Condensation Polymers
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what forms a polyester and water
Molecules containing alcohol and carboxylic acid groups react
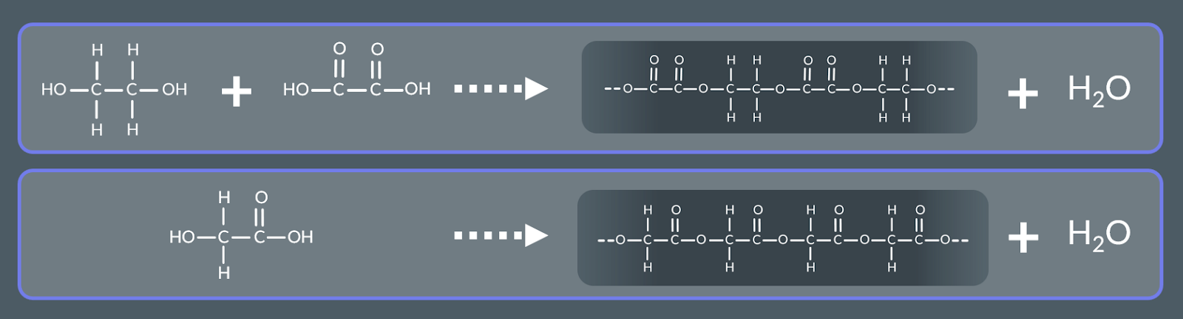
what form a polyamide and water molecules
Molecules containing amine and carboxylic acid groups react
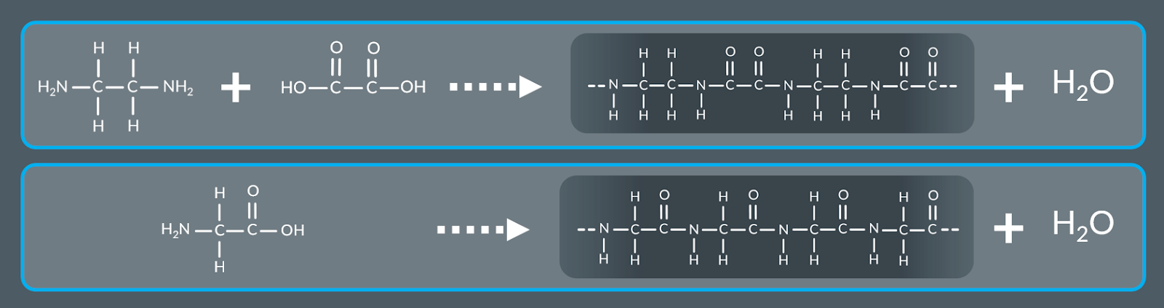
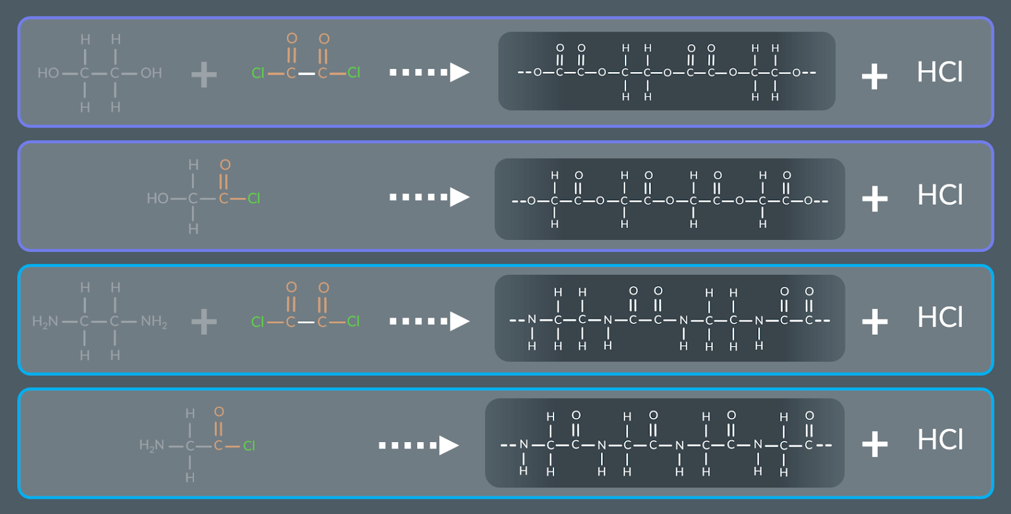
molecules contain amine/alcohol and acyl chloride groups can react to form
a polymer and HCl molecules.
