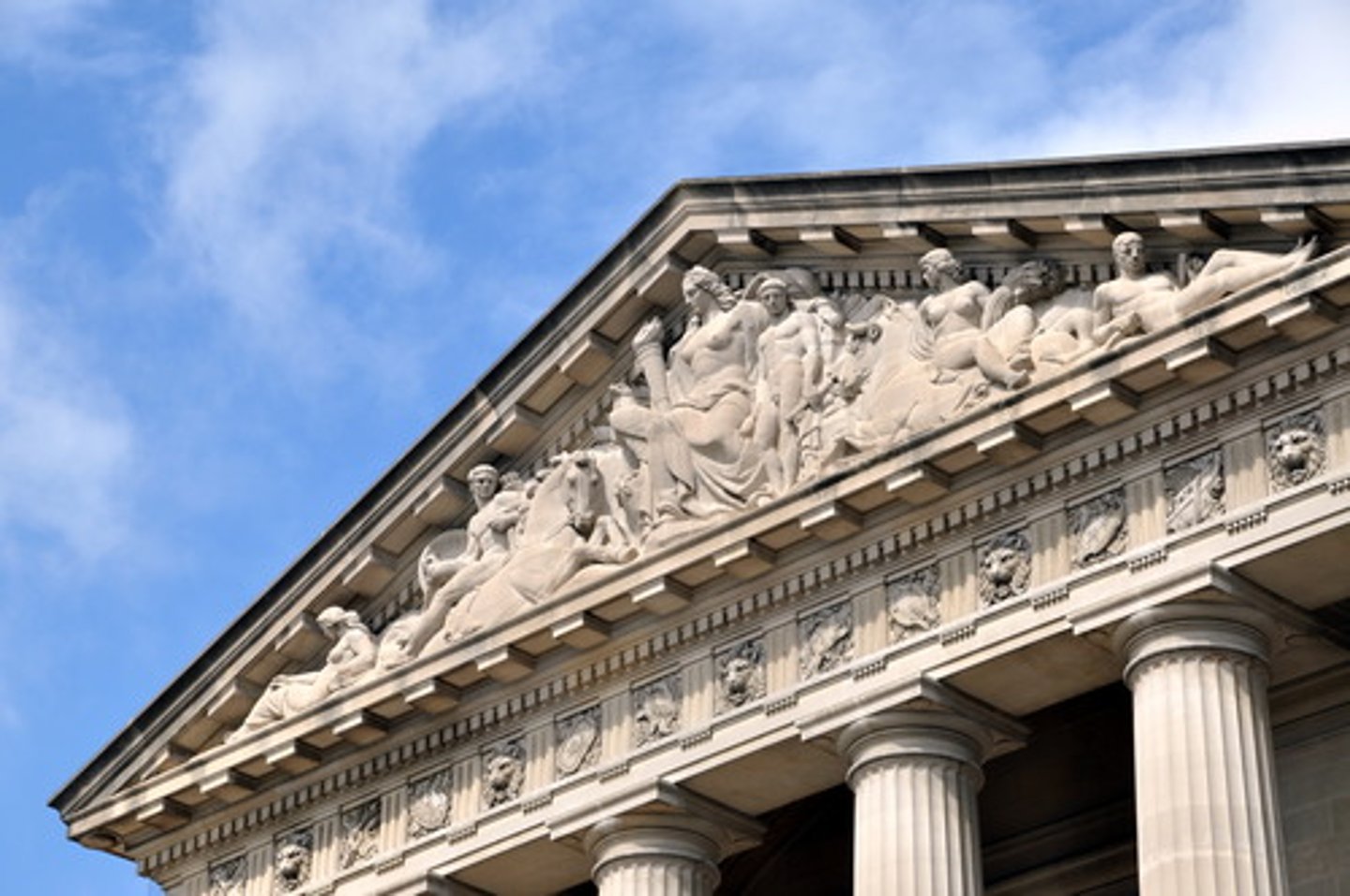
pediment
a triangular gable between a horizontal entablature and a sloping roof

cella
The chamber at the center of an ancient temple; in a classical temple, the room (Greek, naos) in which the cult statue usually stood.
