Wheelchairs, Community Mobility & Driving🦼🚘
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Building W/C Compliance Dimensions (doorways, hallways, pathways, ramps, parking spaces, counters)
-Doorways- minimum 32” (but ideally 36”)
-Hallways- minimum of 36” (need room for person to propel W/C without scraping hands)
-Pathways/walkways- minimum of 36”
-Ramps- minimum of 36” wide
for building ramps for every 1 inch of height, need 1 foot of length
Railings should be 34-36” high
Curbs/edge protectors should be 4” tall to prevent wheel/walker/cane/crutch tips from slipping off edge
Landings should be a 5×5 ft and are needed for long ramps and ramps that lead to doorways
-Parking spaces- ideally 5 ft of adjacent space, but minimum 48”
-Countertops- maximum height of 36” (lower usually preferred)
Ways to Widen Existing Door
-removing door stops adds 3/4” of width
-replacing hangers with offset hinges can add up to 2” of width

What do state One-Stop Centers, Vocational and Educational Services for Individuals with Disabilities (VESID), Offices for Vocational Rehabilitation (OVRs) and Divisions of Vocational Rehabilitation (DVRs) do?
Pay for home/work mods AND/OR driver rehab if they enable a person to go to work or school
Different Types of Walkers & their Indications
Standard Walker
Requires pt to have fair balance/ability to lift device with UE
Rolling Walker
Useful for pts who cannot lift a standard walker
Hemi-Walker
Pt uses on non-affected side
Useful for those who are unable to use both hands AND need more stability than a cane
Rollator (Three-Wheeled Walker)
Has large wheels and fold-down seat for pt’s who need increased stability and/or fatigue easily
Benefits, Purposes & Drawbacks of Scooters
-helpful for distances and navigating uneven/steep terrain
-good alternative to a manual W/C for people who have good trunk stability but poor strength/endurance for propelling W/C
-lighter/more portable/cheaper than power W/C
-less supportive/less customizable than power W/C
-larger turn radius than power WC
Wheelchair Arm Rest Types & Benefits (Detachable, Height Adjustable, Desk Arms, Full Arms, Wraparound)
Detachable
helpful for transfers
Height Adjustable
helpful for transfers
Helps to support lap tray
Desk Arms
allows person to move closer to work surfaces
Full Arms
Helps to support lap tray
Wraparound
AKA space saver arm rests
Reduces width of W/C by 1 in.
Wheelchair Foot Rest Types & Benefits (Swing-away, Detachable, Elevating, Limb Board)
Swing-away
helps for safe transfers and front approach to W/C without obstruction
Detachable
gives safe path for transfers
Elevating
good for edema management
Limb Board
provides support to residual limb after a LE amputation
Wheelchair Heel Loop Purpose
Prevent feet from slipping off footrest posteriorally
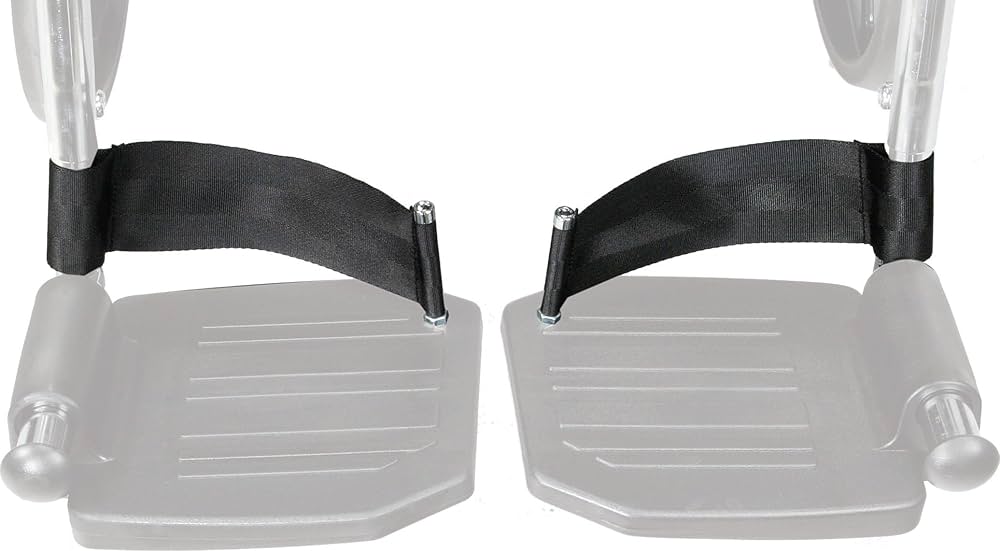

