Module 33 - Skeletal Muscle Gross Anatomy Pt.1
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Origin/Head
Muscle mend attached to the more stationary bone (of 2)
Insertion
Muscle end attached to the bone with greatest movement
Ex: in limbs - origin = proximal, insertion = distsal
Belly + features
Largest portion of the muscle between origin and insertion
Thick, central, contractile portion of muscle
Can muscles have multiple bellies?
Yes
Bicepes has 2 bellies because it has multiple origins
Tendons
Attaches muscle to bone
Aponeurosis
Broad tendon
Flat & sheet-like
Agonist (muscle)
Primary mover that causes the action when the muscle contracts
Antagonist (muscle)
Muscle that opposes the agonist
Example of agonist and antagonist muscles
Movement: Flexing biceps
Agonist: biceps bc its porducing most of the contraction
Antagonist: triceps
Synergists + 2 components
Muscles that work together to cause a movement
Prime mover
Fixator
Prime mover
Muscle that plays major role in accomplishing a movement
Fixator
Stabilizes the joint crosses by the prime mover + prevents movement of the origin of prime mover
Location - Muscle Nomenclature (1/7)
Named after body regions:
Pectoralis (chest)
Brachialis (arm)
Gluteus
Size - Muscle Nomenclature (2/7)
Maximus/minimus (largest/smallest),
Longus/brevis (long/short),
Major/minor (relative size)
Vastus (huge muscle)
Shape - Muscle nomenclature (3/7)
Deltoid > triangle
Trapezius > Trapezoid
Teres > Rounded
Quadratus > Square
Action - Muscle Nomenclature (4/7)
Describes function:
flexor, extensor, adductor, abductor, or specialized roles (e.g., masseter = chewing)
Fiber Orientation - Muscle Nomenclature (5/7)
Rectus: fibers are parallel to midline
Transverse: perpendicular
Oblique: angled
Origins/Insertions - Muscle nomenclature (6/7)
Names reflect attachment sites
Sternocleidomastoid → sternum + clavicle + mastoid process
Brachioradialis → arm + radius
Number of heads - Muscle Nomenclature (7/7)
• Bi- = 2 heads
• Tri- = 3 heads
• OR number of muscles in a group: quad- = 4
Location of Head and Neck muscles
Anterior > flexion
Posterior > Extension
Lateral > Rotation and lateral flexion
Muscles That Cause Flexion of the Neck
Muscles deep within the neck
Originate on the anterior side of vertebral bodies + extend to the occipital bone
AKA anterior muscles
Muscles That Cause Extension of the Neck
Posterior neck muscles
Attach to occipital bone + mastoid process
Attach to processes on vertebrae
Muscles That Cause Rotation & Lateral Flexion + Function
Lateral + posterior muscle groups
Function: side-to-side movement
What are the 2 prime movers of the head and neck muscles
Sternocleidomastoid
Trapezius
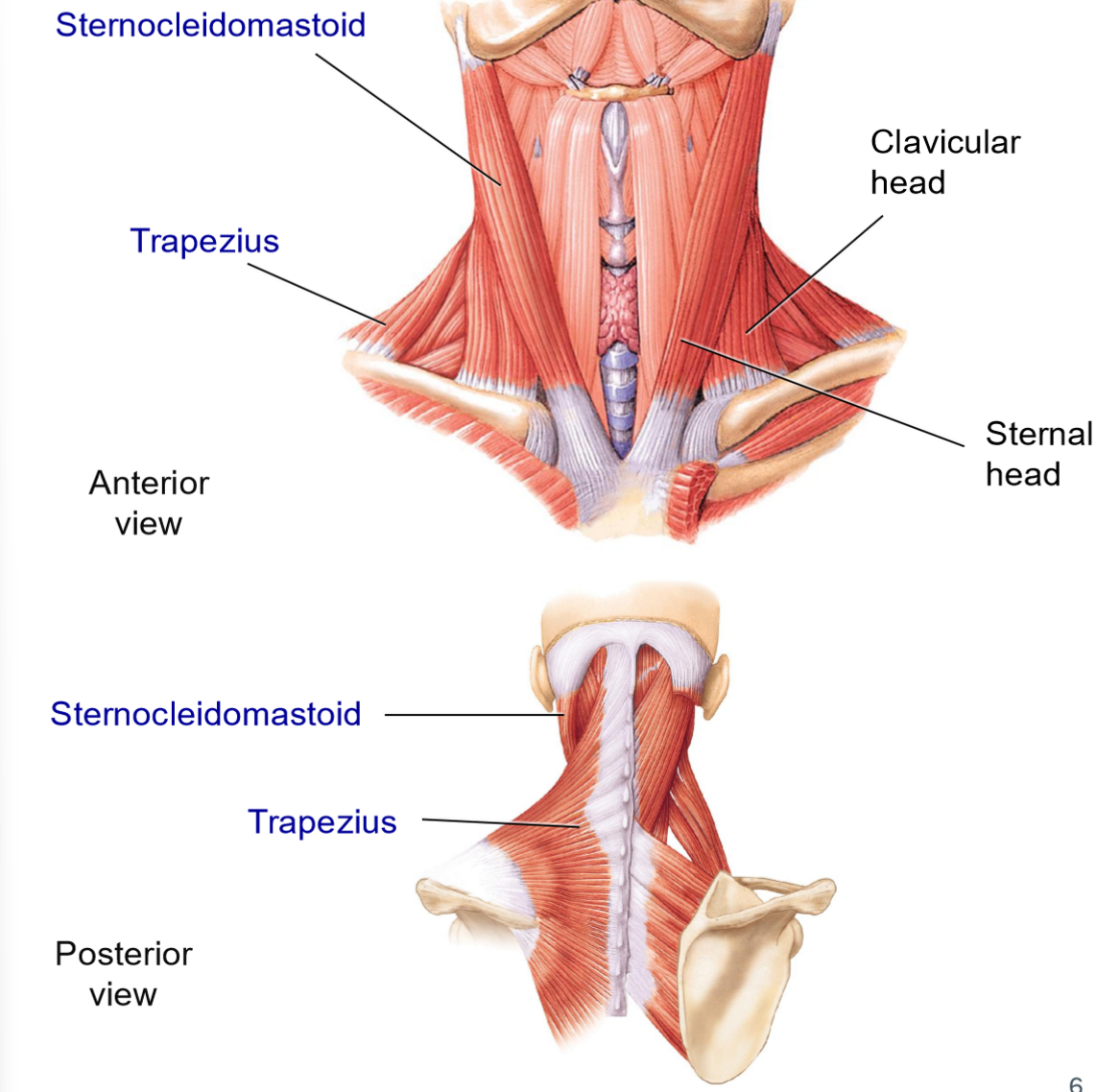
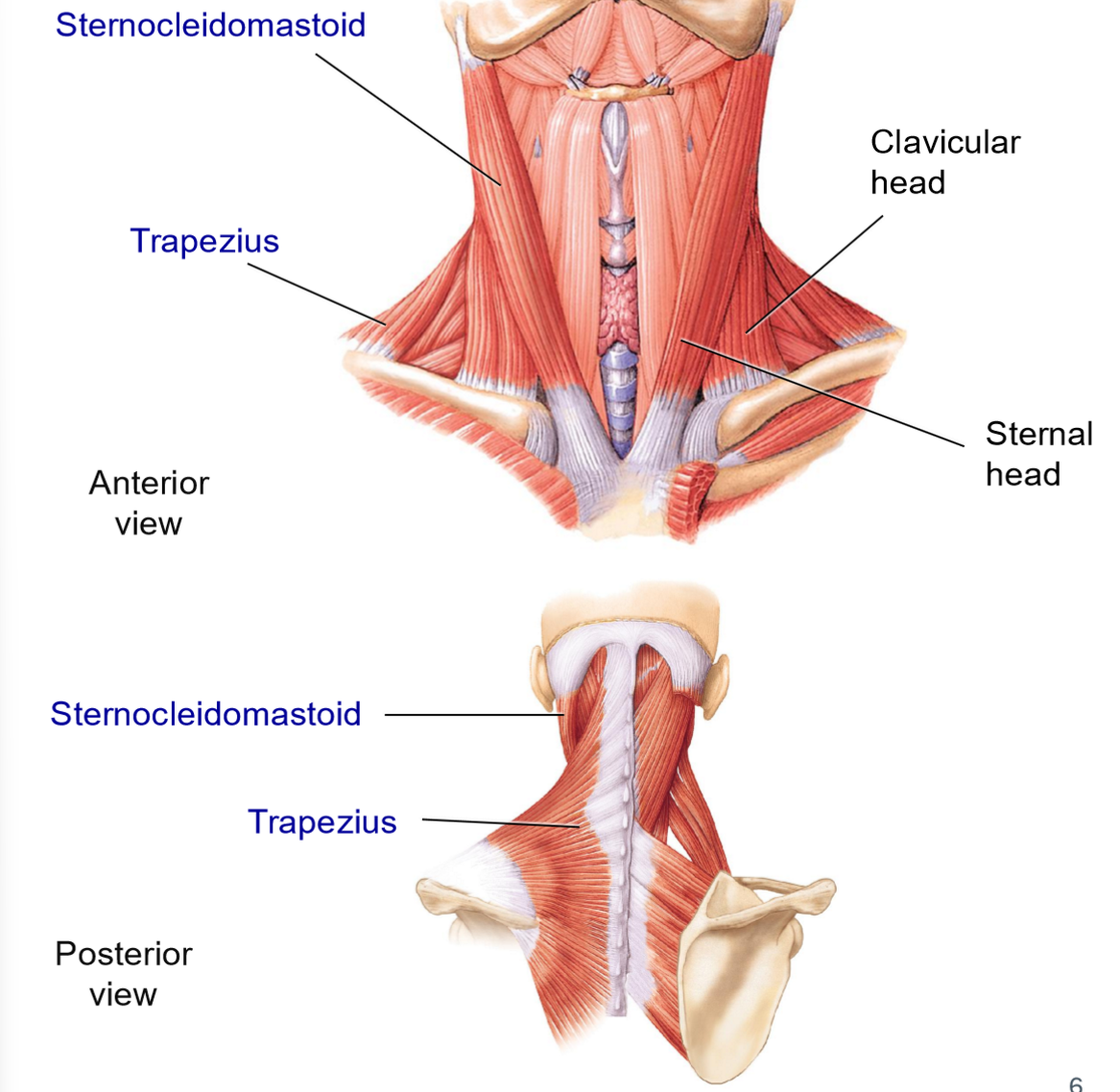
Sternocleidomastoid — Origins & Insertion
Origins: manubrium of sternum + clavicle
Insertion: mastoid process
2 heads
Group: lateral muscle
What actions does the sternocleidomastoid allow?
