ARCH 210 Monuments
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Monuments with pictures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
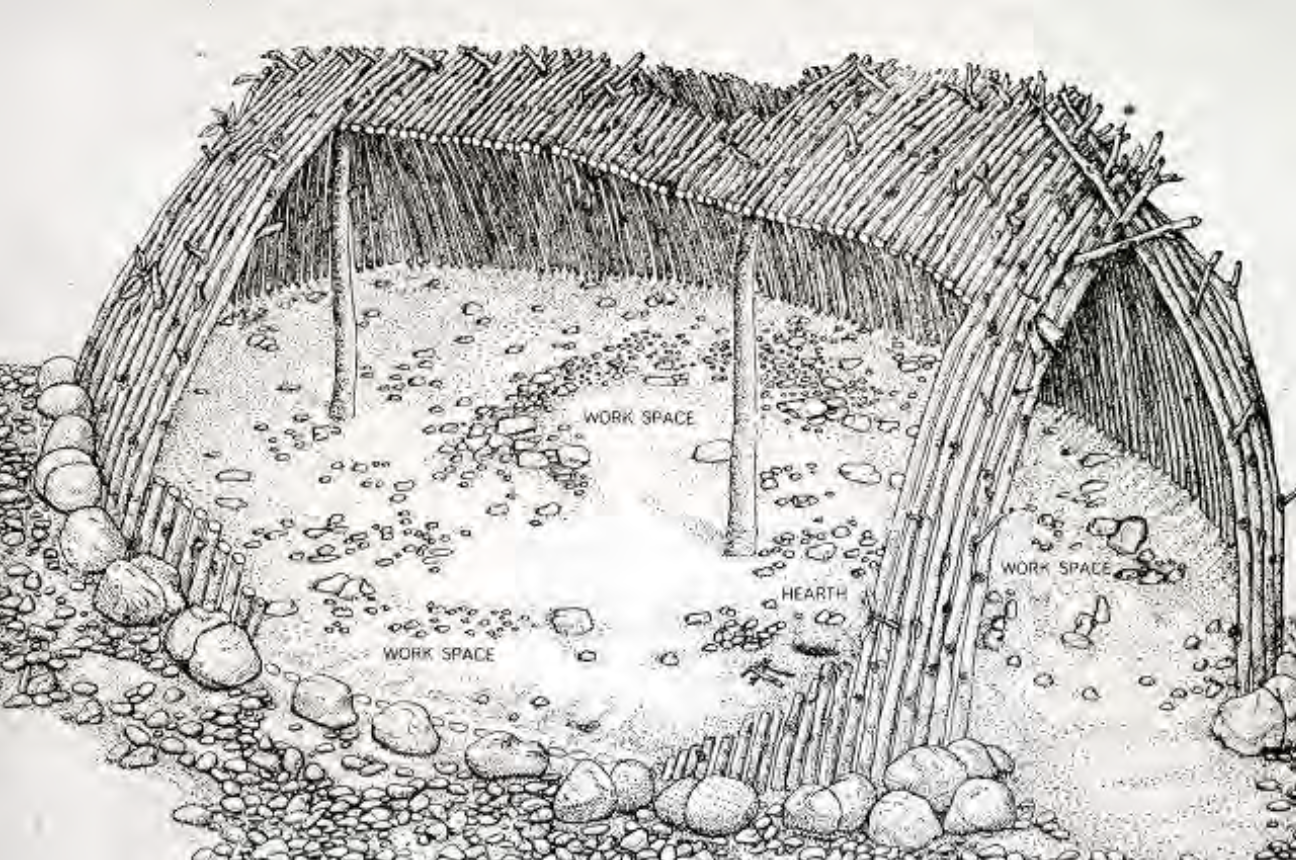
Prehistoric Hut, Terra Amata, France, Paleolithic: hypothetical reconstruction of the huts at this site
Characteristics:

Cave at Lascaux, France, Paleolithic
Characteristics:
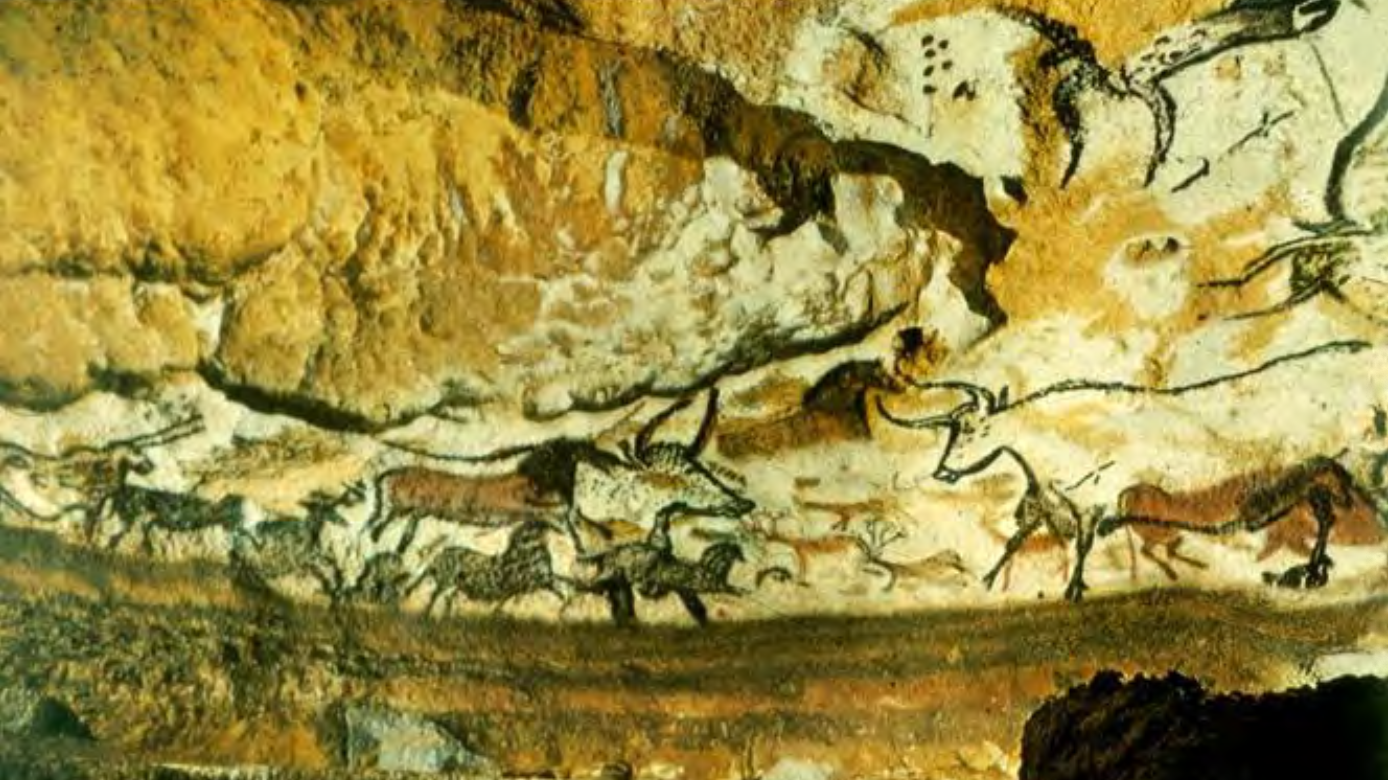

Cave at Lascaux: Hall of the Bulls (Aurochs), Lascaux, France, c17,000-10,000
BCE
Paleolithic Pigment on limestone;
the largest bull painting is 18 feet long
Newgrange Cairn and Passage Grave, Newgrange, Ireland, Neolithic
Characteristics:

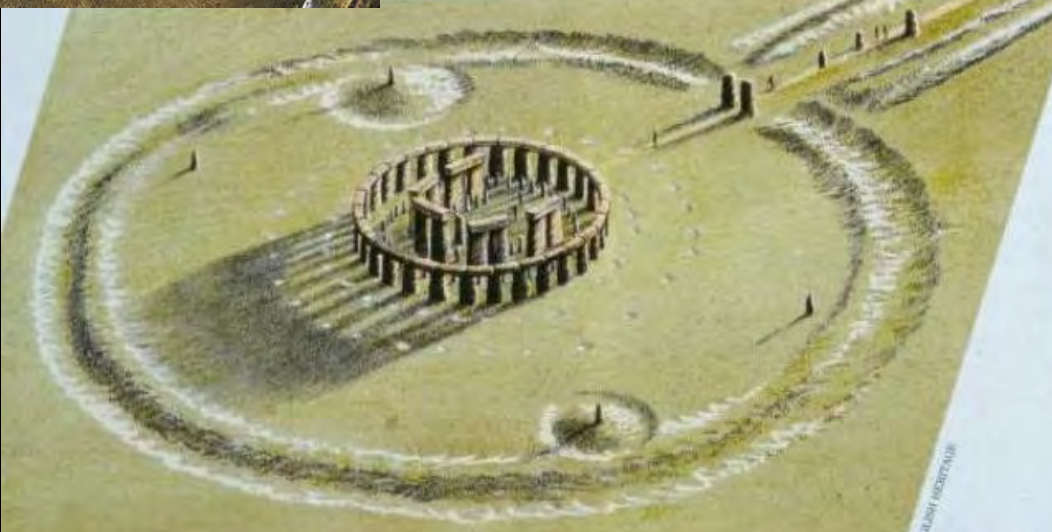
Stonehenge, Salisbury Plain, England, Neolithic

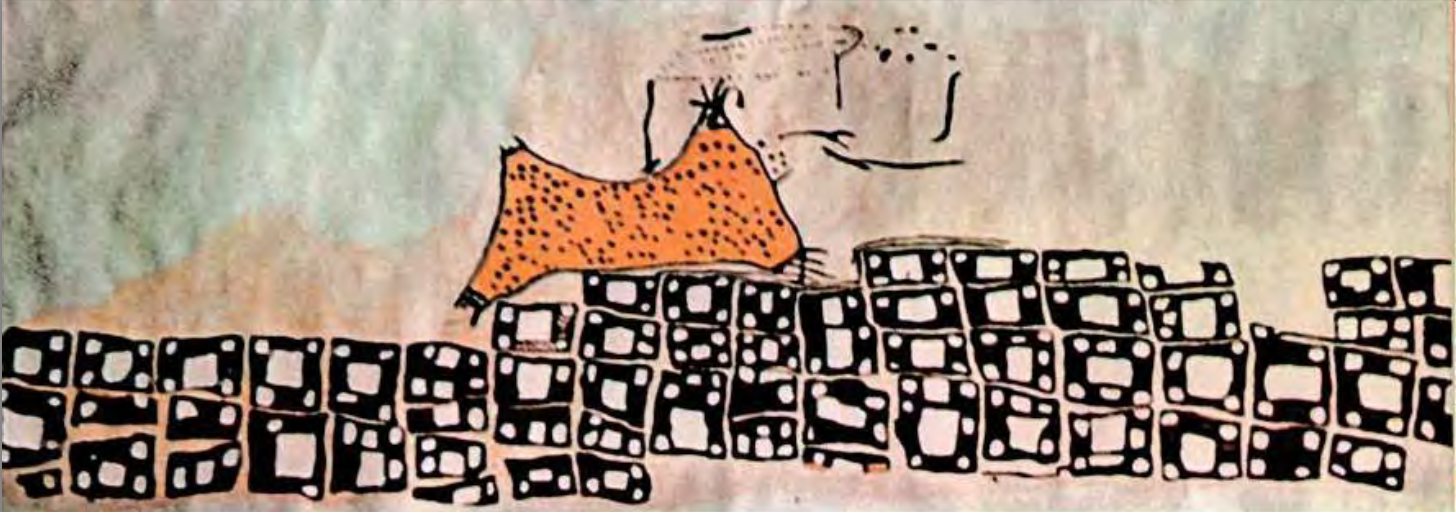
Çatalhöyük, near Konya, Turkey, Neolithic Period: domestic structure
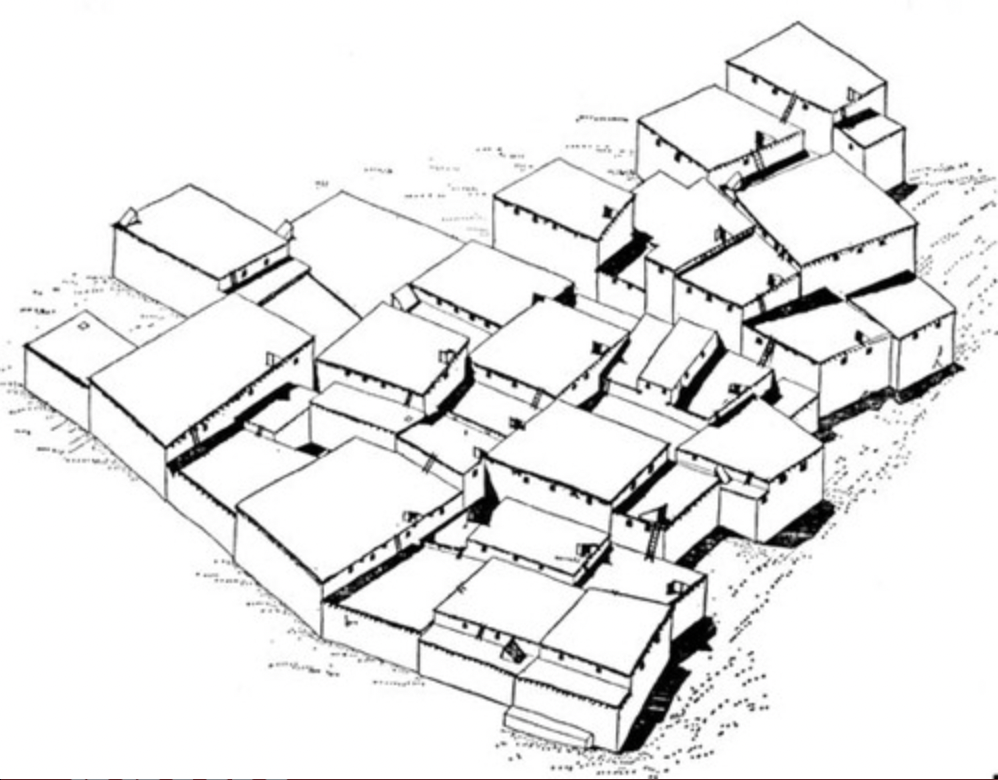
City map and volcano fresco, Çatalhöyük, near Konya, Turkey, c. 5800 BCE,
Neolithic. painted plaster

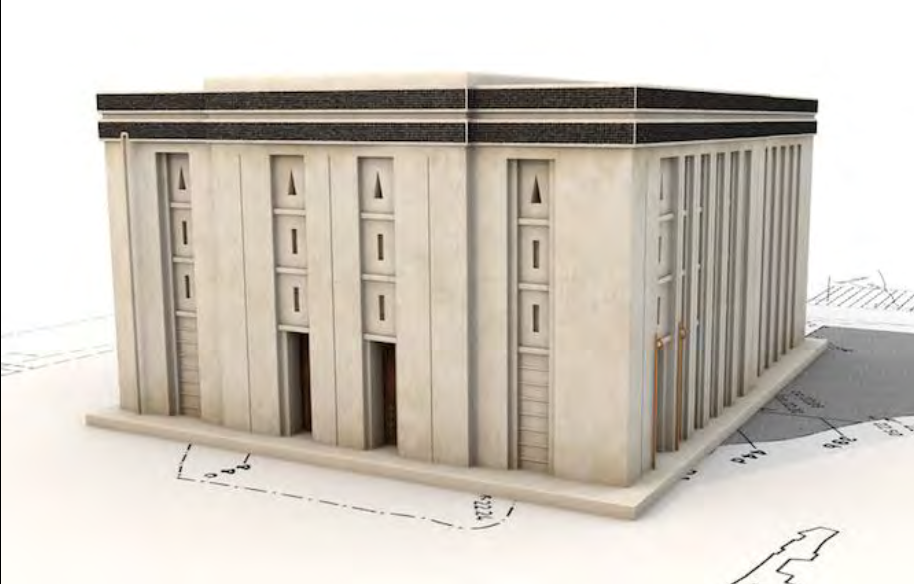
Anu Ziggurat and White Temple, Uruk (Warka), Iraq, c3300-3000 BCE, Sumerian

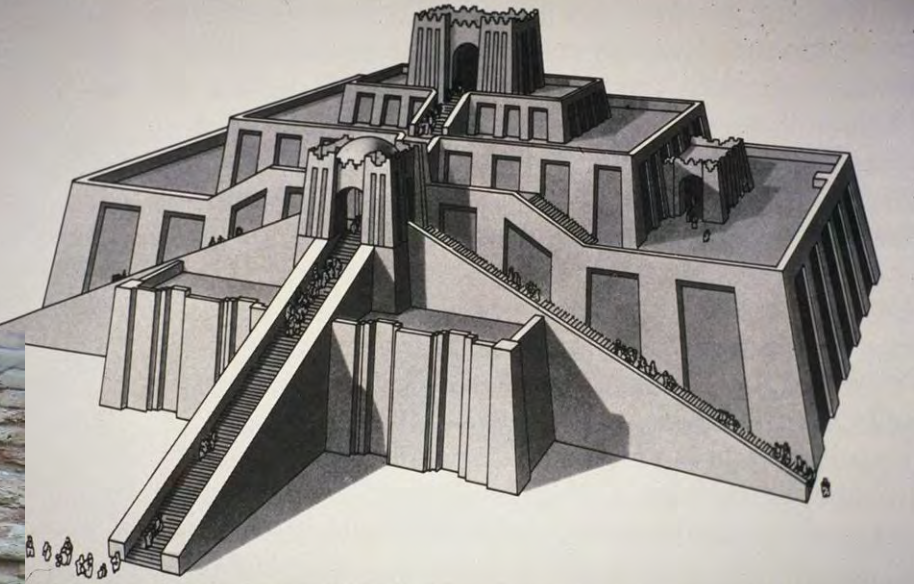
Ur, Iraq, c. 2200-2000 BCE, aerial view with the archaeological remains of the ziggurat and other elements of the city
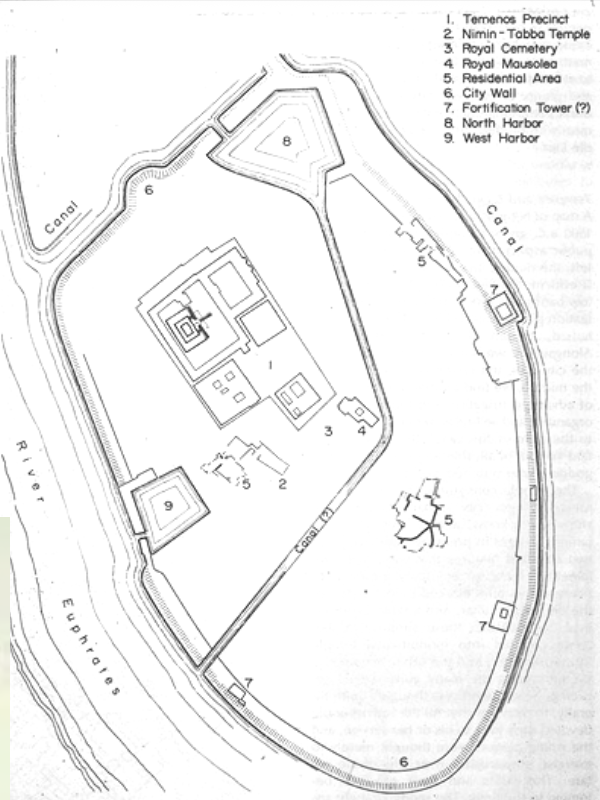
Ziggurat and Temple of Nanna, Ur, Iraq, 2100-2050 BCE, Patron: King Ur-
Nammu (and his son, Shulgi); Sumerian

