AICP Section 1.C/D - Research and Assessment
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Data and source interpretation and evaluation & Data collection strategies appropriate to identify planning issues
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Relevance
The extent to which the data and findings directly address research questions and objectives. Relevant data ensures that the analysis is applicable to the current planning issues and can inform effective decision-making
Validity
The degree to which a study accurately reflects or assesses the specific concept it is intended to measure. High validity indicates that the research findings are credible and accurately represent the real-world scenarios they aim to analyze
Related: Internal validity, external validity
Internal Validity
The extent to which a study can demonstrate a clear cause-and-effect relationship between variables, free from confounding factors. High internal validity indicates that the changes observed in the dependent variable can be attributed directly to the manipulation of the independent variable.
External Validity
The extent to which research findings can be generalized or applied to settings, populations, or time periods beyond the study sample. High external validity indicates that results are relevant beyond the specific context of the study.
Reliability
Consistency of a measure or method over time. Reliable data yields the same results under consistent conditions, ensuring that findings are dependable and can be replicated in similar studies
Related: Stability, repeatability, precision, trustworthiness, reproducibility, uniformity, accuracy, robustness
Data Quality
Assessed based on factors such as accuracy, completeness, reliability, and relevance. High-quality data is essential for producing valid and reliable research outcomes that can effectively guide planning decisions.
Related: Timeliness, precision, validity, integrity, usability
Implicit Bias
Unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that affect understanding, actions, and decisions. Recognizing and mitigating implicit bias that may exist in data sources is crucial to ensure objective, fair, and equitable research outcomes.
Related: Objectivity, fairness, equity, discrimination, awareness, inclusivity
Passive (Data Collection)
Gathering data without direct interaction or intrusion using data sources such as traffic cameras, social media, sensors, and public records to understand conditions and trends
Related: Existing data, automated collection, public records, archival research
Active (Data Collection)
Direct engagement with participants to gather data. Includes surveys, interview, focus groups, and participatory observation, where planners actively solicit information to address specific planning issues.
Related: Field research
Community Involvement
Engaging local residents and stakeholders in the planning process to ensure that their needs, preferences, and concerns are considered. Techniques include public meetings, workshops, participatory planning sessions, and community advisory boards.
Related: Stakeholder engagement, collaborative planning, resident feedback, civic engagement, Alinsky Organizations, Ladder of Citizen Participation (Arnstein)
Alinsky Organization
A type of community organization inspired by Saul Alinsky's principles, focusing on grassroots activism and empowering local citizens to advocate for social change and engage in the political process.
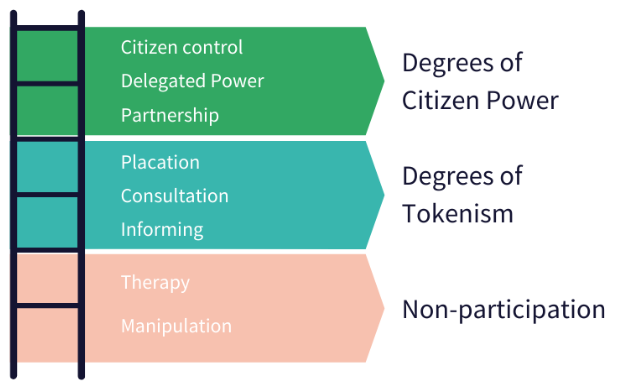
Ladder of Citizen Participation (Arnstein)
A framework developed by Sherry Arnstein to evaluate and depict the levels of citizen involvement in decision-making processes, ranging from non-participation to true citizen power.
Privacy and Confidentiality Concerns
Ethical and legal obligation to protect individuals’ personal information during data collection and analysis.
Methods such as anonymizing data, obtaining informed consent, and adhering to data protection regulations to ensure trust and compliance.
Related: Data protection, confidentiality agreements, ethical standards, legal compliance, personal information, data security, privacy policies, sensitive data, freedom of information, open meetings acts, sunshine laws