Action:
forward flexion > contracts both sides
Rotation to the opposite side + lateral flexion of the same side > contracts 1 side
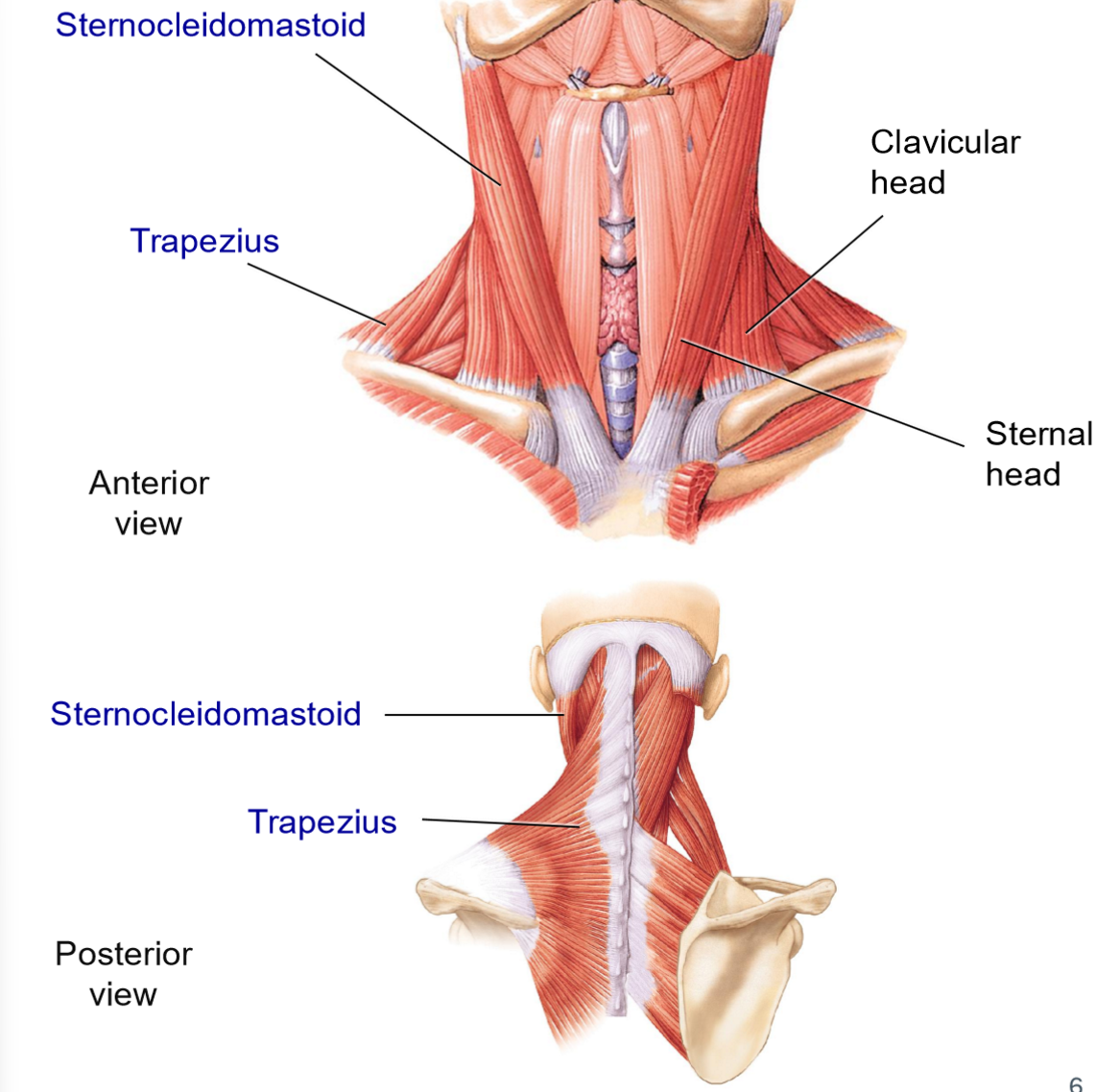
Trapezius (Neck Functions) — Origins & Insertions
Group: posterior muscle
Origins: broad origin along vertebrae + occipital bone
Insertions: spine of scapula + clavicle
What actions does the trapezius allow?
Extension of head
Lateral flexion of neck
The vertebral column muscles allow what movements?
Extension
Lateral flexion
Rotation
Maintaining erect posture
What are the 2 muscle groups in the vertebral column?