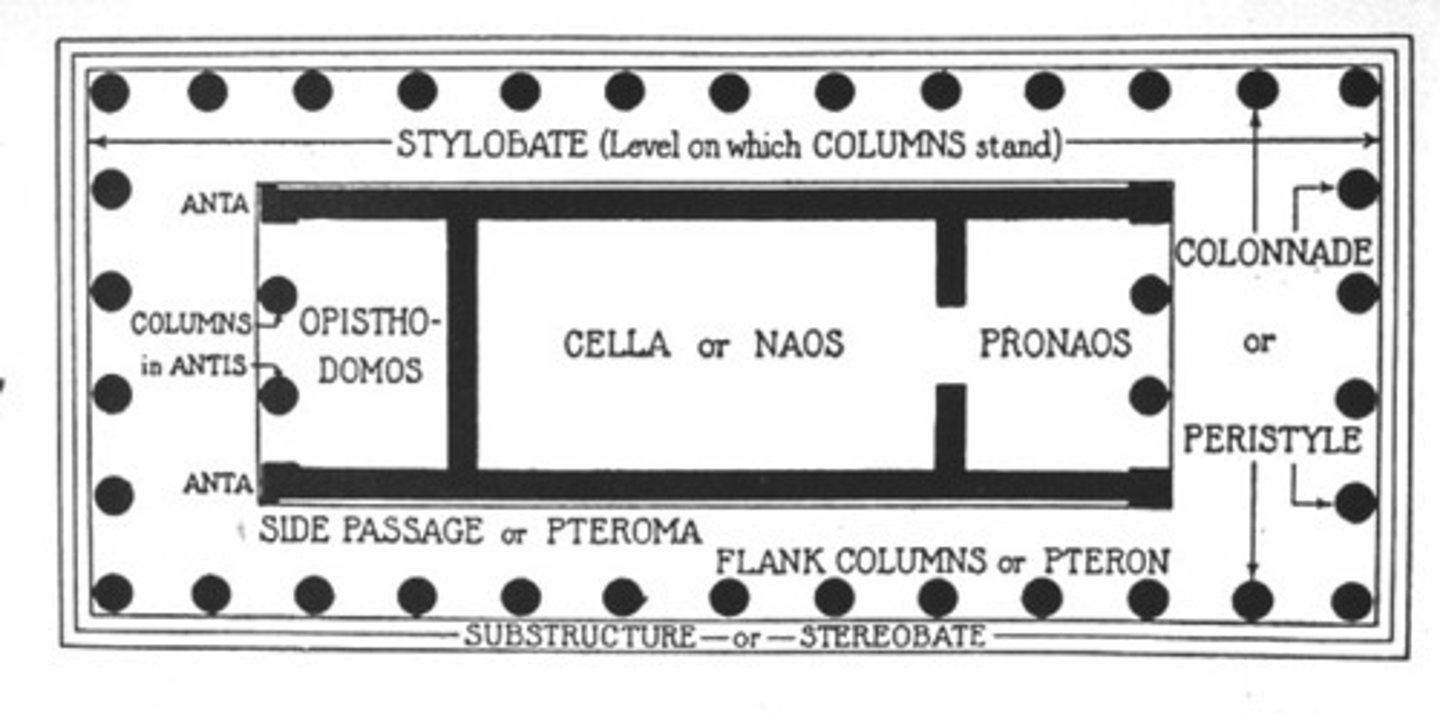
pseudoperipteral
In Roman architecture, a pseudoperipteral temple has a series of engaged columns all around the sides and back of the cella to give the appearance of a peripteral colonnade.
basilica
In Roman architecture, a civic building for legal and other civic proceedings, rectangular in plan with an entrance usually on a long side. In Christian architecture, a church somewhat resembling the Roman basilica, usually entered from one end and with an apse at the other.

