Enzymes - Biochemistry
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are enzymes?
They serve as catalysts - speed up or slow down chemical reactions in the body
Enzymes are make of __________.
proteins
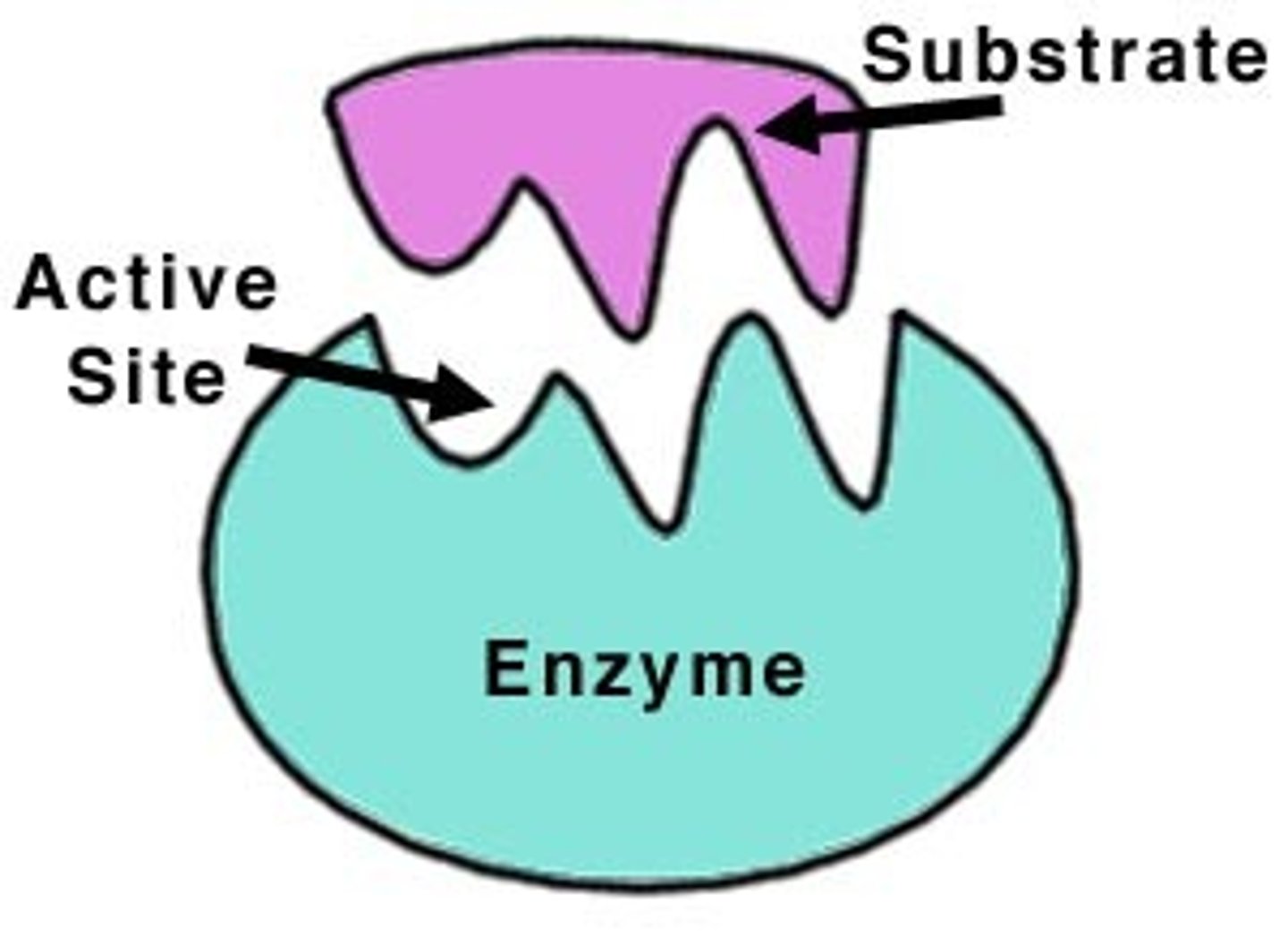
What is a substrate?
The reactant that an enzyme acts upon...
What is an active site?