Plan of the Citadel, Mohenjo-daro, Pakistan, c. 2500 BCE (mature phase, earlier settlements in the area going back to 5000 BCE), Harappan/Indus Civilization
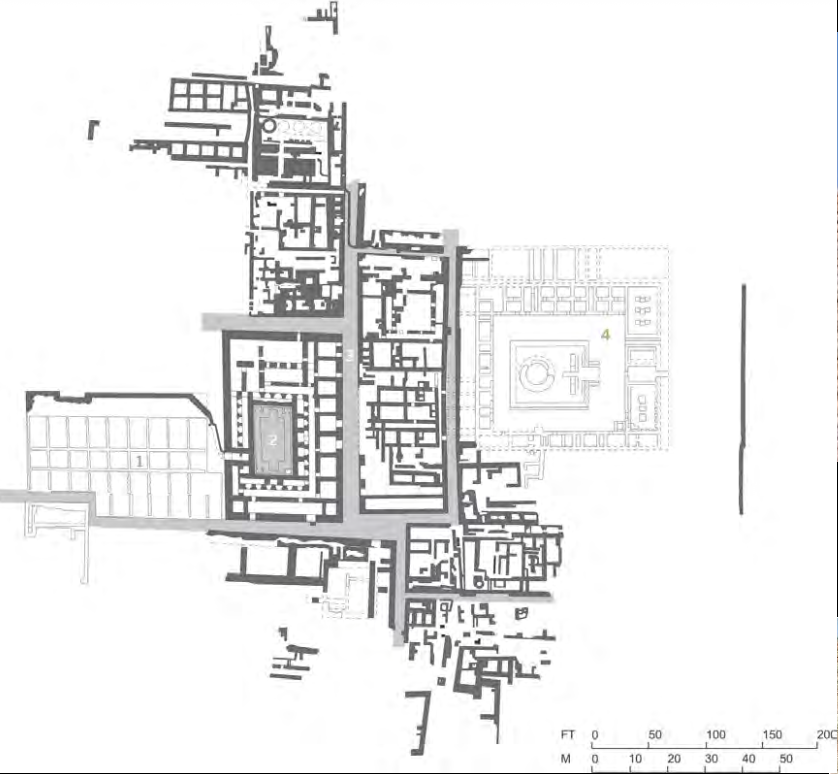
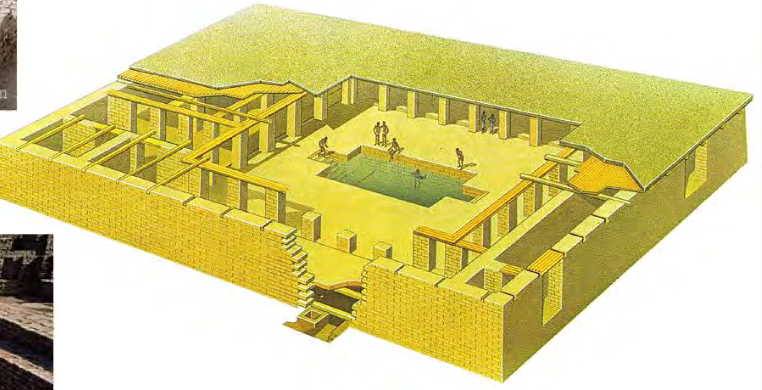
Great Bath, Mohenjo-daro, c. 2600-1900 BCE, Harappan/Indus Civilization
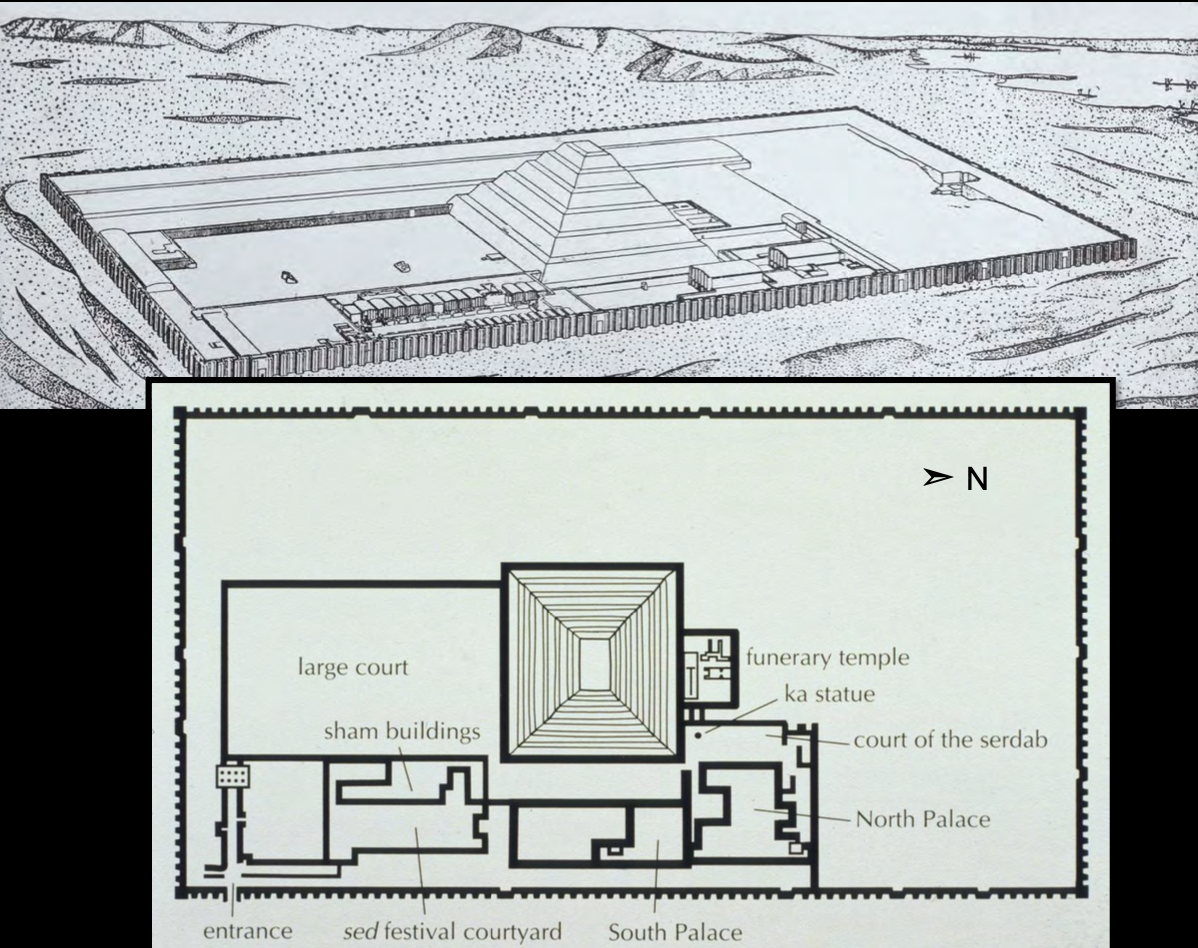
Mortuary Complex of Pharaoh Djoser, Saqqara, Egypt, c2650 BCE, Architect: Imhotep, Old Kingdom Egypt.
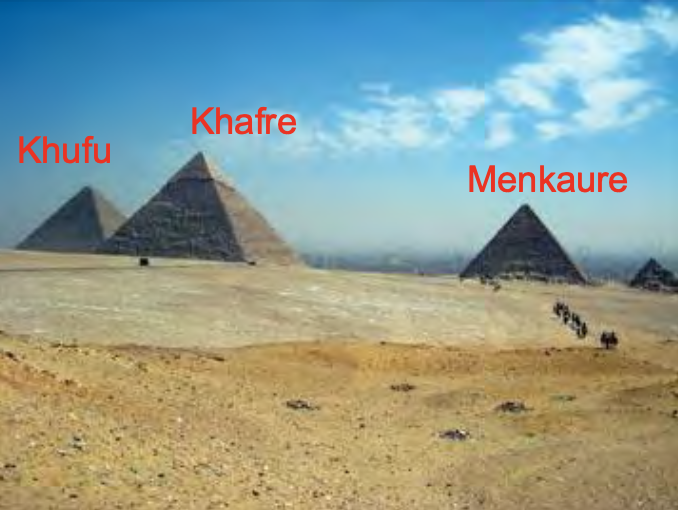

Great Pyramids, Giza, Egypt, 2600- 2400 BCE, Old Kingdom Egypt
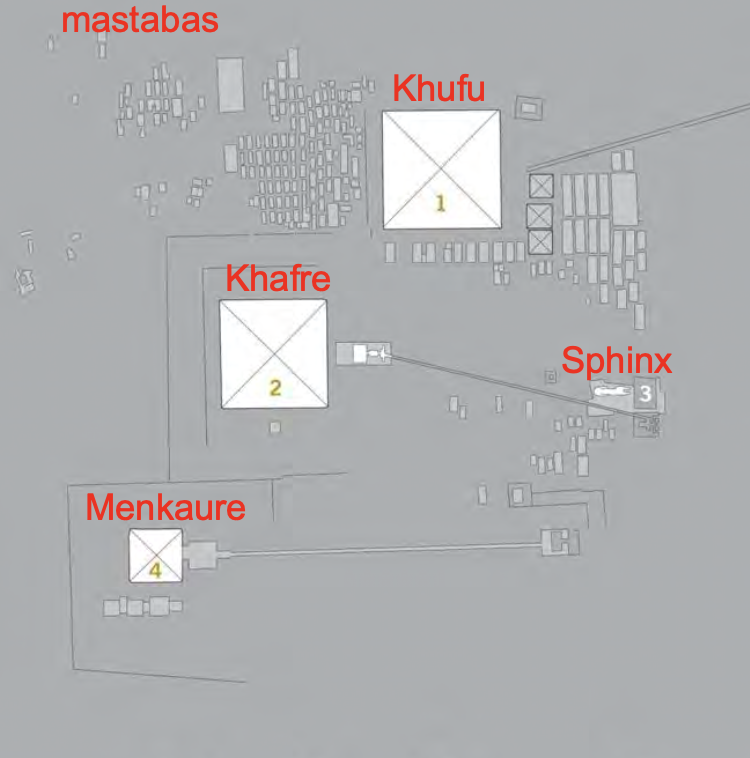
Pyramid of Khufu (Cheops), Giza, Egypt, c. 2570 BCE, Old Kingdom Egypt
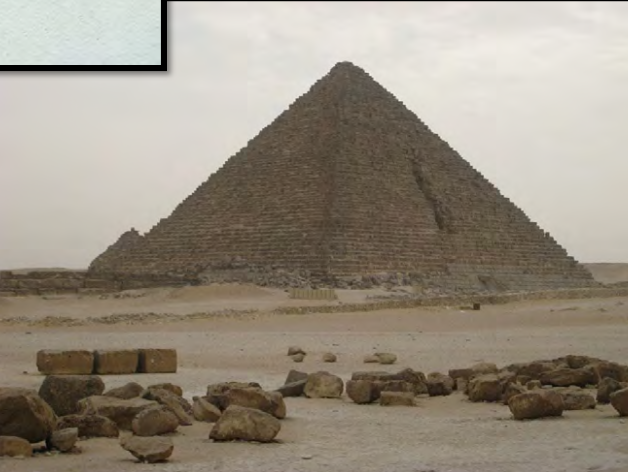

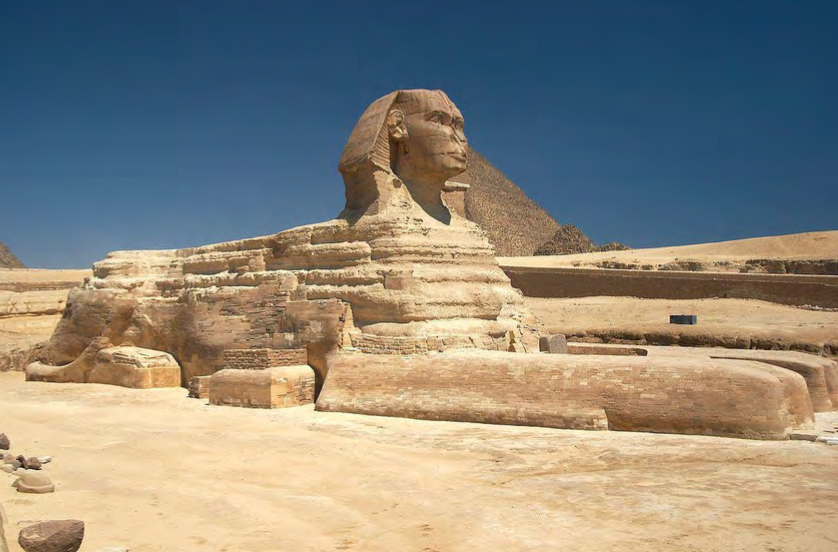
Pyramid of Khafre/Chephren (2), and the Sphinx (3), Giza, Egypt, c. 2650 BCE, Old Kingdom

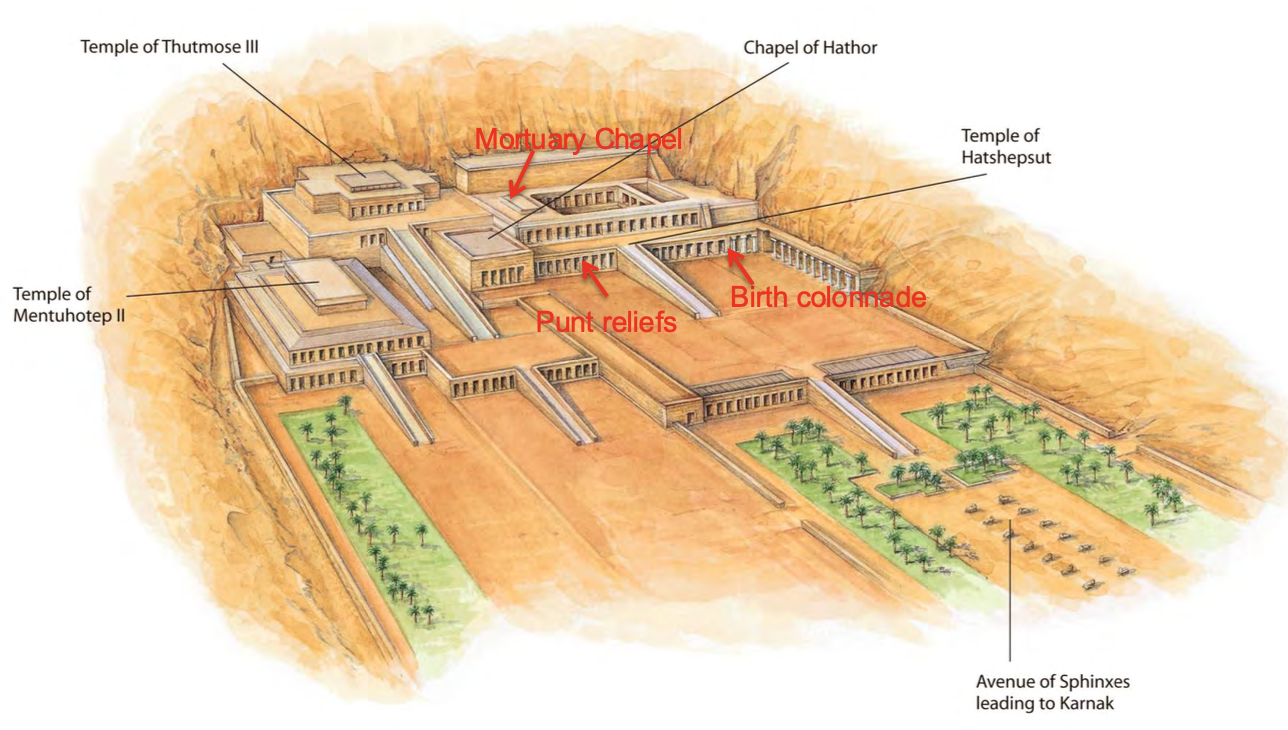
Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut, Deir el-Bahri, Egypt, c. 1480 BCE, New Kingdom Egypt (next to temple of Mentuhotep II)
Remains and plan of Persepolis (Takht-e Jamshid), Iran, c. 500 BCE, Persian Achaemenid Empire. Patron: Darius I
Changes: 1. now carved into hillside rather than rising from landscape. 2. One dominant axis rather than approachable from all sides. (Axiality; carved from the living rock/cliff-face)
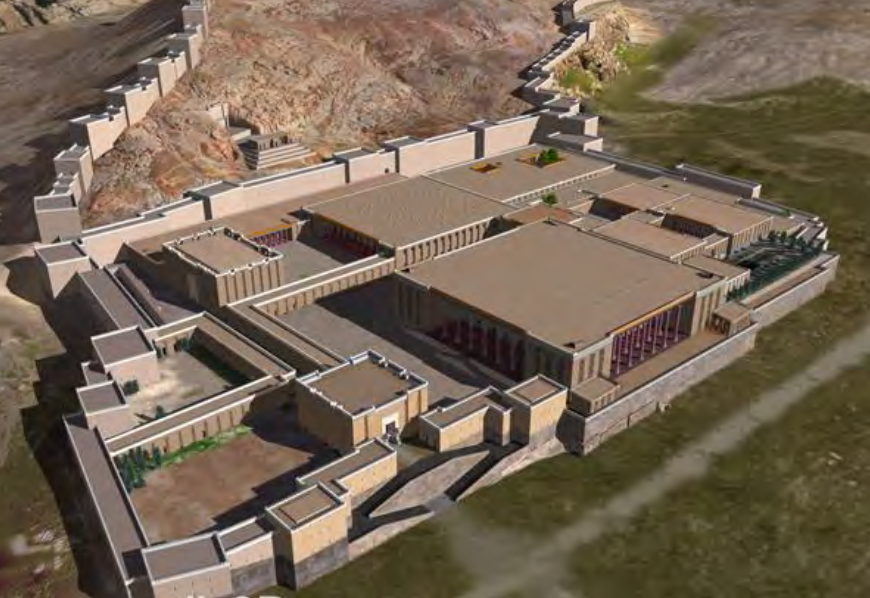