Wheelchair Arm Trough Purpose
-Support hypotonic UE
-Prevent edema through elevation
-Good for individuals with stroke/hemiplegia
-Lapboards can help with the same while also adding a surface to work on
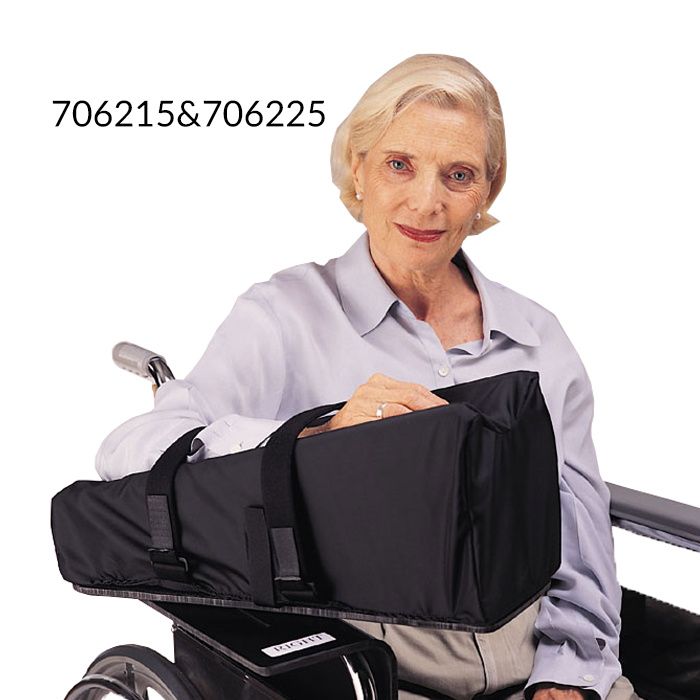

Wheelchair Head Support Purpose
-Improves neutral head positioning for better eye contact, communication, and feeding

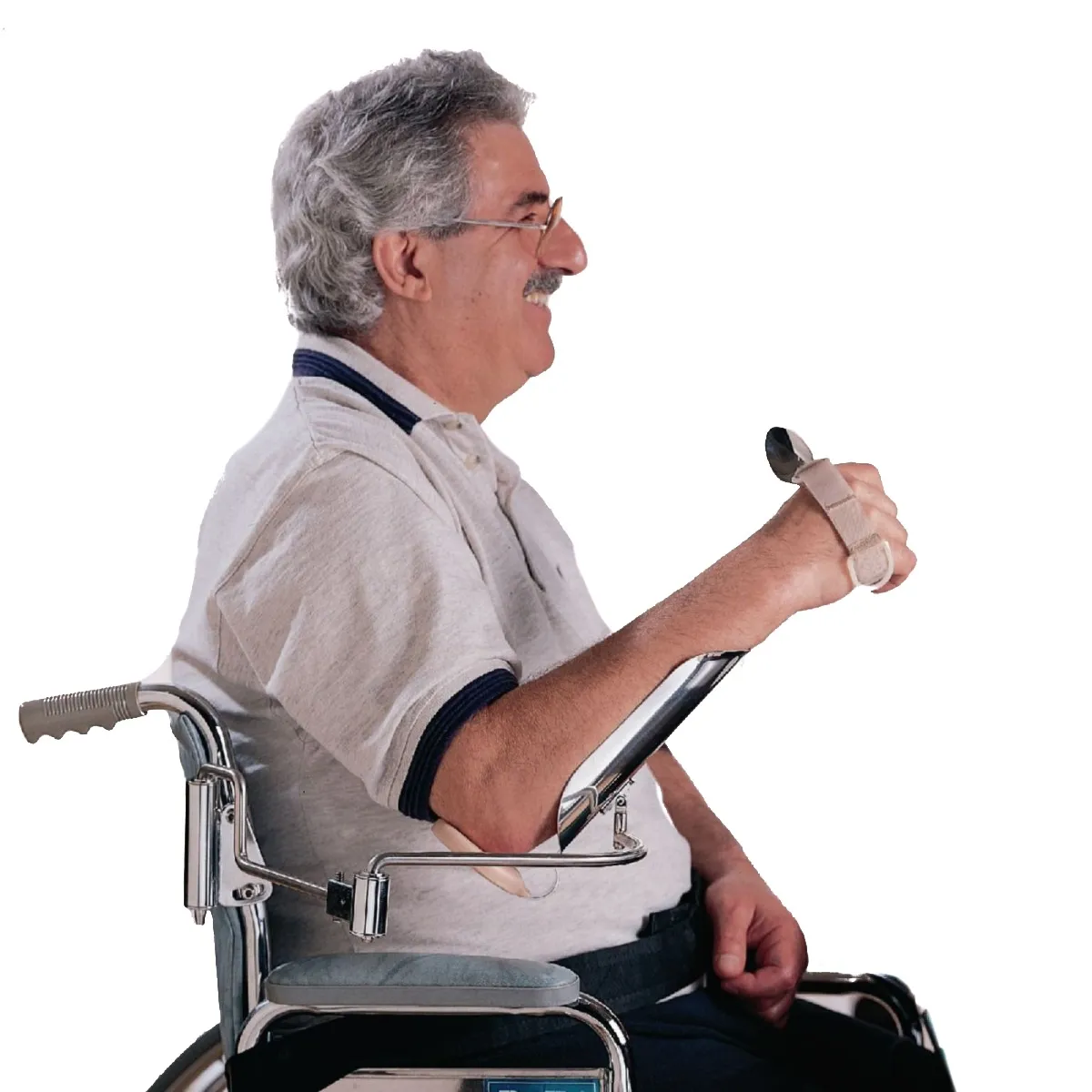
Mobile Arm Support Purpose
-Helps to use UE that has proximal weakness for feeding and other activities
-Useful for high level SCI pts