mosaic
patterns or pictures made by embedding small pieces of stone or glass (tesserae) in cement on surfaces such as walls and floors; also, the technique of making such works

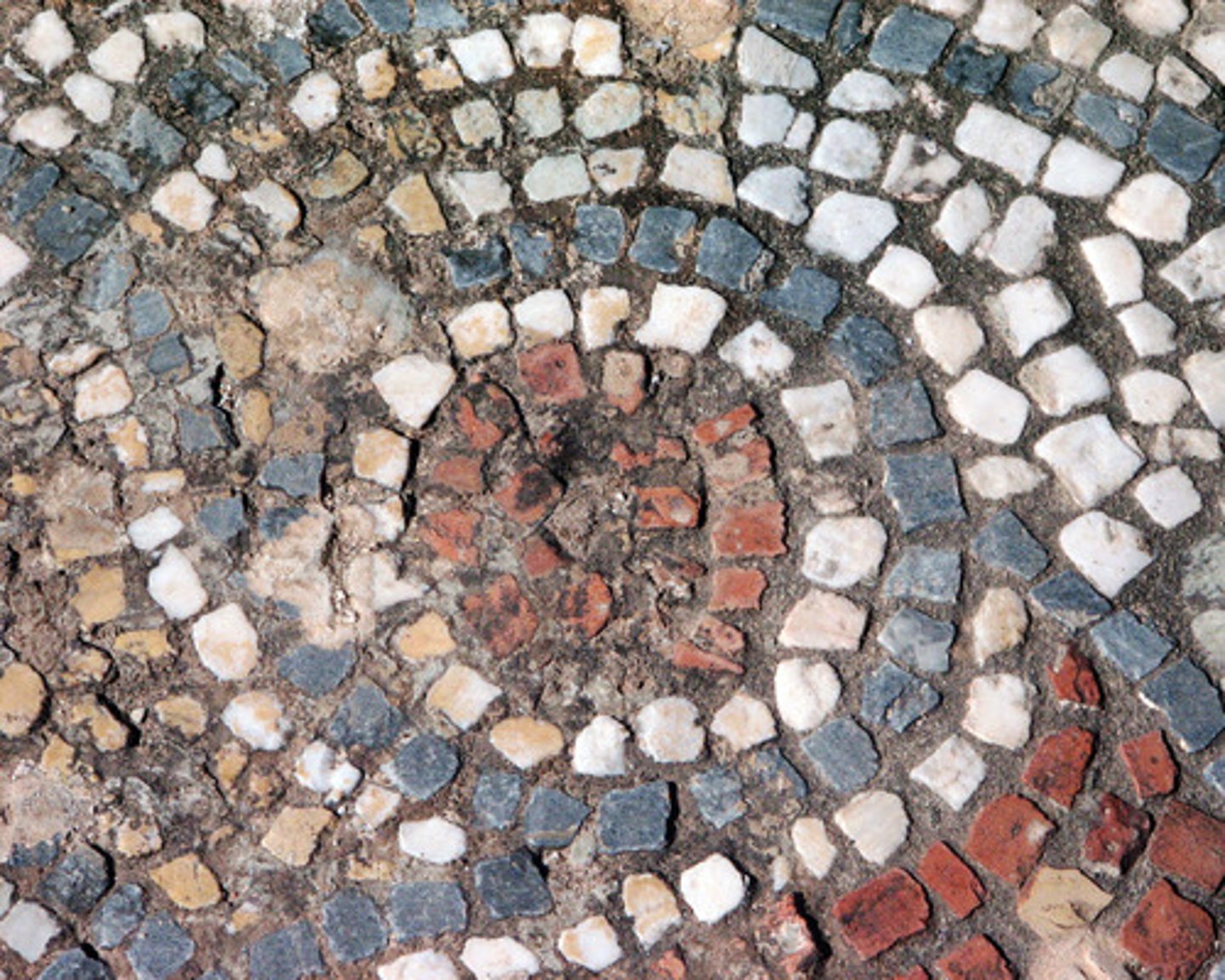
tesserae