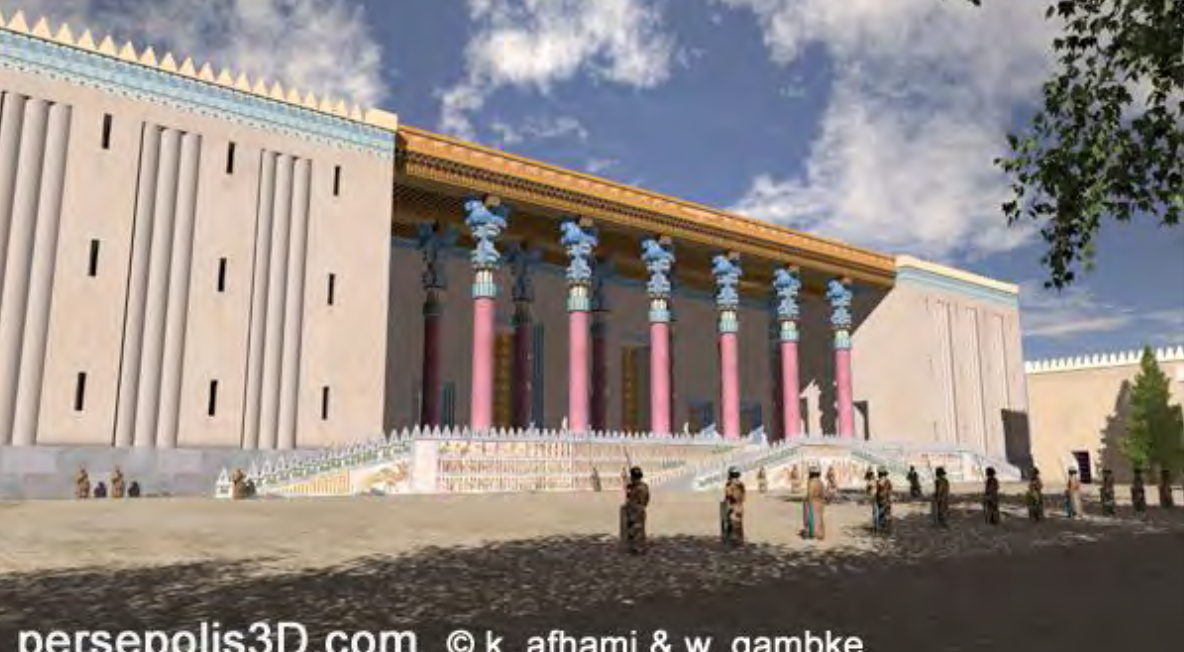
Persepolis (Takht- e Jamshid), Iran, c.500 BCE, Persian Patron: Darius I. Achaemenid Empire.
Apadana,Throne Hall, and the Gate of Xerxes
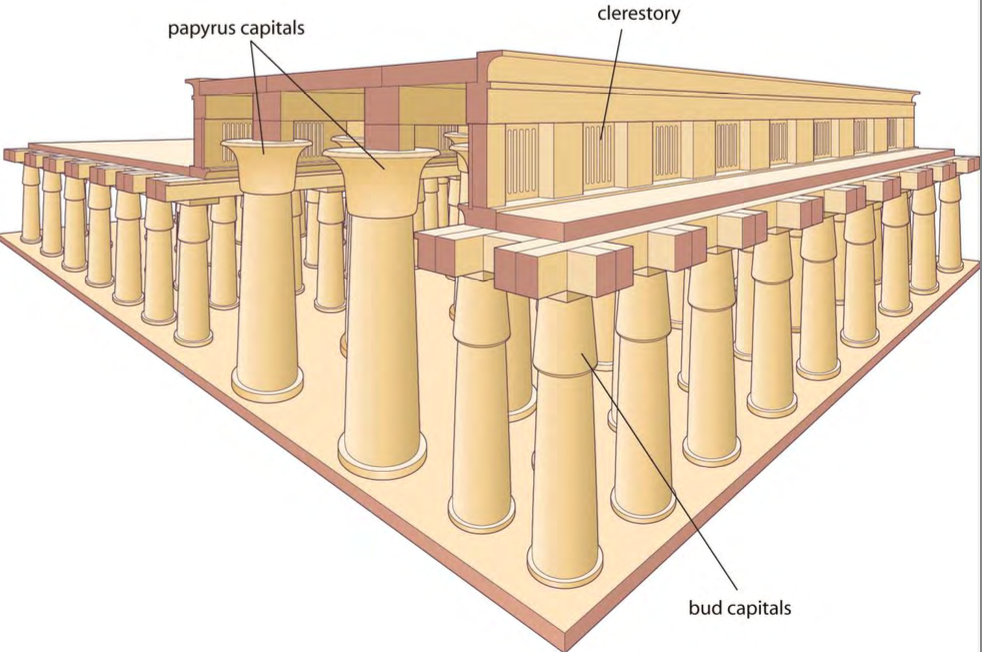
Great Hypostyle Hall, Temple Complex of Amun-Re, Karnak, Egypt, 1417-1379 BCE, New Kingdom
The Apadana, or Audience Hall, Persepolis, Iran, c 500 BCE, Persian Achaemenid Empire

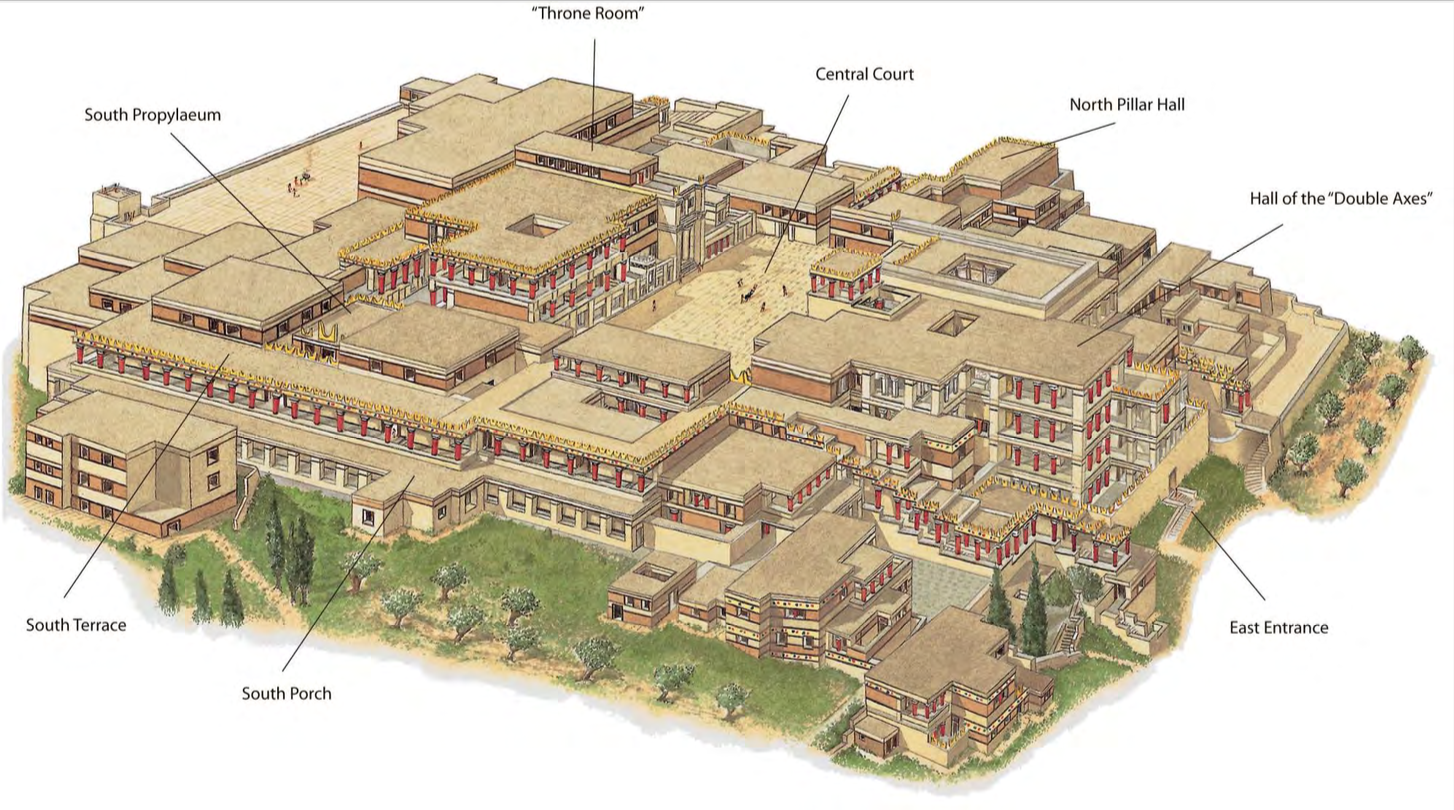
Labyrinth/Palace of Knossos, Knossos (Crete), Greece, c. 1450 BCE, Minoan
Ziggurat and Temple of Nanna, Ur, Iraq, 2100-2050 BCE, Paron: King Ur-Nammu
(and his son, Shulgi); Sumerian
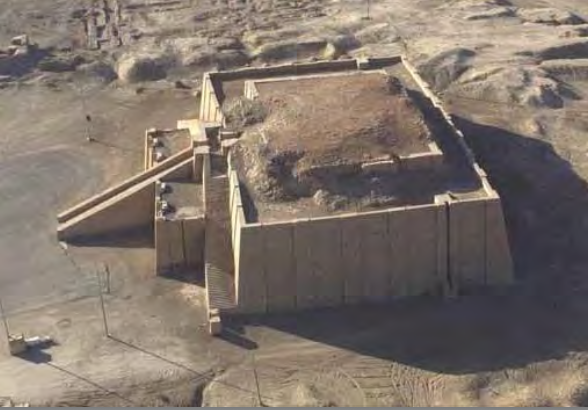

Citadel, Mycenae, Greece, 1600-1200 BCE, Mycenaean
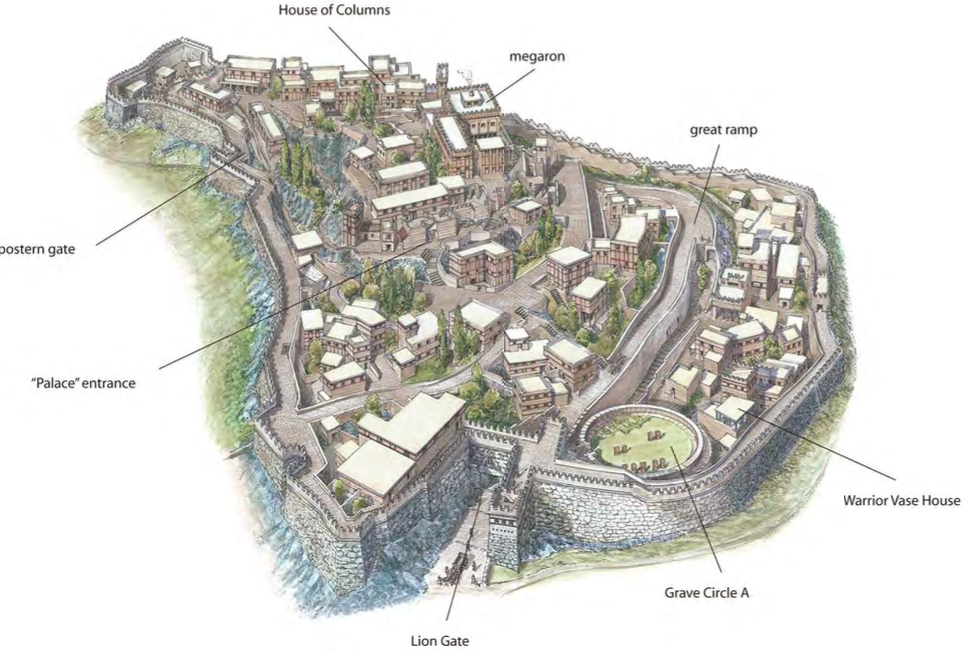
Lion Gate, Citadel, Mycenae, Greece, 1250 BCE, Mycenaean [limestone relief , 9 ½ feet high]

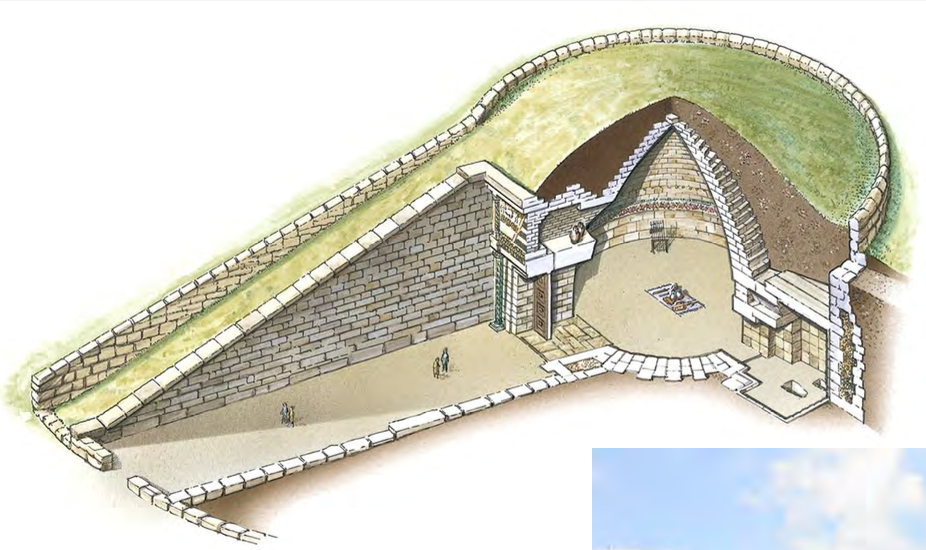
“Treasury of Atreus,” Mycenae, Greece, c. 1250 BCE, Mycenaean
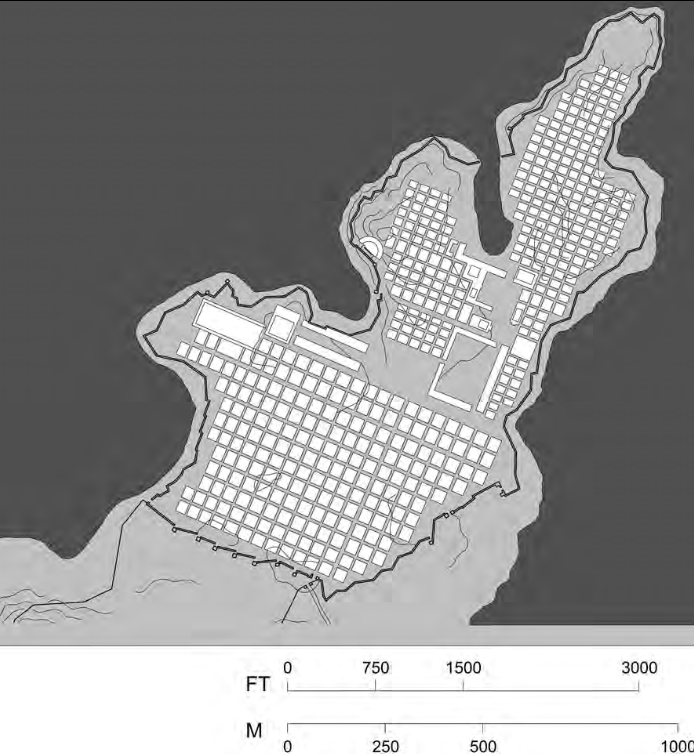
Hippodamian Plan of Miletus, (Western) Turkey, c470 BCE, Classical Greek

Temple of Hera, Paestum, Italy. c. 550– 540 BCE, Archaic Greece(DIAGRAM)
The Acropolis of Athens, reconstruction plan in Classical period
The rebuilding of the Acropolis, was a votive (a ritual gift/offering of thanks) to Athena, was under the direction of Pericles, leader of the city in the mid-fifth century BCE
The Acropolis is a site of collective memory for Athenians; t helped shape the identity of the city and its people, based on historical, mythological/religious events

