Aircraft Instrument Systems (Entire Jeppesen Airframe Chapter 11)
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Define Pressure
The force differential between two points
What is the difference between Absolute Pressure, Gauge Pressure, and Differential Pressure?
Absolute Pressure is pressure relative to a vacuum
atmospheric pressure + gauge pressure
Gauge Pressure is the difference between the atmospheric pressure and the pressure being measured
Differential Pressure is the comparison between tow different pressures
Define/Explain Aneroid Wafer
A device with a sealed chamber that is evacuated of all air; this vacuum can be used as a reference to measure atmospheric pressure
How does a bourdon tube-type instrument work?
A curved, hollow brass tube is open at one end to a fluid to be measured, while the other end is closed. When pressure is applied to the tube, it tries to straighten, which will cause a needle connected to this tube to deflect accordingly.
How does a bellows-type instrument work?
Typically bellows are used in a differential bellows type instrument, which uses two enclosed bellows, each filled with their associated pressures, that are opposed to each other. the bellows with the greatest pressure compresses the other bellows and moves the pointer on the gauge.
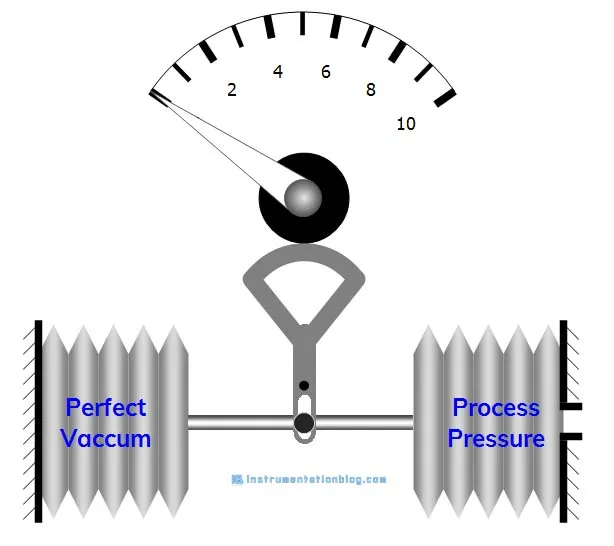
What is a pressure switch?
A microswitch activated by the movement of a bellows under the pressure applied to a fluid
Basically fluid pushes on a diaphragm until the switch activates.
typically used for “oil pressure too high/low” lights, any sort of warning light.
What is the difference between MSL and FL altitude measurements?
“MSL”, or Mean Sea-Level is what a pilot references their altitude to when they are flying under 18,000 feet.
This indication is read as the actual altitude in feet (ex. 12 thousand feet MSL)
“FL”, or Flight Level is an operating condition where pilots measure their altitude adjusted to pressure altitude, or the standard sea level pressure of 29.92 inches of mercury.
This indication is read differently, FL 310 indicates a pressure altitude of 31,000 feet
Define/Explain Density altitude
Density altitude is just pressure altitude corrected for non-standard temperature.
What is an altimeter used for?
Altimeters are used to display the height of an aircraft above a calibrated reference point.
Explain the function of an analog altimeter
Analog altimeters use an evacuated bellows that is surrounded by ambient pressure around it; expansion and contraction of this bellows mechanically moves a needle on a gauge to display altitude.
What FAR requires all altimeters to be tested and inspected?
FAR 91.411
How often does a 91.411 test have to be done?
At least every 24 calendar months.
Explain the basics behind conducting a 91.411 static system test.
A Pitot-Static system tester is used, with tubes connecting the pitot tube and the static port to the tester. This tester simulates different altitudes and airspeeds by applying pressure to the pitot tube and vacuum to the static port. A mechanic watches to ensure that the altitude/airspeed indicated by the aircrafts gauges match what is indicated by the testing equipment
What procedure is commonly done at the same time as a 91.411 Test?
A FAR 91.413 test, which test the transponder system.