Deep group: extends from vertebrae to vertebrae
Superficial group: extends from vertebrae to ribs
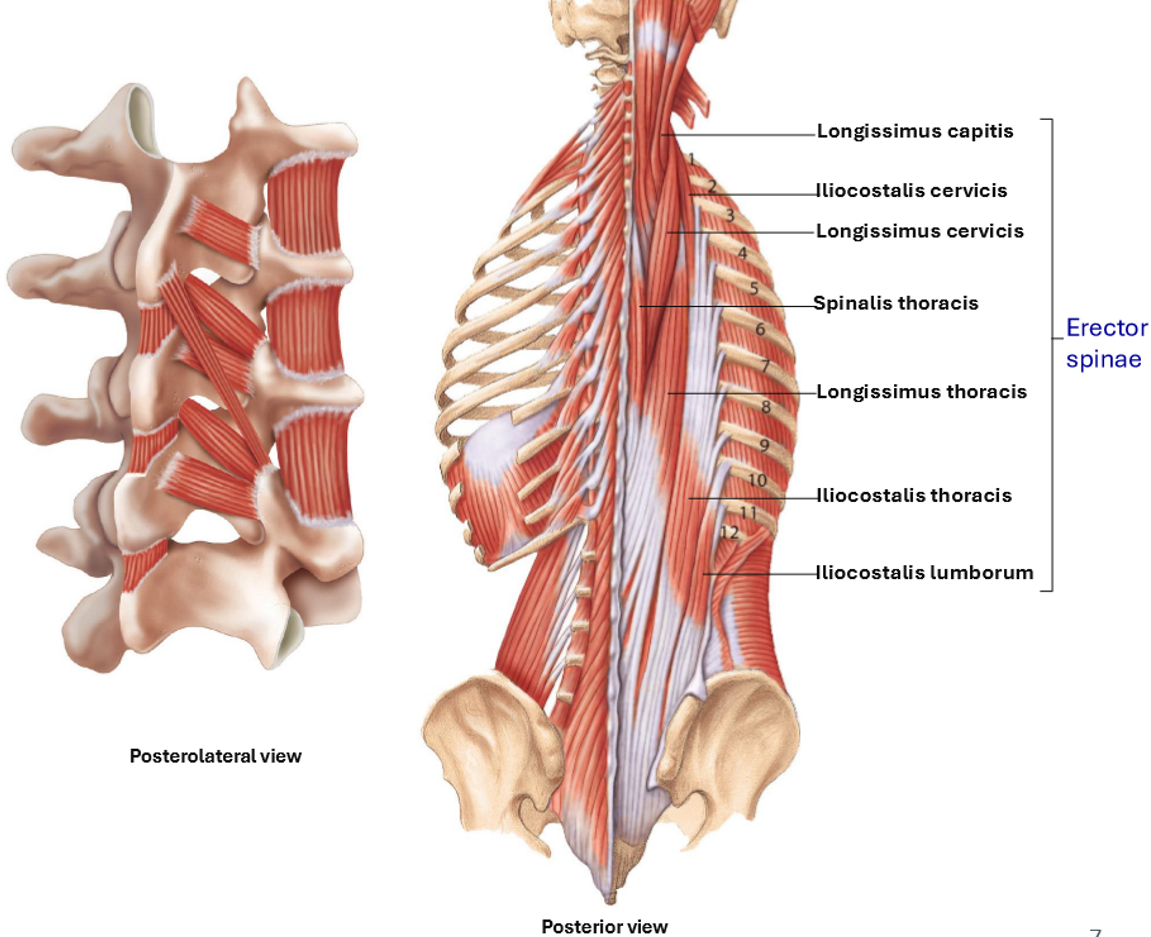
Prime mover of the superficial group muscles of vertebral column
Erector Spinae
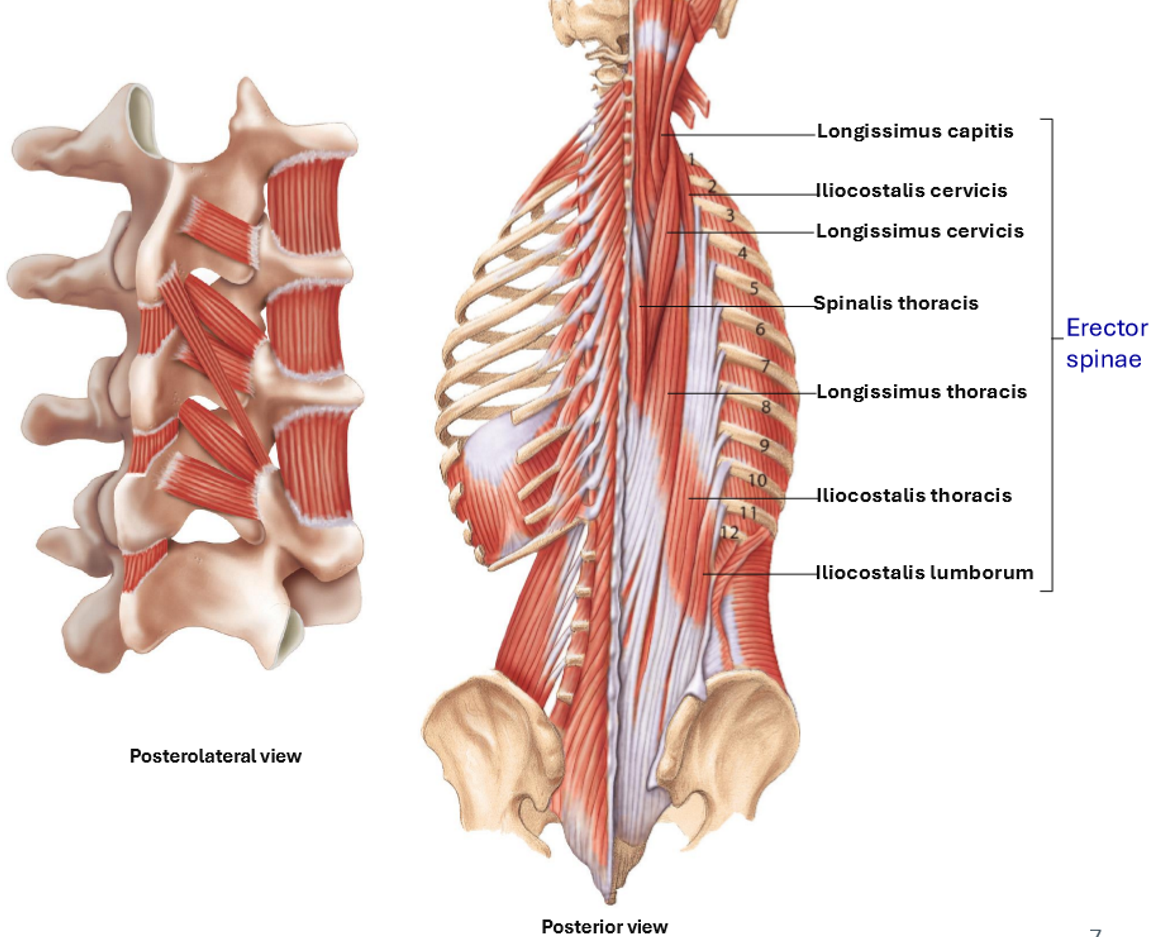
Erector Spinae – Components (3 Subgroups)
Spinalis: most medial
Longissumus: intermediate
Iliocostalis: most lateral
The vertebral column muscles are mostly what kind of fibers?
ST - Type I fibers (60-70%)
For endurance
Thoracic Muscles are important for…
Breathing
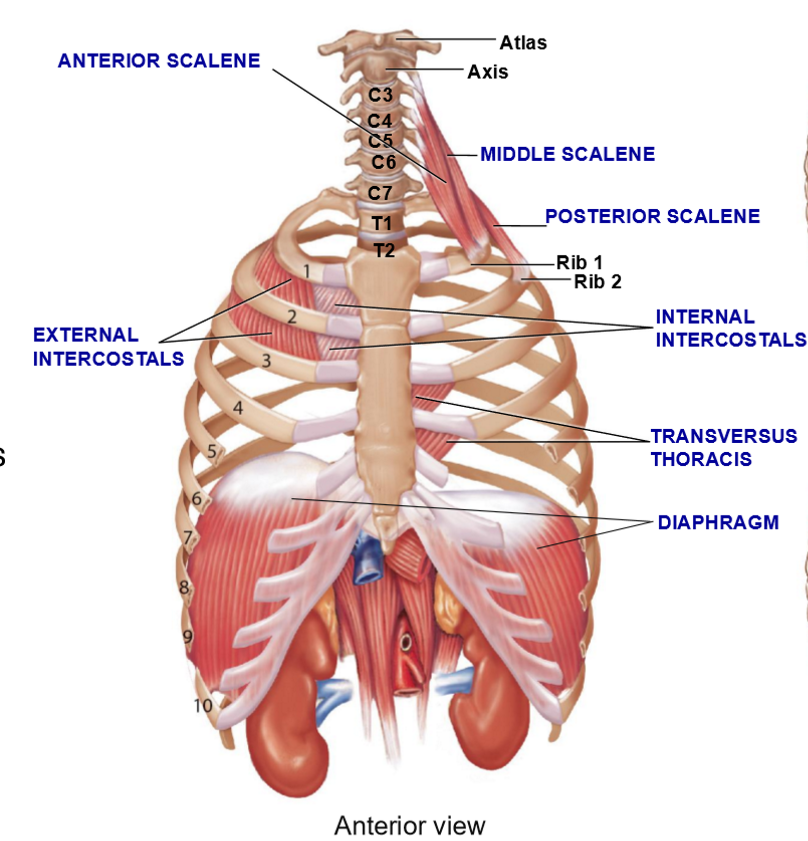
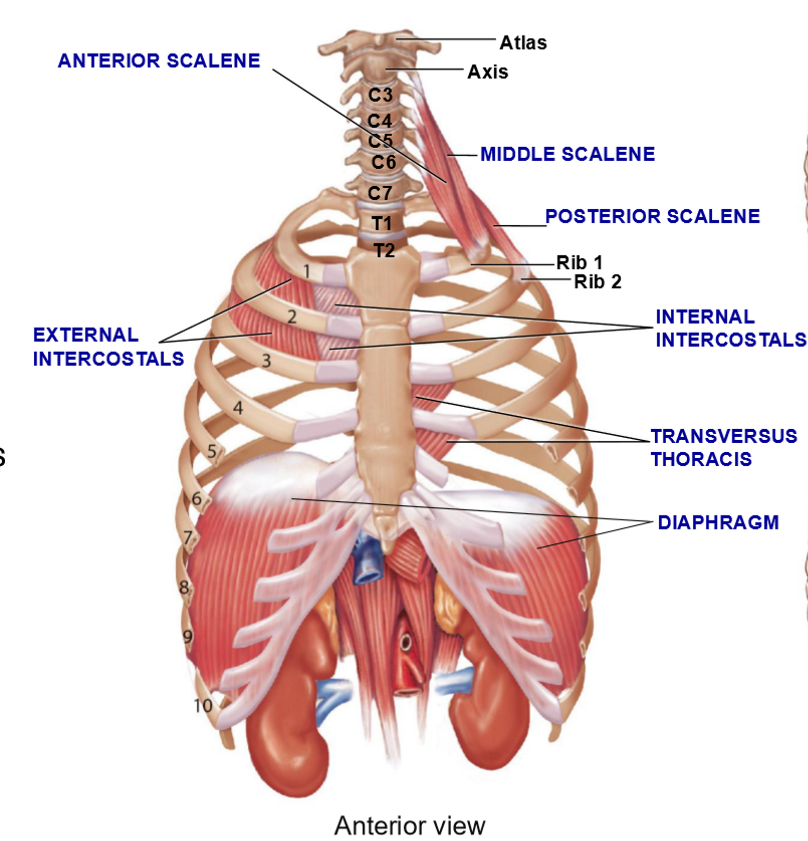
4 Muscle Groups Associated with Rib Cage
Scalenes
External intercostals
Internal intercostals
Transversus thoracis
Diaphragm
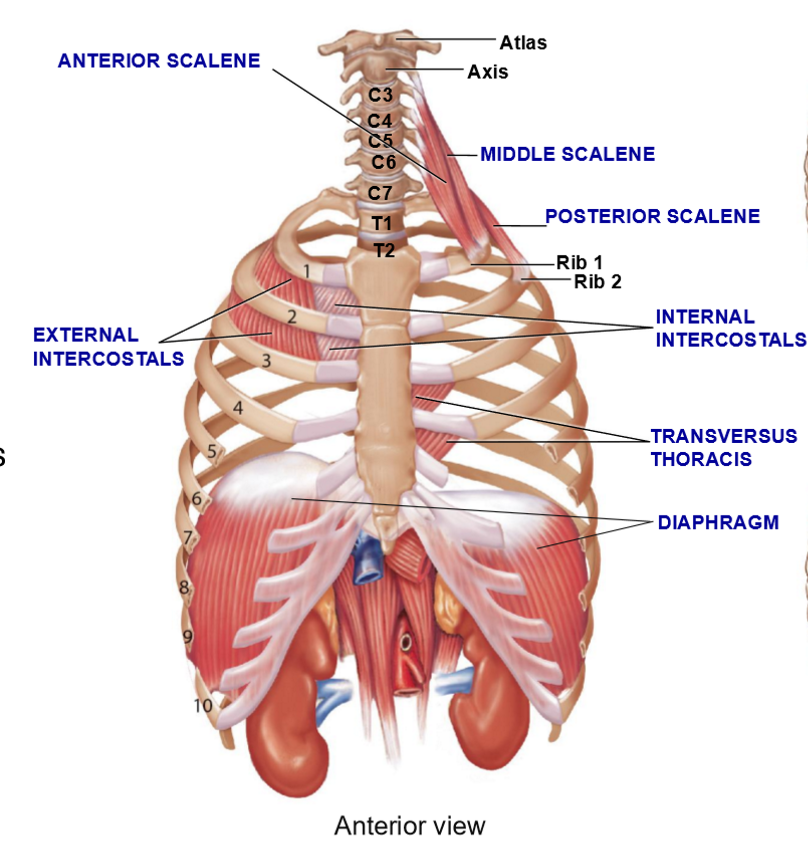