Parthenon, on the Acropolis, Athens, Greece, rebuilt 447-432 BCE, Patron: Pericles (leader of Athens); Architects: Iktinos and Kallikrates; chief sculptor: Phidias, Classical Greek
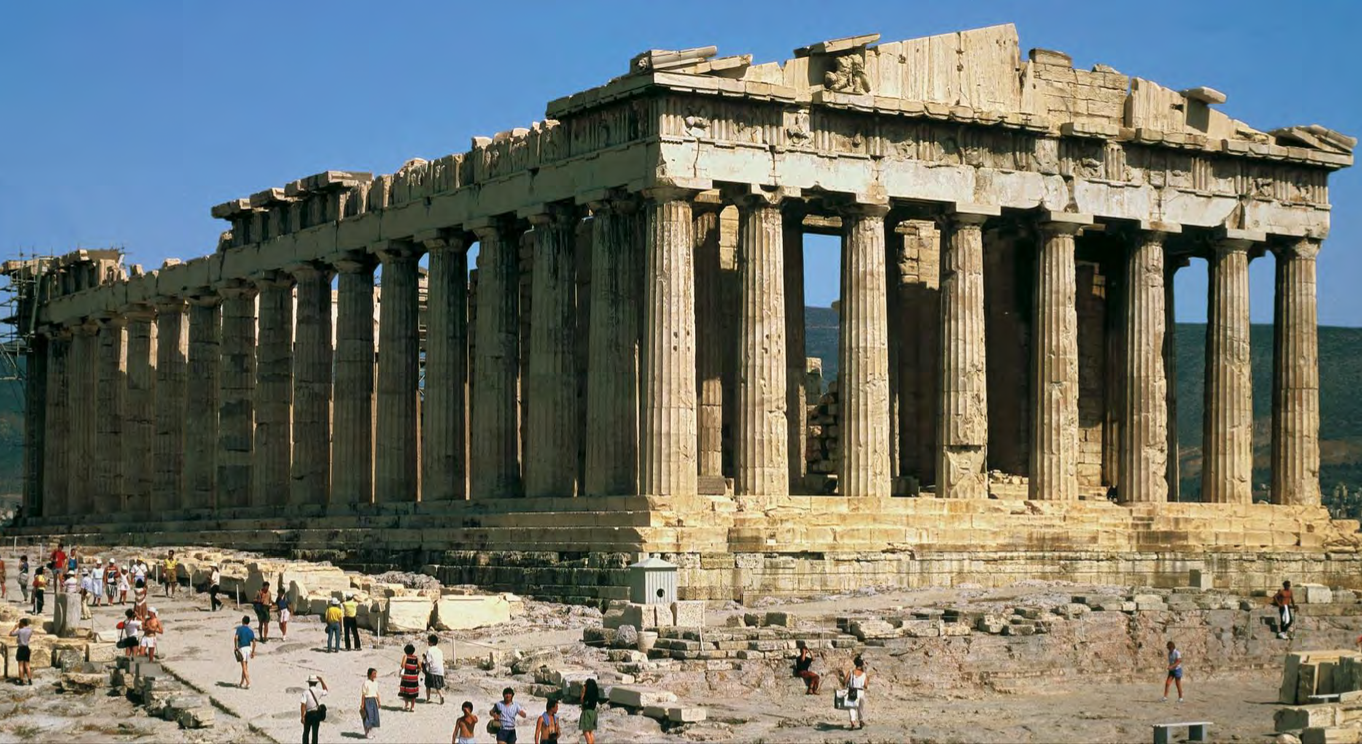

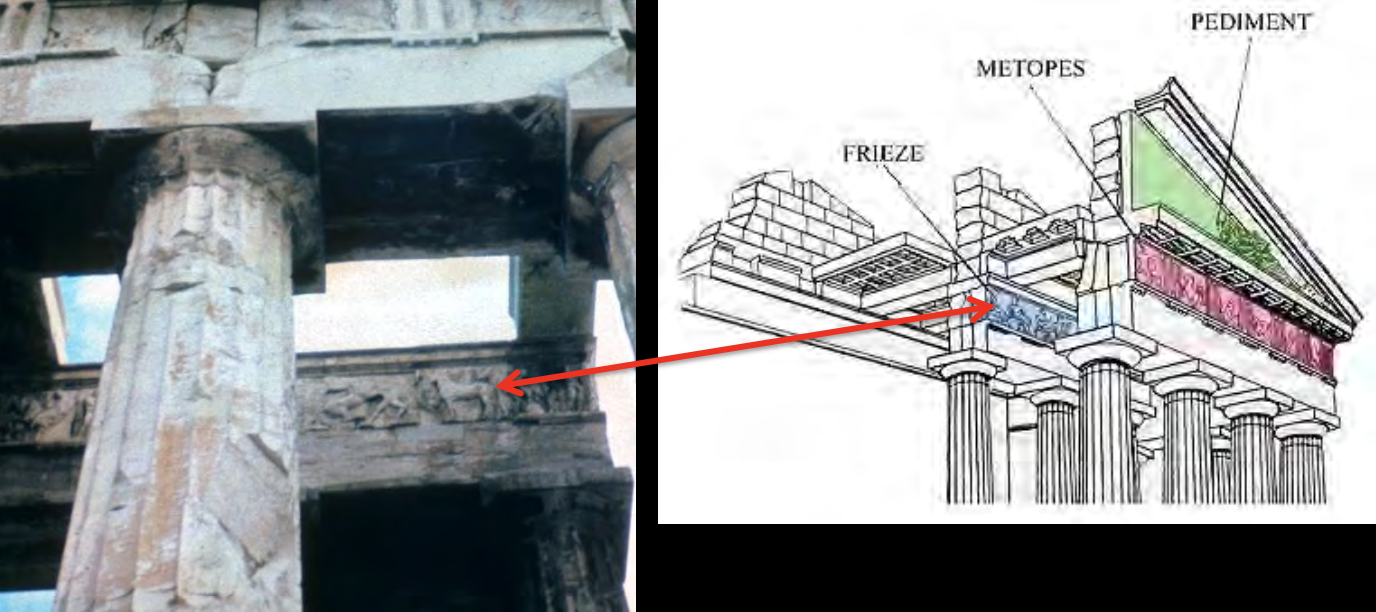
Parthenon Inner Frieze
the inner frieze here is an anomaly (it is unusual), making the Parthenon unique; it shows the Panathenaic procession
Reconstructions of the Athena Parthenos statue inside the cella f the
Parthenon; Chryselephantine statue by Pheidias (ca 432 BC)

Propylaia, Athens, Greece, 437-432 BCE, Classical Greek (designed by Mnesikles
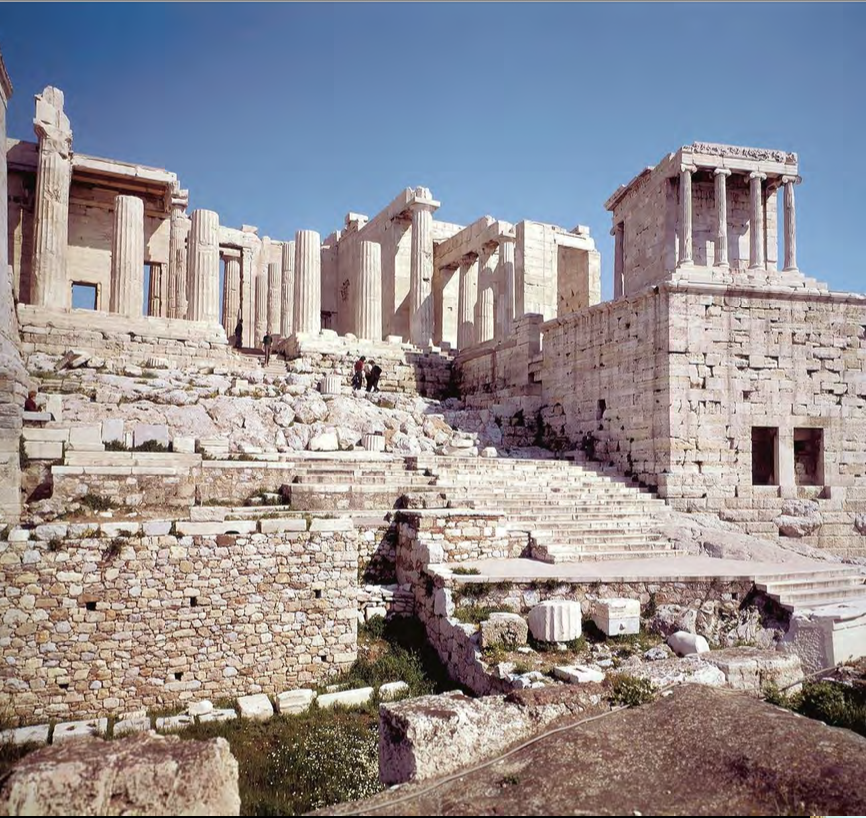

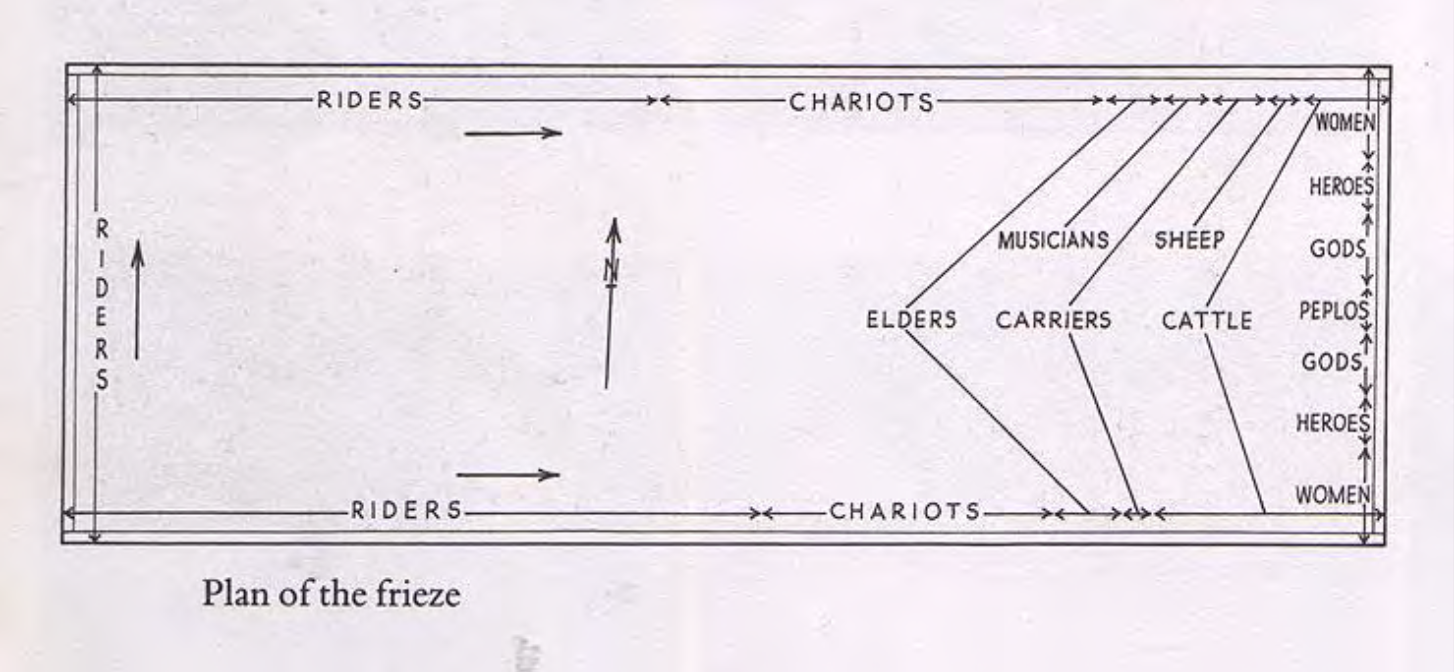
Interior frieze with the Panathenaic Procession, groups from Athenian society
participating in the Panathenaic Procession, marching “in perpetuity”
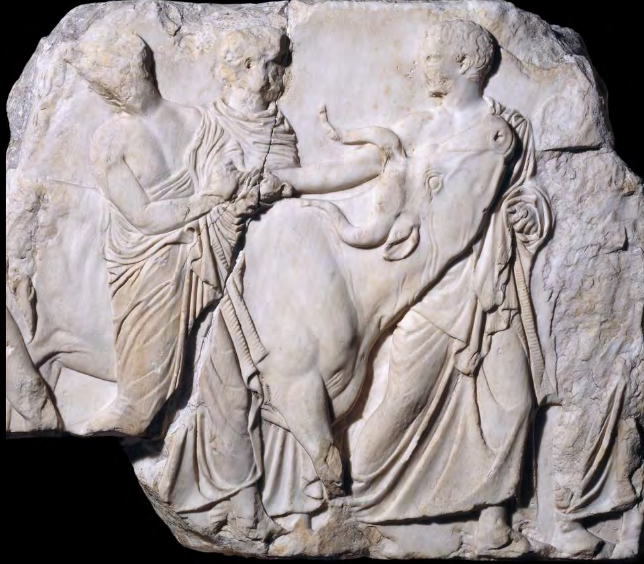
Parthenon Frieze
Shows members of society bringing votives to offer to Athena in thanks, such as the bull to be sacrificed (left), and the peplos, a dress made new each year by the daughters of elite Athenian families; it was used to dress the statue of Athena Polias, which was carried in the Panathenaic Procession.

The metopes create a visual metaphor for Athenians’ (lapiths, men) war and Pericles’ victory over the Persians (shown as the “Other,” foreign, centaurs)
(bears meaning for Pericles’ Athens
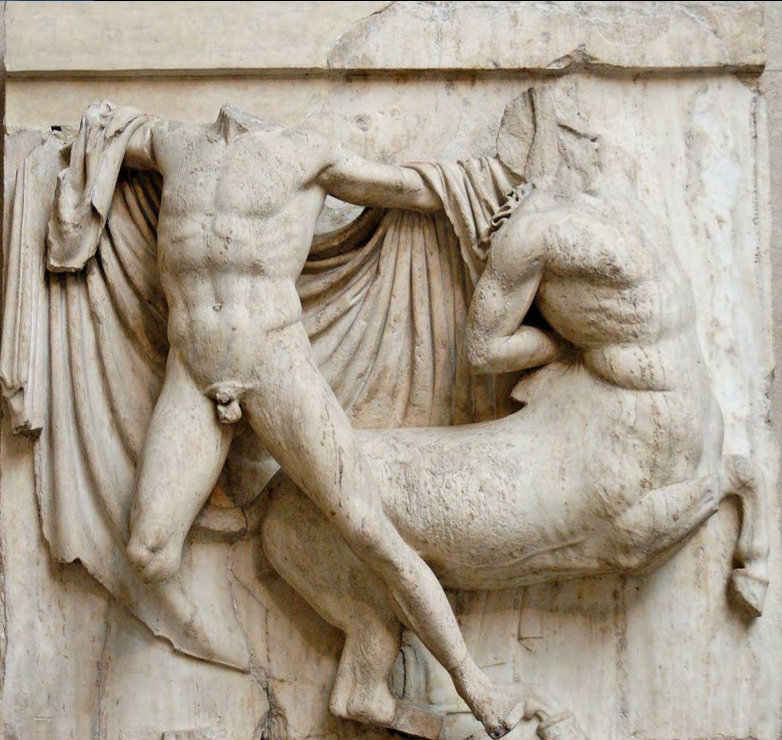

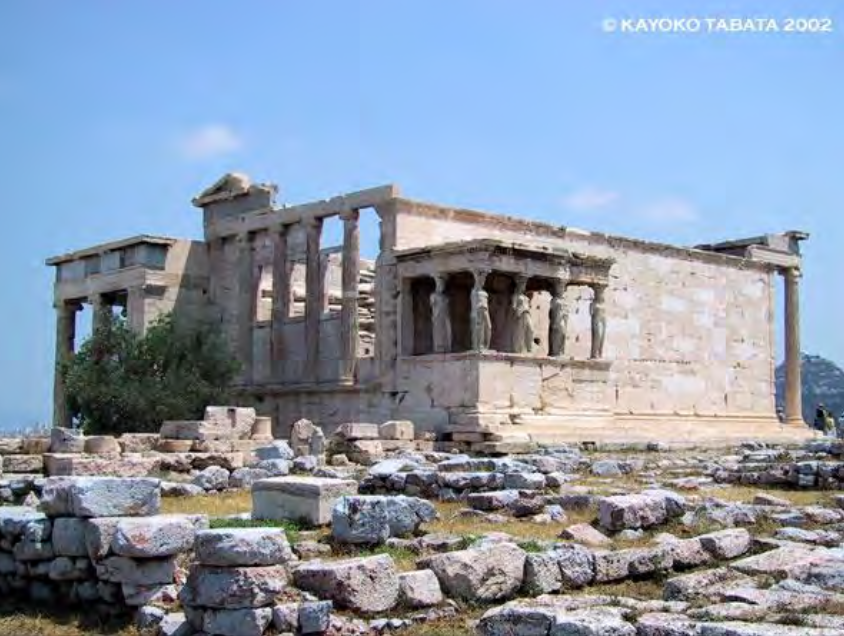
The Erechtheion (on Acropolis), Athens, Greece, 421-405 BCE , Classical Greece

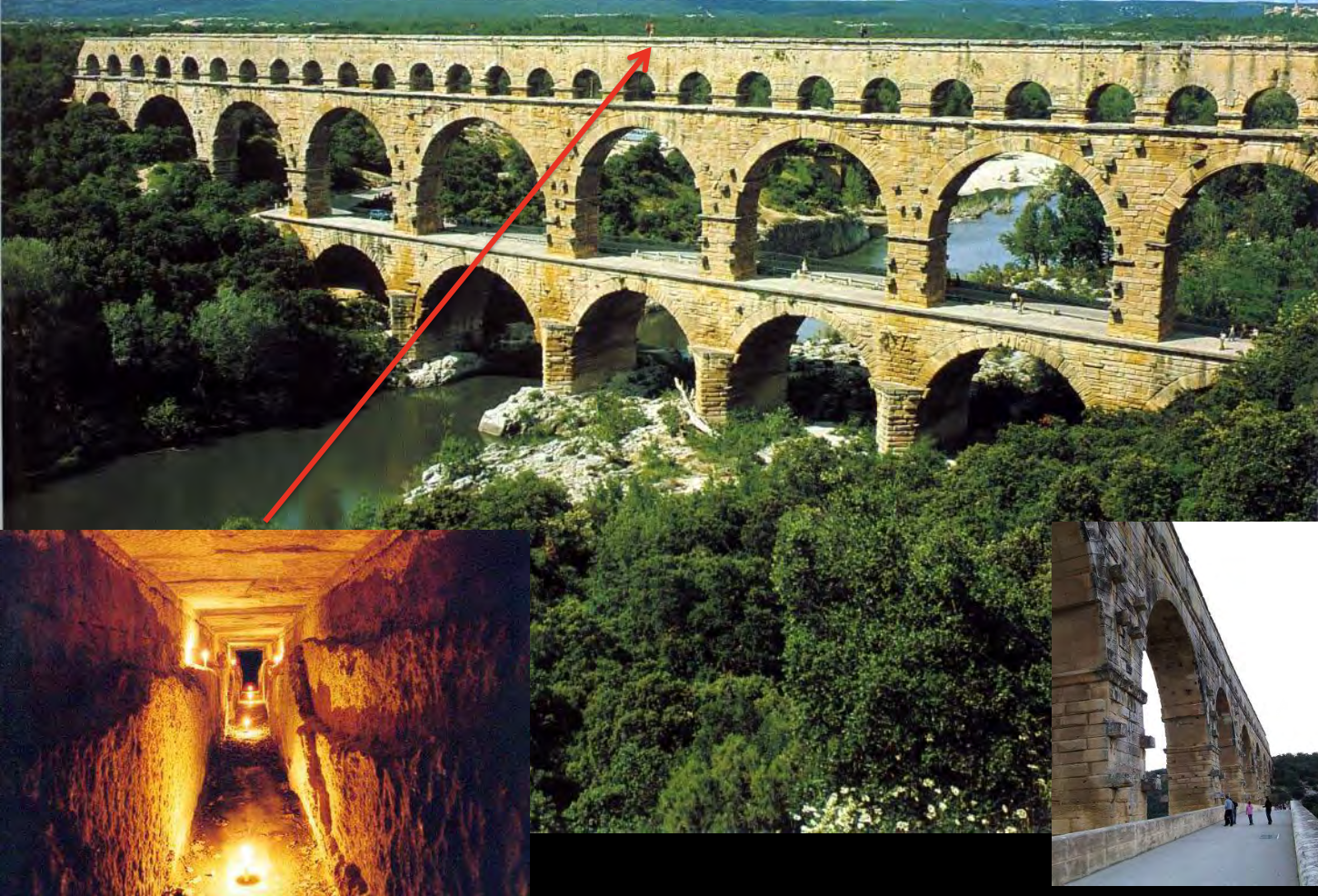
Pont du Gard (aqueduct), Nimes, France, c. 19 BCE, Roman

Roman Kit: 7 parts – forum, (civic) basilica, commemorative monument, temple/religious space, bath, market, entertainment venue.
building blocks used to house necessary institutions throughout the cities of the provinces.
This regularity also created Romanitas – a feeling and identity of “Romanness” spread to many Roman cities throughout the vast territory the empire controlled. This helped Rome govern a vast empire.

