Science Test
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
1
New cards
Base
Bottom of the microscope, where to support with palm
2
New cards
Arm
Grip for microscope when carrying
3
New cards
Platform
Support specimen being observed
4
New cards
Diaphragm
Controls light that goes through specimen
5
New cards
Stage Clips
Holds down specimen
6
New cards
Mirror
Light source
7
New cards
Low power objective lens
4x magnification
8
New cards
Medium power objective lens
10x magnification
9
New cards
High power objective lens
40x magnification
10
New cards
Body tube
Creates magnified image using light from objective to pass upward
11
New cards
Ocular
Further magnifier by 10x
12
New cards
Coarse adjustment knob
Moves stage up and down
13
New cards
Fine adjustment knob
Minute focusing on specimen
14
New cards
Rotating nosepiece
Objective switcher
15
New cards
Why is the image in the microscope flipped?
This is because there are two lenses in the microscope.
16
New cards
When can you use the coarse adjustment knob?
Only on low power
17
New cards
What would be the magnification of low power after multiplying by the 10x from the ocular?
40x
18
New cards
What would be the magnification of medium power be after multiplying by the 10x from the ocular?
100x
19
New cards
What would be the magnification of high power be after multiplying by the 10x from the ocular?
400x
20
New cards
Which is smaller, the coarse or fine adjustment knob?
The fine knob
21
New cards
Why can the coarse adjustment knob only be used on low power?
It can crack the slide.
22
New cards
Why can direct sunlight not be used to observe a specimen?
It can damage the eyes.
23
New cards
What is the most familiar type of microscope?
The compound light microscope.
24
New cards
Nucleus
Structure which contains DNA and controls all cell functions
25
New cards
Nucleolus
Prominent structure in nucleus that makes ribosomes
26
New cards
Nuclear membrane
The part of the cell that envelops the nuclear material and controls what enters and leaves the nucleus
27
New cards
Cell membrane
Semi-permeable structure that separates one cell from the next and controls what enters and leaves the cell
28
New cards
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like substance that is the fluid portion of the cell that helps a cell keep its shape
29
New cards
Golgi body
Responsible for storage and secretion of cell products and modifies, sorts, and packages and then stores materials and proteins from the rough er
30
New cards
Ribosomes
The cellular site of protein synthesis that produces proteins and is in the cytoplasm
31
New cards
Centrioles
Plays a key role in cell division
32
New cards
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Structure that acts as a transport tube for cell proteins and directs them to where they are supposed to go; has ribosomes on the surface
33
New cards
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Creates lipids for the cell and breaks down toxins; does not have ribosomes on the surface
34
New cards
Lysosome
Source of digestive enzymes that break down food into small molecules
35
New cards
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration, where ATP energy for life activities is created; powerhouse of the cell
36
New cards
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll; The site of photosynthesis that captures sunlight for the plants to make into chemical energy(glucose)
37
New cards
Vesicle
Small sac for storage and transportation of materials through cell organelles that is made by the golgi apparatus
38
New cards
Vacuole
Large sac that gives the cell its shape and is filled with water, ions, and nutrients
39
New cards
Cell wall
Rigid layer(cellulose) that provides support and structure
40
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Organizes the cell and gives it formation and shape
41
New cards
Lipid Bilayer
Flexible double-layered sheet that makes up the cell membrane and forms a barrier between the cell and its surroundings
42
New cards
Which organelles are found only in plant cells?
Central Vacuole, chloroplast, and cell wall
43
New cards
Which organelles are not found in plant cells?
Centrioles and lysosomes
44
New cards
What is Trichology?
The scientific study of the structure, function, and diseases of human hair.
45
New cards
What is a wet mount?
Adding a drop of water to the specimen and holding the cover slip at a 45 degree angle before placing it on top the specimen
46
New cards
What are the 3 layers of a hair shaft?
Cuticle(the outer layer), the cortex, and the medulla
47
New cards
What is the cuticle?
The outer layer of the hair shaft that consists of overlapping scales that are directed toward the tip of the shaft.
48
New cards
What is the cortex?
The inside of the hair shaft that is made up of compact, elongated cells and often contains pigment granules.
49
New cards
What is the medulla?
The central core of the hair shaft that is composed mostly of air spaces. It can be either absent, continuous, or fragmented.
50
New cards
What does a cell membrane have the same consistency of at normal temp?
Olive oil
51
New cards
What is found on the surface of some proteins(glycogen)?
Carbohydrates which are important for cell-to-cell recognition
52
New cards
What is cholesterol to the cell membrane?
An integral component of the cell membrane which has a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head which helps maintain integrity of the membrane which decreases fluidity, immobilizing outer surface. Helps secure important proteins to the membrane.
53
New cards
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Triphosphate
54
New cards
What happens when the bond between the last two phosphates is broken(hydrolyzed)?
A large burst of stored energy is released.
55
New cards
What is the uncharged form of ATP?
ADP
56
New cards
Where is all the energy stored?
In the last two phosphates
57
New cards
Where is movement during active transport?
Against the concentration gradient. This is when substances move from a low to high concentration
58
New cards
What are channel pumps?
Certain channel proteins in the cell membrane push molecules against their concentration gradient to maintain unequal levels using ATP. They work into or out of the cell.