Pelvic Stabilizer
-Limits pelvic tilt/rotation/obliquity
-AKA belt, SubASIS bar
Thoracic Supports
-Facilitates trunk stability, prevents/slows scoliosis
Wheelchair Thigh Supports
-Help to control abduction/adduction of thighs
-Good for windswept deformity
Hand-Rim Projection Purpose & Drawback
-Help ind. with weak hand grip to propel independently
-Inc. width of W/C
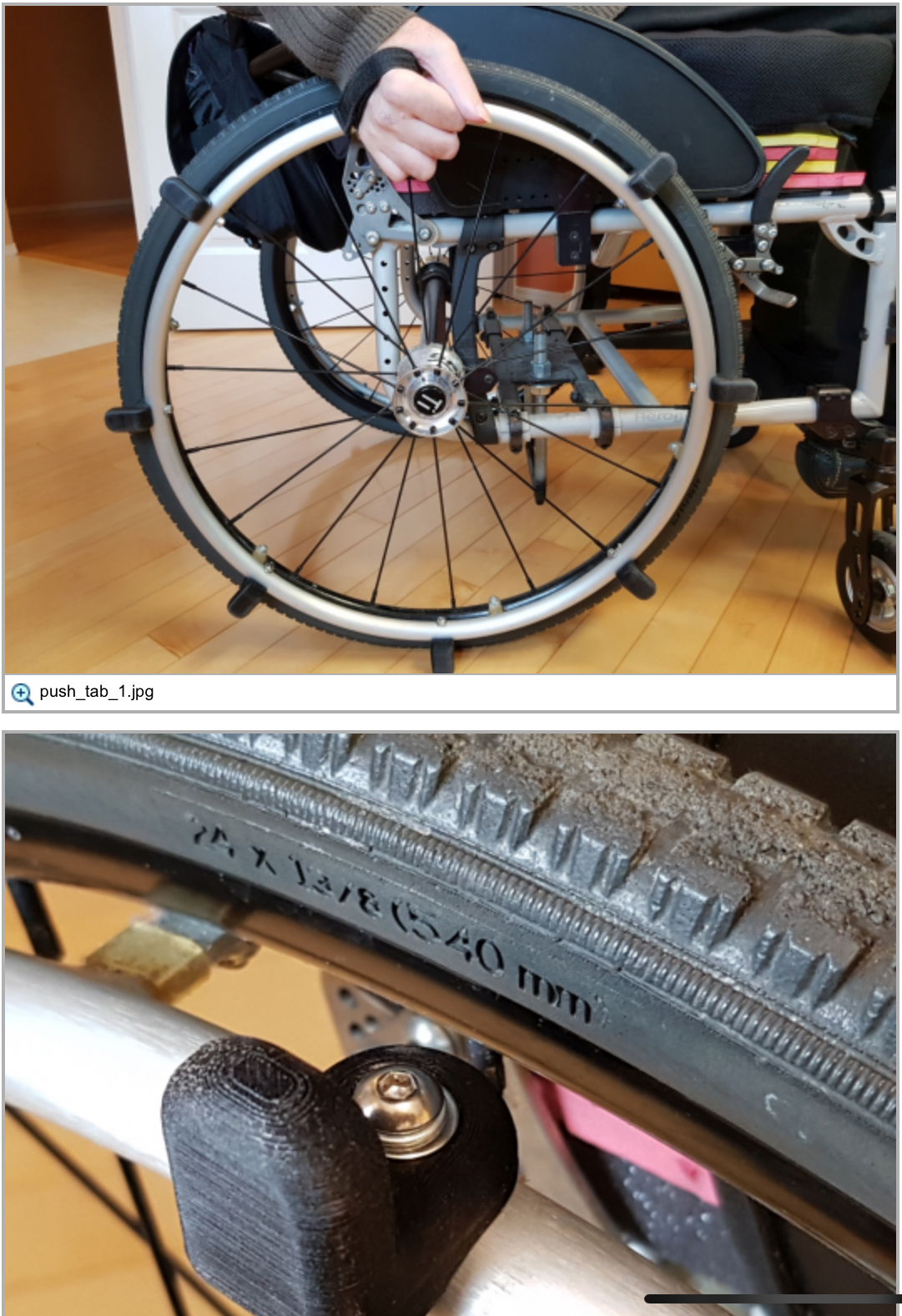

Hillholder Device Purpose
-Allow W/C to move forward but automatically brake when the chair goes backward with a level that attaches to each wheel
-Useful for ind. who have difficulty going up a steep grade without resting
What does increasing the camber (outward angle) of wheelchair wheels do?
Provides greater lateral stability, smoother ride, and increased maneuverability of W/C
⚡️helpful for W/C rugby

