Clinical skills 2 Exam 2 camelids/sheep/goats
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
In south america
camelids are not fed mineral supplements, concentrates and are rarely given cured hay.
They live on native grasses

Llama (Lama glama)
largest of the new world camelids (up to 350lb)
longer face and ears than alpacas, higher set tail, more level back than the alpaca.
used historically for transport and meat.
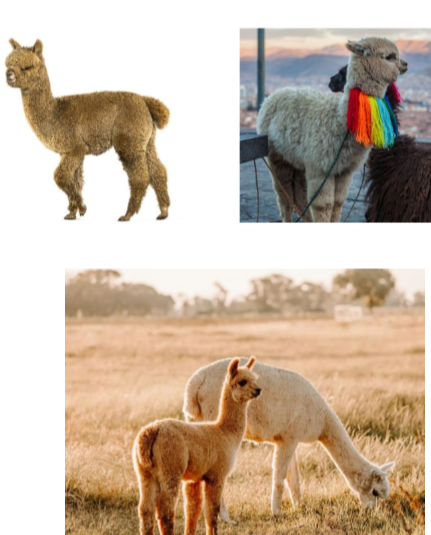

Alpaca (Vicugna pacos)
smaller than the llama (around 150lb)
much more valuable wool.
shorter noses and ears than the llama.
lower set tail and its back is more arched
bred for their wool
also used for their meat.
female that has reproduced
hembra, dam, mare
Male
Macho, bull
Father
sire
Castrated male
gelding
Group of camelids
herd
Young /baby
Cria
Gestation and breeding
females → induced ovulators
gestation
llama = 335-360 days
alpaca = 325-345
non-seasonal breeders in temperature climates with good condition (often where they are found in hobby farms)
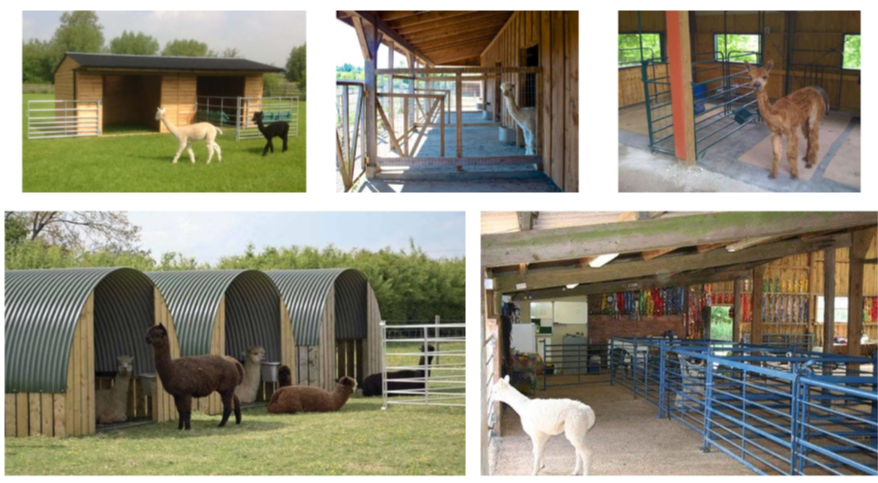

Housing
dont need much except in th emost extreme of conditions
a 3 sided shelter usually provided as minimum
can be housed with goats and sheep
intact males should be housed individually
appropriate ventilation
dry
safe access for caregivers
secure gates and latches
soft flooring - bedding or rubber matting
ample space
non-slip cushioned flooring
protection form predation
Fencing
fencing needs to be strong but dont need barbed wire fencing
1.2-1.5m high fences usually sufficient
prehensile lips can open gates so double latches recommened
4-6 alpacas or 2-3 llamas per acre.
indoor housing → 1 alpaca per 2.5m2 area
llamas and alpacas tend to defecate in one area of pasture called a middern.
Diet
Bulk feeders → evolved to survive on poor forage in harsh conditions
slow gut passage time to allow for efficient extraction of nutrients
eat deep rooted plants in natural environment so very mineral resistant/require a high mineral componenet to their diet.
diet should consist of 75-90% long forage(long plant stems - hay , haylage, grass)
feeding
supplements eg pelleted feed should not exceed >25% of total feed.
feeding should be consistent in the amount and time each day.
sudden cahnges can cause GI problems
any changes should occur slowly over a 2 week minimum period.
there should always be plenty of hay/pasture and water at all times → 24 hours per day.
llamas and alpacas are not tolerant to these and can cause copper toxicity - liver necrosis.