Where the substrate bind to the enzyme
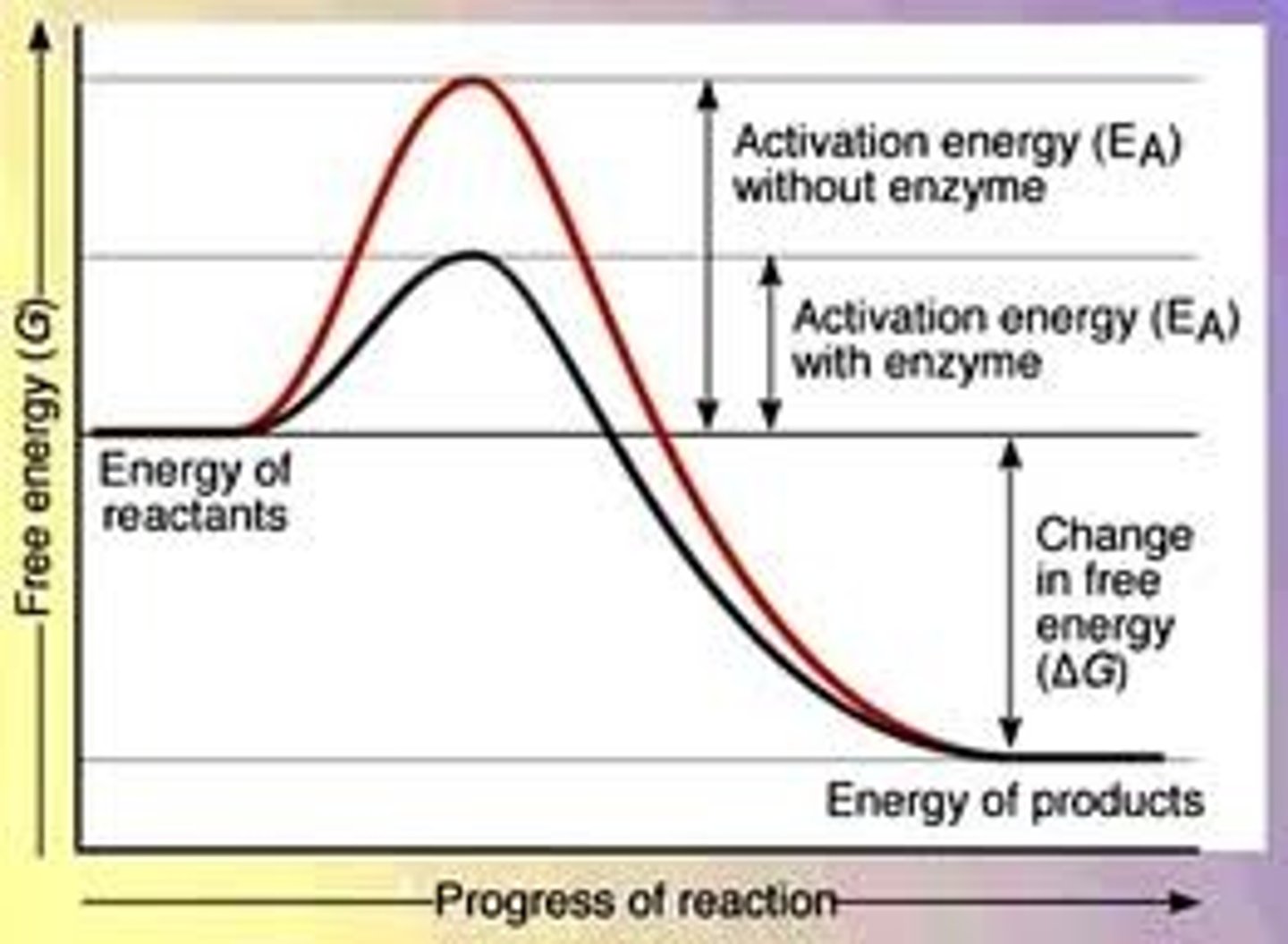
How do enzymes catalyse reactions
They lower the activation energy - they DONT increase amount of product, just the speed at which it is produced.
What if an enzyme isn't present for a reaction?