Standard Dimensions for Wheelchairs (Adult & Pediatric)
W/C Type | Seat Width (in.) | Seat Depth (in.) | Seat Height (in.) |
Std. Adult | 18 | 16 | 20 |
Narrow Adult | 16 | 16 | 20 |
Slim Adult | 14 | 16 | 20 |
Hemi-/Low Seat | 14 | 16 | 17.5 |
Junior | 16 | 16 | 18.5 |
Child | 14 | 11.5 | 18.75 |
Tiny Tot | 12 | 11.5 | 19.5 |
*Hemi-height W/C makes it easier for client to self-propel using their feet
What does observation of pt sitting on a mat table tell you? (Hands-free vs. hands-dependent vs. propped)
Hands-free
W/C can emphasize mobility, stability (stable base of support), and comfort
Hands-dependent
W/C needs pelvic and trunk support
Propped
W/C needs total body support
Wheelchair Custom Measurements
Seat Width
measure widest point at hips/thighs and add 2 in.
Seat Depth
measure between back of butt and back of knee (popliteal fossa) then subtract 2 in.
Measure both LEs and use SHORTEST length
This prevents rubbing that could lead to skin irritation/ulceration
Back Height
Varies depending on trunk control, size, activity level, and strength
Higher back height
Provides more support for person with weak trunk
Can make W/C harder to fit into car
Lower back height
Allows for better mobility
Useful for sports chairs
Seat Height
Knees/ankles should be positioned at 90 degrees
Measure from side of thigh to heel and use SHORTEST length between both LEs then add 2 in. To give clearance to floor
Remember seat cushion adds height
Armrest Height
Shoulders should be neutral with elbows flexed to 90 degrees
Measure under each elbow to cushioned seating surface
Armrests that are too low
Cause person to lean forward
Armrests that are too high
Cause shoulder elevation
Make self propelling difficult
Reason to Move W/C Rear Axle Forward
-To maximize stability for obese individuals since they have a center of mass that is further forward
-Allows for more efficient arm push that requires less wrist extension
-Makes propulsion easier to have axle in front of center of gravity, but reduces stability (add rear anti-tippers)
Reason to Move W/C Rear Axle Backward
-To maximize stability for individuals with LE amputations since they have a center of mass that is further backward
-May instead want to add anti-tippers in back to avoid tipping over backwards
Tilt-and-Reclining Wheelchair
-High back reclines independently of rest of the chair
-Provides pressure relief, regulates BP, improves respiration, and provides support for individuals who are unable to independently maintain upright sitting position
-Since these W/C extend angle of hips, they can elicit flexor/extensor spasms and SHOULD NOT be used with clients who have spasticity
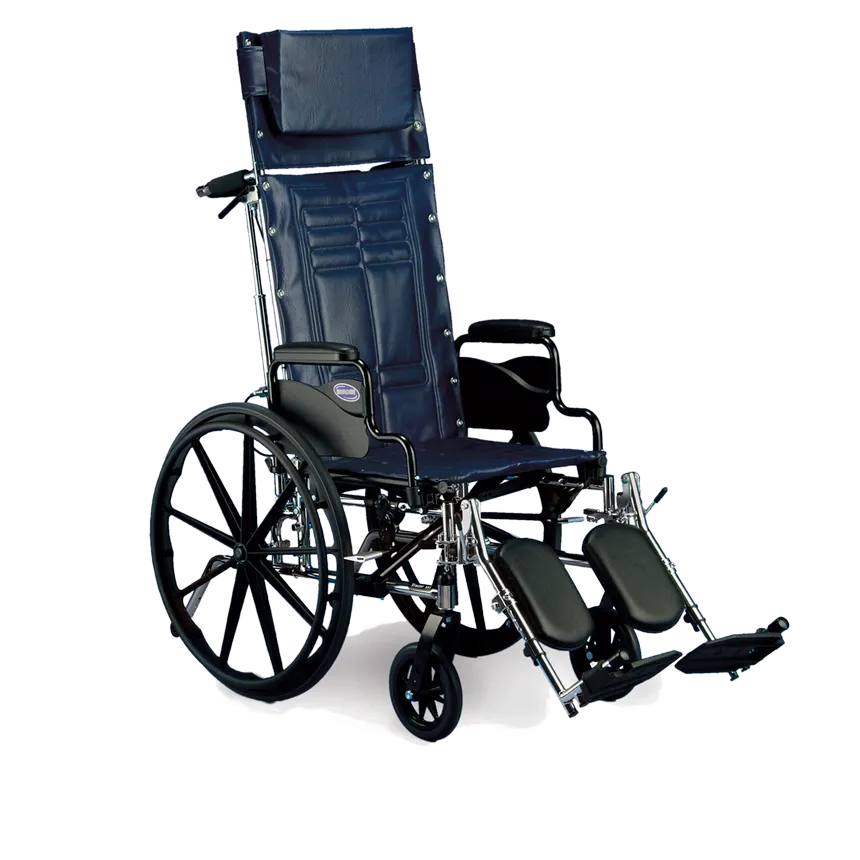