the small piece of stone, glass, or other object that is pieced together with many others to create a mosaic

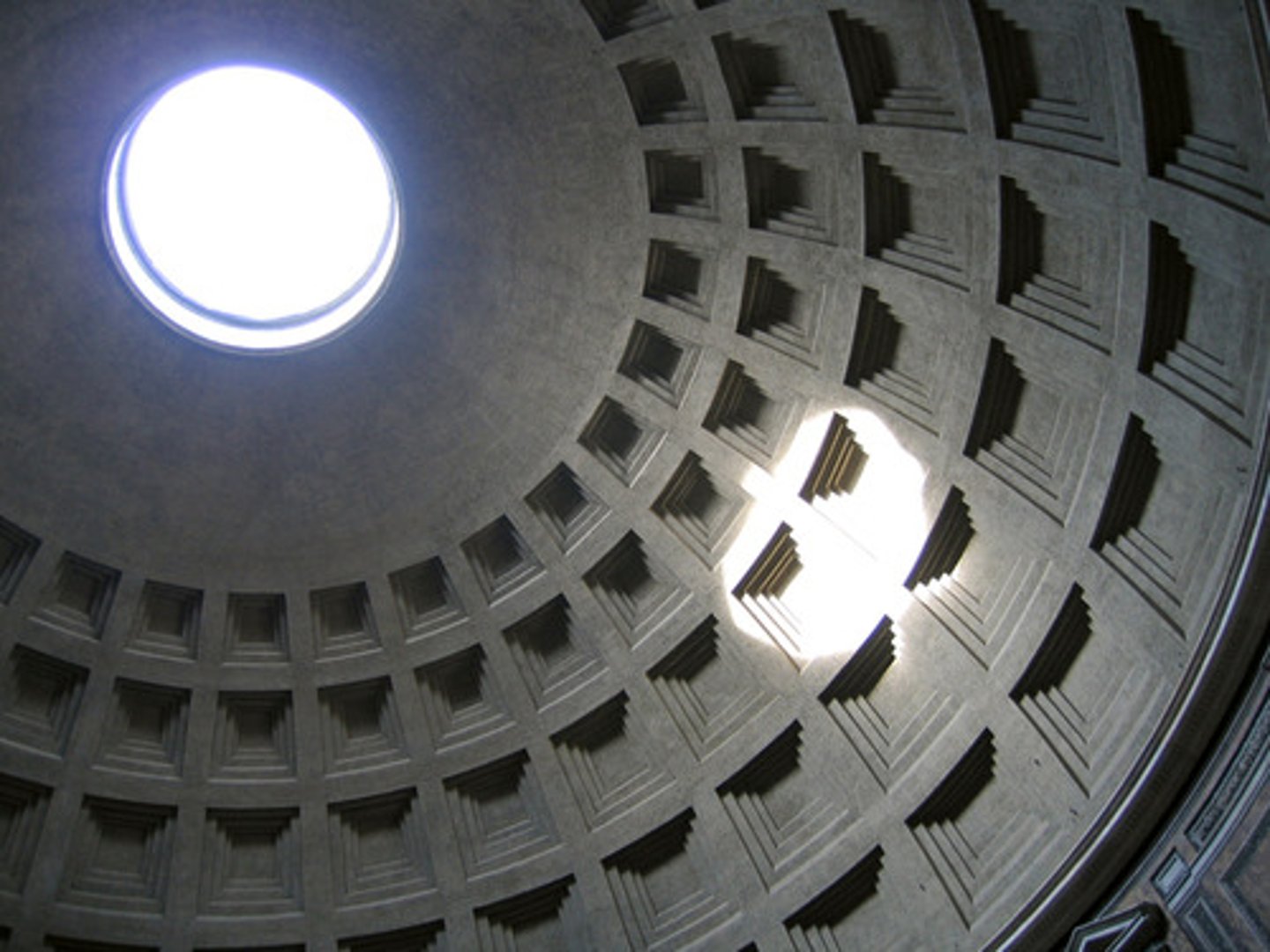
oculus
Latin, "eye." The round central opening of a dome. Also, a small round window in a Gothic cathedral.
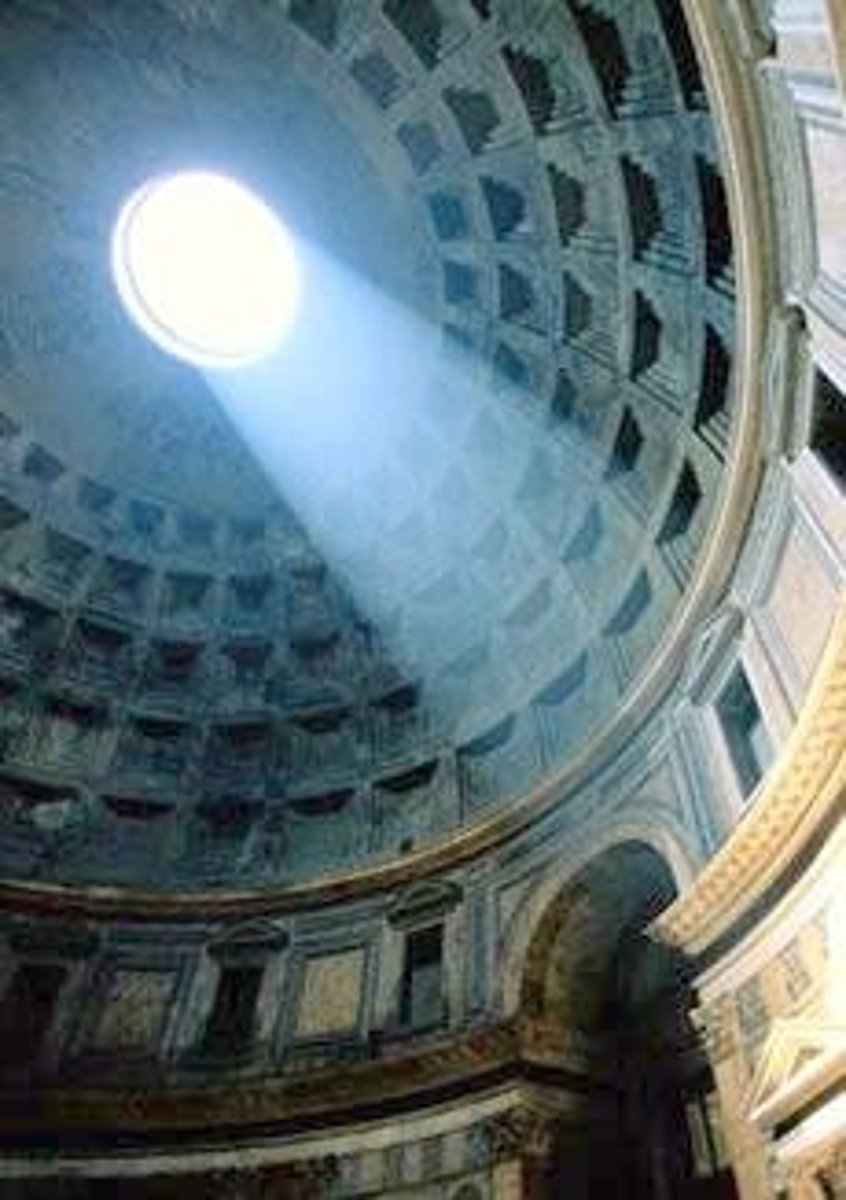