Scalene Muscles – Structure + Function
3 muscles w/different origins/insertions
Function: Elevate the first 2 ribs during inspiration
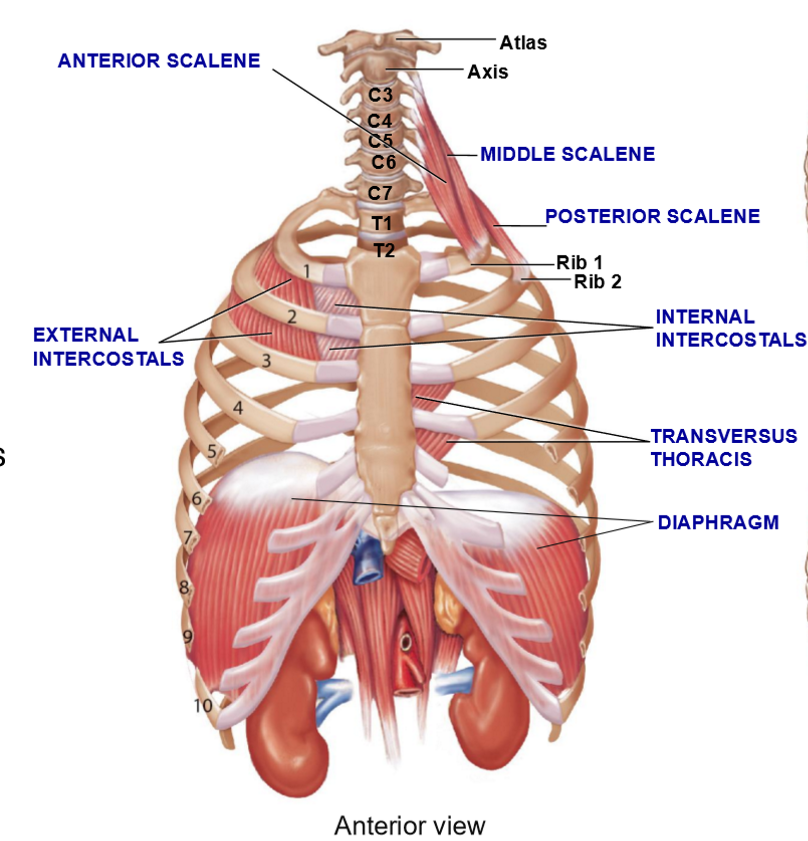
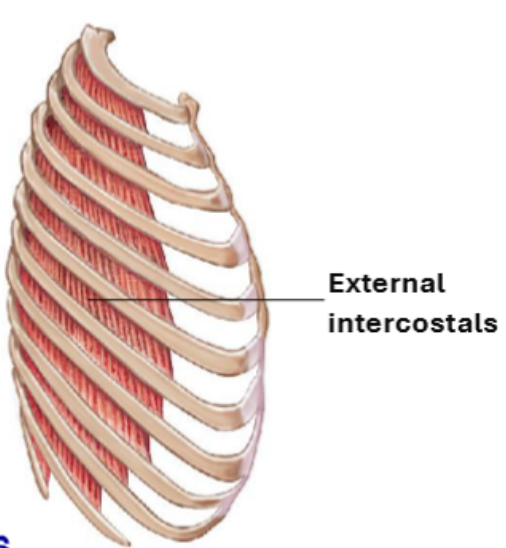
External Intercostals – Structure & Functions
Located between ribs, superficial → deep
Fiber direction = “hands in your pockets”
More superficial than internal intercostals
Function: Elevate ribs → inspiration
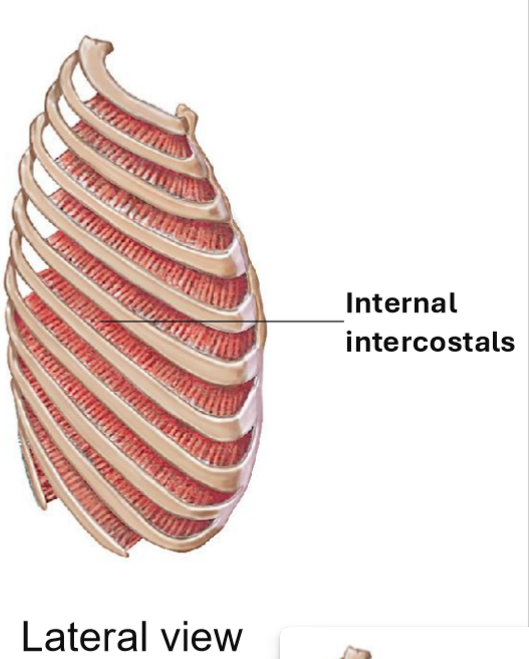
Internal Intercostals - Strucrue & Functions
Fibers run opposite to external intercostals
Muscle is deeper than external intercostals
Function: Depress riibs during expiration
Pulls inferior ribs back to place
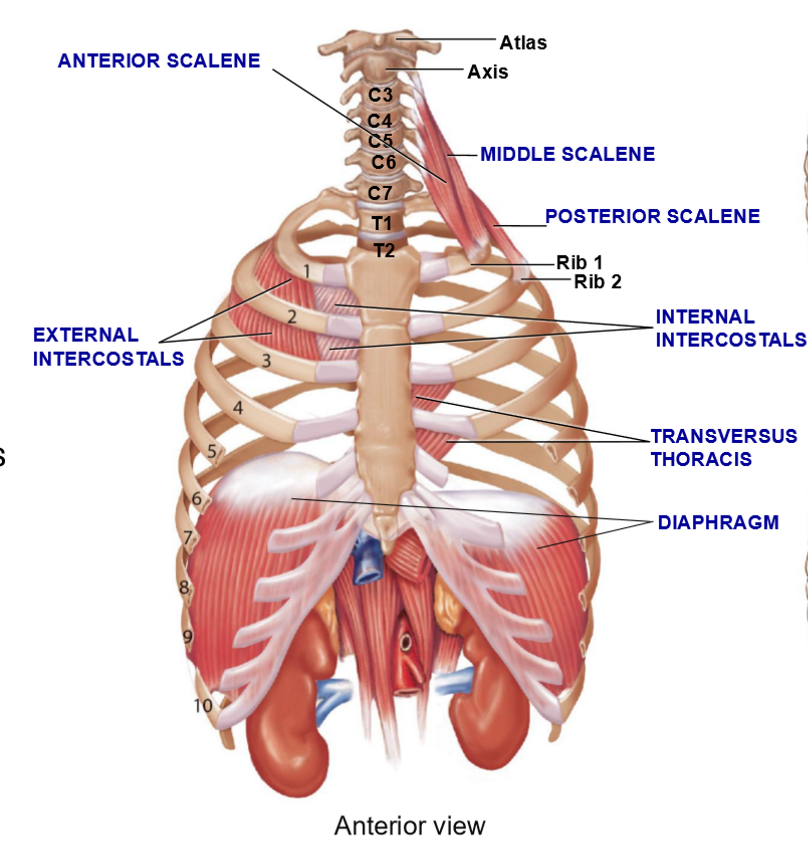
Transversus thoracis - Structure & Function
Extends from sternum to costal cartilages