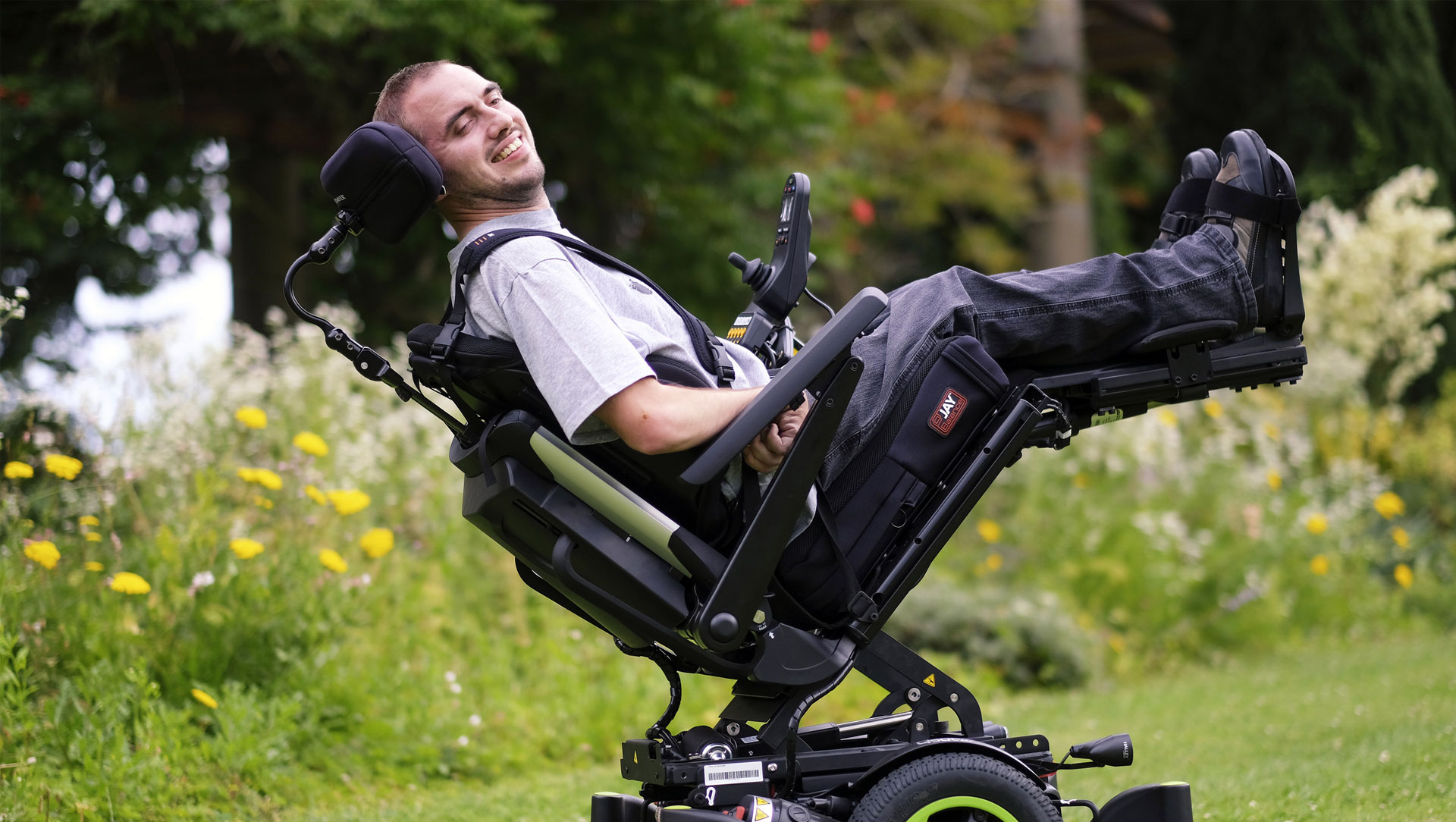
Tilt-in-space Wheelchair
-Entire seat and seat back tilt, maintaining 90 degree seated position
-Helps provide pressure relief, regulate BP, improve respiration, and mimics abnormal tone’s impact (like severe extensor spasms that can throw a person out of the chair)
⚡️Space Mountain (seat reclines like a rollercoaster)

One Arm Drive Wheelchair
-Individual can propel and steer W/C using cane-like device on one side
-Useful for clients with hemiplegia or a single UE amputation

Important Education to Provide for New Wheelchair Users
-Proper sitting posture
-Pressure relief methods and time schedule
typically weight shift every 15-30 mins
-Purpose and use of devices added to wheelchair (cushions, lapboard, etc.)
-Methods to propel W/C
-W/C safety
locks
Moving leg rests/arm rest for transfers
Safely using power W/C
How to fall from W/C and get back in as safely as possible
How to secure W/C on public transportation
-How to maneuver W/C through community
Wheelchair Cushions- Heavy vs. Light
-Light cushions often preferred by individuals who self-propel long distances
-Heavy cushions are more comfortable and are often preferred by individuals who spend long periods of time seated without propelling far
Passive (Static) Stander
-Remains in one place (CANNOT be self-propelled)

