Quiz 5-Chapter 16
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the driving force for loosing a proton as the last step in electrophilic aromatic substitution?
to rearomatize the ring system
What is the reactive intermediate formed in the addition-elimination mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
carboanion
What are the3 two distinct pathways for nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
Addition-elimination and elimination-addition
Which of the following substituents is a meta director?
SO3H

II < I < III < IV
What is the reactive intermediate formed in the elimination-addition mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
Benzyne
How can polyalkylation be minimized in Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
use large excess of benzene relative to the alkyl halide
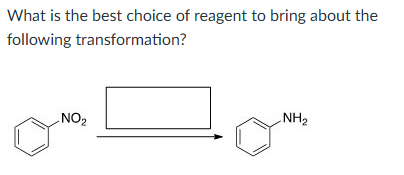
H2, Pd-C
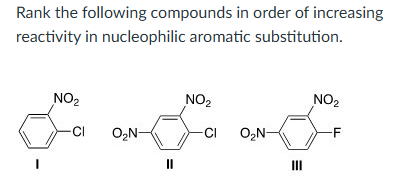
I < II < III
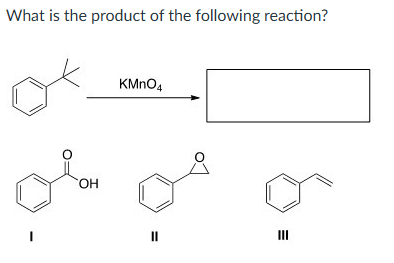
none of them
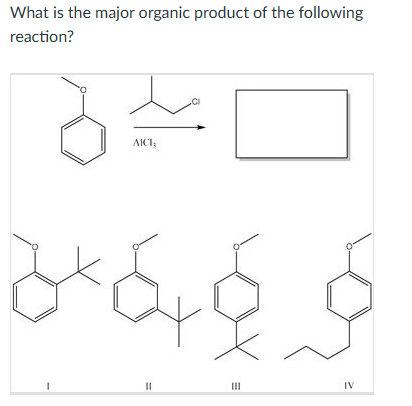
III
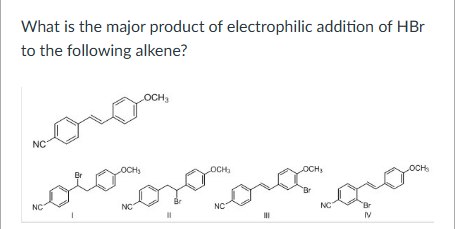
II
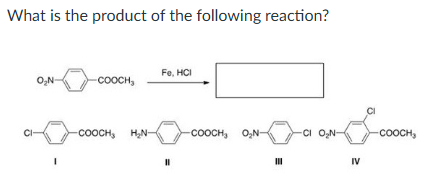
II
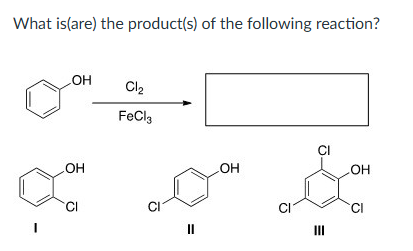
Only III

CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3. Zn(Hg), HCl
What is the electrophile in aromatic nitration?
NO2+
Which of the following substituents is a deactivator in electrophilic aromatic substitution?
(CH3)3N+

IV
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of electrophilic aromatic substitution is not true?
the transition state of the first step is lower in energy
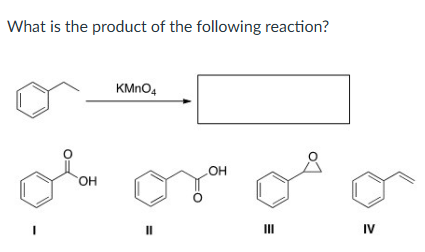
I
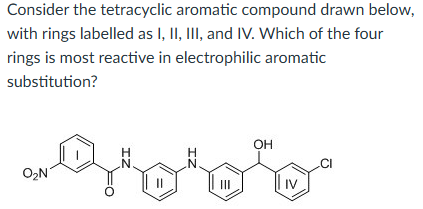
II
Which of the following statements about nucleophilic aromatic substitution is true?
the elimination-addition mechanism is not as common as the addition-elimination mechanism
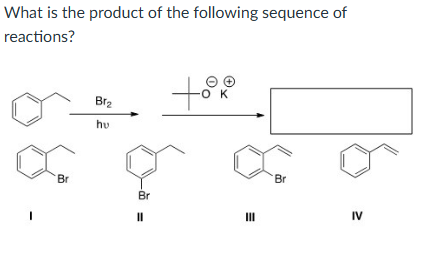
IV
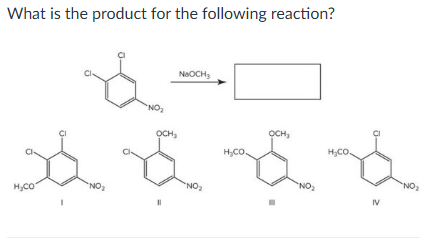
IV
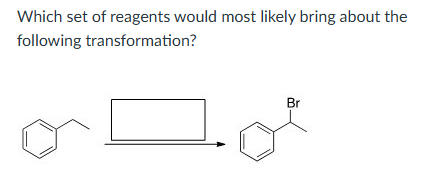
NBS and light