Alpaca wool
two types
Huacaya → soft, dense and sheep-like fibre (~90% alpacs)
suri → silky, pencil-like locks (~10% alpacas) dread like looking black one
suri wool is better suited for woven good and fine clothing, whereas huacaya is better for knitting
shorn once per year, usually in the spring
the suri breed of alpaca was reserved for royalty during inca times.

Behaviour
Can look at behavior based on neck, tial and ear position
may spit - defence mechanism
often very docile but may bite, charge, rear and chest butt or kick
usually cow-kick (to the side) or forwards
dont get too comfortable because can also kick straight back.


Aberrant behavior syndrome/Berserk llama syndrome
not a true disease but the result of poor human interaction, lack of training, and inappropriate soxialization
not common for bottle fed crias

Handling and restraint
strong herd instinct
always handle camelids in groups of at least 2 individuals
if you want to isolate an individual, move all into a smaller space and then separate the desired individual
mom and baby together
resent head being handled
basic restraint of lamoids involves one arm aorund the base of the neck and another holding the flank region on the opposite side.

Cush behavior
animal sits in sternal recumbency. very classic of a llama or alpaca who doesnt want to be lead somewhere
dont attempt to pull on the halter when this happens
best thing is to come back later if possible.

Spitting - defence mechanism
pay attention to the body language
head pulled back
ears pinned back
nostrils flaring
gurgling or movement in the neck of stomach fluid coming back up / straightening of the neck.
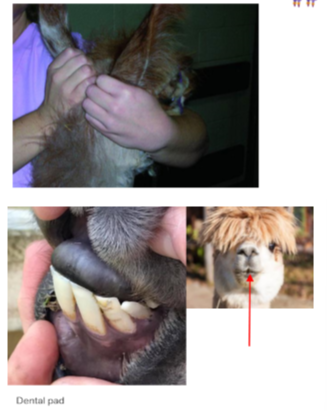
Calming techniques for restraint
Ear twitch - same as horse. dont bend the ear as can damage the cartilage.
dental pad massage - place the finger in teh split of the upper lip and massage the dental pad where there are no upper teeth - relaxation technique.
Tail massage - hold the base of the tail and rotate the tall in a circular motion
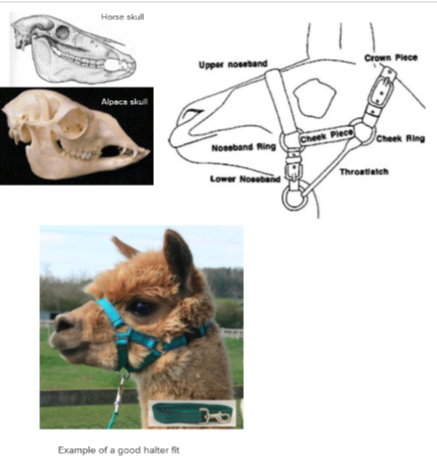
Haltering
need to ensure the correct size halter.
can collapse the nasal passages as the distal portion of their nose is cartilage and not bone.
semi-obligate nasal breathers → so need to be aware of them being able to breathe.