Prone Stander
-Requires good head control
-Can reduce effect of TLR
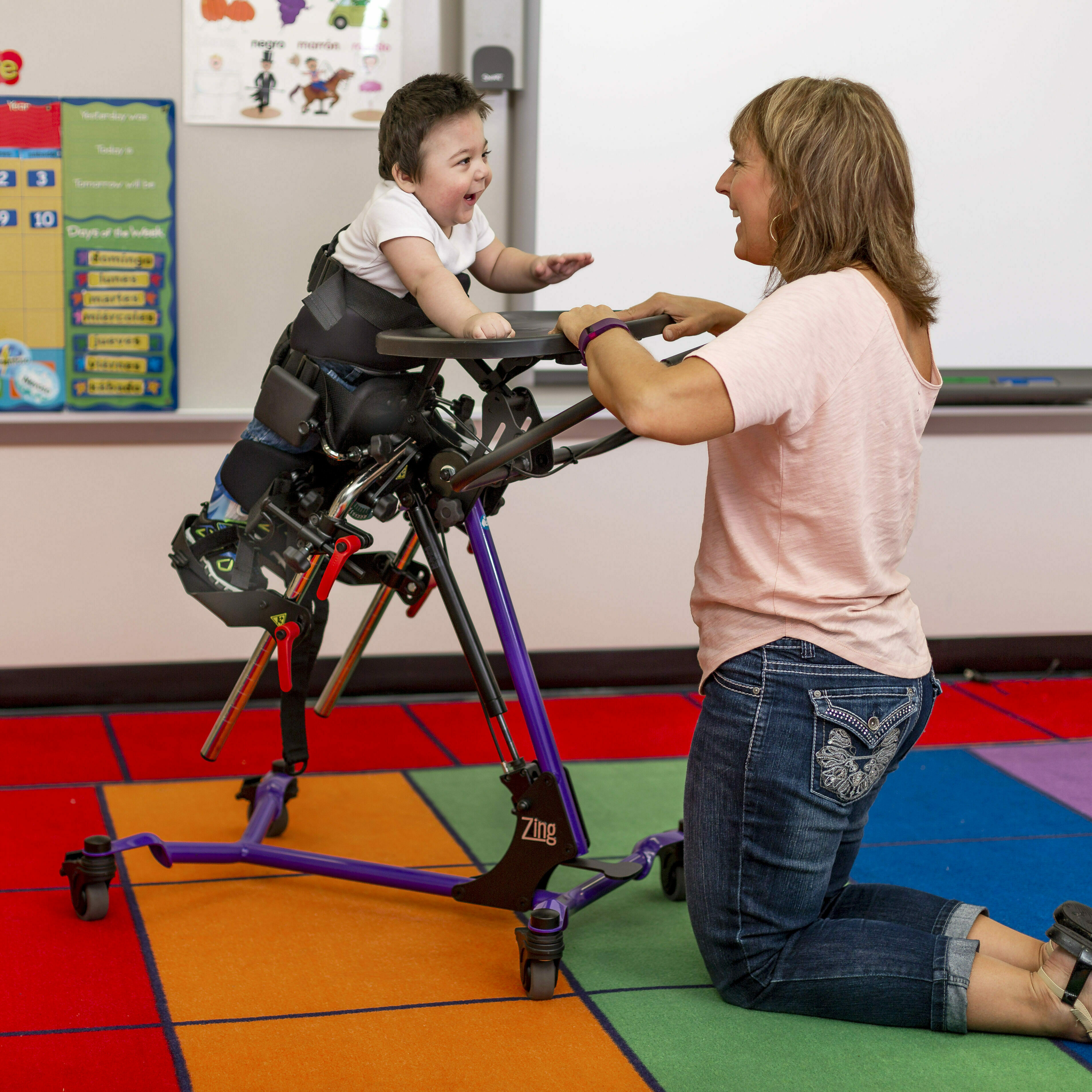