The product will be the same, except it would have been quicker if the enzyme was present
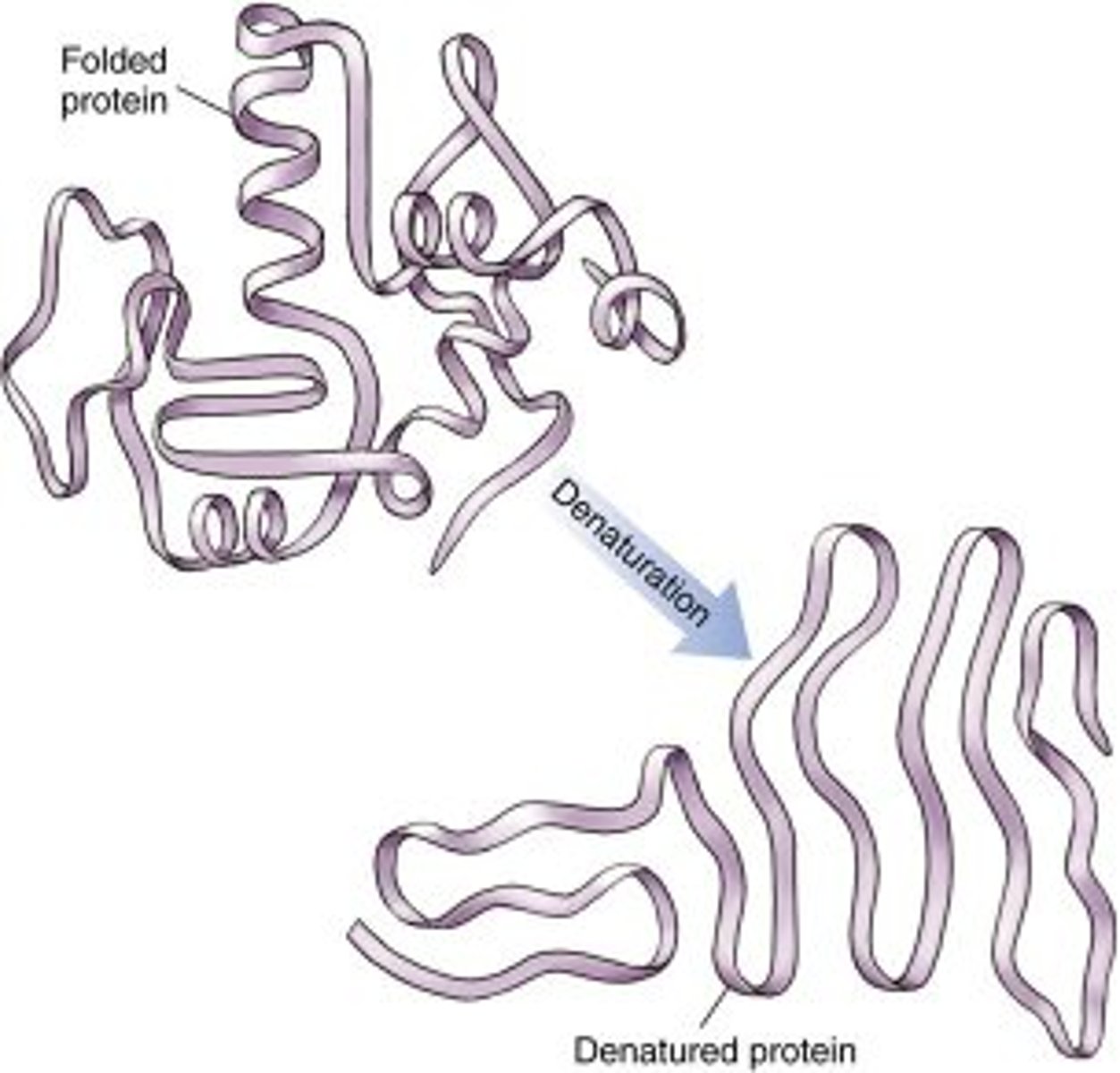
What if an enzyme is denatured?
It's structure will change and the function is lost. They cannot be fixed.
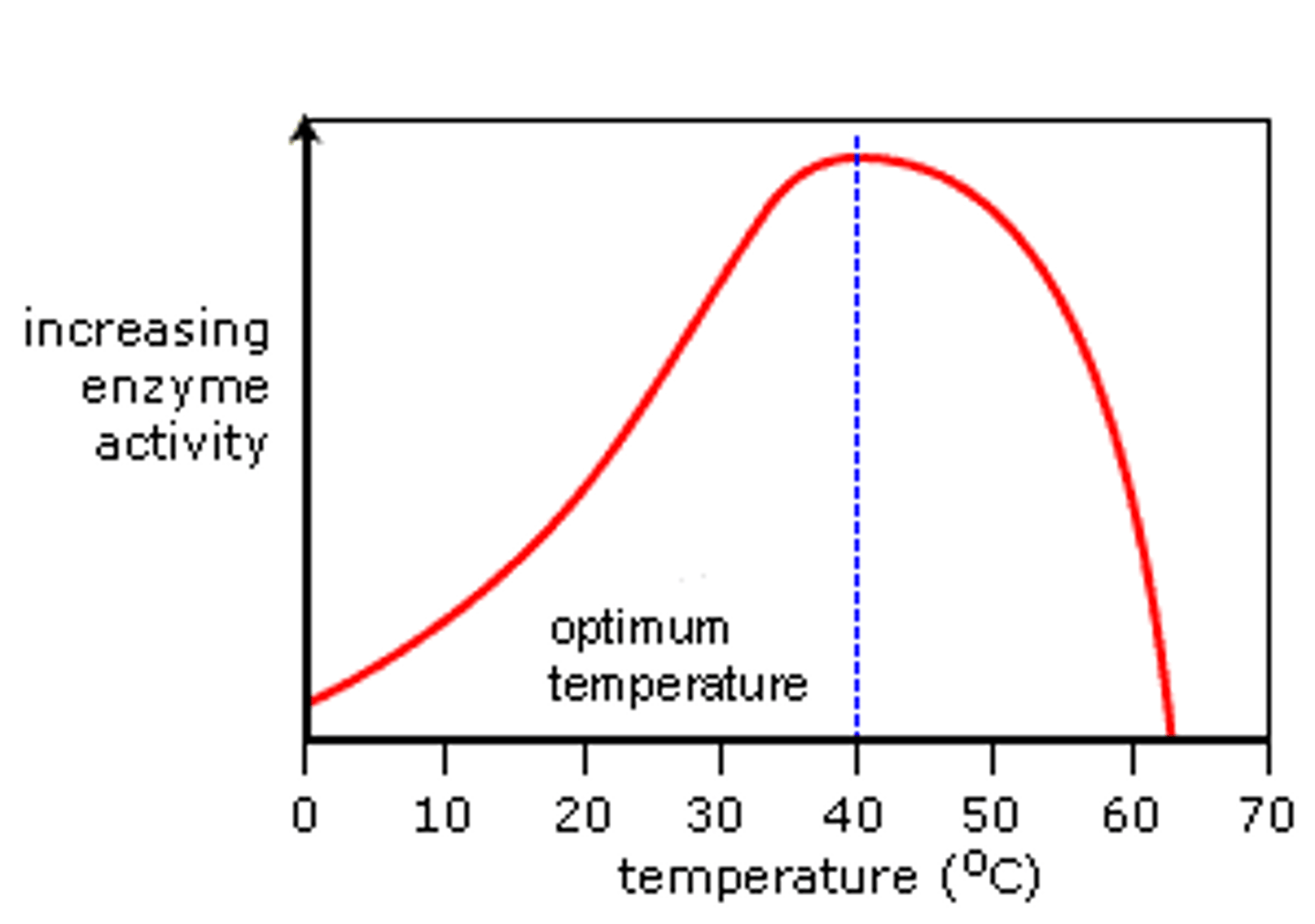
What does high temperature do to enzymes?
After optimum temp, the enzyme will denature and lose its function
What does low temperature do to enzymes?
