Bio fungi
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Eukaryotic
Their cells have a proper nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Heterotrophs
Can't make their own nutrients by photosynthesis, they have to consume already existing organic matter.
Habitat
Aquatic, terrestrial (varies but usually moist)
Extracellular digestion
Digestive enzymes are released from the cell & the food molecules are digested outside of the cell
Parasites
Feed on other living organisms, benefit to their detriment, host might die eg. Ophiocordyceps
Saprophytes/ saprophyts
Feed on dead organic matter, breaking it down eg. Shaggy ink cap
Mycorrhizae
Symbiotic asociacion with plant roots, integrated into the root, feed on the nutrients made by plant eg. King bolete
Predators
Develop extensive hyphae which serve as a trap, trap their prey (nematodes, rotifers), feed on them eg. Shaggy ink cap
Hyphae
Thread like filaments or tubes, composed of protoplasm, subjected to branching
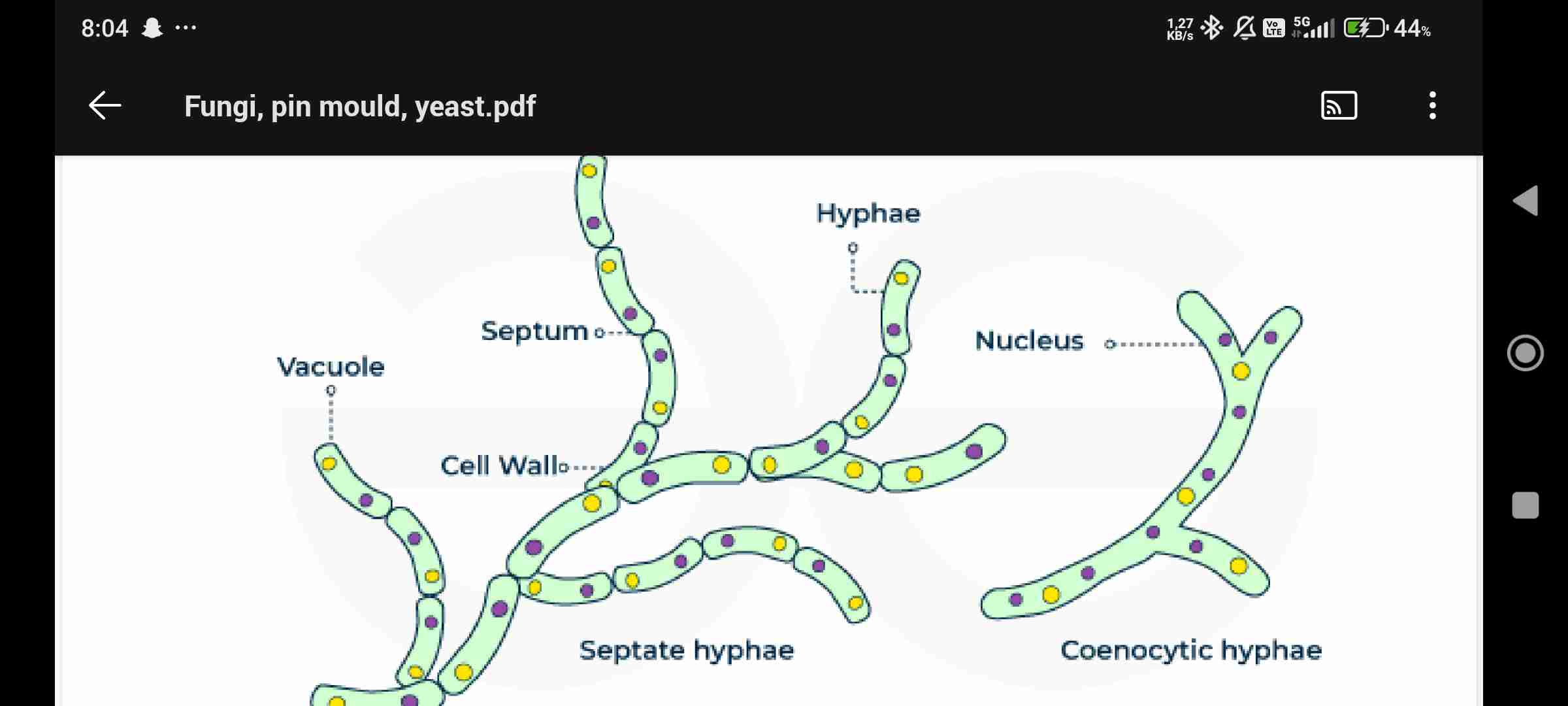
Mycelium
Network of hyphae allows transport and uptake of nutrients, often grow underground
Fungal cell
Rigid cell wall, contains polysaccharide called chitin
Budding (asexual reproduction)
A bulge from the side of the cell, the nucleus divides & the cell detatches itself from its mother cell
Fragmentation (asexual reproduction)
Mycelium separates into pieces, each piece grows into a mycelium
Producing asexual spores (asexual reproduction)
Created by one parent only through mitosis
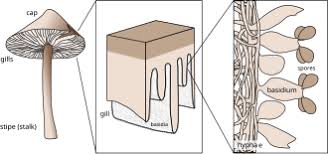
Basidiomycota
produce large fruiting bodies called basidiocarps, they form sexual spores on specialized structures called basidia, eg. fly amanita, all types of russula
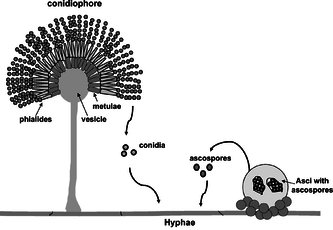
Ascomycota
production of ascocarps - fruiting bodies containing specialized sac-like structures called asci,each ascus typically contains eight spores, eg. morel (morchella), penicillium