Dynamic Stander
-Stander remains stationary but ind. can move on base of stander
[Picture isn’t totally spot on]
![<p>-Stander remains stationary but ind. can move on base of stander</p><p>[Picture isn’t totally spot on]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/da9f21d2-e94b-4d14-8194-af20c34fea8e.jpg)
Positioning Cushions (see page 574 in TherapyEd)
-Anti-thrust
Keeps person from sliding forward
Key for pts who have tendency to push against back of W/C
May person with lumbar lordosis have a more neutrally positioned pelvis
-Wedge
Reduces forward sliding for person who slumps by angling them to slide towards the back of the chair
Useful for clients who have pelvic kyphosis
-Pommel
Helps keep hips/knees separated
Good to prevent shearing
Good post hip replacement
Blocks person from sliding out of chair
-Lateral Leaning Cushion
Corrects position for Ind. with pelvic obliquity/tendency to lean to one side
Different Cushion Materials
Air Filled
Lightweight
Even pressure relief
Bad for postural stability
Alternating Pressure
Provides scheduled pressure relief through alternating levels of inflation/deflation
Reduces postural stability
Foam
Lightweight
Cheap
Can flatten out over time
Heat and moisture can build up
Shearing and wight=shifting capability are reduced
Gel
Adequate for postural control/good postural stability
Sensitive to temperature
Heavy
Can Leak
Honeycomb-shaped Plastic
Lightweight compared to gel
More stable compared to air filled
Provides uneven pressure relief
How long can a custom W/C take to ship?
Up to 6 months
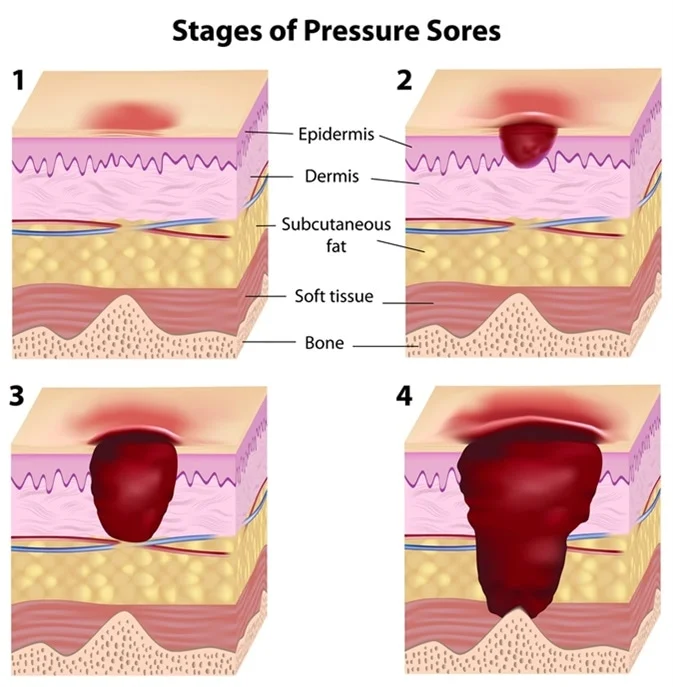
Ulcer Stages
Mobility-Related Activities of Daily Living (MRADLs)
-According to Medicare these include
toileting
Bathing
Grooming
Dressing
FeedinG
-For Medicare to cover mobility assistive equipment (MAE) they must help a person participate in otherwise impaired MRADLs
General Transfer Advice for Patients
-Anterior pelvic tilt (to move the center of mass over the center of the client’s body)
-Angle heels toward the surface to which the client is transferring (for easier pivot)
-Pushing up from transfer surface (i.e. bed/WC armrest) to assists in the transfer; client may also reach toward surface they are transferring to (i.e. bed or wheelchair)
Medicare WC Codes
Standard- K0001 (weighs 36 lbs or more)
Lightweight- K0003 (weighs 34-36 lbs)
High-strength Lightweight- K0004 (weighs less than 34 lbs and has adjustable frame)
Ultra-lightweight- K0005 (weighs less than 30 lbs, has adjustable rear axle, rear wheels have quick release, chair is more customizable)
Heavy-duty- K0006/K0007
Assessment of primary client factors that are essential for driving (e.g. cognition, vision, visual-perceptual skills, motor skills)
Driving Risk Assessment
A comprehensive blueprint for maintaining social participation through diverse means of community mobility as an alternative to independent driving or to facilitate transition process to a non-driver
Transportation Plan
True/False- Community mobility is the right of every person?
True
True/False- Driving is the right of every person?
False- driving is a licensed and regulated privilege
Public Transportation (Fixed-Route Systems, Demand-Responsive Systems, Paratransit Service)
Fixed-Route Systems
Use defined routes with predetermined stops on a schedule
Ex: bus, subway, train, light rail
Most economical and predictable
Demand-Responsive Systems
Transport for ind. with impairments that limit access to regular fixed-route systems
Rides are generated by calling transit operator
Transportation is provided between specific point of origin and specific requested destination (i.e. from supervised apartment to work)
Often multiple passengers with different destinations in same vehicle
Availability of physical assistance for riders varies
Paratransit Service
ADA compliant transportation that picks ideas up outside of their home and takes them to specific locations
Curb-to-curb- picks up passenger at curb of home and drops off at curb of destination
Drivers may assist with getting rider on and off vehicle, but not beyond the curb
Door-to-door- riders are assisted from doorway of origin to the entrance of their destination
Drivers do not assist beyond entries
Ex: van, shuttle, microbus
5 A’s for Determining Ideal Senior-Friendly Supplemental Transportation
Availability
Acceptability
Accessibility
Adaptability
Affordability
Assistance Levels of Supplemental Transportation
Door to door
Door through door- assists passengers to exit from their pickup spot to vehicle and enter into the building of their destination
Arm through arm- similar to door through door, but species physical assistance
Commercial Transportation
Airline/train- aka commercial carriers
Taxi
Rideshare
Shuttle/Van Service aka small-vehicle fleet
Safe, Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act
(SAFETEA)
-Creates safer environments around schools to encourage children to bike/walk to and from school
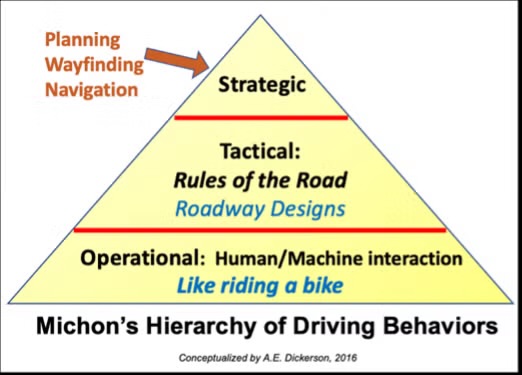
Hierarchy of Driving Behavior (3 Levels)
- Strategic Behaviors- general goal decisions (trip decisions)
Occur before/during driving
Can occur in minutes or hours
- Tactical Behaviors- conscious decisions made while operating a vehicle in response to changes in road conditions and traffic/driving risks (maneuvers, car handling, staying safe distance from other cars)
Can occur in seconds to minutes
- Operational Behaviors- primarily subconscious (steering, accelerating, turning, braking, backing up, parking)
Occur in seconds
Driving & Vision
-Acuity
test with Snellen chart
If corrected vision is WORSE than 20/40, refer to vision specialist
-Ocular Motor Skills
Fixation- ability to hold eyes steady
Saccades- ability to accurately change visual targets
Pursuits- ability of eyes to follow moving targets
-Visual Field- the more narrow the field, the more dangerous the driver
-Contrast Sensitivity- poor sensitivity is especially dangerous at night, in rain, or in fog
Commonly associated with cataracts and glaucoma
Visual Perception & Driving
-Visual closure skills are important because drivers need to be able to mentally “fill in the blanks” when part of environment is occluded
ex: part of sign is covered by tree branch
-Visual spatial skills are important because drivers need to know where they are relative to other drivers and objects in the environment
Cognition & Driving
-Limitations can lead to difficulty with finding the way, recognizing signs, dual-task driving, and could lead to increased distracted driving
-Minor limitation can be compensated for, but significant impairments warrant driving cessation
OT Driving Screening Skills & Tools
-Screen client’s reaction time, visual acuity, and decision making skills
-Common tools
General Assessment of Driving Related Skills (Clinician’s Guide to Assessing and Counseling Older Drivers)
Driving Health Inventory
OT-Drive Model
Motor-Free Visual Perception Test
Clock Drawing Test
Useful Field of View
Assessment of Motor and Process Skills
Trail-Making Test
-Refer to driving rehab specialist if there are concerns
General Assessment of Driving Related Skills (Clinician’s Guide to Assessing and Counseling Older Drivers)
Document from American Geriatric Society that includes screenings/assessments, clinical interventions, ethical/legal issues of driving, state licensing/reporting laws and medical conditions
Driving Health Inventory
Computer-based assessment that looks into various contributors to crash risk…
vision
Cognition
Motor function
OT-Drive Model
Model that helps with decision making about driving/community mobility
risk determination is based on evidence and clinical judgment
Motor-Free Visual Perception Test
Assesses various visual-perceptual abilities…
spatial relationships
visual closure
visual discrimination
visual memory
figure ground
Do not need to use any motor skills to make responses