Enzymes & substrates collide less often. Reaction rate is slow
Lots of active sites and few substrates present is caused from ______________________
High enzyme concentration
Low substrate concentration Causes what to the reaction?
Lots of active sites and few substrates therefore reaction will be fast
High substrate concentration and few active sights causes the reaction to be what?
Few active sites and more substrates therefore reaction will be slow
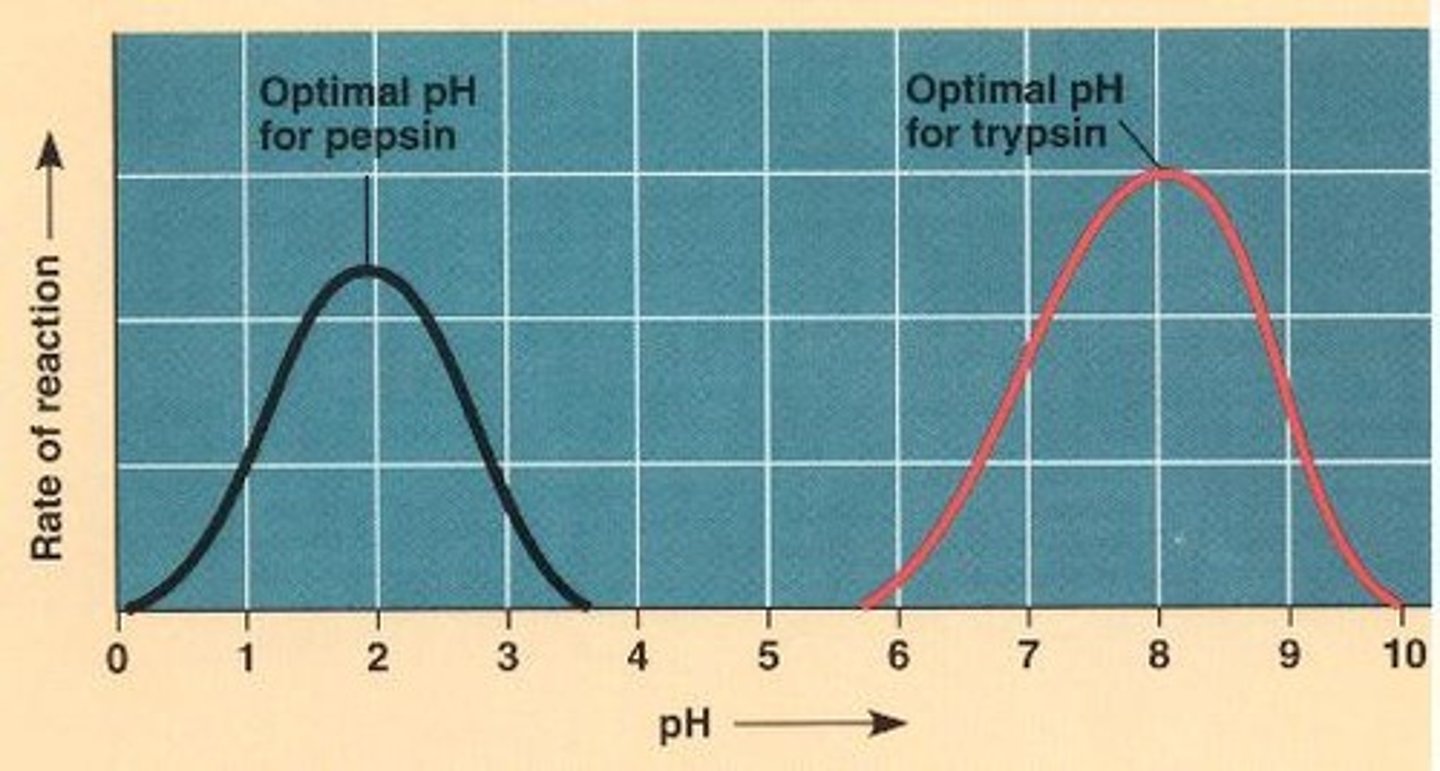