What are the 6 things, according the Part 43 Appendix E, an altimeter should be tested for during a 91.411 test? List/Define them.
Scale Error — The altimeter must indicate the same altitude as the tester, within an allowable tolerance
Hysteresis — The reading taken as altitude is increasing should be the same as the altitude is decreasing
After Effect — The altimeter should return to the same indication after the test that it was at before the test started.
Friction — The instruments altitude indication should not have a large difference between altitude readings before and after the instrument is vibrated
Case Leak — At 18,000 feet indicated on the altimeter, the altitude should not leak down more than a certain amount in a certain time frame
Barometric Scale Error — The connection between the barometric scale and the indication of the altimeter should be correct within a certain tolerance.
How does a basic airspeed indicator work?
A differential pressure gauge measures the difference between the pitot pressure and the static pressure. this direct reading is called Indicated Airspeed
Why would indicated airspeed be any different than a “more correct” calibrated airspeed?
The static port is almost always in a spot that is susceptible to small airflow disturbances.
What is the difference between Indicated, Calibrated, and true airspeed?
Indicated — Not corrected for anything, as its measured with pitot and static ports.
Calibrated — Corrected for small airflow distortion that may be encountered by the static port.
True — Same as calibrated, but also corrected for non standard pressure and temperature
What does a Machmeter do?
Measures the aircrafts speed relative to the speed of sound (which varies with temperature)
What is a vertical speed indicator used for?
Indicating the rate of climb/descent, and changes in pitch, of the aircraft
How does an analog vertical speed indicator (VSI) work?
A bellows is connected to the aircrafts static source and vented to the inside of the instrument case through a diffuser, which provides an accurately calibrated leak.
What is the purpose of an instantaneous vertical speed indicator (IVSI)?
To make up for the vertical speed indicator’s indication lagging behind, an IVSI has accelerometers to help the instrument immediately indicate changes in vertical speed
What are the 5 temperature instrument types? (Hint: 3 are non-electrical, 2 are electrical)
Liquid Expansion — like a household thermometer
Solids Expansion — 2 metals heat up differently, cause a pointer to bend
Gas Expansion — uses a temperature bulb connected to a bourdon tube
Resistance Type — AKA Wheatstone-bridge, a variable resistors resistance that changes with temp is compared to a fixed resistor
Thermocouple Type — two metals with different expansion coefficients to create a small voltage proportional to the temperature change
Define thermocouple, and give an example of where one may be used.
A temperature sensing device that uses two metals with different expansion coefficients to create a small voltage proportional to the temperature change to be indicated.
What is the purpose of a Synchroscope?
To indicate which engine has a higher RPM, used to help pilots synchronize the rpm of the two props.
What are the two types of Tachometers?
Mechanical Tachometers
Electric Tachometers
How does a Mechanical Tachometer function?
An indicator is physically connected to the engine by a physical drive shaft; as the engine rotates, a gear rotates this drive shaft at the same speed as the engine RPM. Centrifugal force acts on flyweights inside the instrument, which deflect a gauge to indicate Engine RPM.
How does an Electric Tachometer function?
A small AC generator mounted to the engines gear case. as the engine turns, it drives the generator, which produces a frequency proportional to the speed of the engine. Wires connect this generator to the indicator, which has a drag cup (a cup that surrounds a spinning magnet, as the magnet spins faster, the cup deflects) that indicates engine RPM.
What two characteristics make gyroscopes useful in aviation? List/Describe them.
Rigidity in Space — the principle that when a wheel is spun rapidly, it will try to remain in a fixed position on the plane in which it is spinning.
Precession — The gyro, when an outside force tries to tilt it while it is spinning, will respond 90 degrees further around in the direction of rotation.
how are gyroscopic instruments typically spun up on smaller aircraft?
With a vacuum pump or electric motor
What is the purpose of a heading indicator?
To maintain a constant heading indication regardless of the heading of the aircraft.
How does a heading indicator work?