Shearing
in alpacas fore legs tied forward and hind legs backward
prevents struggling and rolling
shearer gets longest straight blows making the shearing process more efficient and faster.
llamas can be sheared stnading, holding the base of the ears as gentle restraint
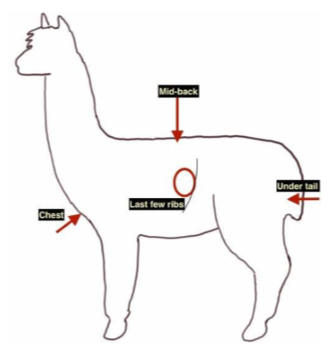
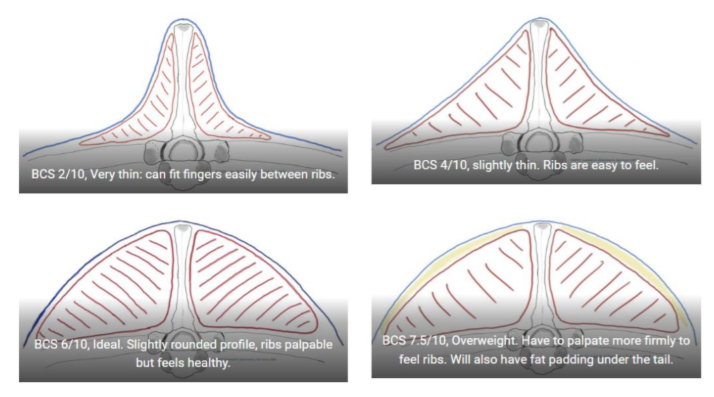
Lamoid body condition score
scale 1-9
four main sites:
mid back
last few ribs
chest

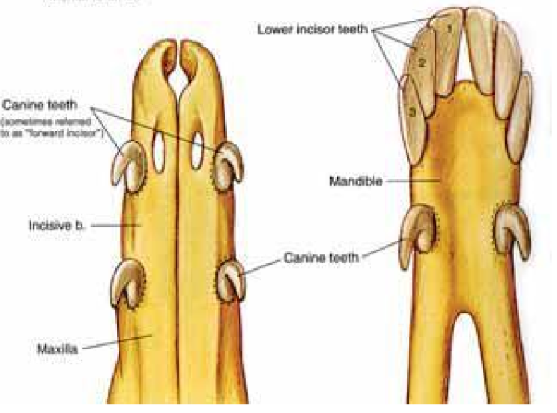
camelids - Dentition
Prehensile and split upper lip
there are 6 fighting teeth or tusks 2 on the top gum and 1 on the bottome on each side of the mouth
eruption times of permanent teeth:
central incisors I1: 2 to 2.5 years
middle incisors I2: 3 to 3.5 years
corner incisors I3: 4 to 6 years
tusks: 2-2.5 years
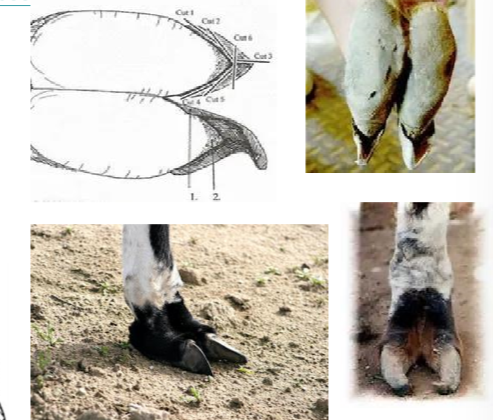
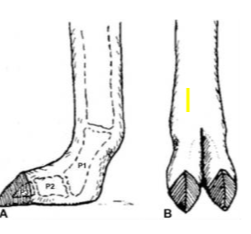
Feet trimming
camelids bear weight on both P2 and P3
compared with most large animal species weight bear on P3
no navicular bone
claw covers the distal phalanx and is not weight bearing but used for propusion and traction.
the digital cushion supports P2 and P3
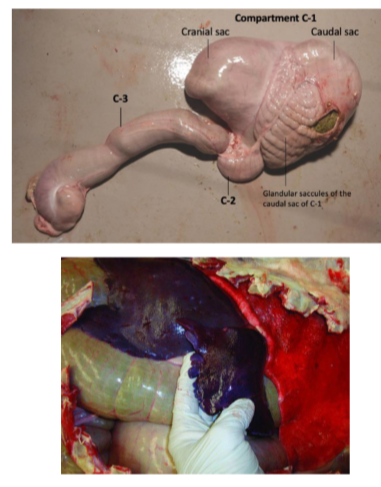
Camelids - Abdomen
Stomach → transit slower through C1 → proloned fermentation → greater plant cell wall degradation.
consequence of this → reduced feed intake compared to other ruminants.
have glandular saccules in C1 and glandular cells in C2 in comparison to the papillae of normal ruminants.
C3 - has two distinct regions
cranial protion is lined with many folds of glandular epithelium → highly absorptive.
the caudal 20% is secretes hydrochloric acid and proteases and is the true stomach portion of camelids
the caudal border of the liver is fimbrinated / rough which is considered normal.
dont have gallbladder.
Camelid physical exam parameters
temp - 99.5-101.5
heart rate - 60-90
respiratory rate - 10-30
feces - pellated, use dung pile
urine - clear, pale yellow to amber
Camelids - thoracic / abdominal auscultation