A high pH and low pH causes enzymes to ____________
Enzymes denature
Enzyme
Biological catalyst - special type of protein that speeds up chemical reactions
Activation Energy
The amount of energy needed to start a reaction
Desaturaization happens when____________________?
This is caused by extreme temperatures and pH's - bonds are disrupted in the enzyme and it loses its shape and can no longer speed up reactions
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
By lowering the activation energy
Catalyst do what
Speed up chemical reactions
Lactase does what?
An enzyme that breaks down lactose.
What is lactose?
A disaccacharide found in milk - substrate that fits in the active site of lactase.
Sucrose
A disaccharide found in table sugar - substrate that fits in the active site of sucrase.
Sucrase does what
An enzyme that breaks down sucrose.
Factors that affect Enzyme Activity
pH, temperature, and concentration of enzyme or substrate
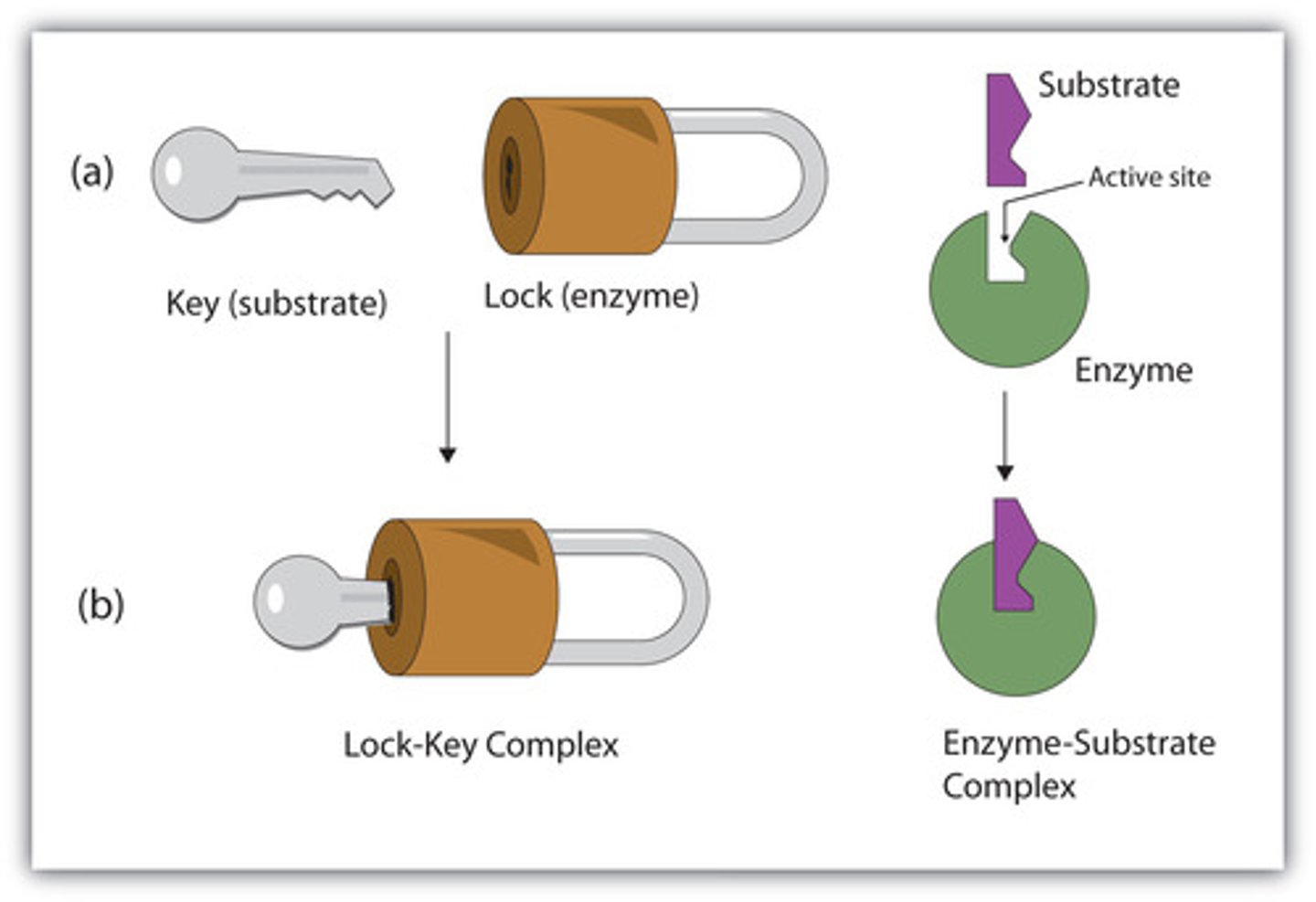
What is the Lock & Key concept
the concept that enzymes and substrate fit perfectly with each other
What is the active site?
Specific part of an enzyme where a substrate fits
Lock and Key Model
Enzymes and substrates fit together based on their specific shapes like a key fits a lock
pH, Temperature, and Concentration
Three factors that affect enzyme activity
