English Honors Final, Ms. Murphy
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
alliteration
the occurrence of the same letter or sound at the beginning of adjacent or closely connected words.
allusion
an expression designed to call something to mind without mentioning it explicitly; an indirect or passing reference.
analogy
a comparison between two things, typically for the purpose of explanation or clarification.
ballad
a poem or song narrating a story in short stanzas. Traditional ballads are typically of unknown authorship, having been passed on orally from one generation to the next
blank verse
-unrhymed iambic pentameter
-Element of drama
-Line of verse consisting of 5 metrical feet in unstressed/stressed pattern
■ Facilitates memorization
■ Mimics human speech
■ Sounds like heartbeat
characterization
-the process by which the writer reveals the personality of a character
comedy
-follows hero’s rise rather than their fall
-Has a happy ending but isn’t necessarily funny
-farce- outlandish and exaggerated comedy
-Taming of the Shrew, Waiting for Godot
conflict
-between hero and person/force (antagonist)
-contributes to hero’s downfall
-resolved when tragic hero meets their doom with courage and dignity →grandeur (splendor or impressiveness) of the human spir
couplet
two lines of verse, usually in the same meter and joined by rhyme, that form a unit.
denouement
-the final part of a play, movie, or narrative in which the strands of the plot are drawn together and matters are explained or resolved.
-the climax of a chain of events, usually when something is decided or made clear
diction
the choice and use of words and phrases in speech or writing.
drama
form of storytelling where characters, often through dialogue and action, engage in conflicts and explore emotions, typically intended for performance on stage
dramatic irony
what appears to be true to a character is known to be false by the
audience
epithet
a descriptive word or phrase used to characterize a person, place, or thing
fable
a short story that uses animals, inanimate objects, or forces of nature as characters to illustrate a moral lesson
falling action
-Act (lV)
-the part of a narrative that occurs after the climax, leading towards the resolution or conclusion, conflict lessens as characters dealwith consequences of their decisions
free verse
poetry that does not rhyme or have a regular meter
metaphor
-does not use like or as
-figure of speech that compares two different things by stating that one is the other, highlighting similarities for emphasis or symbolism
simile
-a figure of speech involving the comparison of one thing with another thing of a different kind, used to make a description more emphatic or vivid
-use like or as
situational irony
occurs when an event happens that is the opposite of what is expected or intended, often creating a sense of humor or tragedy
symbolism
A thing that represents or stands for something else, especially a material object representing something abstract.
verbal irony
-sarcasm is an example
-a figure of speech where the speaker says one thing but means the opposite
farce
a comic dramatic work using buffoonery and horseplay and typically including crude characterization and ludicrously improbable situations
motif
A recurring theme, subject or idea
Pun
joke exploiting the different possible meanings of a word or the fact that there are words which sound alike but have different meanings.
Denouement/Resolution
-Act V
-the part of a story's plot where the main conflict is resolved or solved
conclusion; events of story wrap up
rising action
-Act 2
-the section of a story where the plot thickens, tension increases, and the main conflict develops
Satire
Satire is a literary genre that uses humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people's stupidity or vices
stereotype
a widely held but fixed and oversimplified image or idea of a particular type of person or thing
tone
The author’s attitude or persona towards a subject or topic conveyed through language and style
What is Romanticism? What was it a reaction to? What was Romanticism attempting to escape from?
Artistic, literary, & intellectual movement that started in Europe in the late 1700s
- Peak: 1800-1850
-reaction to: Industrial Revolution/political norms and rationalization of nature
-escape from reality (inspiration in medieval books), urban sprawl, and industrialism
What was the Enlightenment characterized by?
-reason and individualism rather than tradition
-knowledge=freedom=happiness
-died out because of romantic movement
What are the characteristics and motifs of Gothic literature?
- Apprehension/impending doom
-fallen man, fallen world
-alone working through issues
-orphans
-night or tight environment
-ascending or descending
-secret passages
-pursuit of maiden with threat of kidnap and rape
-physical decay
-revenge
-family curses
-blood and gore
-doppelgängers
-demonic
-black magic
-Madness
-sexual taboos broken
What is a Byronic hero?
Arrogant, intelligent, educated outcast who somehow balances his cynicism and self-destructive tendencies with a mysterious magnetism and attraction
-intelligent
-cunning
-ruthless
-arrogant
-violent
-depressive
-self-aware
-emotionally and intellectually tortured
Describe each of the characters in Rebecca.