Camelids Vaccinations
all vaccine use in camelids is considered off label
vet recommend:
Clostridium perfringens type C and D vaccine
tetanus
rabies
initial vaccination at 3 months with a booster 30 days after, followed by annual boosters.
other vaccines:
west nile virus
EEE and WEE
lepstospirosis
equine herpesvirus 1
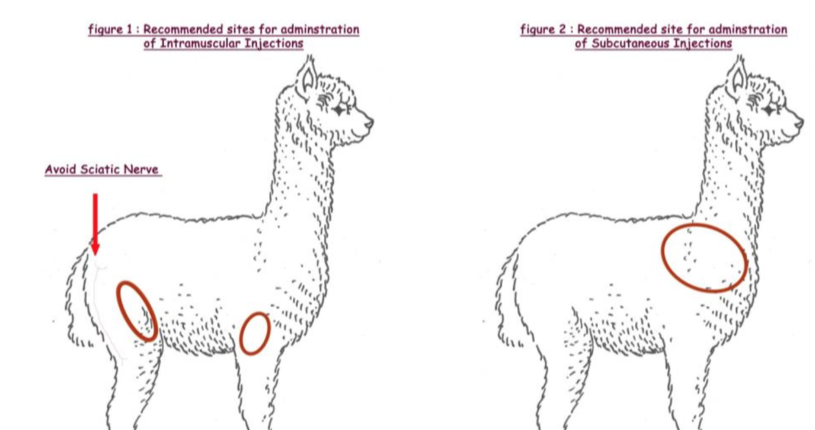
Giving injections to camelids
subQ
shoulder area
IM
infront of armpit
behind the flank in leg m.
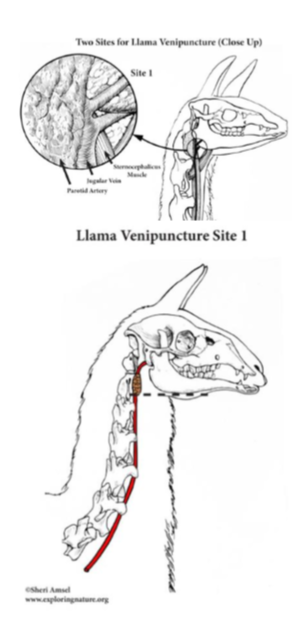
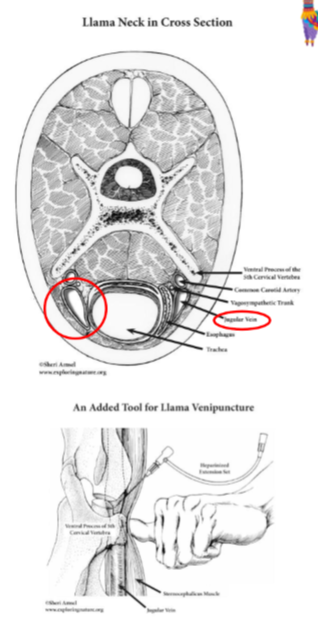
Jugular Venipuncture
1st site: cranial portion of the neck at the level of the mandible
skin very thick, need a longer needle, good restraint. more superficial and not as close to the carotid artery.
Jugular vein - not as superficial compared to other farmed species. needle 1.5inch
jugular vein runs medial to the ventral projections of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebra and lateral to the trachea.
experienced handler is important- keep the head slightly raised and turned away from the injection site.
right jugular is recommended because if this does happen a haematoma is less likely to compress the oesophagus.
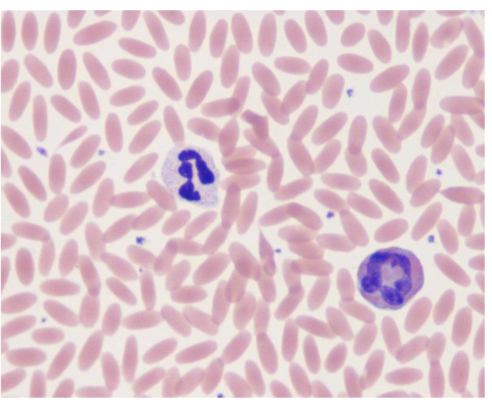
Camelid Haematology
have a lower MCV (mean cell volume)
RBC count is higher
cells contain more haemoglobin than in cattle
have on average a higher leukcocyte count than rumiannts with neutrophils being the most numerous.
more resistant to anemia
have an elliptical shape → makes them much more resistant to changes in blood osmolality.
RBCs have comparetively high haemoglobin concentration → theorised to increase the ability of the cell to carry oxygen while the small size and flattened shape provide increased membrane surface for oxygen exchange (higher surface/volume ratio)
Small Ruminants Taxonomy
Sheep
Ovis aries
Ovine
order: Artiodactyla
Even-toed ungulates
Multi-purpose:
wool, meat and milk

