Isomers
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
isomer
a compound with the same formula but different arrangement of atoms and different properties
structural isomer
molecules with the same molecular formula, but their atoms are arranged in a completely different order
3 types of structural isomers
1) chain isomers
2) positional isomers
3) functional group isomers
chain isomer
an isomer made up of two or more carbon atoms or other compounds with the same molecular formula but different atomic arrangements (often consist of one straight chain isomer and multiple branched chain isomers)
position isomer
isomer where the basic carbon skeleton remains mostly unchanged, but important groups are moved around in that skeleton
functional group isomer
when isomers contain different functional groups, meaning they belong to different families of compounds (different homologous series) despite having the same molecular formula
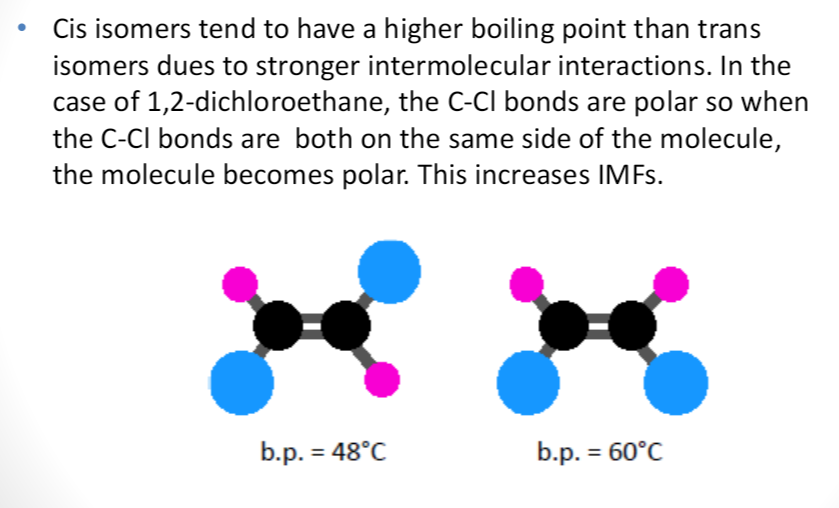
geometric isomer
when different groups of atoms are arranged around a double bond (each carbon in the double bond must be attached to 2 different groups)
2 types of geometric isomers:
cis → larger groups are attached to the same side
trans → larger groups are attached to opposite sides
properties of cis and trans isomers:
→ cis generally has higher MP/BP than trans
→ this is due to stronger IMFs
→ see image for example