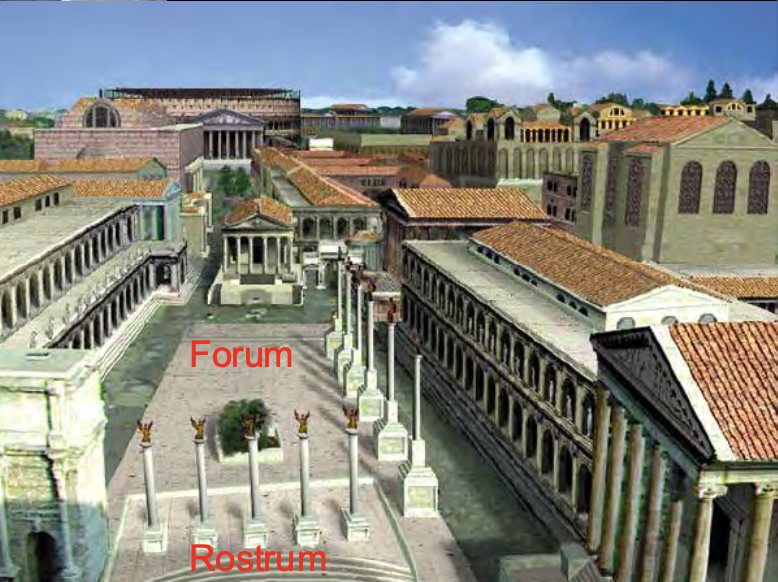
Roman Forum as today and a reconstruction as it would have appeared in Imperial Roman period
Forum Romanum and the first imperial fora (plural of forum): each emperor built his own, successive forum and the group of buildings around it: a basilica, a temple, a memorial statue, and usual markets

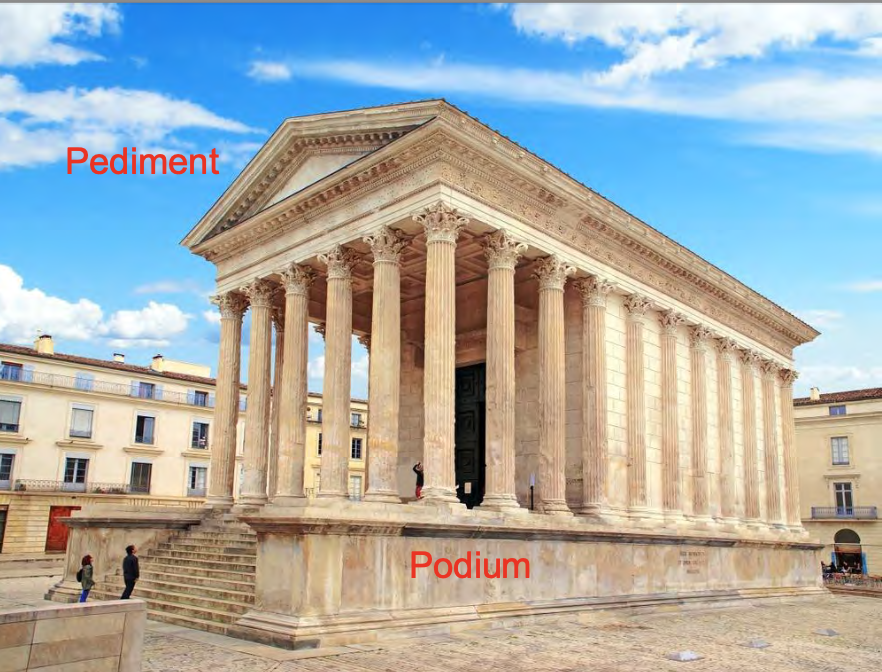
Forum of Trajan, Rome, Italy (in the), 98-117 CE, Patron: Emperor Trajan,
Architect: Apollodorus of Damascus, Imperial Roman
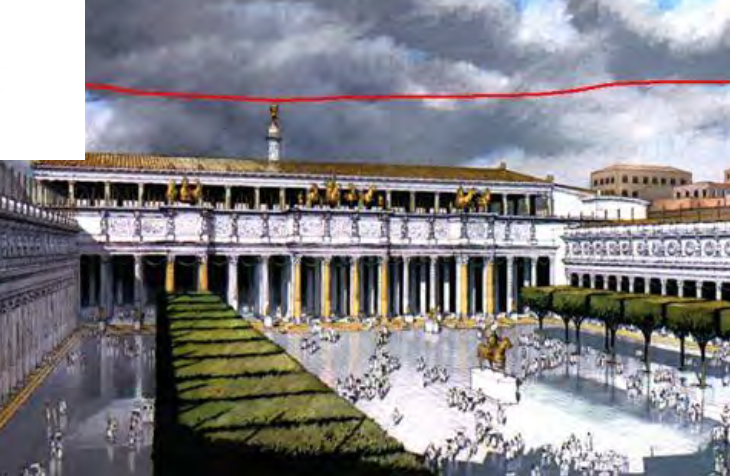
Basilica Ulpia, Rome, Italy (in the Forum of Trajan), 98-117 CE, Patron: Emperor Trajan, Imperial Roman

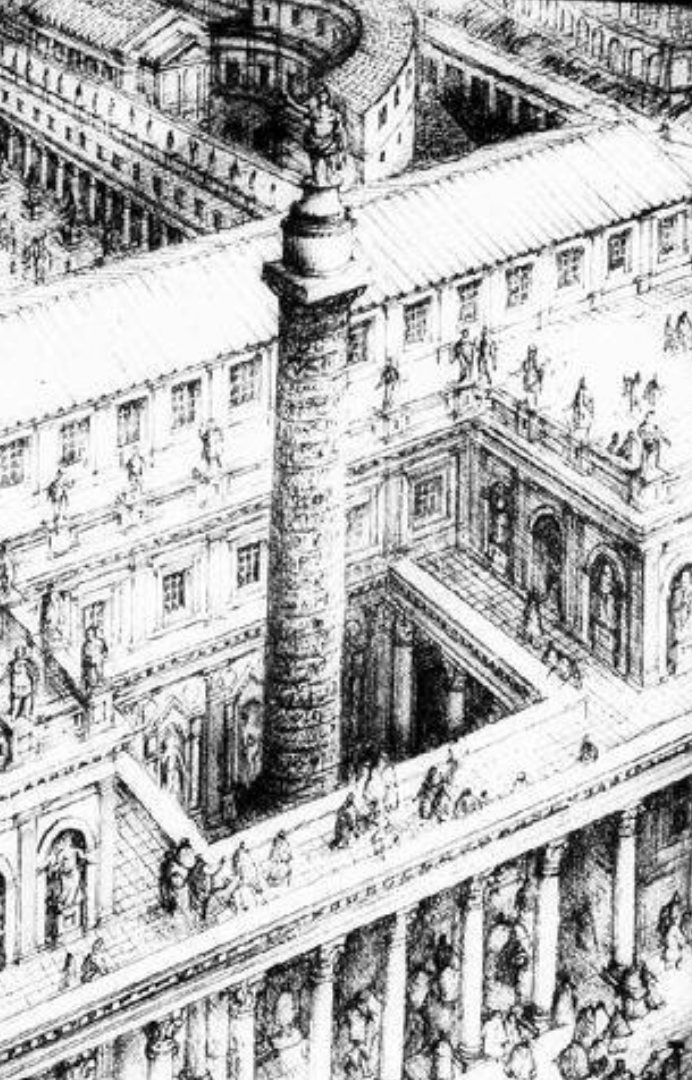
Column of Trajan, Rome, Italy, 113 CE, Patron: Emperor Trajan. Imperial Roman.
Maison Carré, Nîmes, France, c20 BCE, Imperial Roman

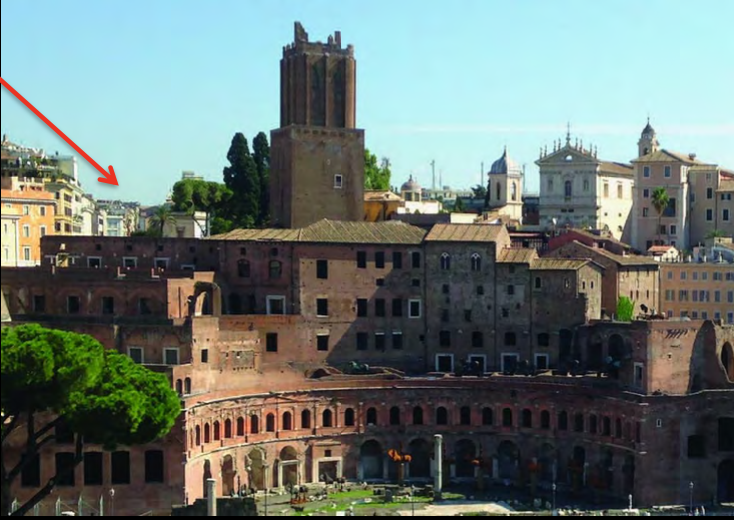
Markets of Trajan, Rome, Italy (in the Forum of Trajan), 98-117 CE, Imperial
Roman, Patron: Emperor Trajan

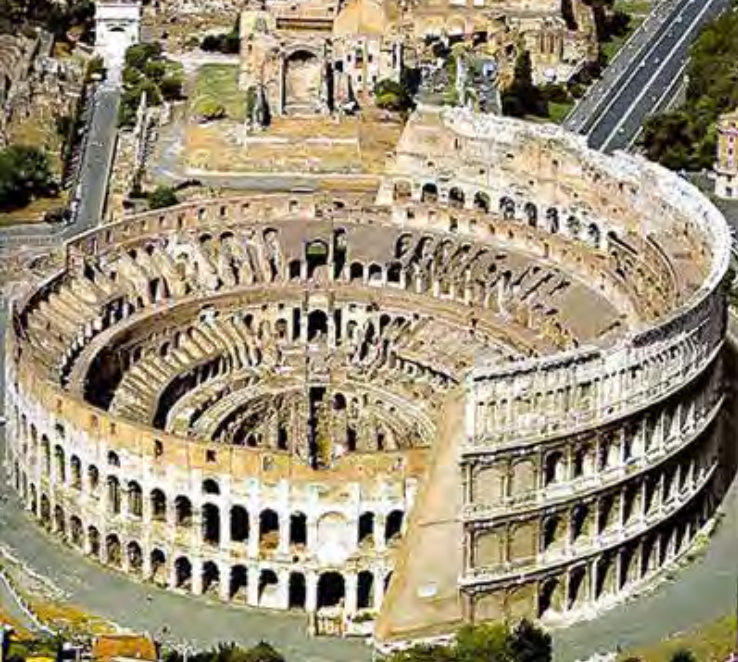
Colosseum (actually called the Flavian Ampitheater), Rome, Italy, c. 70-82 CE,
Patron: Emperor Vespasian, Imperial Roman

Baths of Caracalla, Rome, Italy, 212- 216 CE, patron: Emperor Caracalla, Imperial Roman
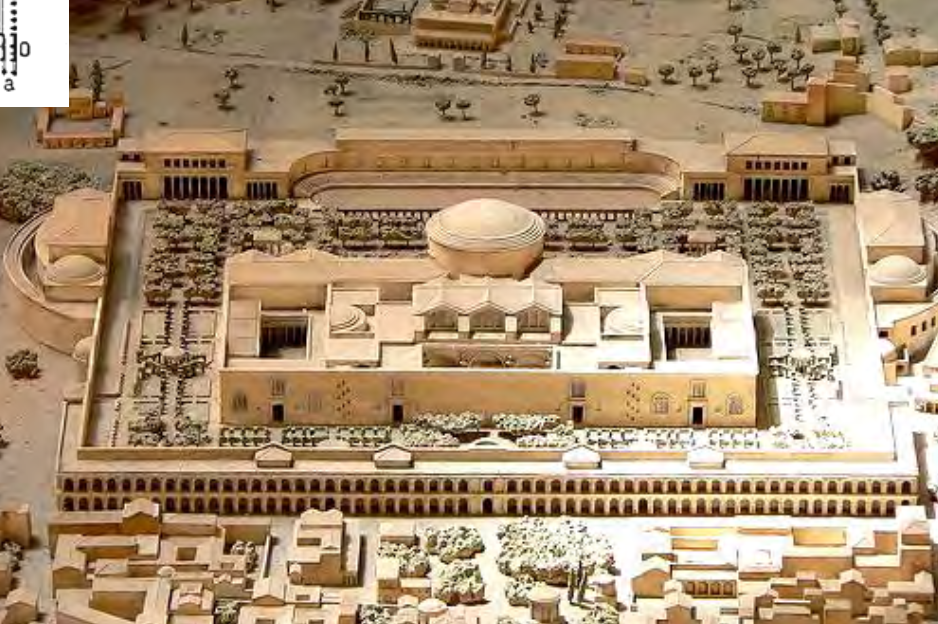

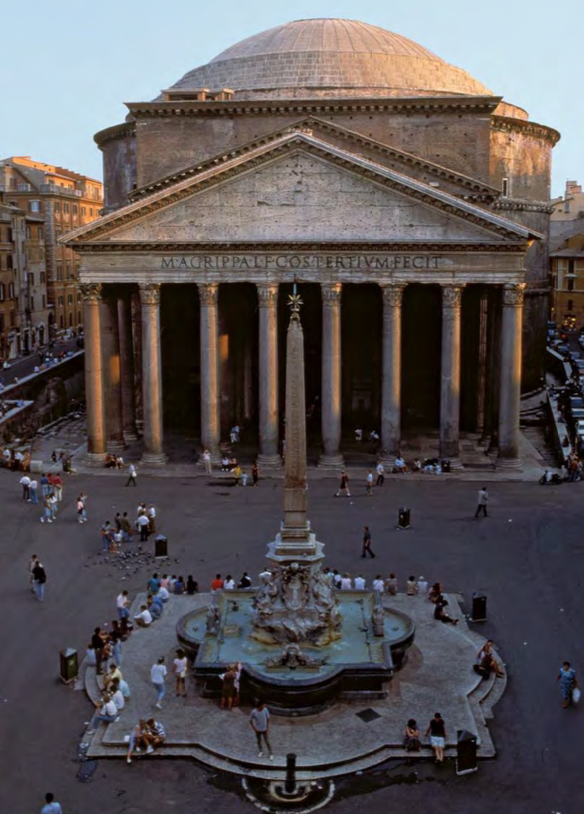
Pantheon, Rome, Italy, 114-128 CE, patrons: Emperors Trajan and Hadrian,
Imperial Roman.

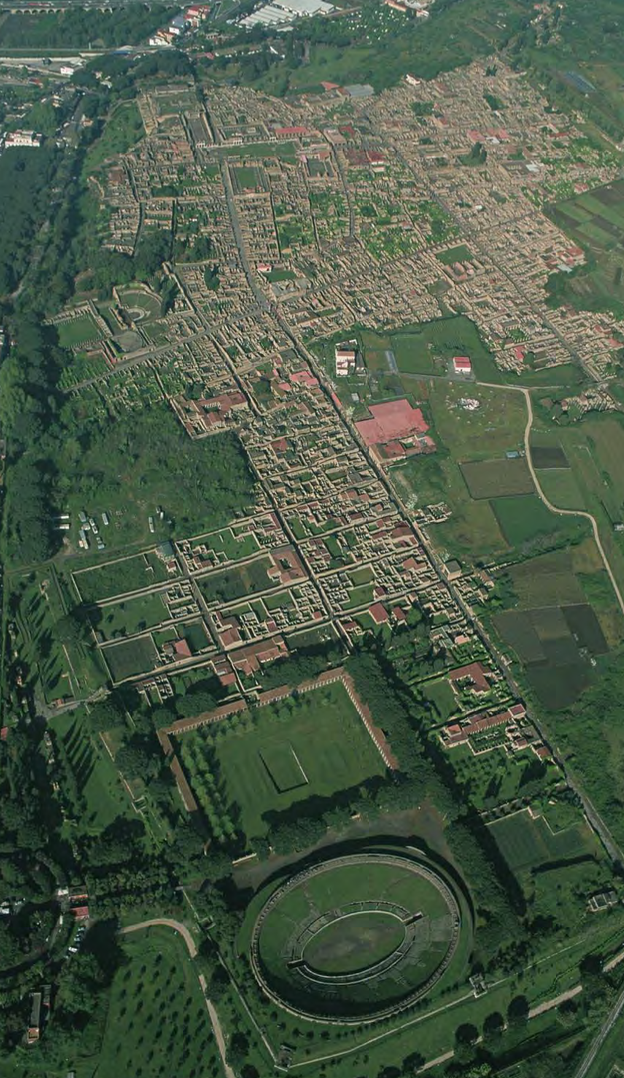
Pompeii, Italy, part of the empire from 80 BCE until its destruction by the eruption of the Vesuv