Function: Assist internal intercostals in rib depression during expiration

Diaphragm - Structure & Function
Major muscle of inspiration
Dome-shaped, contracts + flattens during inspiration
Function: increase thoracic cavity volume, separate thoracic and abdominal cavities
Actions of the abodminal wall muscles
Flexion + rotation of vertebral column
Decrease volume/compress abdominal + thoracic cavities during:
Forced expiration
Vomiting
Defecation
Urination
Childbirth
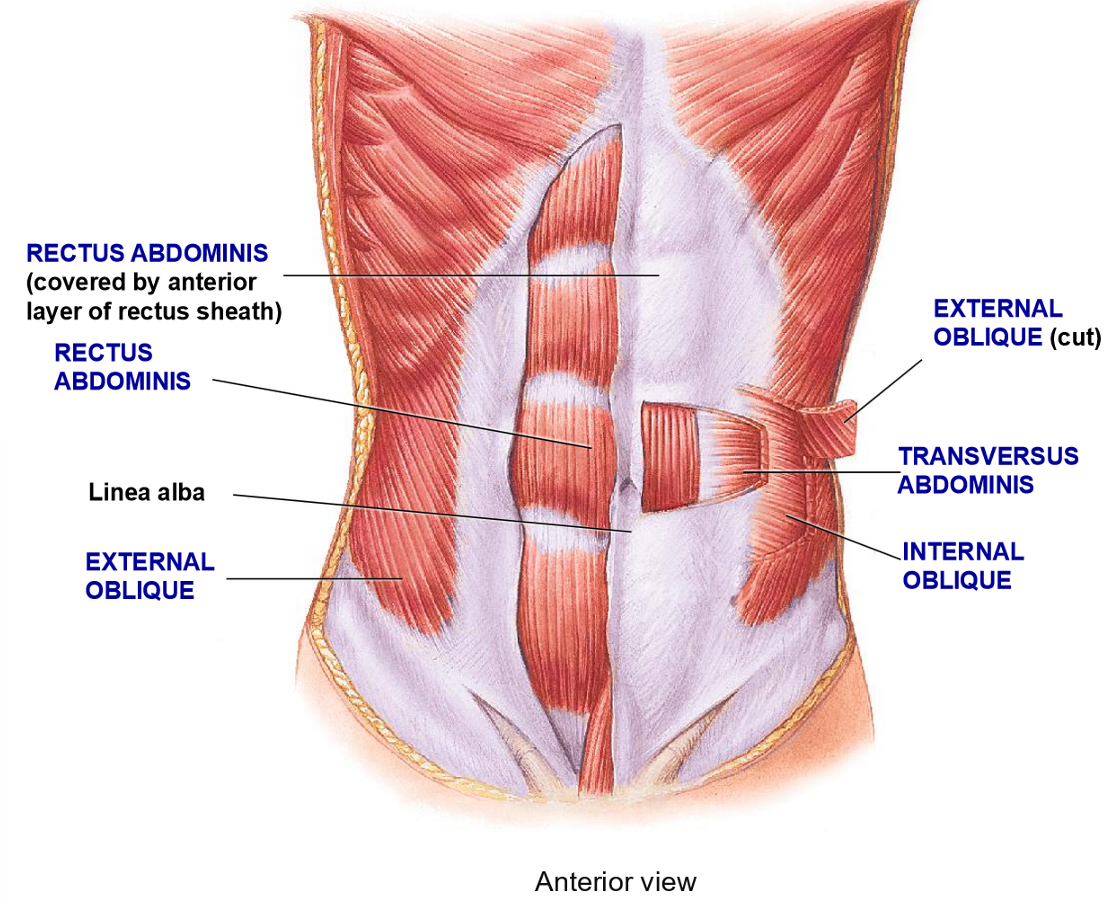
How is the abs structured to add strength?
Crossing pattern of muscles to support organs
Multiple layers with different fiber orientation
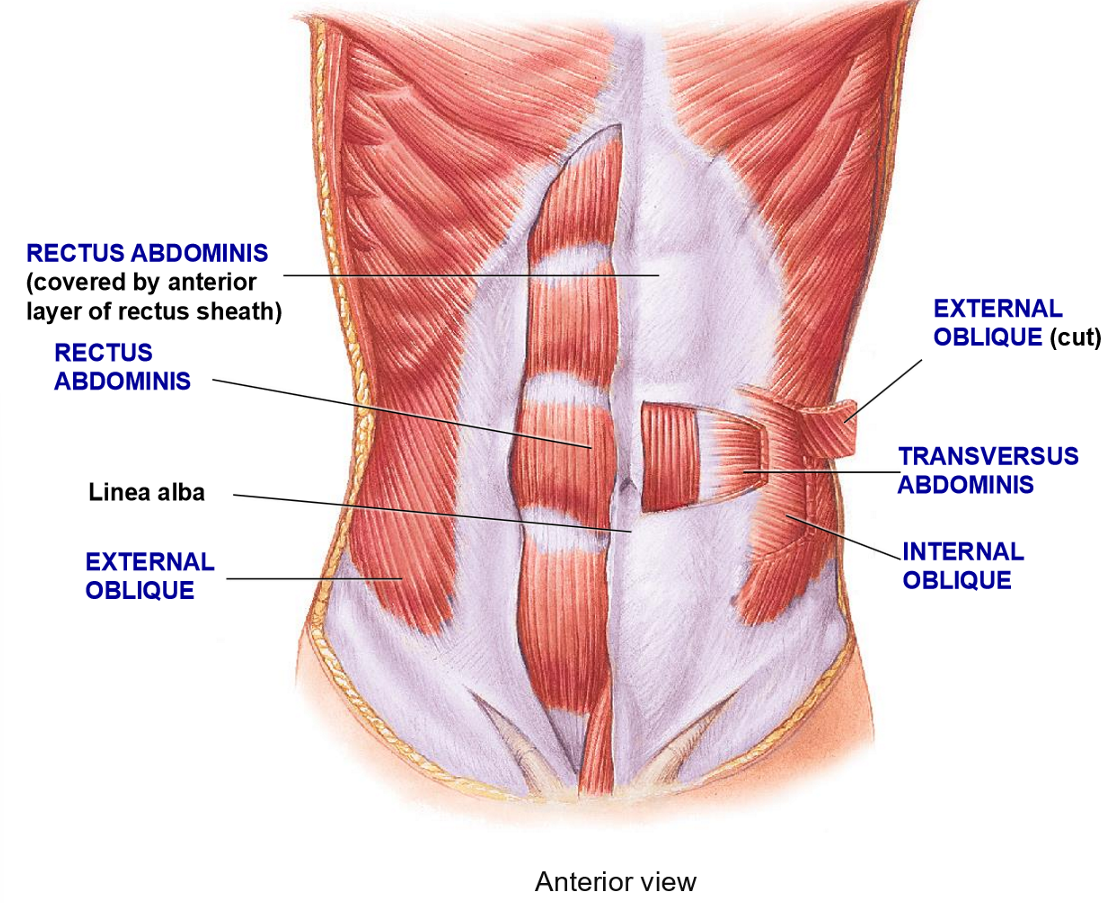
All layers connect to the
Linea alba
What are the 4 layer of the abdomen wall from superifical to deep?