coffering
A sunken panel, often ornamental, in a vault or a ceiling.

concrete
A building material invented by the Romans and consisting of various proportions of lime mortar, volcanic sand, water, and small stones.

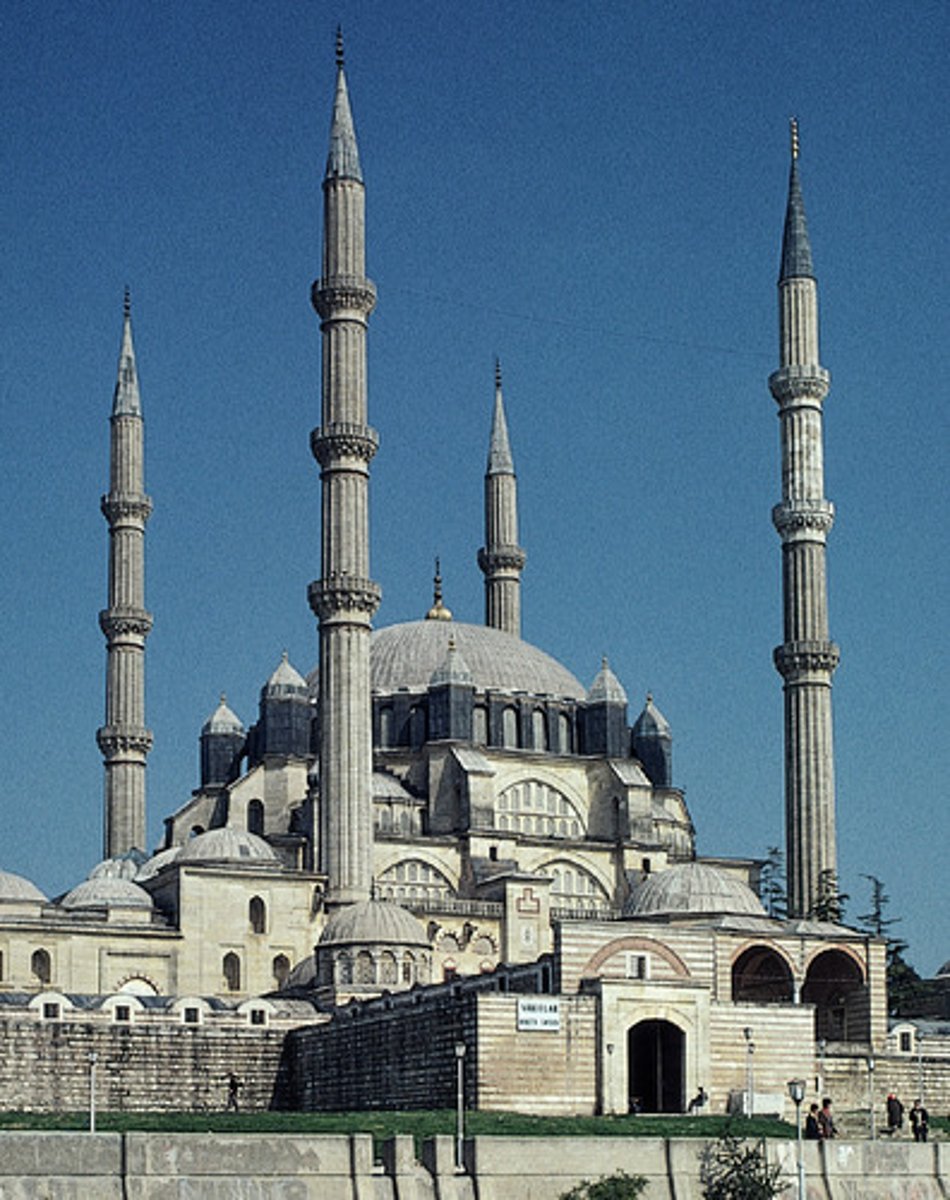