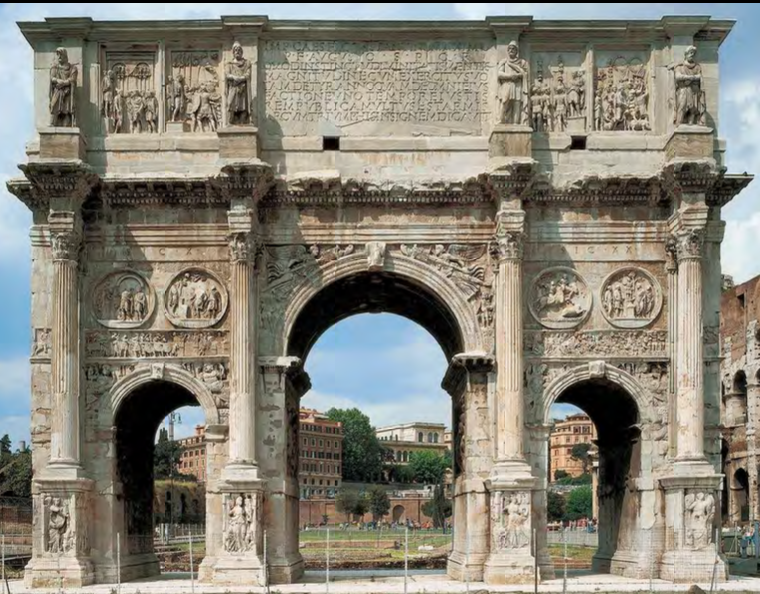
Arch of Constantine, Rome, Italy, 315 CE, Imperial Roman

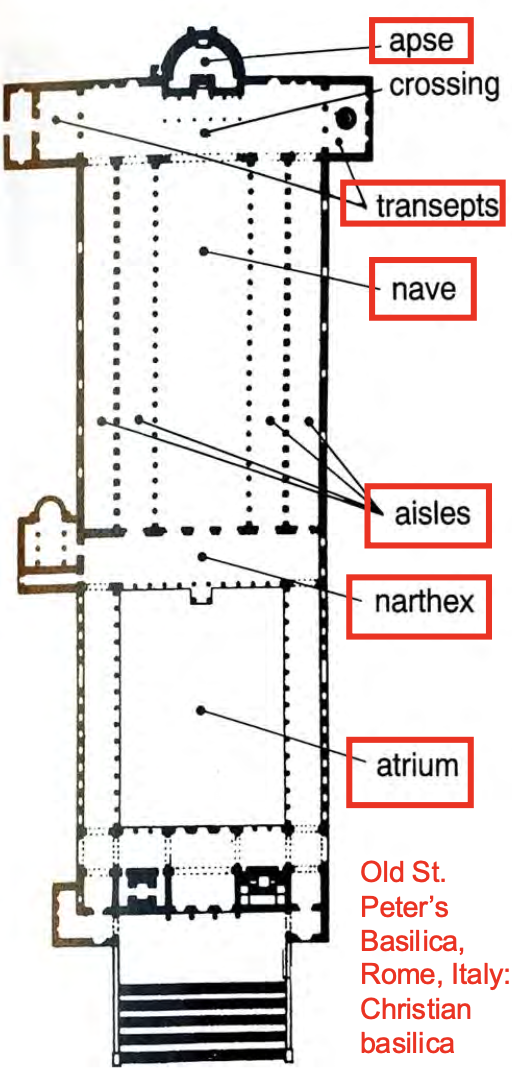
Old St. Peter’s Basilica
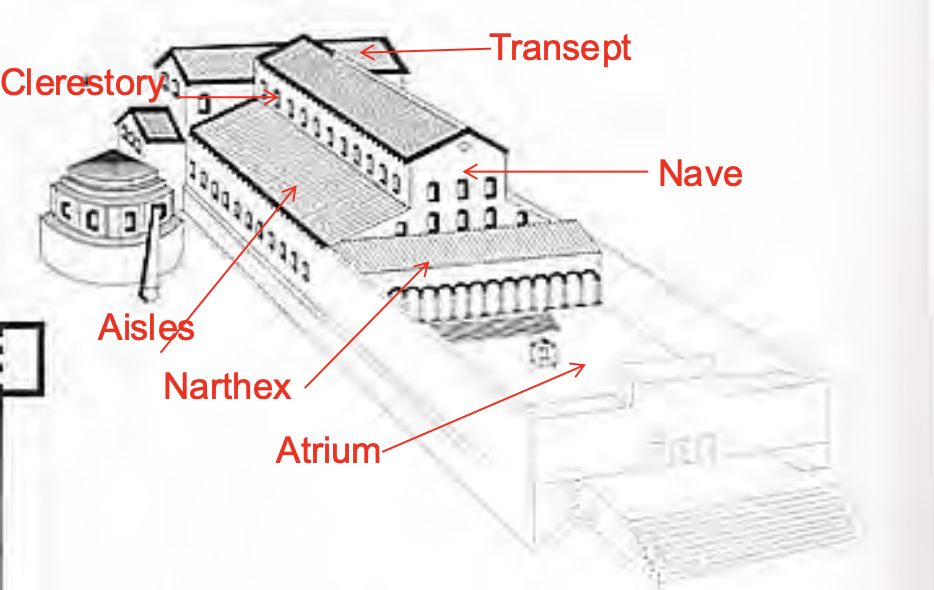
The Christian Basilica
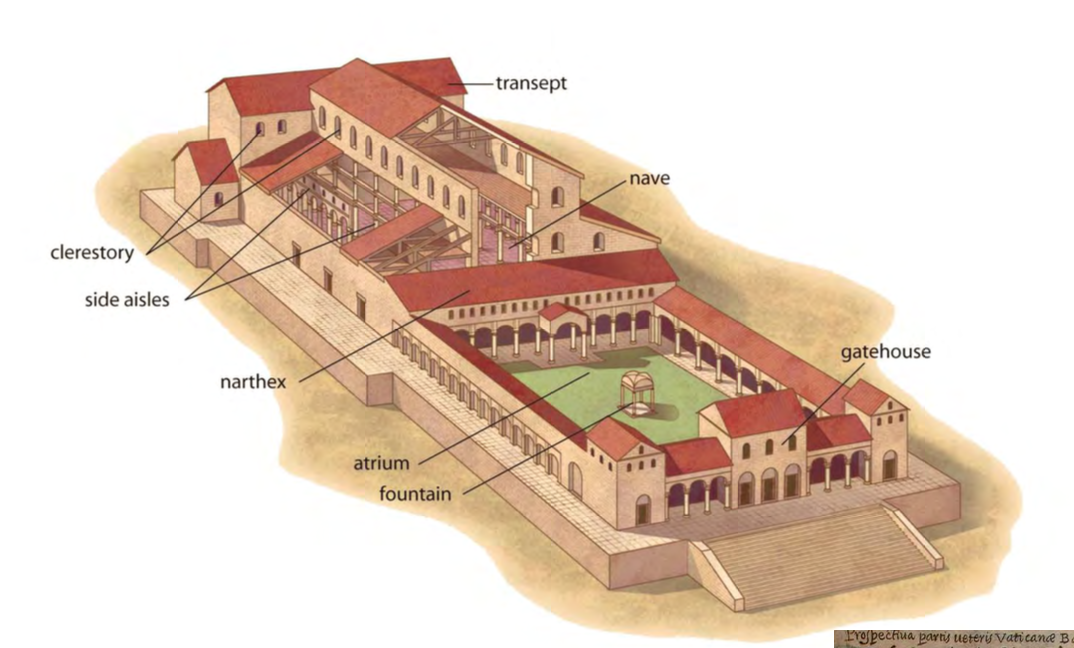
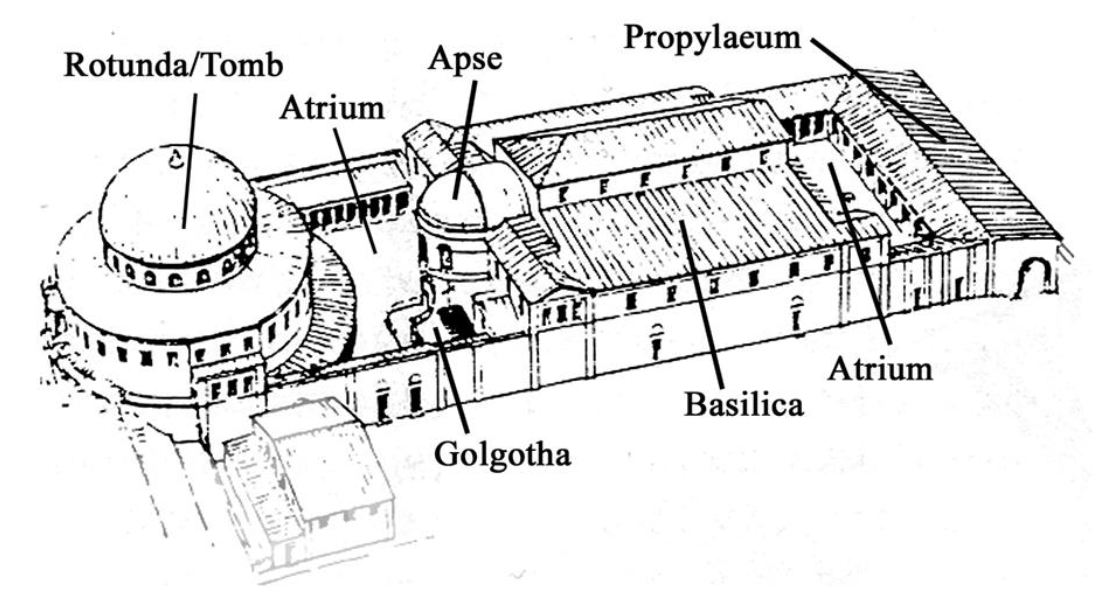
Church of the Holy Sepulcher, Jerusalem, Israel/Palestine, c320-26 CE, Late Antique
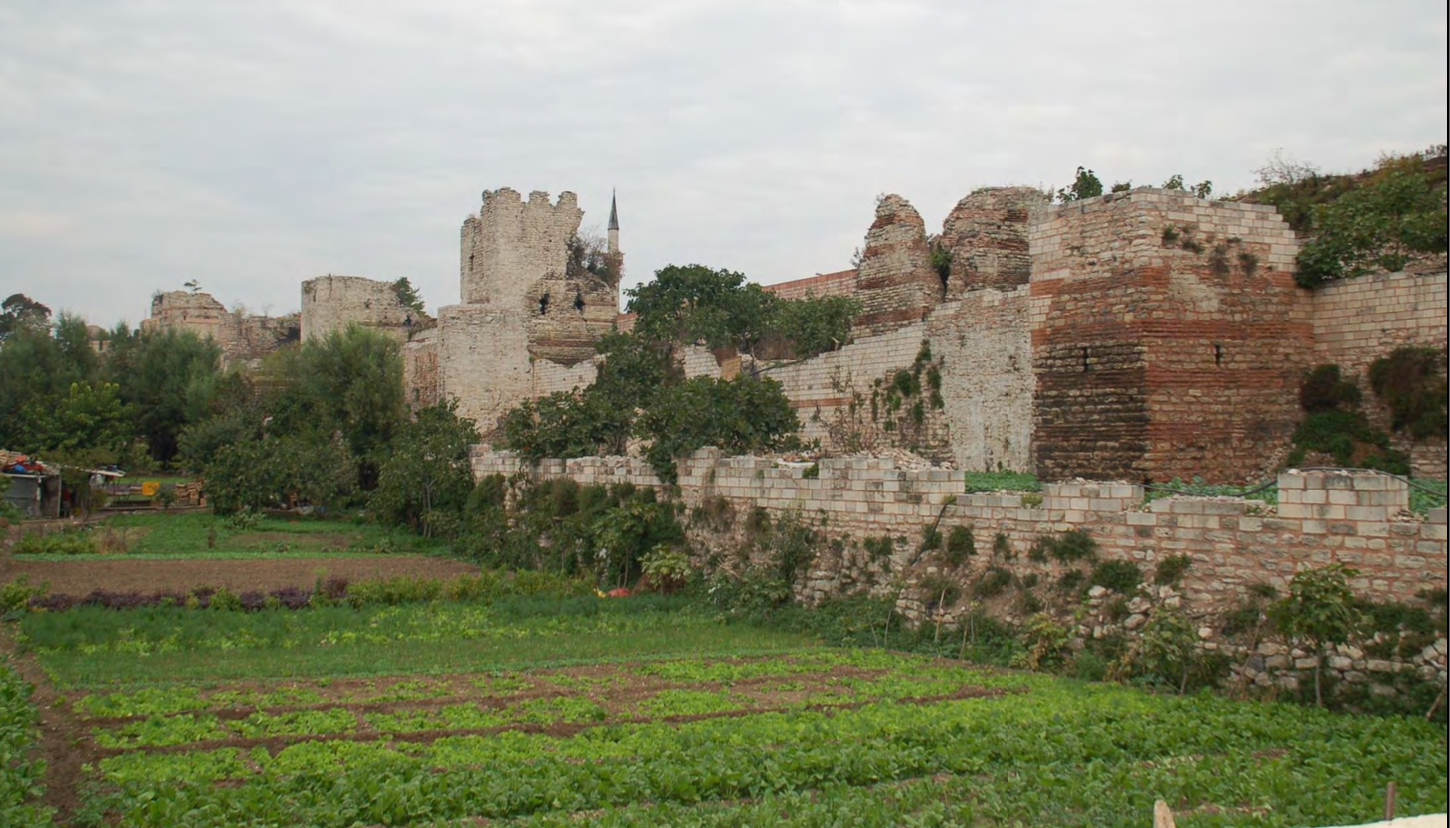
Land Walls of Theodosius II, Istanbul, Turkey, 412-415, Patron: Emperor, Theodosius II Early Byzantine

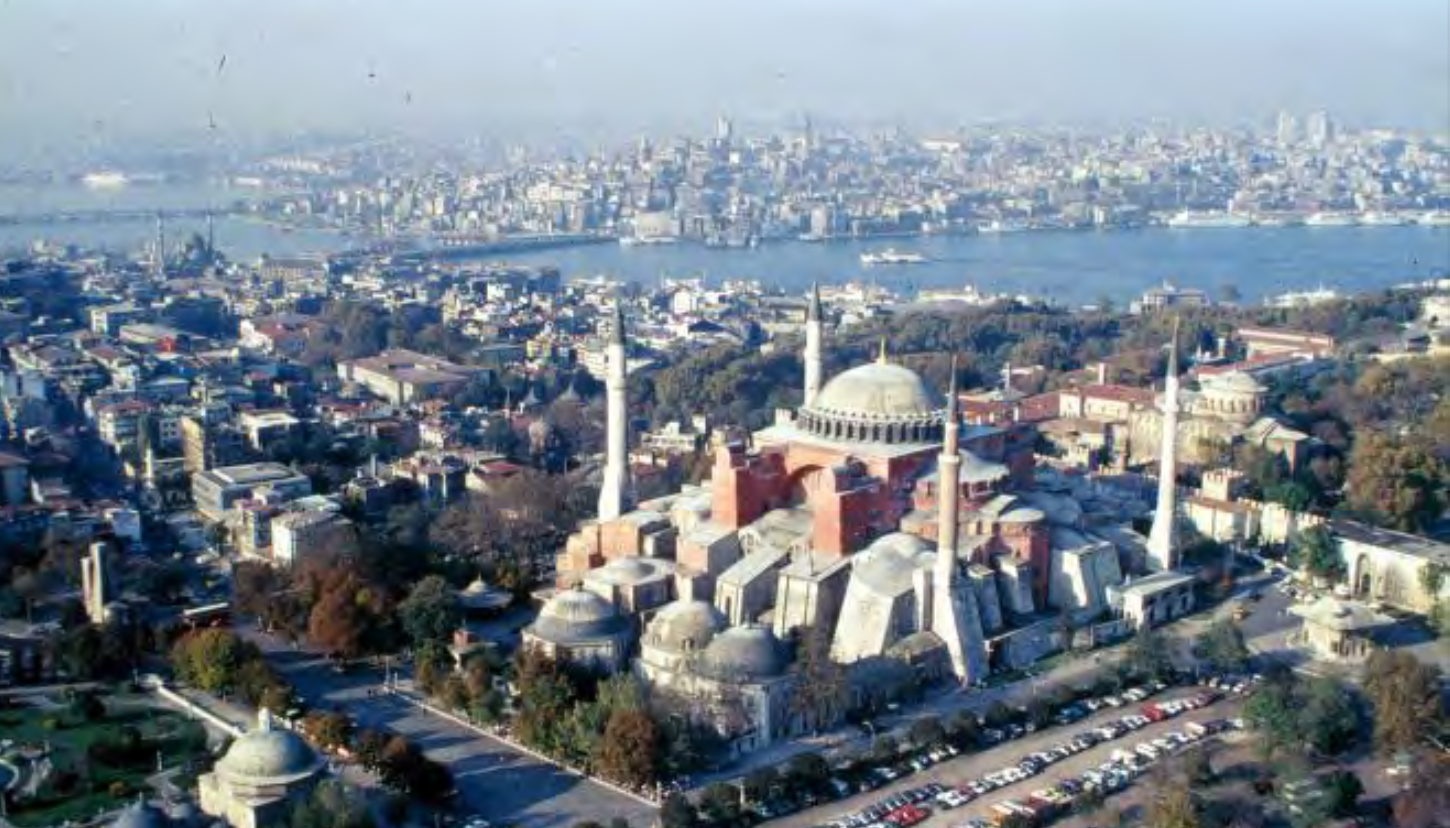
Hagia Sophia (“Holy Wisdom”), Istanbul, Turkey, 532-537, Patron: Emperor
Justinian, Architects: Anthemios of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus, Early Byzantine
Fuses two Roman building types – centralized and longitudinal – into a single,
distinct plan not seen before in other Roman nor Byzantine buildings