External Abdominal Oblique
Rectus Abdominis
Internal Abdominal Oblique
Transversus Abdominis
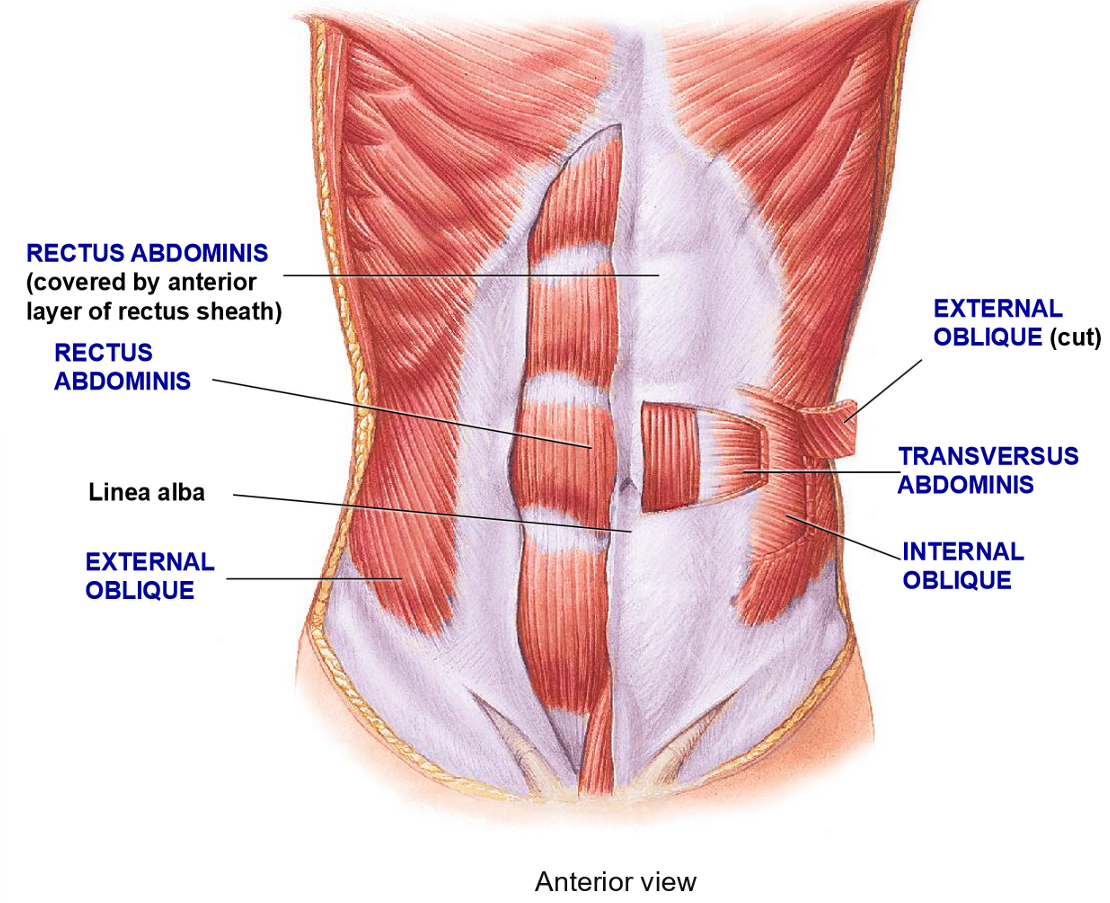
Resctus Abdominis - Structure + Functions
Structure: Most medial ab muscle, fibers run in vertical (rectus) formation
Function: flexion of vertebral colum + compression
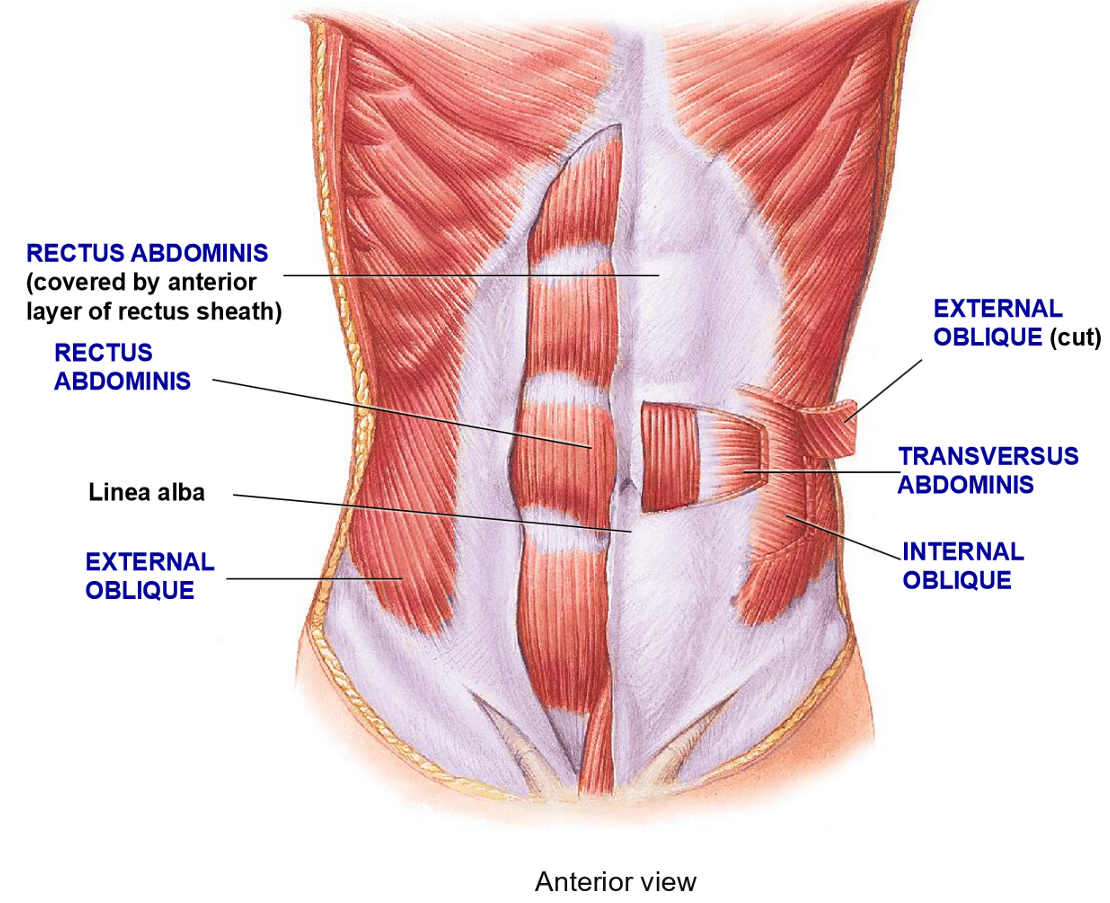
External Oblique - Structure + functions
Structure: Most superificial layer, fibers run obliquely (hands in your pocket)
Function: Flexion, rotation, compression of vertebral column
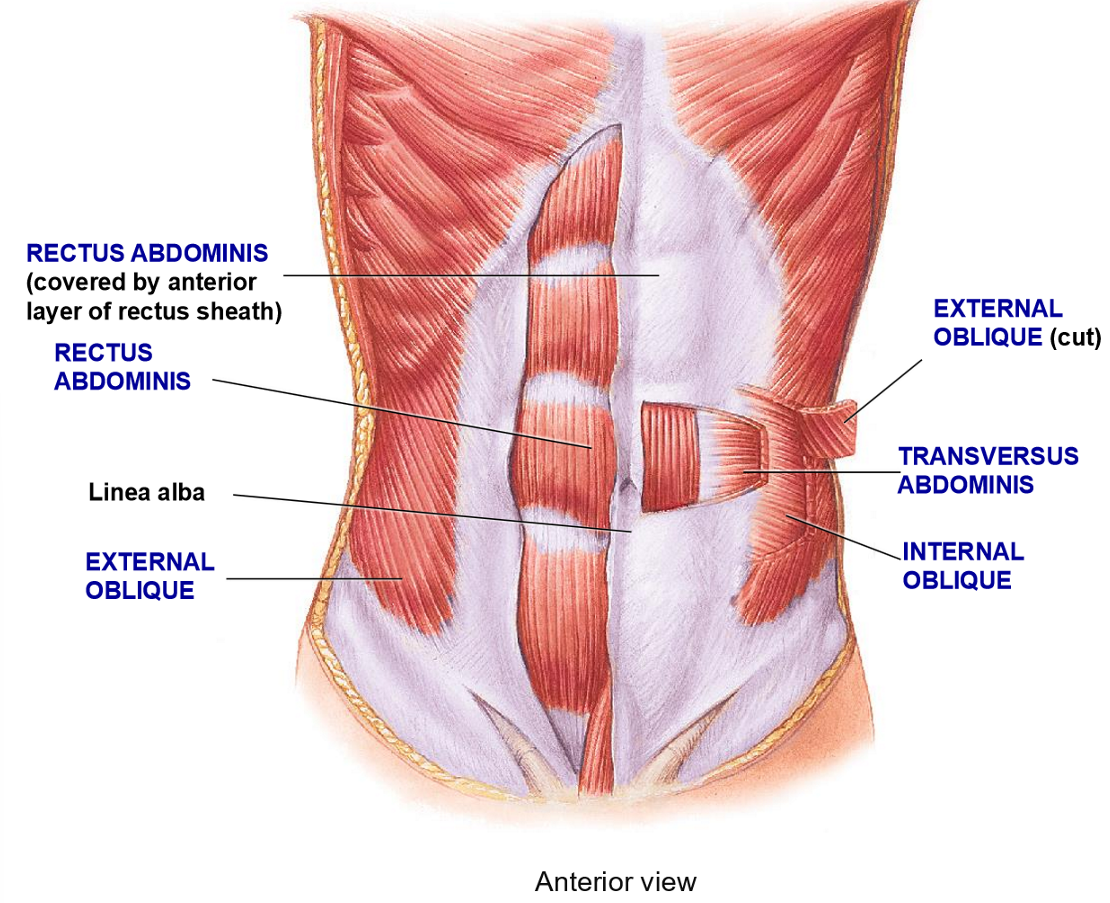
Internal Oblique - Structure + Function
Structure: deep to external oblique, fibers run perpendicular to external oblique
Functions: Flexion, rotation, compression
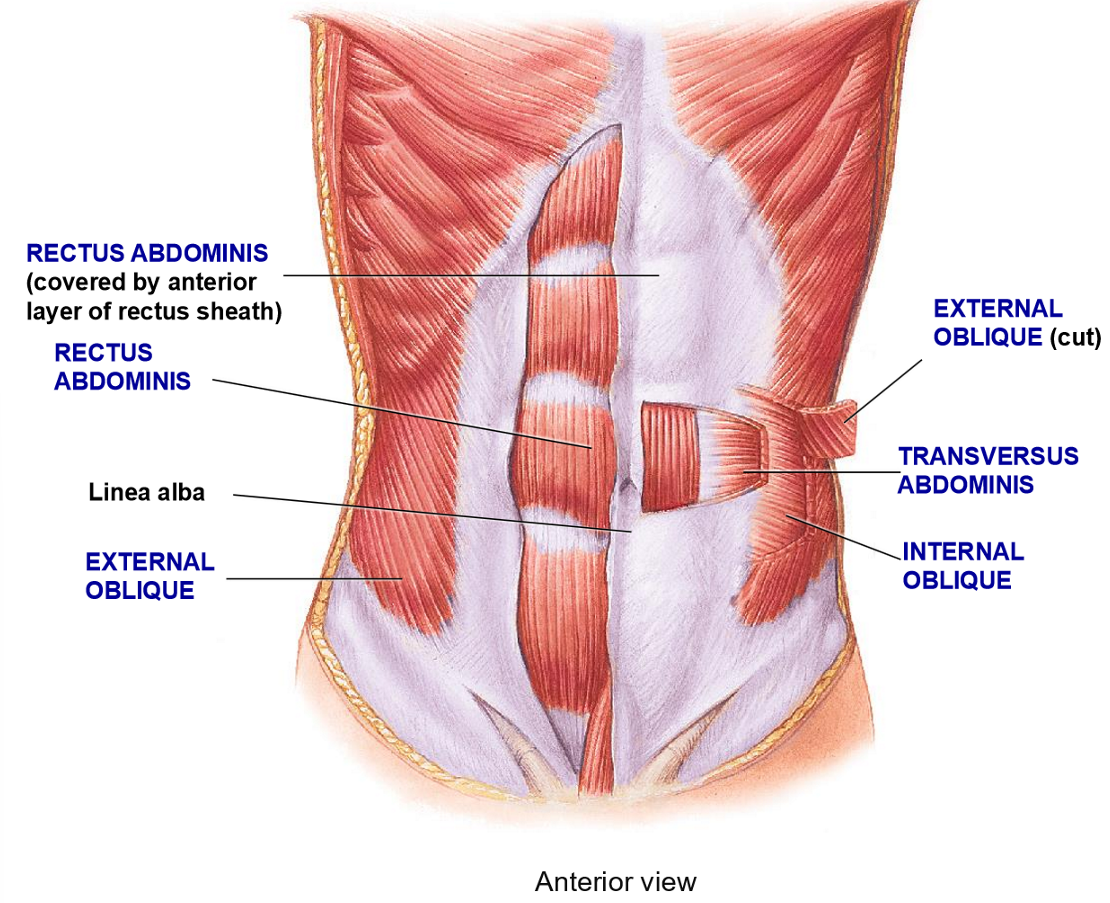