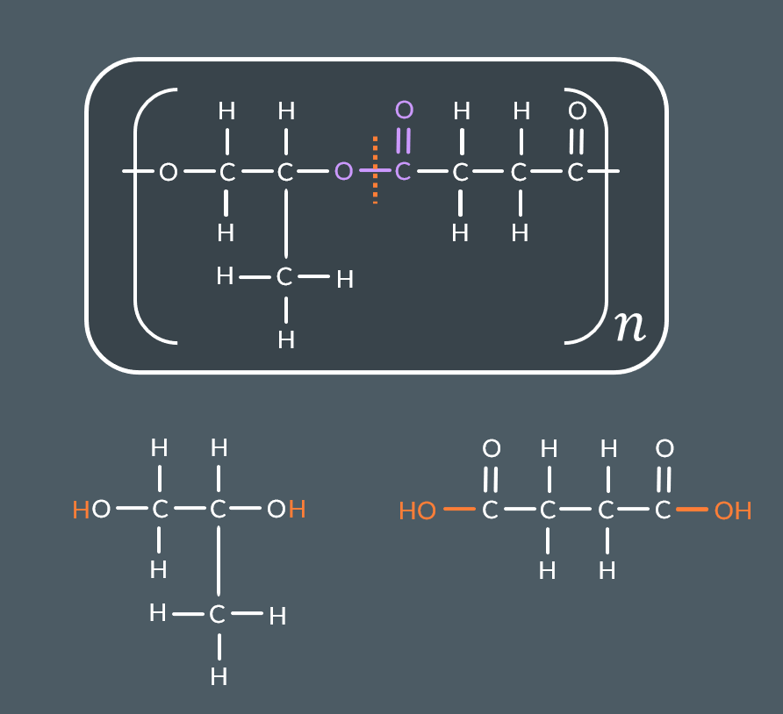
If you’re shown a polyester and are asked to identify its monomers:Break all ester links
Break all ester links
Add HH to all the C-O groups created by step 1
Add OHOH to all the C(=O)- groups created by step 1 (or ClCl if you’re told that the monomer(s) include acyl chloride groups)
If you’re shown a polyamide and are asked to identify its monomers:
Break all amide links
Add H to all the N groups created by step 1
Add OH to all the C(=O)- groups created by step 1(or Cl if you’re told that the monomer(s) include acyl chloride groups)
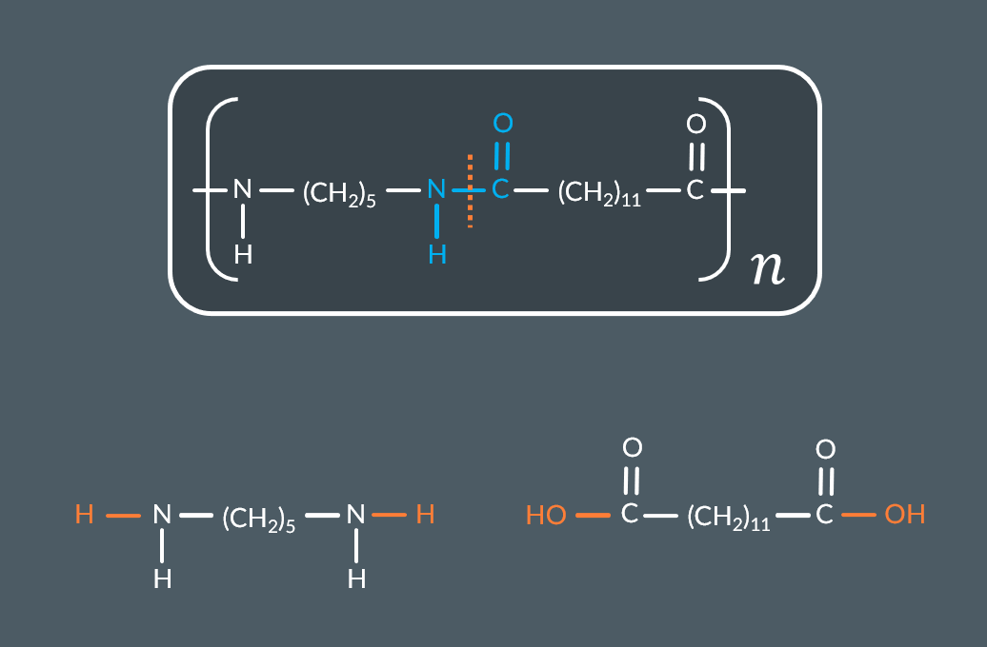
Polyamides are held together by strong:
Van der Waals forces
Permanent dipole-dipole forces
Hydrogen bonds
Polyesters are held together by strong:
Van der Waals forces
Permanent dipole-dipole forces
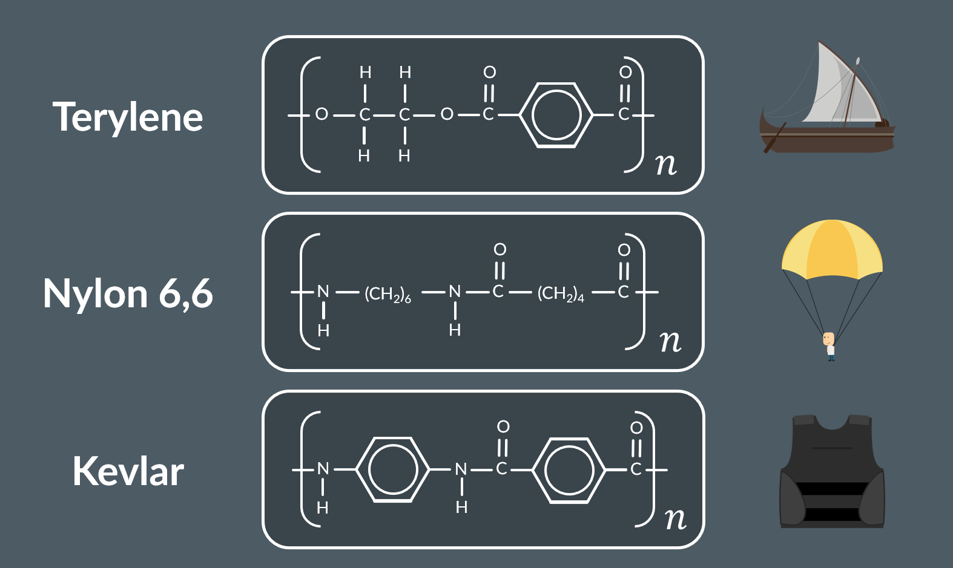
Terylene use
ship sails
Nylon 6,6 use
parachutes
Kevlars use
bulletproof vests
strucutre of Kevlar , Nylon 6,6 ,Terelyne
Ways to dispose of plastics
Store them in landfill
Burn them to generate electricity
Recycle them
Advantages of recycling:
It reduces the need for landfill sites
It reduces the production of the harmful chemicals released when plastics burn or decompose in landfill
It reduces our reliance on non-renewable resources
It’s cheaper than making new plastics
Disadvantages of recycling:
It’s an expensive and difficult to do
You can’t make some plastics using recycled materials
The plastic you’re recycling can easily get contaminated
Some plastics aren’t recyclable
what is Biodegradable plastics
Biodegradable plastics can be broken down by living things into naturally occurring molecules within six months.
why are Many condensation polymers are biodegradable
because they contain a polar C=O bond, which means their chains can be attacked and broken down by nucleophiles like water and OH–
why are Most addition polymers aren’t biodegradable.
because their chains are made of strong, nonpolar C-C bonds, which cannot be attacked and broken by nucleophiles.