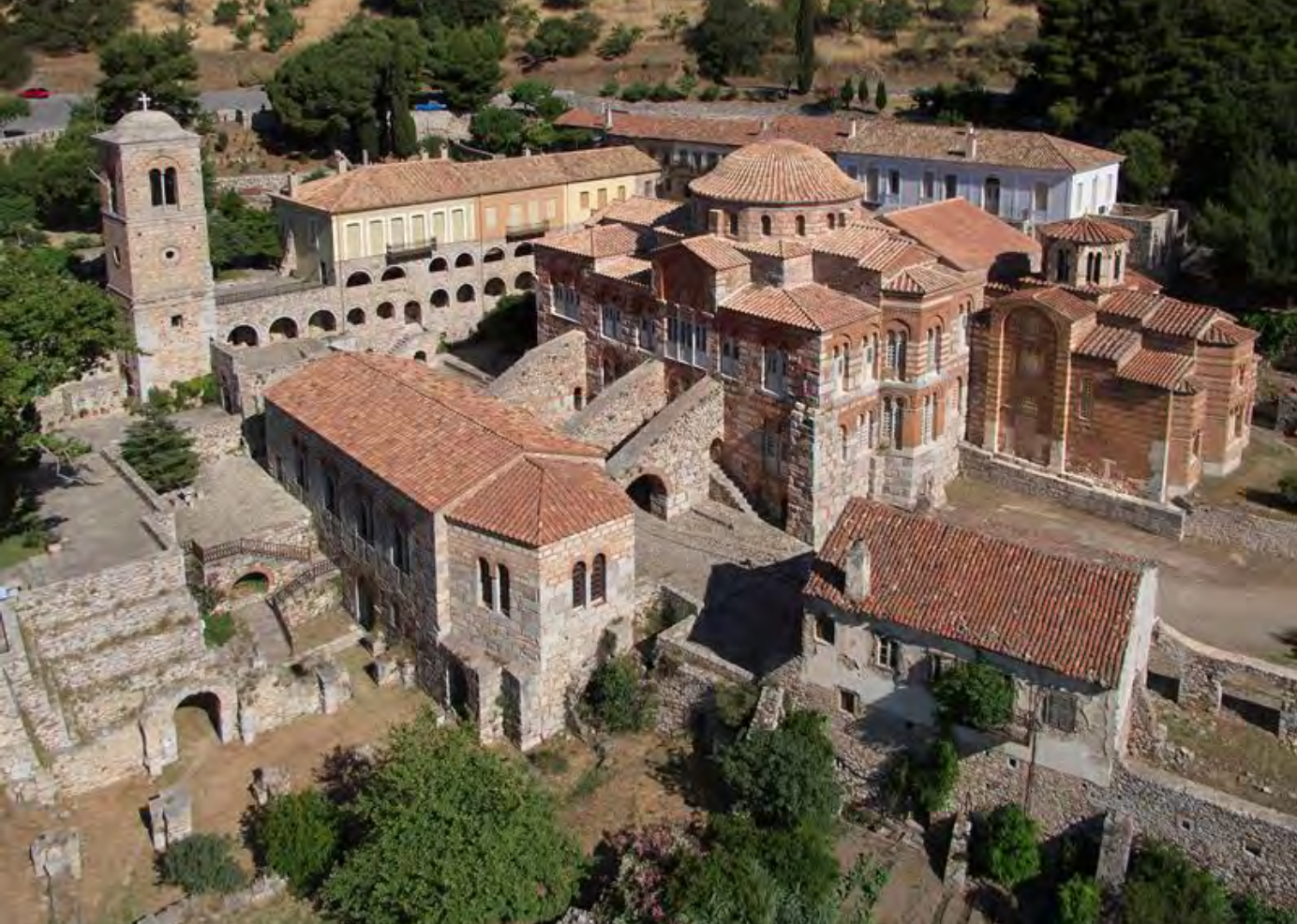
Hosios Loukas Monastery, Stiris, Greece, c 1020-1040, Middle Byzantine
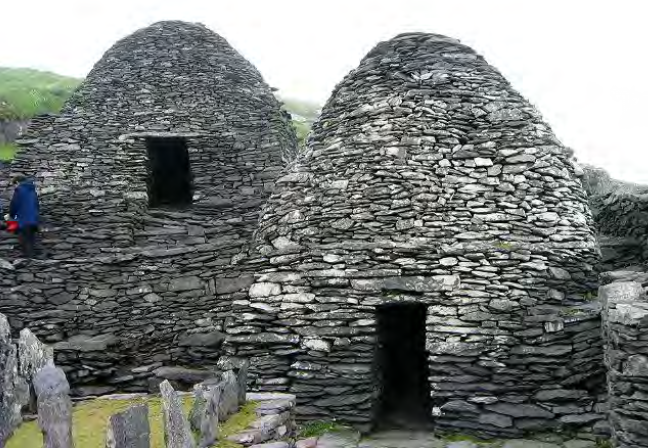


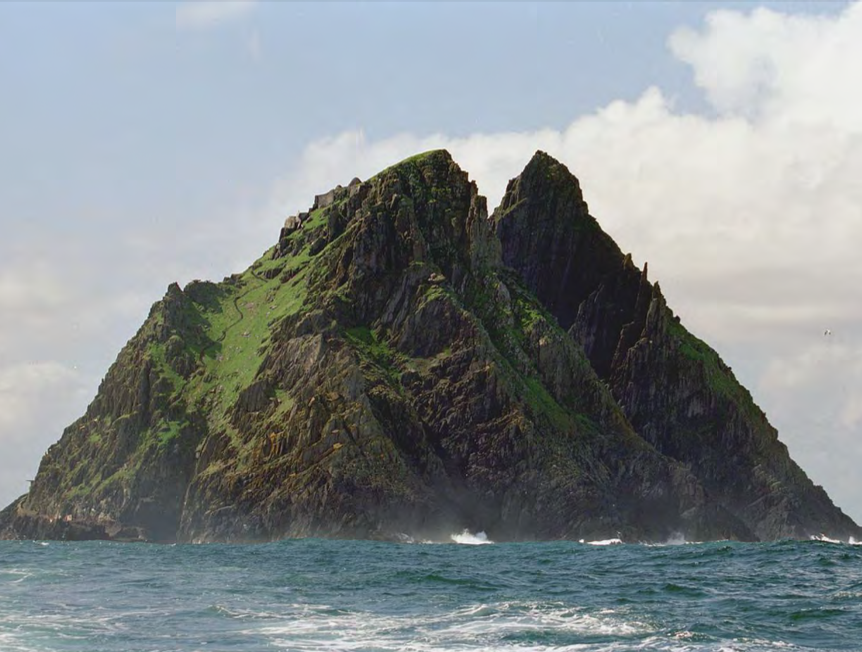
Skellig Michael, off western coast of Co. Kerry, Ireland, rebuilt c823 or 860, no patron known, Early western Medieval
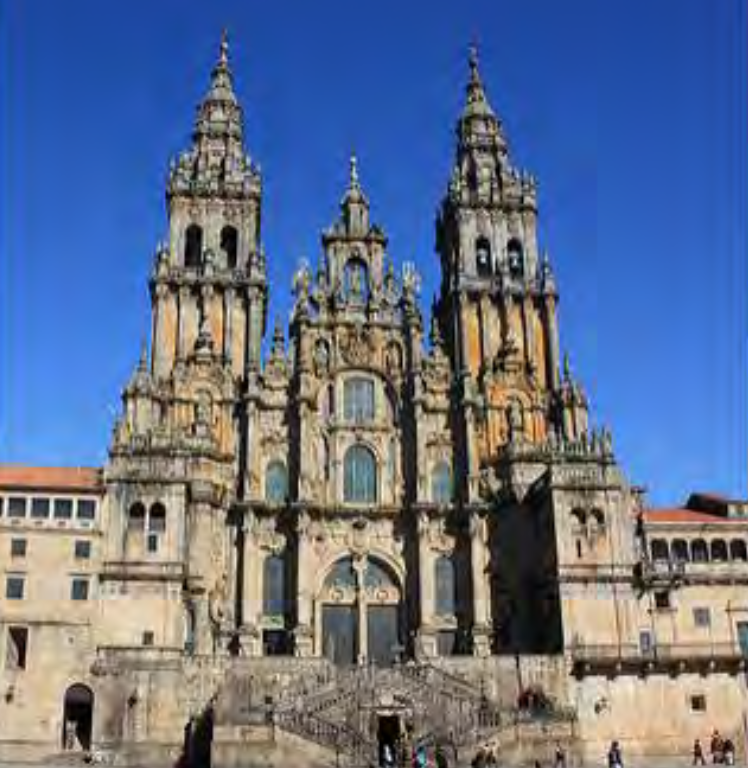


Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1075-1115, completed by Bishop Diego Gelmírez, Romanesque
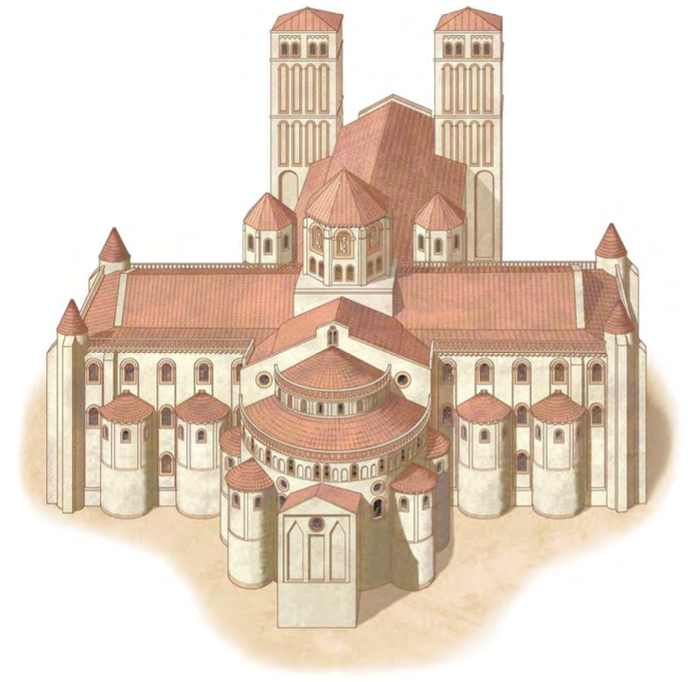

Monastery Sainte Foy, Conques, France, ca. 1050-1120, Romanesque
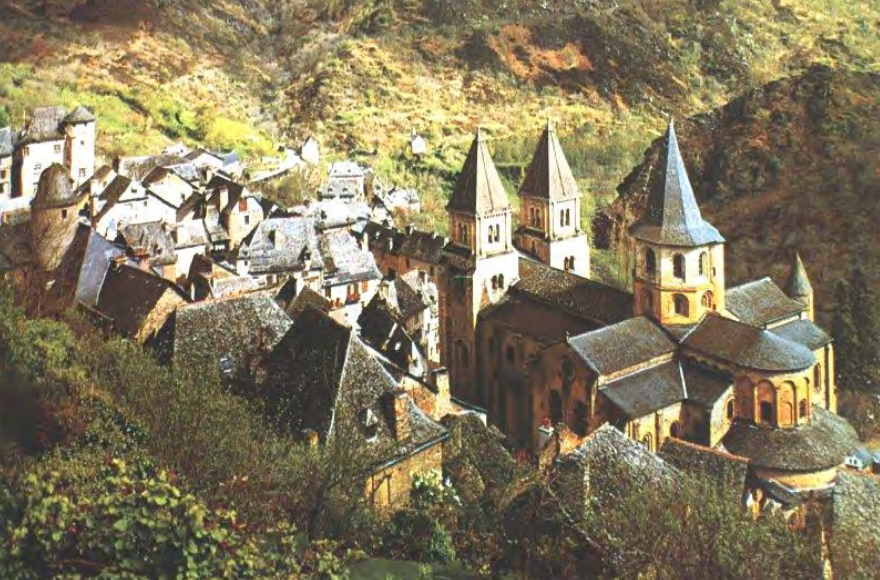

Romanesque portal
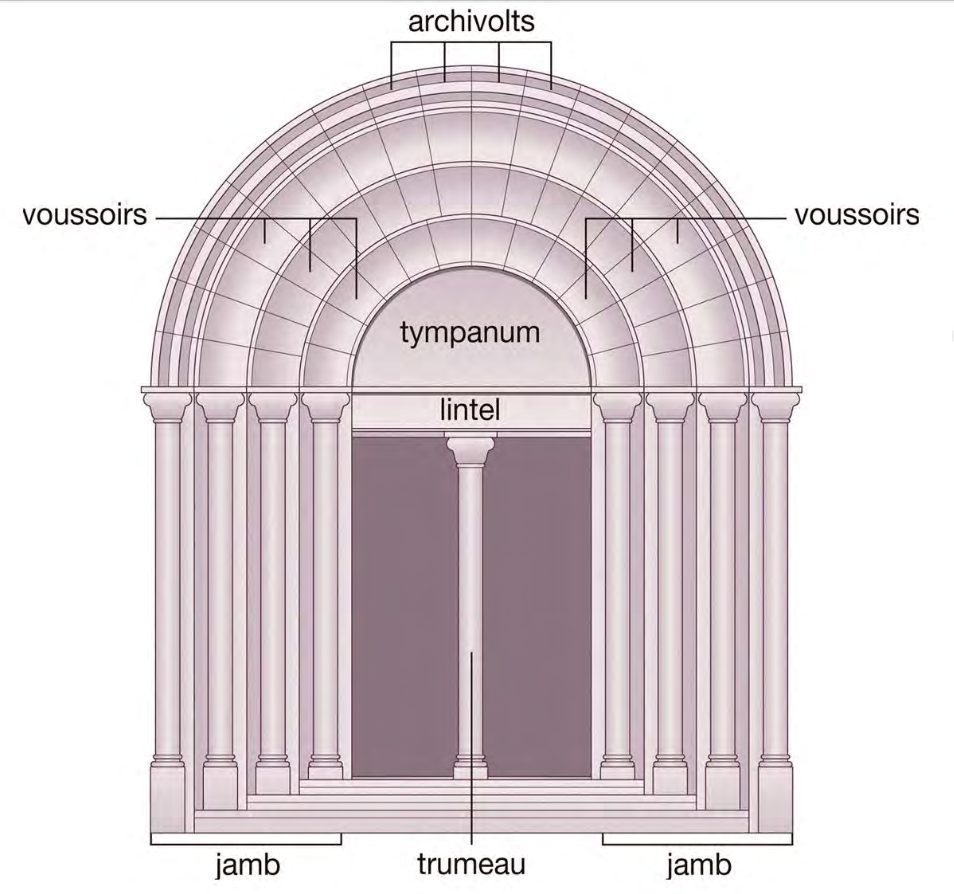
Conques Façade tympanum
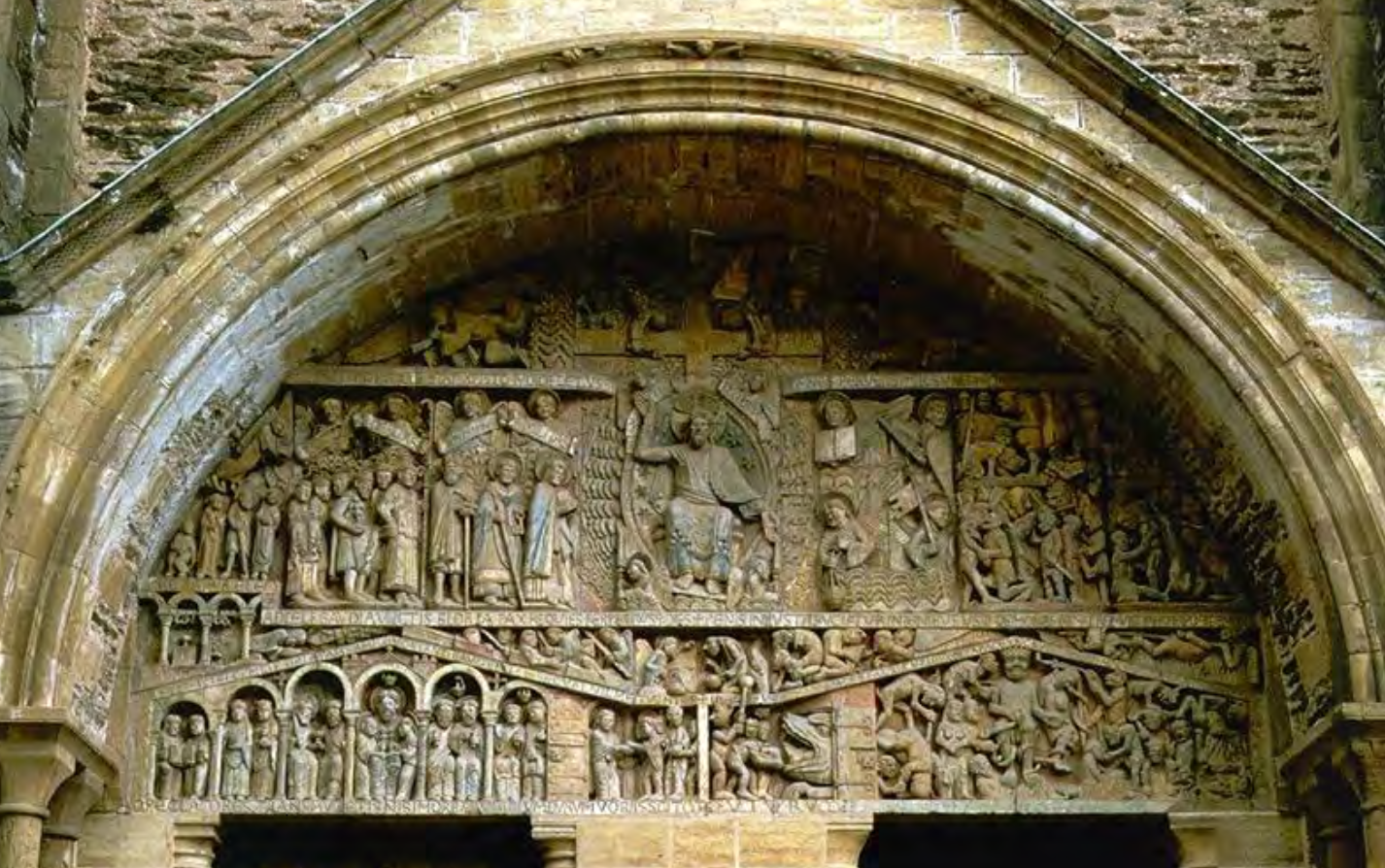