Mrs. de Winter: desperate, doesn’t fit in Manderley, young, insecure
Maxim de Winter: withdrawn, secretive, burdened by Rebecca
Mrs. Danvers: devoted to Rebecca, sinister oppressive atmosphere
Rebecca: pervasive influence, manipulative, charismatic, Manderley impactor
Beatrice Lacy: witty chatty woman with a fondness for the new Mrs. de Winter, sees good in new Mrs. de Winter
Giles Lacy: cheats with Rebecca, drawn to her
Mrs. Van Hopper: American woman who hires narrator, gossipy
Jack Favell: incestful in love cousin of Rebecca, pursues Maxim as murderer, alcoholic
Frank Crawley: estate manager, loyal and trustworthy for Maxim and narrator
Ben: mentally retarded man who works estate, knows Rebecca was murderer
Dr. Baker: gynecologist involved in Rebecca’s death
Colonel Julyan: investigator for Rebecca’s death
Where is the narrator at the start of Rebecca?
In the start of Rebecca the narrator is in Monte Carlo in Europe
How would you describe Manderley? Where is Manderley located?
Grand, large, beautiful, and yet haunted by Rebecca in every way. It was located in Corwnwall coastline in England
Who is the narrator of Rebecca? How would you describe the narrator?
-Mrs. de Winter
-shy, self conscious
-unreliable narrator
How old is the narrator? How old is Maxim?
-narrator-early 20s
-Maxim-42
What is the narrator’s job at the beginning of the story
travel companion to Mrs. Van Hopper
How does the narrator feel about Mrs. Van Hopper?
-snobby
-manipulative
-spider
-fat
What deal does Rebecca make with Maxim in the beginning of their marriage?
-promising to be a perfect hostess and mistress of Manderley in exchange for freedom to live her life as she pleases, including having affairs
-family name and rep, maxim agrees
How would you describe Mrs. Danvers?
-dead looking
-chilling
-head housekeeper
-devoted to Rebecca
-pathetic yet frightening
What is the name of Rebecca’s boat? What does it mean in English?
Je Reviens or I Will Return
How do most people believe Rebecca died?
Most people believe Rebecca drowned in the lake because the boat capsized in rough weather and her body was supposedly found at sea and identified by Maxim
When they pull Rebecca’s boat out of the water, what do they find inside the cabin?
a body identified as Rebecca’s
What does Rebecca tell Maxim on the night she dies?
She is pregnant (not true, she had cancer)
What does Dr. Baker reveal about Rebecca?
Infertile with cancer
What happens to Manderley at the end of the novel?
It is burned down
What is the goal of an argument?
A point of view on a subject that is supported with evidence
To support a point of view
What is a claim?
States the main idea of the argument
-position author is taking/how they feel
What are the three parts of every rhetorical situation?
-Exigence: the motivating event that prompts writing about the topic (demand)
-the audience (who speaker is addressing, how much they know, who will agree)
-speaker (presenting, who, qualifications, interests, biases, why should I listen)
What is ethos?
Trust/repuation
-credibility of speaker
-shared values emphasized
What is logos?
Appeals to logic and reason
What is pathos?
Appeals to audience emotions
What does it mean to concede an argument?
-persuasive technique where author recognizes the merit of the counter, but still believes his point is better and restates it
What is a counterclaim
Main objection to or concern some people might have to the claim
-mark of good academic argument if this is acknowledged
What do you call the person or organization presenting an argument?
The speaker
What is the effect of using more than one appeal in an argument?
makes the argument stronger, appeals to different aspects of audience thinking
Be able to identify examples of ethos, pathos, and logos in ads.
reputation/ethics/facts=ethos
Cute or sad=pathos
Logical, makes sense=logos
What is oral tradition?
originally sung or said by a bard, passed down by mouth
What is Freytag’s pyramid?
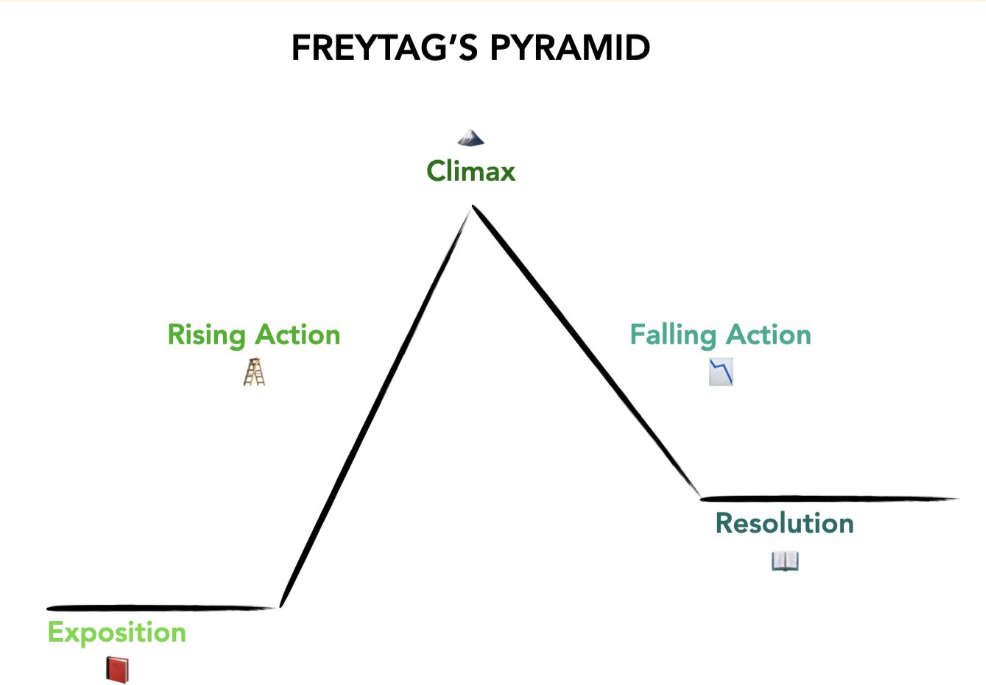
What is first person point of view?