Transverse Abdominis - Structure + Functions
Structure: Deepest layer, fibers run in a transverse plane (horizontally)
Function: compression only
What do scapular movement muscles do?
Attach upper limb to body
Stabilize + move scapula and clavicle
Where do Scapular muscles originate?
All on the axial skeletion
5 Main scapular muscles
Trapezius
Levator Scapulae
Rhomboid
Serratus anterior
Pectoralis Minor
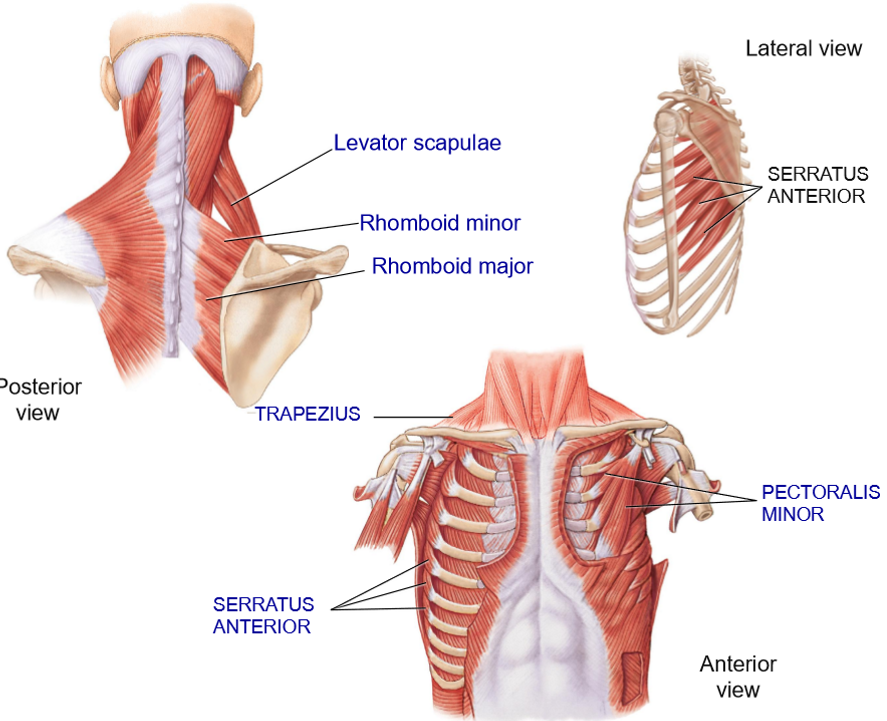
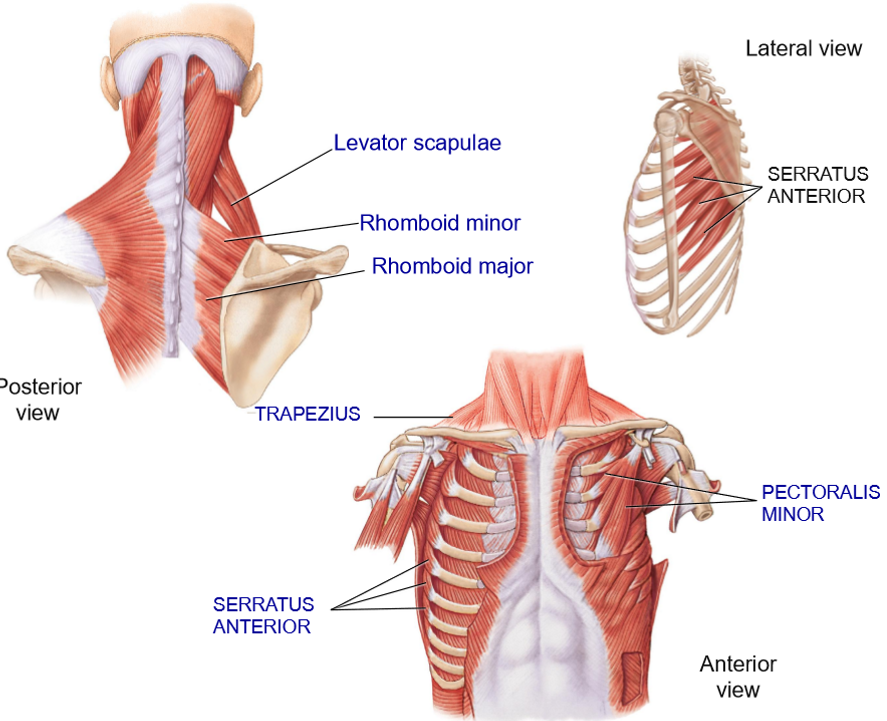
Trapezius - Structure + Functions
Structure: Most superificial muscle in this region, posterior scapular muscle
Functions: Elevation, depression, rotation of scapula
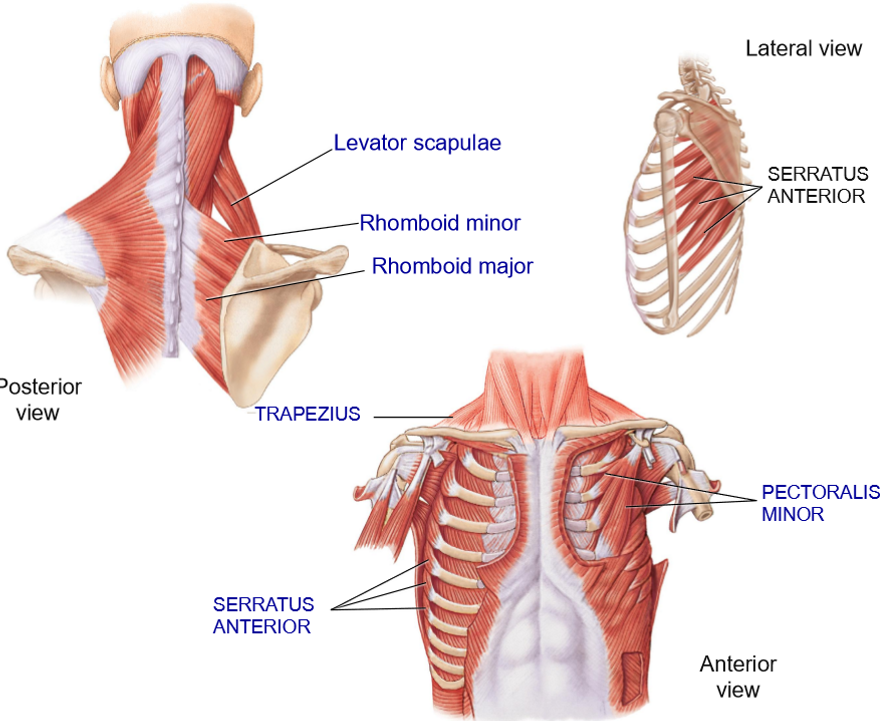
Levator Scapulae - Structure + Functions
Structure: Deep to trapezius, extends from cervical vertebrae to top of scapula