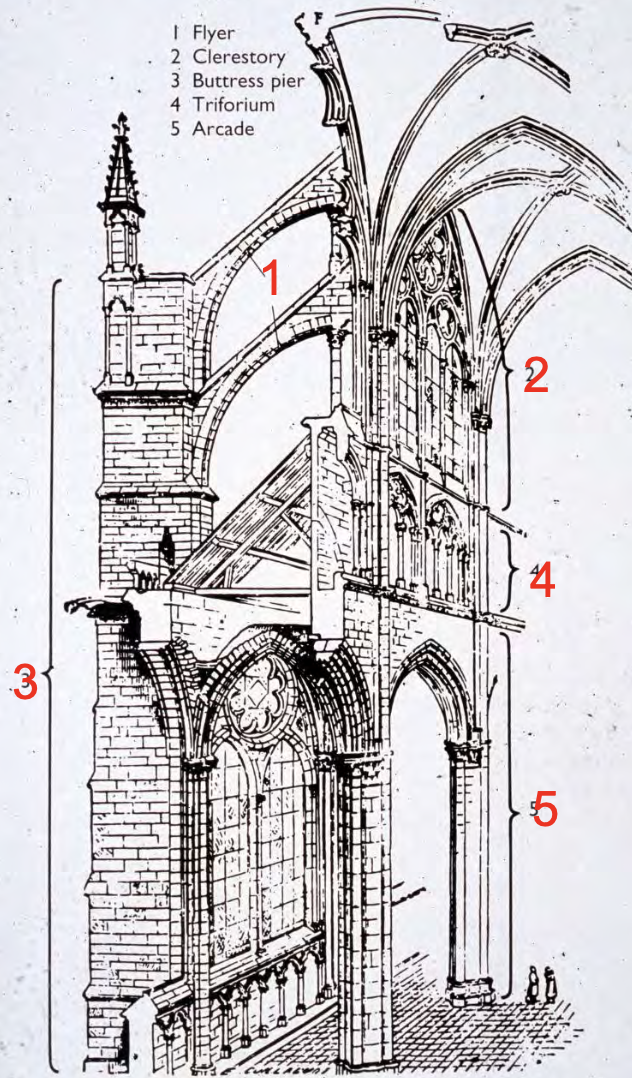
Diagram of Gothic Elevation
1. Flying buttress
2. Clerestory
3. Buttress pier
4. Triforium
5. Ground arcade
Development of Gothic Cathedral Design
1) Get taller over time
2) switch from earlier four-part elevation to a later three-part elevation (the gallery is excised); this streamlines the wall, emphasizes verticality
3) proportions become more equalized between the ground arcade and the upper-level clerestory

Abbey Church of Saint Denis, (near) Paris, France, 1140-44, Gothic

Cathedral of Notre Dame, Paris, France, begun 1163 (choir), nave after 1178, façade 1200-1250, clerestory remodeled in early thirteenth century. GOTHIC
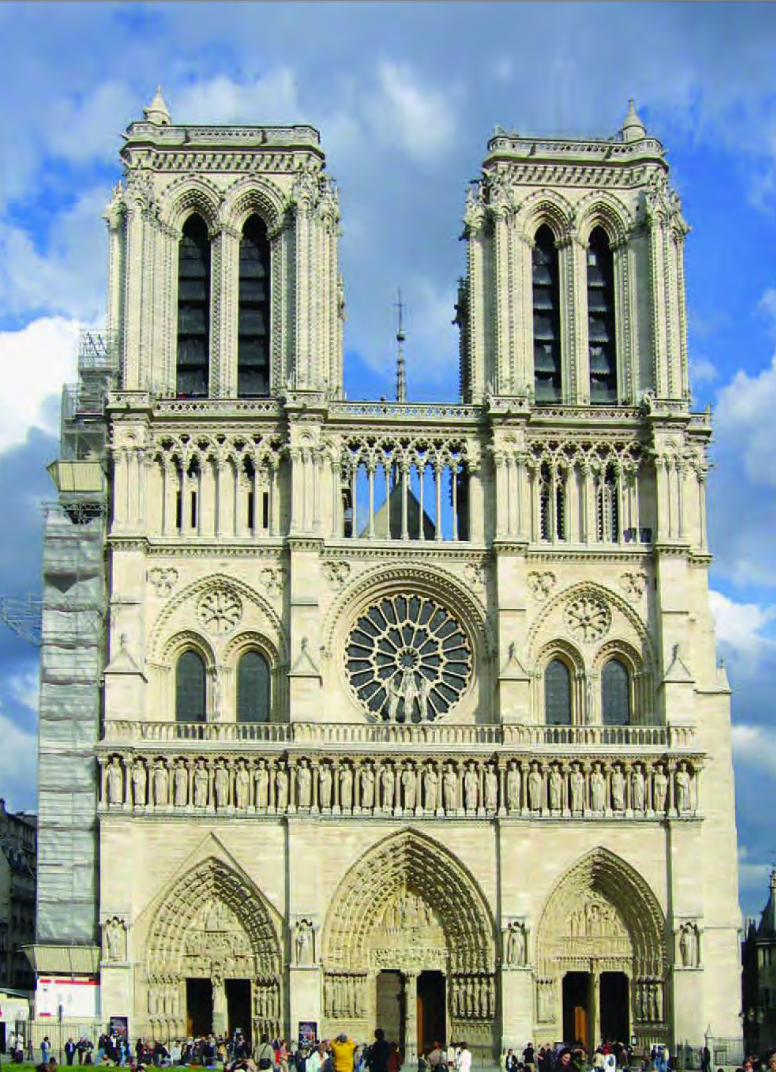

The Sainte-Chapelle, Paris, France, 1242-8, Late Gothic. Patron: King (Saint) Louis IX, as a private chapel for the court and repository for the precious relics of Christ

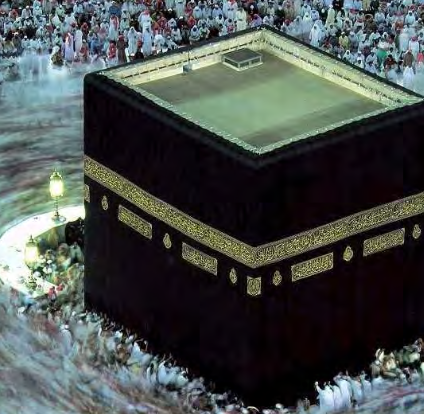
The Kaaba (‘cube’), Mecca, Saudia Arabia, pre-Islamic, rededicated c631-632 CE, Early Islamic

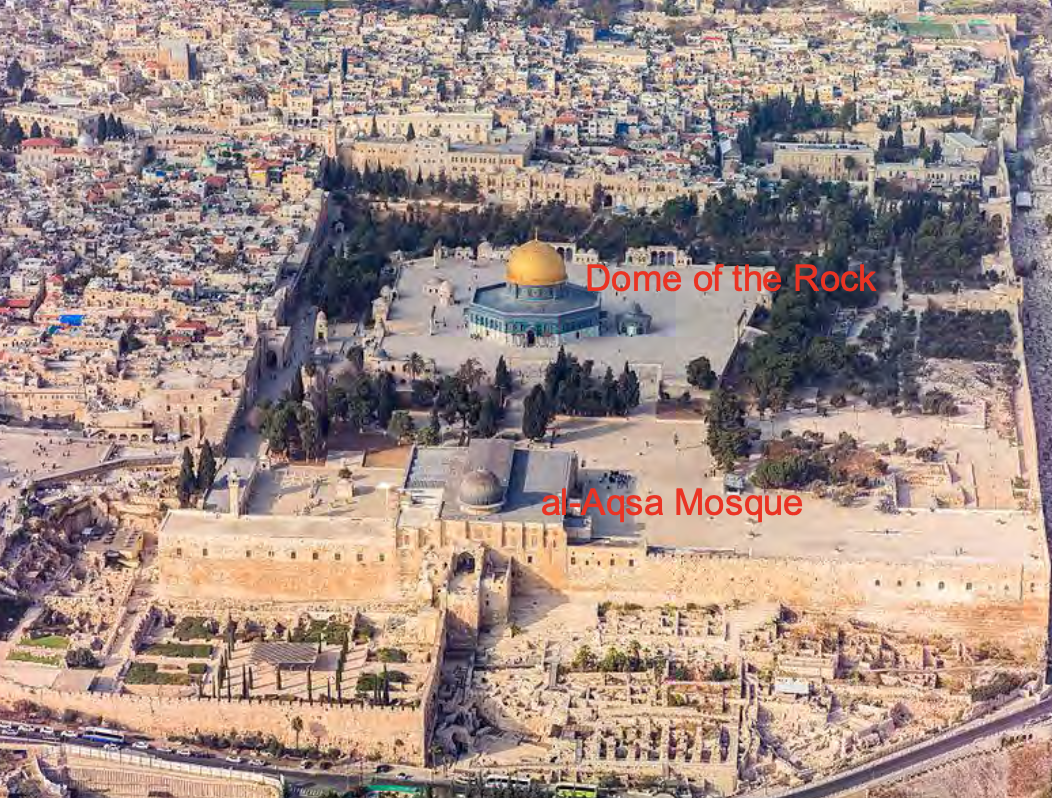
Dome of the Rock (Qubbat al- Sakhra), Jerusalem, Israel/Palestine, completed 691-2 CE. Patron: Caliph (ruler) Abd al-Malik of the Umayyad Dynasty. Early Islamic.
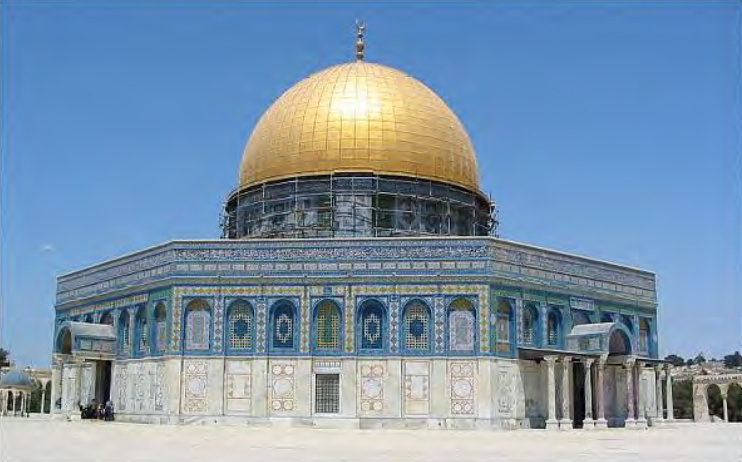

Dome of the Rock on the *Haram al-Sharif/Temple Mount: early allegiance of the
Umayyad rulers with the history of the early Jewish (Abrahamic) rulers of Jerusalem
(Temple Mount is the site of many events and construction by King David, King
Solomon, Prophet Abraham, etc.).
Dome of the Rock is BOTH a MARTYRIUM and a POLITICAL STATEMENT.
House/Mosque of the Prophet Muhammad, Medina, Saudi Arabia, c624 CE, early Islamic
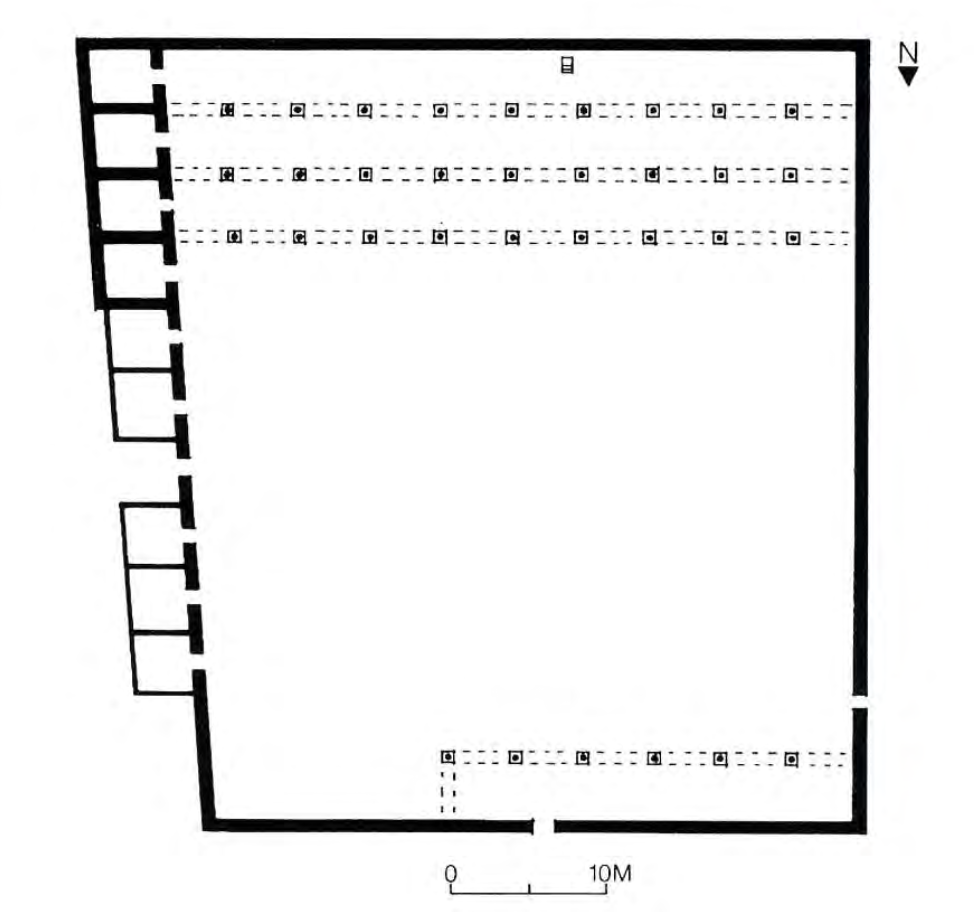

Congregational Mosques (Jami Masjid/Friday Mosque)
Qibla – the direction of Mecca; qibla wall – wall at the qibla side of the mosque
Mihrab – niche in the qibla wall, usually at its center; indicates direction of Mecca
Minaret – tower from which the muezzin’s call to prayer is made (also marker of
sacred space in the city, and of Muslim identity in the region)
Sahn – open-air courtyard, often a fountain is found here for ritual washing
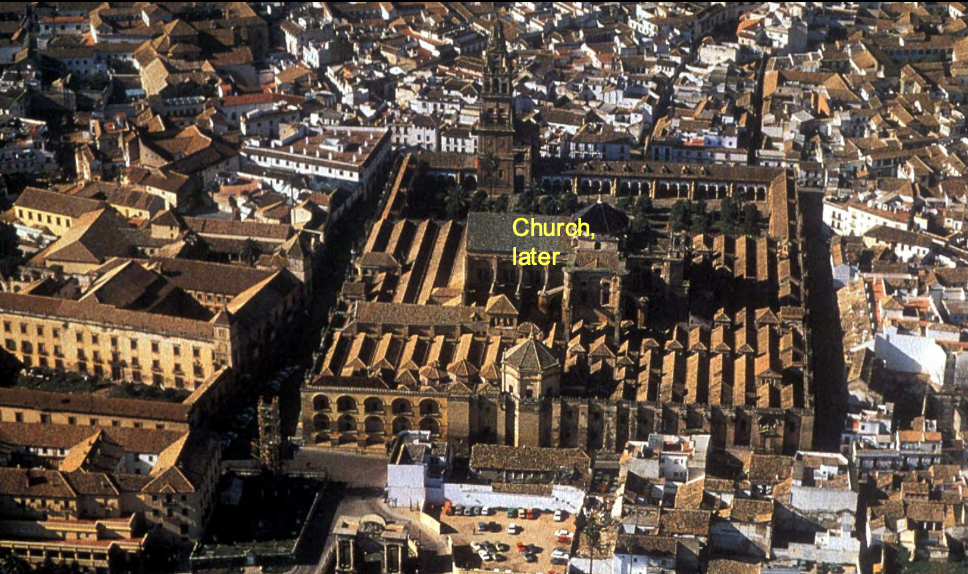
Great Mosque of Cordoba, Cordoba, Spain, 784-6, 9th and 10th centuries, Patron: Spanish Umayyad Caliph Abd al- Rahman, Early Islamic

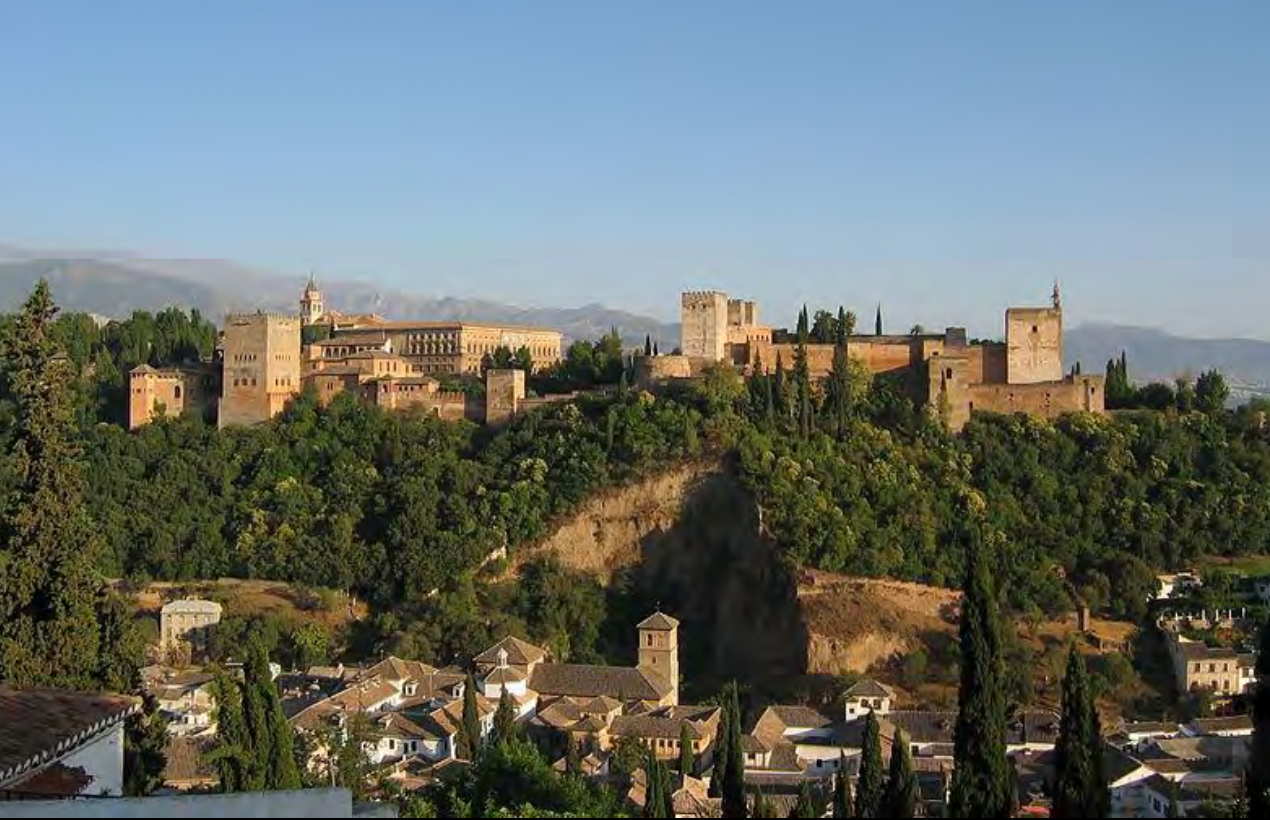
Alhambra (Qal’at al-Hamra/Red Fort), Granada, Spain, 1238-1390s, Patron: Nasrid Dynasty rulers including Muhammad I, Yusuf I, medieval Islamic architecture