Small ruminants Taxonomy
Goats
Capra hircus
Caprine
order: Artiodactyla
Even-toed ungulates
multi-purpos:
meat, milk and fiber
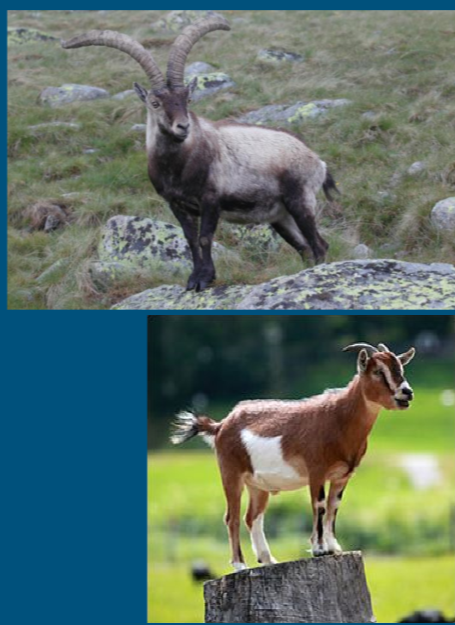


Sheep
Tails point down
have wool or hair
spiral horns
many are naturally polled - male and females
Gregarious - strong flocking instinct
scent glands on face and interdigitally
Grazers


Goats
Tail point up
born wiht short, upright tails
hair or fibre
most are naturally horned
polling usually artificial
natural polling gene closely related to sex deterimination gene
horns weep backward
beards and wattles are common
scent glands behind horns and on neck
browser

sheep terminology
adult female
Ewe
Adult male
Ram
Castrated male
wether
young
lamb
group
flock
meat
lamb/ Hogget / mutton
Goat terminology
adult female
Doe / Nanny
adult male
buck / billy
castrated male
wether
young
kid
group
herd
meat
Cabrito / Capretto / Chevon
Shearing
The act of clipping the whole fleece from the sheep
flece weight = 7-15 lbs

Crimp
The natural wave formation seen in wool
the closer the crimp the finer the wool (crimp per inch)
Crutching
The act of clipping the area around the ewe’s perineum and udder prior to lambing
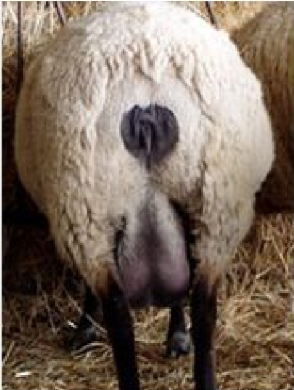
Mulesing
Cutting off flesh/skin at 6-12 weeks old, from the perineum of Merino sheep to reduce the incidence of fly strike
Inherently painful and controversial; illegal in some countries (NZ, Argentina, forbidden in EU. legal in US and Australia)
should be used as a last resort.