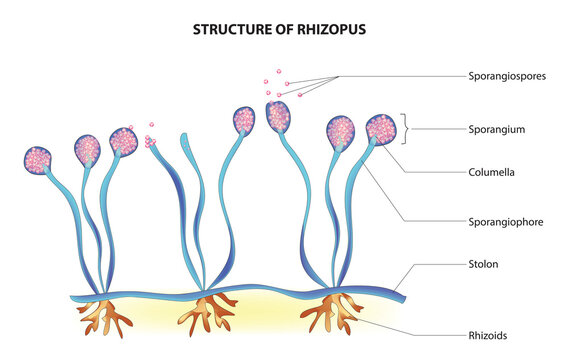
Zygomycota
thick-walled resting spores called zygospores during sexual reproduction, they typically have coenocytic hyphae, eg. mucorales, rhizopus
Chytridiomycota
zoospores, which have flagella for movement,primarily inhabit aquatic environments
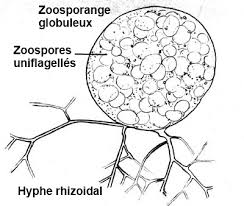
pin mould structure
simple in structure, brown or yellowish-brown in color, and with branched aerial (in the air) filaments that bear the zygospores
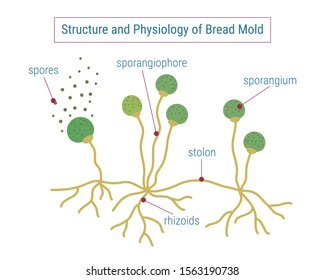
Pin mould reproduction
usually reproduce asexually by producing sporangiospores, Sexual reproduction starts when conditions become unfavorable - two opposing mating strains must fuse or conjugate, thereby, sharing genetic content and creating zygospores
Life cycle of a pin mould
Spore Germination →Hyphal Growth (Mycelium Formation) →Asexual Reproduction →Sexual Reproduction →Dormancy (in unfavorable conditions)
Yeast
eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms, most yeasts reproduce asexually by budding, versatile and can adapt to many environments rich in carbohydrates or decaying matter
Fermentation
when making alcohol, chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically, the yeast converts the sugars in the raw materials into alcohol and carbon dioxide
Leavening
fermentation process into the dough, by which sugars are transformed into carbon dioxide gas and alcohol
Fungal cell vs animal cell
fungal cell has cell wall, animal doesnt; both store nutrients in glycogen; both cannot photosynthesize
fungal cell vs plant cell
plant cell has chloroplasts, can photosynthesize, fungal doesnt; fungal store nutrients in glycogen, plant in starch; fungal - cell wall made of chitin, plant - cell wall made of cellulose
sexual reproduction
conjugation - two compatible fungal cells fuse to exchange genetic material = formation of a zygote, allows for genetic diversity