59
New cards
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
Located on the cell membrane of all animal cells, responsible for 1/5 of total ATP, pumps sodium(Na) of out cells and potassium(K) into cells
60
New cards
Membrane potential
An electrical charge that exists across the cell membrane
61
New cards
Uniport
Moves ions/molecules in one direction
62
New cards
Antiport
Moves ions/molecules in opposite directions(against each other)
63
New cards
Symport
Moves two different ions in the same direction
64
New cards
What do vesicles have?
A phospholipid bilayer.
65
New cards
Endocytosis
The movement of substances into a cell by means of a vesicle.
66
New cards
What is pinocytosis(cell drinking)?
The process of taking up liquid from the surrounding environment(extracellular fluid). Tiny pockets form along the membrane, fill with liquid, and pinch off.
67
New cards
What is phagocytosis(cell eating)?
Extensions off cell membrane surround a particle and package it within a vesicle and then the cell engulfs it.
68
New cards
What is macrophages?
White blood cells
69
New cards
Exocytosis
The movement of substances out of a cell by means of vesicle which is done by the golgi apparatus to export proteins.
70
New cards
What are the methods of active transport?
Channel pumps and vesicles
71
New cards
What are the three rules of cell theory?
1: All living things are made up of cells.
2: Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living things.
3: All cells come from pre-existing living cells.
2: Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living things.
3: All cells come from pre-existing living cells.
72
New cards
Prokaryotic
Simple in structure; no membrane bound organelles; unicellular; cell wall for protection and support which allows bacteria to live in varied environments
73
New cards
Eukaryotic
Complex in structure; membrane bound organelles;
74
New cards
Bacteria
Microscopic living organisms; among oldest living organisms; some are harmful some are good
75
New cards
What can prevent bacteria spread?
(Usually) antibiotics, antiseptics, disinfectants, and sterilization
76
New cards
Antibiotics
Selective poisons that seek to kill specific bacteria but they cannot kill viruses
77
New cards
Probiotics
“Good bacteria” that offer some type of health benefit to the host
78
New cards
How are bacteria antibiotic resistant?
They reproduce very quickly and therefore evolve quickly along with mutations, people not taking antibiotics for as long as they’re prescribed, and overuse of antibiotics.
79
New cards
Bacteria ways of movement:
Cilia and Flagella
80
New cards
Bacteria ways of obtaining energy
Photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, decomposers
81
New cards
Name three types of main bacteria:
Coccus, bacillus, and spirullus
82
New cards
Archaebacteria/extremophiles
Oldest known organisms; beginning of life on earth?- chemosynthesis; live in extreme environments
83
New cards
Eubacteria
Current form of bacteria; live all around us; constantly evolving
84
New cards
Name the extreme environments archaebacteria have been found in: ____philes
Thermophiles- Heat addict
Halophiles- Salt addict
Alkaliphiles- Base addict(pH 9+)
Acidophiles- Acid addict(pH 3-)
Psychrophiles(cryophiles)- Cold addict
Halophiles- Salt addict
Alkaliphiles- Base addict(pH 9+)
Acidophiles- Acid addict(pH 3-)
Psychrophiles(cryophiles)- Cold addict
85
New cards
Cellular transport
Movement of materials across the semi-permeable cell membrane to maintain homeostasis.
86
New cards
Hypertonic
More water in the cell than in the solution ex: cell-90% solution- 85% water
87
New cards
Hypotonic
More water in solution than in cell ex: cell-85% solution- 90% water
88
New cards
What are the two kingdoms or bacteria?
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
89
New cards
Difference between homeostasis in unicellular and multicellular organisms
Unicellular organisms have one cell that performs homeostasis and performs all tasks while multicellular organisms have cells with specialized tasks that communicate to maintain homeostasis
90
New cards
What is cystic fibrosis?
When the cells that control mucus and sweat are disordered and then in turn leads to mucus build up that damages airways and the lungs.
91
New cards

Label a microscope
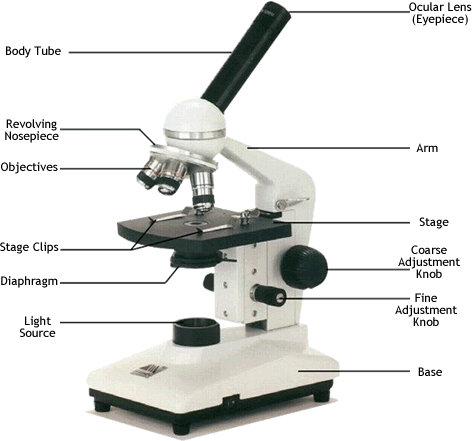
92
New cards
Passive Transport
Movement across the cell membrane that does not require any energy to occur; occurs due to concentration gradient; high concentration to low concentration
93
New cards
What are the three types of passive transport?
Diffusion, osmosis, and ion channels
94
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of a substance down the substance’s concentration gradient from high to low concentration; dissolved particles that are small and nonpolar can diffuse directly through cell membrane(Co2 and Oxygen)
95
New cards
Concentration gradient
A difference in the distribution of substances across a space
96
New cards
Equilibrium
A condition in which the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a space
97
New cards
Solute
Substance being dissolved
98
New cards
Solvent
Dissolver
99
New cards
Osmosis
Movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane through aquaporins
100
New cards
What happens when water moves out of the cell? What about in?
Out: Cell shrinks(hypertonic)
In: Cell enlarges(hypotonic)
In: Cell enlarges(hypotonic)