Acids, alkalis & titrations
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is the colour change of phenophthalein for acidic, neutral & alkaline solutions?
Acidic → colourless
Neutral → colourless
Alkaline → pink
What is the colour change of methyl orange for acidic, neutral & alkaline solutions?
Acidic → red
Neutral → yellow
Alkaline → yellow
What is the colour change of litmus solution / paper for acidic, neutral & alkaline solutions?
Acidic → red
Neutral → purple
Alkaline → blue
What is the pH scale?
A scale (0-14) that measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution
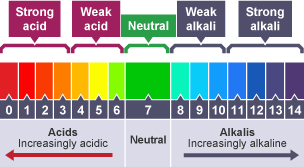
How can the universal indicator be used to measure the approximate pH value of an aqueous solution?
Add a few drops of aqueous solution to a piece of universal indicator paper
Observe the colour change of the paper & compare it to the pH scale to find its pH value
What do acids produce in aqueous solutions?
Hydrogen ions (H+)
What do alkalis produce in aqueous solutions?
Hydroxide ions (OH-)
What is a neutralisation reaction?
When an acid and alkali react together to neutralise each other, producing a salt & water (acid + alkali → salt + water)
The name of the salt can be worked out from the name of the acid & the alkali
What is a titre?
A small measured volume
What is an acid-alkali titration?
An experiment where titres of acid / alkali are added to a measured volume of acid / alkali containing a pH indicator until the solution becomes neutral
Describe the method of an acid-alkali titration
1. Wash a burette using acid & then water
2. Fill burette to 100cm3 with acid
3. Use a pipette filler to put 25cm3 of alkali into a pipette & then add it into a conical flask
4. Add a few drops of phenophthalein indicator to the conical flask
5. Add titres of the acid from the burette into the alkali until the solution turns from pink to colourless
6. Calculate the volume of acid needed to neutralise the alkali by subtracting the new reading of the burette from 100cm3
7. Repeat the experiment & calculate an average