Shep Breeds: Dairy
“New” industry
primarily East Friesian breed
white
polled
rat tail
heat intolerant
highest milk production
(400-500 lb/ewe/year over 180 day lactation)

Sheep breeds: Dual purpose
Advantages
meat conformation is superior compared to wool breeds.
Improved herding instincts compared to meat breeds.
Good “all- rounders”
limitations
lack genetic strengths to be outstanding in high-level meat or fleece production.
Polypay
Corriedale
Gulf Coast Native

Sheep Breeds: Long Wool Breeds
Advantages
Heavy fleeces, long fibers:
used for hand-knit crafts
protect from harsh climates and wet weather
footrot resistant
limitations
coarse fleeces of lower value
not adapted to hot, dry climtes
slow to mature to market weight
Leicester
Lincoln
Cotswold

Sheep Breeds: Meat/Market Breeds
Black face = meat breed
Advantages:
outstanding meat conformation
high avg. daily gains to reach market maturity early
Limitations
Lower quality fleece, dark fiber contamination
lack strong herding instinct
Suffolk
Hampshire
Dorper

Sheep Breeds: Fine Wool Breeds
Advantages:
Rugged, adaptable to variations in climate
high quality wool used in making high-end clothing
easy to handle
Limitations:
subject to fly strike due to wrinkles and skin folds
Lack meat-type conformation
Merino
Rambouillet

Boer goat
meat breed
originated in south africa
cross btw Kalahari Red and Savannah
most popular meat breed in US
low maintenance breed
good kidding rate
3 kiddings ever 2-years
do well with out of season breeding
Great performance
rate of gain
carcass quality

Kiko
New Zealand breed
Developed through cross-breeding native animals with improved breeds.
Hardy, parasite resistant
Good rates of gain and carcass characteristics

Angora
Goat fiber
Produce mohair
5.3 lbs / shearing
shear q 6 months

Cashmere
fiber goat breed
>60 goat breeds
produce cashmere
2.5 lb / shearing
Shear or brushed q 12 months

Saanen
Dairy breed
Swiss breed
white coat, very little pigmentation
high milk producers
sensitive to excessive sunlight / heat

Lamancha
Dairy breed
Tiny ears
American breed
Distinctive ears
Hardy breed

Angulo-Nubian
Diary Breed
English breed
Ctf goats 🐐
highest % butterfat
large variety of color
Roman nose and long ears

Dairy Animals
Both goats and sheep are easily trained to milking routine
small emulsified fat globules, soft curd
Sheep:
180-210 days lactation (6-7 months)
4-7 lb milk/day
Goats:
average 284 days lactation (10 months)
6-8 lb milk/day
Nachi
Dancing goats of Pakistan

Damascus goat
Worlds ugliest goat

Colorado
is the leading lamb state
Predator control
Est 65% of mortality loss due to predators
common predators - dogs, coyotes, foxes, bobcats etc (dep on area)
prey animals
fencing (dependent on predator)
livestock guardians
Dogs
donkeys
Llamas
Ostrich/Emu

Reproductive management
puberty
sheep - 5-8 months
goat - 4-8 months
age first breeding
sheep - 8-10 months
goats - 8- 10 months
estrous cycle
sheep - 16-17 days (seasonally polyestrous)
goat - 18-23 days (seasonally polyestrous)
estrous
sheep - 36 hours
goat - 12-24 hours
gestation period
sheep 148 days (5 months)
goat - 150 days (5 months)
average birth weight
single - 8-13 lbs
twins - 7-10 lbs
Bucks and Rams reprouctive management
Bucks in rut have a strong odor
pheromones (sebasceous scent gland at base of horn)
urinate on front limbs and face
may be more aggressive / difficult to handle when in rut
Rams have breeding flush
preorbital scent gland and inguinal glands
rule of thumb: 3 males / 100 females
leave male in with females for 1-1.5 oestrus cycles
flehmen response
greatest libido and fertility observed in the fall and spring
seasonal breeders:
rams > bucks