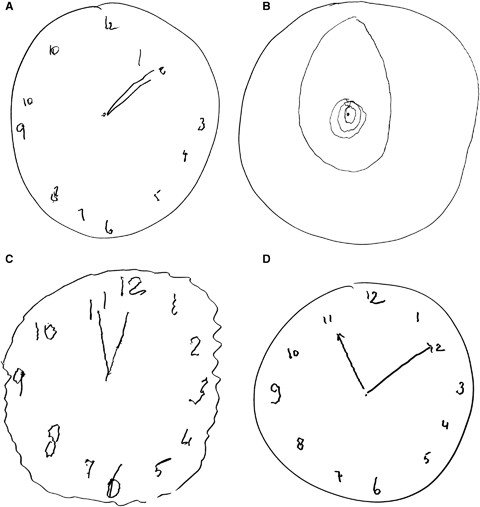
Clock Drawing Test
Can detect difficulties with visuospatial skills, visual perception, selective attention, memory, abstract thinking, and executive functioning
Useful Field of View
3-part computer-based cognitive assessment to determine crash risk by assessing…
central vision loss
cognitive processing speed
Divided attention
Selective attention

Assessment of Motor and Process Skills
-Standardized/observation-based assessment of quality of ADL performance
Trail-Making Test
Measure cognitive flexibility, motor control, perceptual complexity, visual scanning, and executive function
Driving Habits Questionnaire
Self-report that gathers info about avoidance behaviors that are often compensatory strategies in older drivers
Fitness-to-Drive Screening Measure Short-Form
Self-report with 21 items used to screen at-risk older drivers

Assessment of Readiness for Mobility Transitions
Assesses readiness of older adults to make transitions regarding mobility, including driving cessation
Assessment for Driving Related Skills (ADReS)
-Quick 10 minute clinic screening for driving related performance for DOCTORS/PHYSICIANS developed by AMA
When should OTs refer to certified driver rehab specialists?
When clients have community mobility issues that go beyond general evaluation and intervention
Driving Education, Adaptive Equipment & Compensatory Strategies
-Educate on visual scanning techniques
-Adaptive Equipment for Driving
HandyBar/Stander/Logan/Utah- gives stability for entering/exiting car
Leg Lifter- helps to position legs with weakness in/out of car
Manual/power seat lifts- help with transfers in/out of car
W/C Lifts/Ramps- help get W/C between street and car
-Compensatory Strategies for Driving
Only use familiar routes
Do NOT drive at night
Drive during off-peak hours
Avoid freeways
For visual field deficits clients can compensate with extra head turns and eye movements
Driver Rehab Adaptations
Many help for individuals with amputations/hemiplegia/ high level SCIs
Hand controls- replace gas and break foot pedals
Steering knobs- for one-handed steering control
Standard Round Spinning Knob- need one intact UE
Ring- accommodates prosthesis
Tri-Pin/Cuff- accommodates absent/weak grasp
Pedal extensions- help if feet do not reach standard pedals
Zero/Reduced Effort Steering- accommodates for decreased ROM, strength, and endurance
Back Up Camera- helps with limited neck mobility
CarFit
-Improves fit and use off vehicle to enhance performance and safety
-Developed by AAA, AARP, and AOTA
Driving Intervention Areas for Teens
increasing independence
Managing impulse control
Reducing stress
Regulating sensory input
Handling an emergency
OT Services/Supports for Driving Cessation/Inability to Begin Driving
Training in other transportation options
Introducing client to community mobility resources
Providing travel training for fixed-route transit systems
Developing community mobility plan
What ethical principle does reporting unsafe driving fall under?
Nonmaleficence