mosque
A Muslim house of worship.

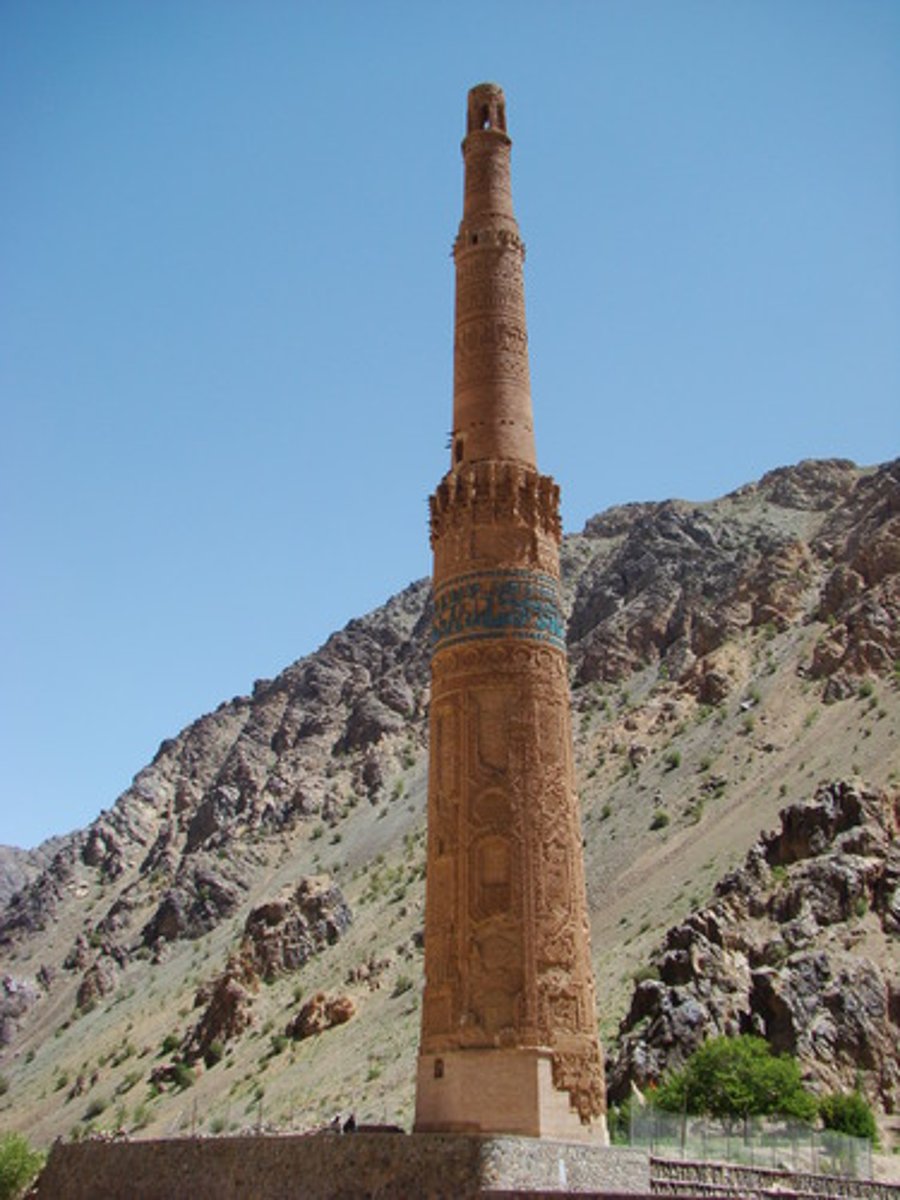
minaret
tower that's part of Islamic mosque; function is to call people to prayer

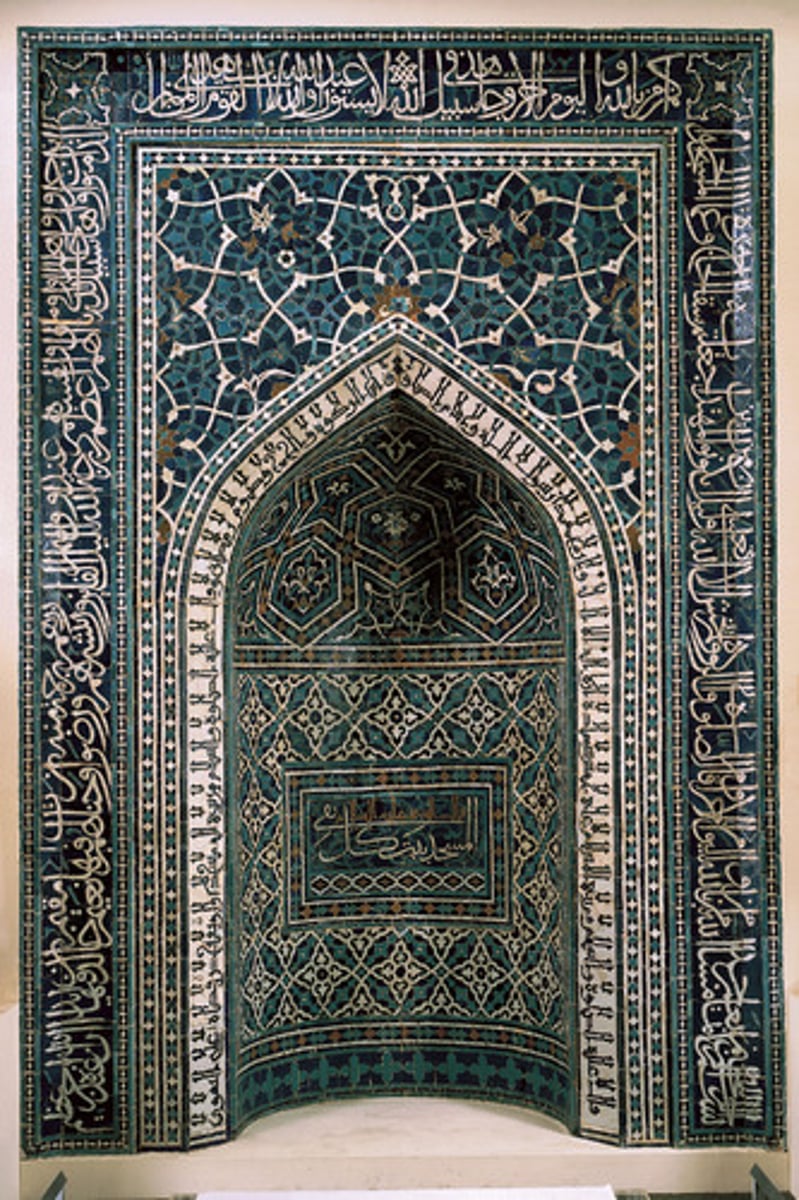
mihrab
in center of Qibla wall' supposed to mark where Muhammad would deliver sermons from
"A semicircular niche set into the qibla wall of a mosque."

Muqarnas dome from the Hall of the Abencerrajes, Alhambra,
"Stucco decorations of Islamic buildings in which stalactite-like forms break a structure's solidity."