Ewes and Does reproductive management
Maintain BCS between 2.5/5 - 3.5/5
Flushing
females with low BCS can be flushed with additional energy for the 2-3 weeks leading up to breeding
improves condition
encourages superovulation
Ram effect / Buck effect
placing a male with females is a strong stimulus to induce estrous in 6-7 days a simple way to heat sync females
females must have had not contact with a male for the preceding 1-3 months for this to be effective
marking harness / raddling:
placed to males to monitor breeding program
used to identify “problem” males and females - repeat breeders
nutritional considerations
adults at maintenance will eat 1.8 - 2.4 % BW DMI/day
omasum larger in sheep vs goats
Copper
sheep are very sensitive
goats need copper to maintain health/immunity
cant feed the same diet and expect both species to do well
Pregnancy toxemia (ketosis)
ewes/does with mulitple fetuses more susceptible (higher energy requirments)
obstructive urolithiasis
seen most often in wethers on high concentrate feed
to prevent balance calcium to phosphorus ratio in the diet

individual handling
stanchion and yoke stand

remove a single animal from the herd
select animal
grasp above the hock
pull animal back toward you
grasp under the chin and lift head
Gambrel restrainer
suitable for shorter periods of restraint
alternative to light sedation
not suitable for painful procedures
works better in sheep > goats (goats vocalized
Sitting / Rumping a sheep
Sheep only
Restrain animal with hand under jaw, standing on side of sheep
one hand: turn animals head to its flank
other hand: push down on hip at the same time
grasp forelimbs and pull them upward
sheeps back leans against your legs
Animal rests on its hips, not directly on its dock
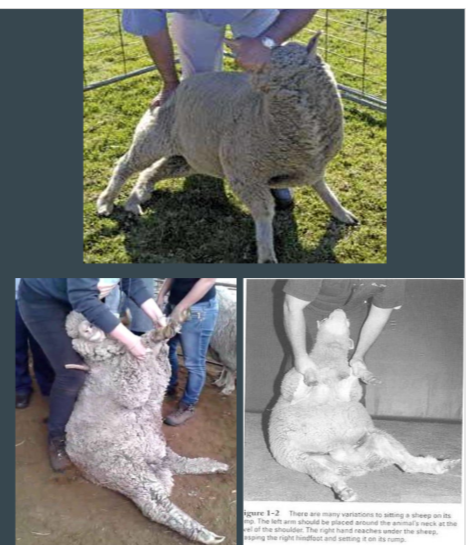

individual restraint: what to avoid
DO NOT catch or restraint by grabbing the fleece/skin/haird
DO NOT drag the animal by a horn, tail or ear

Body condition score - sheep
Backbone, short ribs, eye muscle
sheep deposit fat subcutaneously
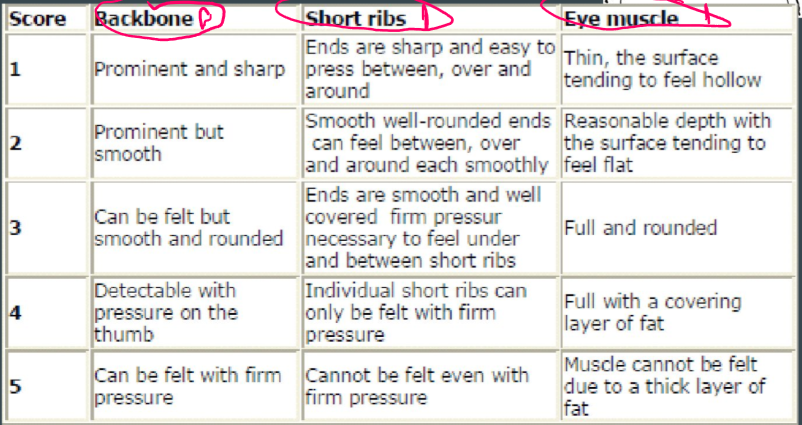

body condition score goats
same as sheep
goats first deposit fat intra-abdominally
thus we add 0.5 to the BCS score for goats on a 5 point scale