A system of gyros, suspended on a gimbal, spin on the horizontal plane. These gyros will remain rigid regardless of the heading of the aircraft. A drum type card indicates the current heading and can be adjusted/correctly set before takeoff.
What is the purpose of a Attitude Indicator?
AKA “artificial horizon”; to give the pilot information on their pitch and roll as it relates to the ground or horizon.
What is the purpose of a Turn Indicator?
To give the pilot a measure of their rate of rotation around the aircrafts vertical axis
What are the two types of Turn indicators? How do they differ?
Turn and slip indicator — can sense both rate of roll AND rate of turn
Turn coordinator — can only sense rate of turn
If an aircraft needed pneumatic power for gyroscopic instruments but did not use a vacuum pump of any kind, how might this aircraft get its pneumatic power?
By using a venturi mounted on the outside of the aircraft to generate suction for powering pneumatic instruments.
Explain the two types of vacuum pump systems and why one is better than the other.
“Wet” Pump Systems — Used on older planes, where oil was required to internally lubricate the pump itself. The downside of this style is that it requires an air-oil separator to recover oil from the outgoing air.
“Dry” Pump Systems — Newer, more modern. Uses carbon vanes in the pump which self-lubricate, eliminating the need for oil or an air-oil separator.
Name the typical components of a vacuum pump system.
Vaccum Pump
Suction Relief Valve
Filter (possibly inlet and outlet filter)
Suction Gauge
Why would a positive pressure system be preferable to a vacuum pump system?
above 18,000 feet MSL, the vacuum pump cant draw enough air for operation of the system.
List the 3 types of fuel quantity indicating systems and how they function.
Mechanical Indicators — A float in the fuel tank directly connects to the indicator; the float is magnetically coupled to the indicator to smooth out any sloshing or sharp movements of the float
DC Electrical Indicators — Converts mechanical motion of the float into a varying DC current that is then read by the instrument.
Capacitance Fuel Quantity Systems — measures mass of fuel by measuring the dielectric constant between the two plates, which changes as fuel/air come between the plates.
What problem do fuel injection system flowmeters have?
If the orifice (that is used to create a pressure drop that corresponds to fuel flow) partially clogs, the pressure drop across it increases, which causes a higher fuel flow when the actual flow has decreased.
What benefits are offered by having something like an Electronic Flight Instrument System (EFIS), an Integrated Flight Deck, or any other modern indicating system?
Easier access to important information for the pilot
can be customized to the preference of the pilot
better indication if something is going wrong (it will yell at you)
Greatly increased reliability
reduced maintenance costs
What is the “Basic T”?
A common setup of 4 critical instruments, which are all typically in the same spot on most aircraft.
Top left ———— Airspeed Indicator
Top Middle ——- Attitude Indicator
Top Right ———- Altimeter
Bottom Middle — Directional Gyro
Why should instrument panels be installed with shock mounts?
To protect the instruments and isolate them from any vibration that might occur during landing or in rough air.
“The instrument panel or electrical equipment must be ____________ ______ to the structure”
The instrument panel or electrical equipment must be electrically bonded to the structure
What is a slippage mark? What is its purpose?
A slippage mark is a mark placed on a gauge that has range marking on the front glass. This slippage mark ensures that the glass does not rotate in reference to the case of the instrument.
On an airspeed indicator, what does a yellow arc indicate?
Max continuous operating range
On an airspeed indicator, what does a green arc indicate?
Normal operating range
On an airspeed indicator, what does a red line indicate?
Never-Exceed Speed
On an airspeed indicator, what does Vₙₑ indicate?
Same as red arc, Never-Exceed Speed
What is a compass swing test?
A test where a technician takes an aircraft to a compass rose and adjusts the compensation of a magnetic compass. Once adjustments are done, a calibration card is filled out and placed in the cockpit.
What is a Leakage Test for?
A type of static check that tests if the altimeter indication drops more than 100 feet (from 1,000 feet) in one minute. If this happens, there is a leak somewhere in the static system.