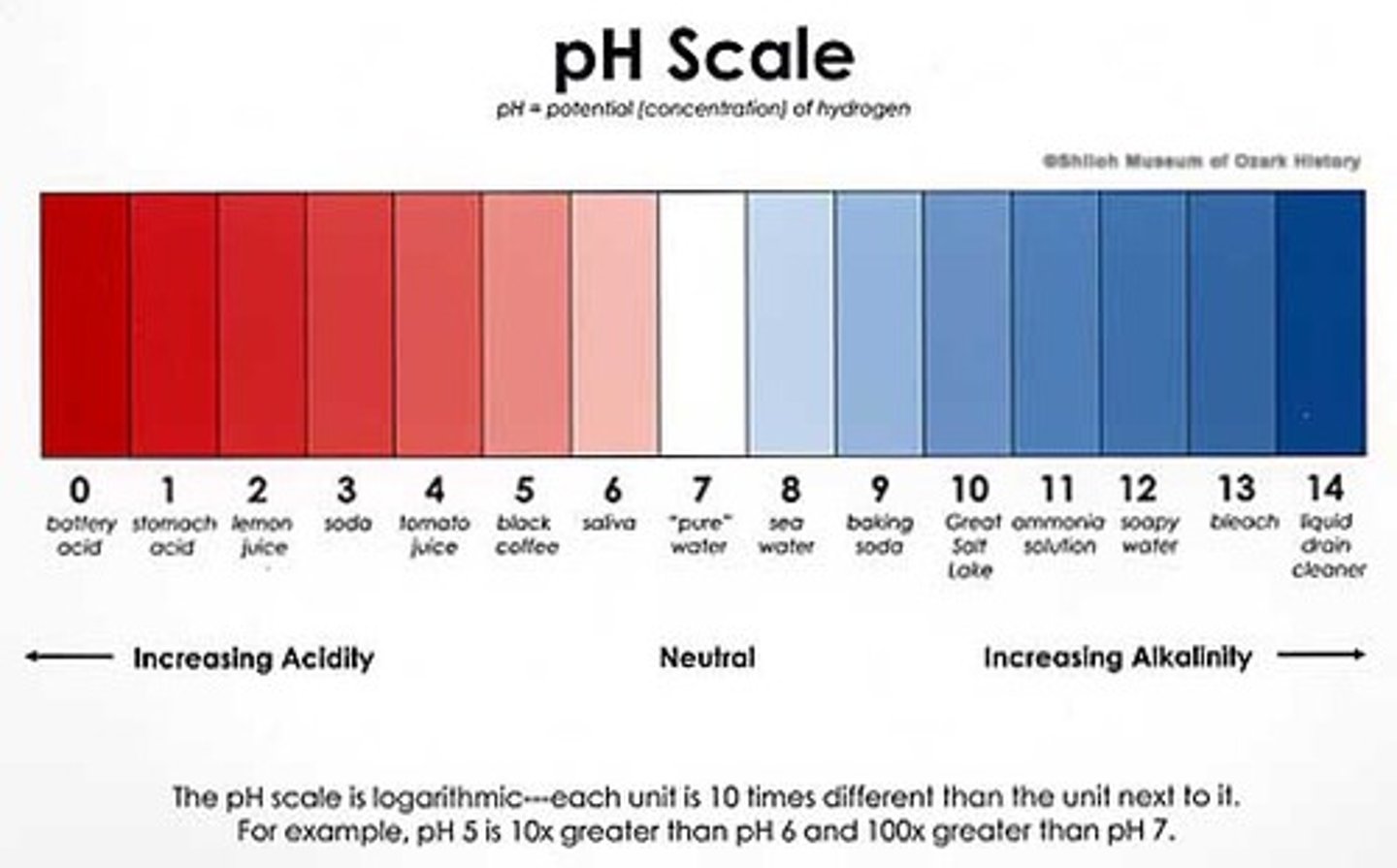
Acids on pH scale are
ph between 0-7
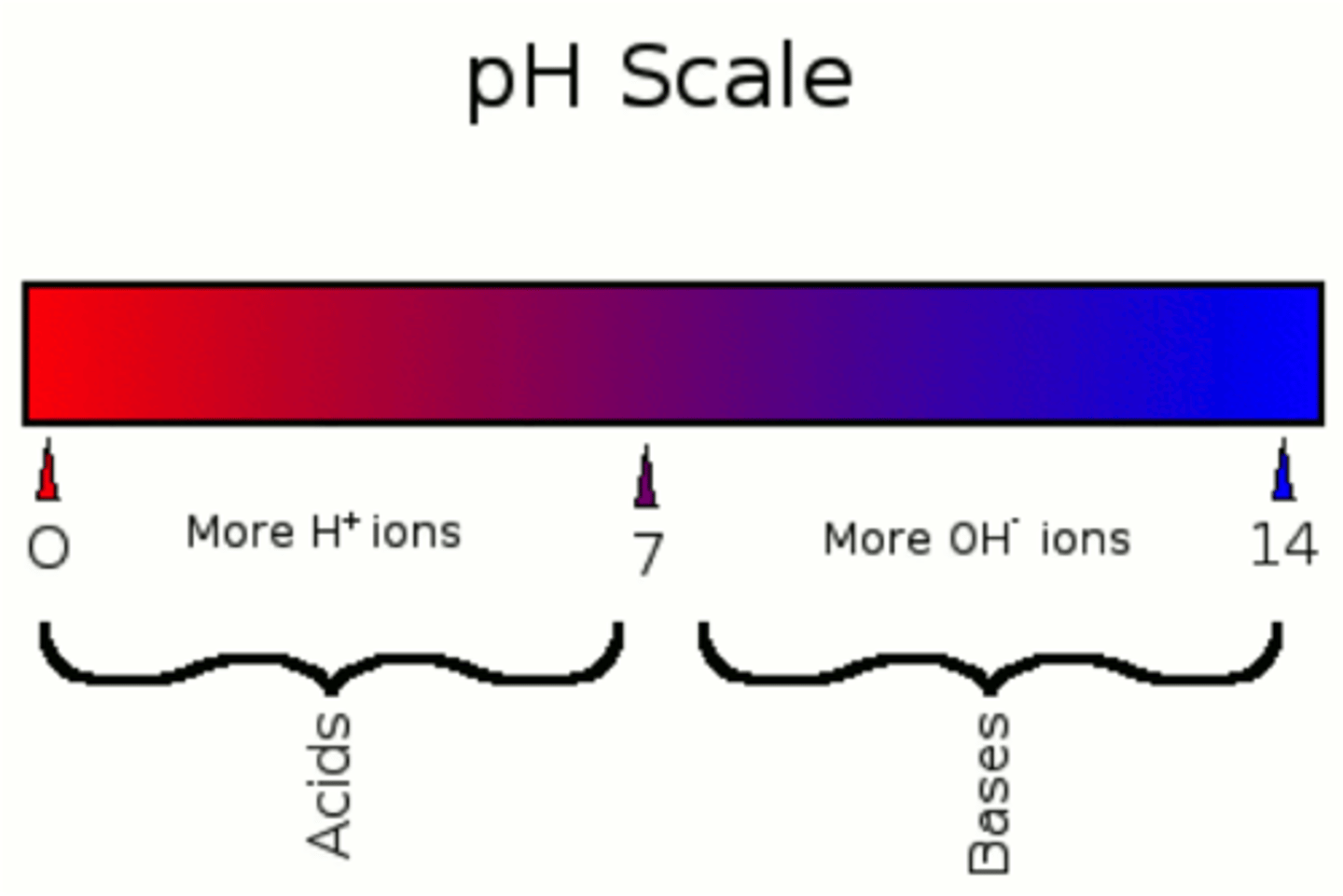
Base (alkaline) on the pH scale is
pH between 7-14
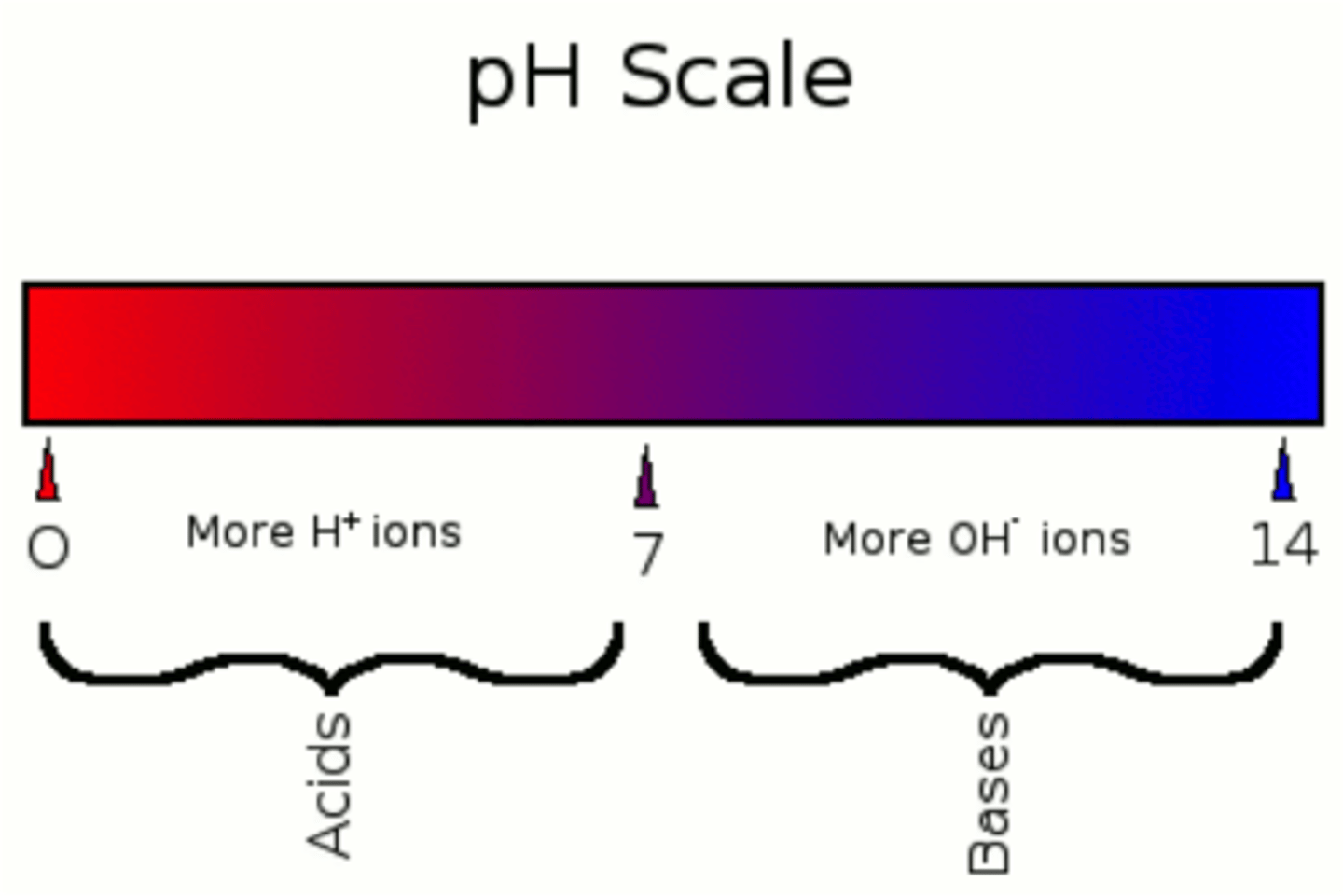
What is a neutral pH?
pH of 7
Optimal temperature
Temperature at which enzyme works the best
Denature
Change in shape of an enzyme due to extremes in temperature of pH, causes the enzymes to stop functioning
Optimal pH
pH at which an enzyme works best