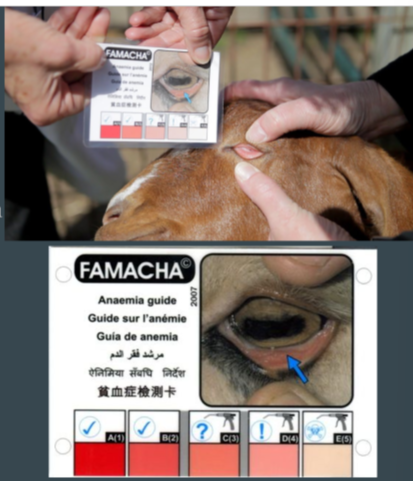
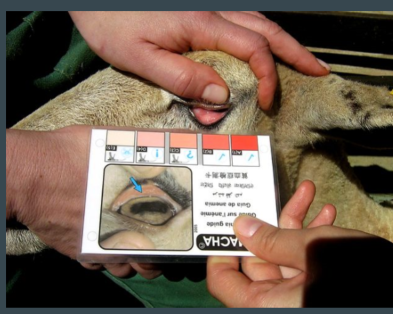
Famacha
Anaemia scoring system using ocular conjunctiva (ventral)
indication of level of anaemia
score of 1 (pink) - 5(pale)
used as representation of blood sucking parasite burden in particular Haemonchus contortus (barber pole worm)
purpose: targeted deworming
technique
head adequately restrained
Cover eye with upper eyelid, pushing down gently on the globe (eyelashes will curl up)
pull down lower eyelid to expose ventral conjuctiva
compare to FAMACHA card.
TPRR (vital signs)
temp - 101.5 - 103.5
pulse - 70-80 bpm
respiration - 15-30 bpm
rumination - 1-2 contractions per minute
MM/CRT - pink / <2s
Physical Examination
thorax:
cardiac auscultation (heart rate)
pulmonary ausculatation (repiratory rate)
Abdomen:
rumen auscultation, percusission, succussion
Ballottement - pregnancy check
lymph nodes:
palpable - submandibular, prescapular and prefemoral
limbs
udder/testes
temperature
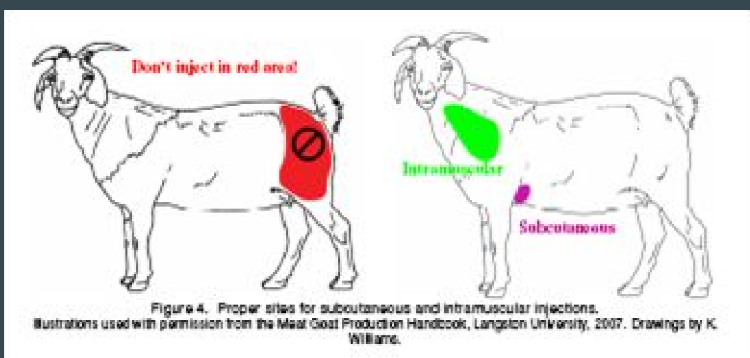
Parenteral drug adminisration
Subcutaneous injection (SQ)
behind the elbow
Intramuscular injection (IM)
neck muscle
alt semiten/semimem
Intravascular injection (IV)
jugular vein
ALWAYS ASPIRATE
Orogastric tube
administer oral medication
oral rehydration
colostrum administration
measure tube to last rib and mark
direct tube to left oropharynx
allow animla to swallow and pass tube
ALWAYS CHECK
blow - hear bubbles in rumen
listen - if air movment with respiration vs smell rumen, hear bubbles
test with a little water first - no coughing can proceed and administer
when done, KINK the tube prior to removal
remove smoothly

goat preventative medicine
very few products are registered for use in goats: Extra-label use
goat metabolism is higher than sheep and react differently to certain carriers in medication
Core vaccination (CDT)
Clostridium perfringens type C and D
Clostridium tetani
Vaccination schedule
lambs and kids
4 weeks
8 weeks
annually
Breeding animals
6 weeks prior to breeding season
4-6 weeks prior to lambing / kidding