Functions: Elevate + rotate scapula
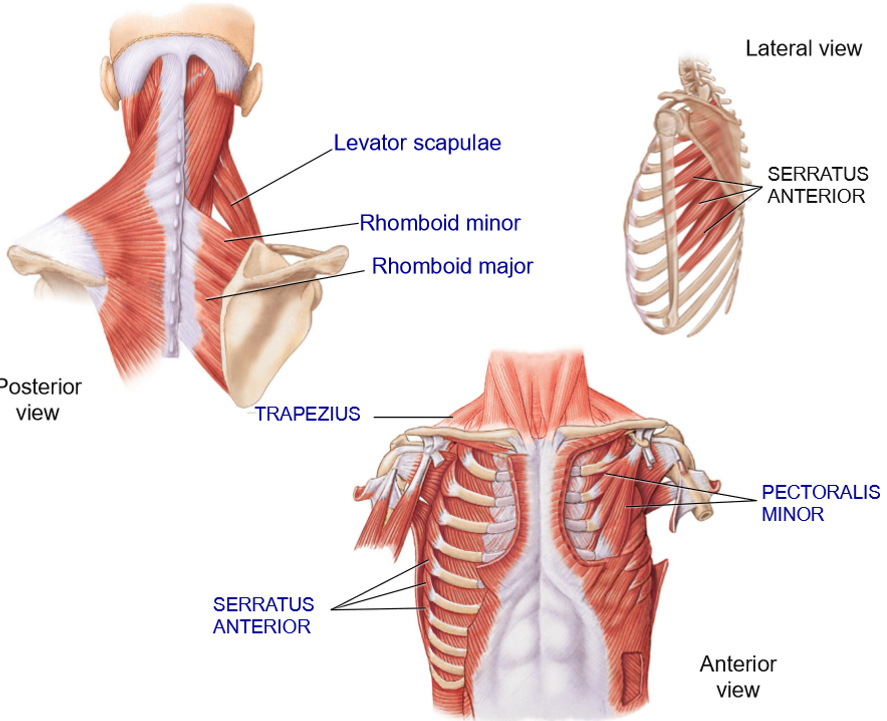
Rhomboid Minor + Major - Structure + Functions
Structure: Extends from vertebrae to the medial border of scpula
Functions: retraction of shoulders + elevation
Which of the rhomboids (minor or major) is the lower one?
Major

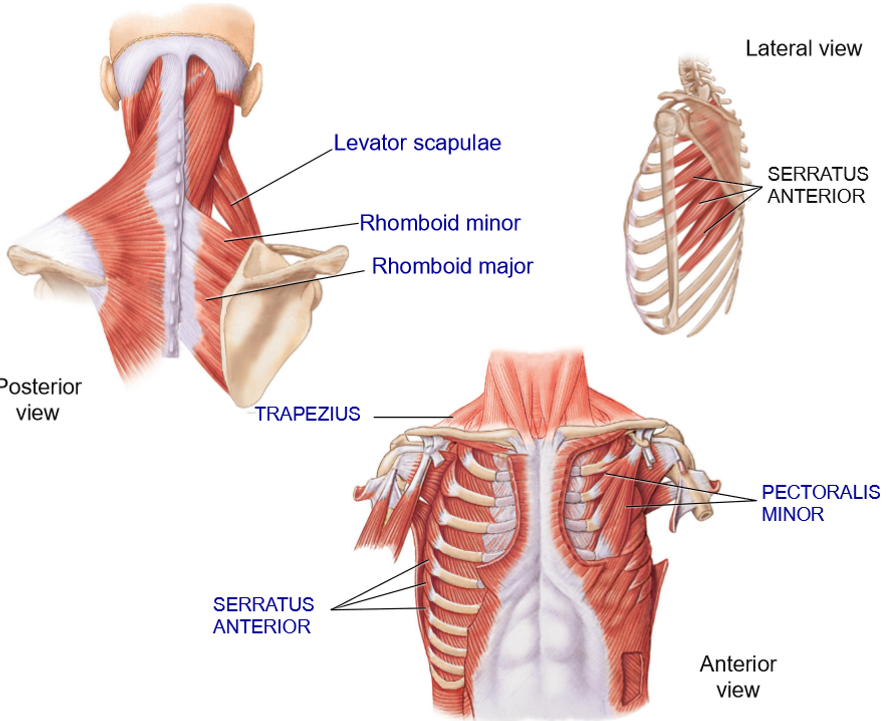
Serrus Anterior (Boxer’s muscles) - Strucure + Functions
Structure: Anterior to scapula
Extends from lateral ribs > under the scapula > medial border of scapula
Functions: hold scapula in place on the thoracic cage, protraction of shoulders, rotation
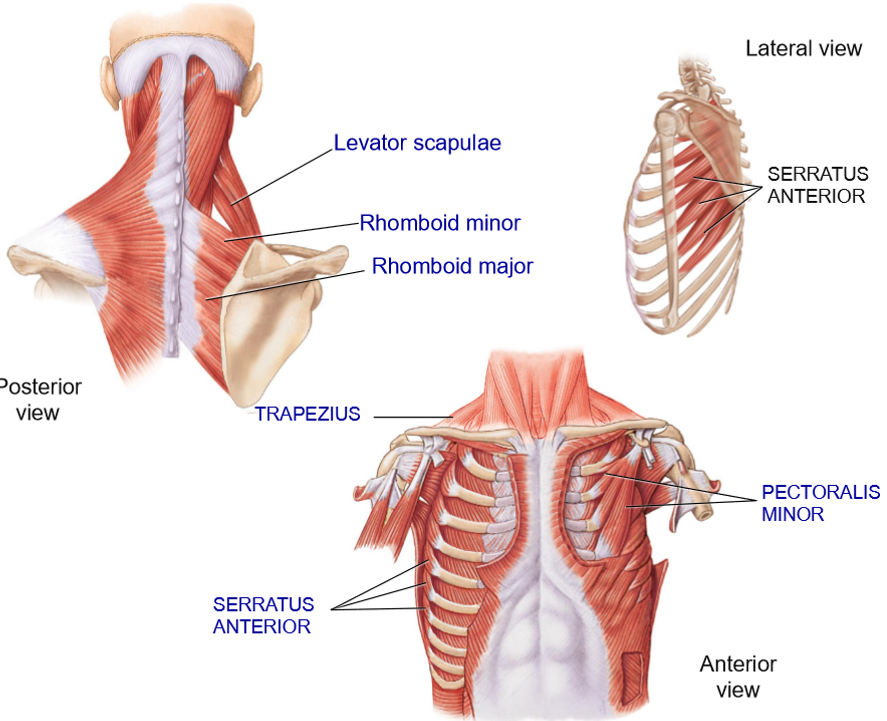
Pectoralis Major - Structure + Function
Structure: Extends from 3rd-5th ribs (Origin) to the coracoid process (insertion)
Function: Depress the scapula