a story is told from the perspective of a character using "I," "me," "my," etc
What is a second person point of view?
the pronoun "you" to address the reader directly, making them a character in the story
What is a third person point of view?
a story is narrated by someone outside the characters, referring to them with pronouns like "he," "she," or "they"
What is a limited point of view
reports dialogue, setting, and actions of characters, but not thoughts (detached)
What is an omniscient point of view?
knows everything that happens and reveals what each character thinks and feels
What is a limited omniscient point of view?
knows everything that one or only a few characters think and feel
What is foreshadowing?
technique where an author hints at or suggests events that will happen later in the story
What is a foil?
character whose actions contrast with another character in order to highlight certain aspects/traits (Sherlock & Watson, Buzz & Woody - others?)
What is an antagonist?
-The bad guy against the protagonist
-opposes protagonist intentionally or unintentionally
- Their goals run contrary to the protagonist, but they aren’t necessarily bad
What are the four types of conflict in literature? Be able to identify them in examples.
- Man v. man - conflicts among characters
- Man v. society - character conflicts with government,
system, or societal mindset
- Man v. nature - character’s conflict is with weather,
animal, terrain, or other facet of nature
- Man v. self - character’s inner struggle (fear, flaw,
obligation
direct characterization
When the book specifically describes the character
mood
-general feeling or atmosphere of a work
-Set by setting
epiphany
sudden moment of realization or understanding for a character, often triggered by a specific event or experience
point of view
Perspective from which a story is told
Flashback
use of scenes within a story that interrupt the sequence of events to reveal past occurrences
rising action
takes up most of the story; includes major conflicts characters face
frame narrative
- Literary technique that presents a story within a story
- Introductory/main narrative sets the stage for a second
narrative or group of short stories
- Frame story provides important context, key information
subplot
secondary storyline that adds depth to main plot
implied theme
suggested, or stated indirectly, through what happens to the characters
symbol
images, objects, words, or people that represent or evoke another set of feelings beyond their general appearance or significance
in medias res
In the middle of action
Tone
how a work treats a certain topic whether through character action or statement a which shows how they feel about it
indirect characterization
How someone’s actions show their character
universal theme
message about life that is expressed regularly in many different cultures and time periods
irony
literary device in which words are used to express a contradiction between appearance and reality
What word does Mrs. Mallard fixate on in “The Story of an Hour”?
free
How does Mrs. Mallard most likely feel about her marriage in “The Story of an Hour”?
Sulfates and oppressed even though she loves him a bit
What is the main conflict in “The Story of an Hour”?
Man v.s. Self
What topics and themes are explored in “The Story of an Hour”?
Wanting freedom from an oppressive marriage
How you can not hate someone but not love them both
What is the main conflict in “Lather and Nothing Else”?
Man v.s. Self
In “Lather and Nothing Else,” what does Captain Torres mean when he says, “It’s not easy to kill”?
He means that there are emotional burdens that come with murder as he talks to the barber that almost murdered him
What topics and themes are explored in “Lather and Nothing Else”?
-value of life
-duty vs belief
-morality
What is ironic about the title “The Birthday Party”?
The little celebration with an unhappy husband and a cake is not at all like a birthday party
What example of juxtaposition do you see in the imagery of “The Birthday Party”?
The lady is well dressed but sad in a happy hat and
What topics and themes are explored in “The Birthday Party”?
Miscommunication
Marriage issues
social expectations
Rejection
Why are the parents in “The Veldt” so disturbed by the nursery?
Nursery veldt is unnerving and unsettling
Danger and violence in scenery
Children detached
What does David McClean observe about the nursery in “The Veldt”?
Too realistic
deep seated anger and resentment
replacing family and authority
must stop
What does Lydia Hadley mean when she says, “The house is wife…now?”
House takes care of traditional wife roles
Lydia replaced