FORESTRY K1 '25 Flashcards (copied from Erin's <3)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
inner to outer tree layers
xylem, vascular cambium, active phloem, inactive phloem, phelloderm, cork cambium, phellem, periderm (aka outer bark)
secondary cortex parts
inactive/secondary phloem and phelloderm
Root plate
area covered by the 3-10 largest roots, located closest to the trunk and provide primary structural support for the tree
3 types of roots, from largest to smallest
structural roots (aka root plate), transport roots, and absorbing roots
what factors influence the growth pattern of roots?
water availability, gravity, oxygen availability, temperature extremes
terminal bud hormone
uses auxins to inhibit axillary buds
Preventitious lateral buds
formed during growing season, grows inside tree without creating new shoots until signaled by lateral bud or growth regulator
Adventitious lateral buds
form spontaneously at the time it's needed (ie wound, attack), shoot forms during the same growth season
twig year 1
shoot
twig year 2 and 3
branchlet
twig year 4+
branch
Describe how branches are connected to the main trunk using 3 vocab words (not counting trunk flange)
The branch bark ridge is the top of the connection. Located at the area of confluence between the branch and trunk, where xylem tissues criss cross together. On bottom of branch is the branch collar, where the trunk grows a little bit around the smaller branch
Semi evergreen trees
keep needles for a single growing season but never multiple years
does transpiration occur at night?
yes, pull from higher water still strong enough when stomata closed
Factors affecting transpiration rate
humidity, temperature, water availability
how do roots absorb water
transpiration pulls water up, creating an area of lower water pressure inside the root, so water flows in from outside
define mass flow
the movement of dissolved nutrients from the soil into roots. They are pulled through the soil along with water as transpiration pulls the water into the roots
what is translocation
the active transport of sugars from their areas of production (leaves) to where they are needed (rest of tree)
auxin
Control cell expansion & elongation, such as growing roots and shoots or tropism by telling cells where to bend. Created in shoot tips, flow to root tips
Cytokinins
Control cell division in shoots. Produced at root tips and transported to shoots via xylem to tell them if there are enough nutrients to grow or not
Giberellins
short, intermediate msgs, signal flowering and branch development
abiscic acid (ABA)
byproduct of photosynthesis that builds up and eventually inhibits auxins, causing leaf drop
CODIT
Compartmentalization of Decay in Trees
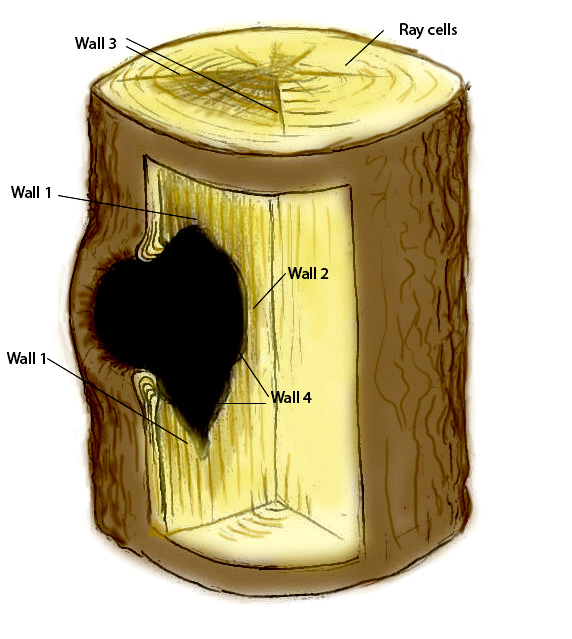
Wall 1
stops vertical spreading of decay by plugging top and bottom of xylem
Wall 2
stops inner spreading by creating a chemical defense in the annual rings inwards of the infection
Wall 3
stops transverse spreading by blocking plasmodesmata in ray cells surrounding the wound
reaction zones
wall 123, occur within first year of the wound
Wall 4
strongest wall b/c both physical and chemical. The cambium on outside of tree creates thick cells called the barrier zone, which prevents the decay from spreading into new growth
how long do root hairs last
2-3 weeks
List the parts of a root cross section from inwards out
Vascular tissue, pericycle, endodermis, cortex, exodermis, epidermis
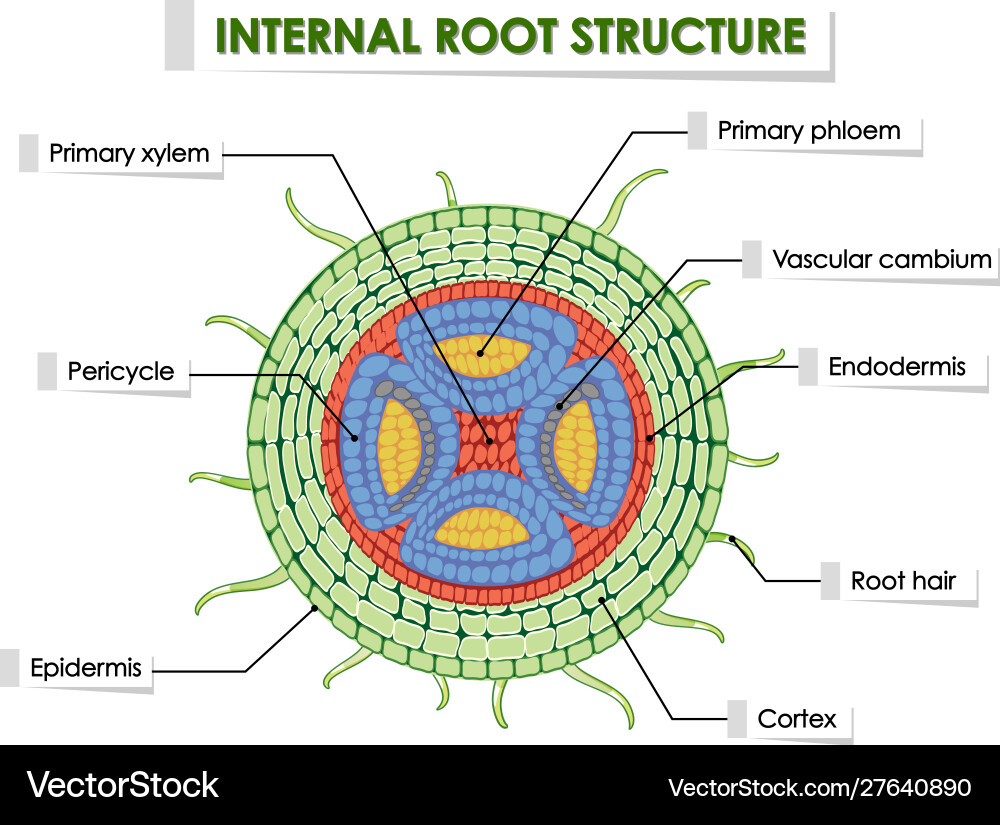
Root cortex 3 functions
transports water from epidermis to vascular tissue
stores energy as starch
separates endodermis from exodermis
epidermis function
partially dead cells, provides physical barrier for protection, insulation, gas control, basic nutrient absorption
Pericycle function
internal support for root, forms new lateral roots
exodermis function
living cells, continuously growing to replace dead epidermis cells
endodermis function
is watertight due to suberin coating and thus regulates water and nutrient movement into vascular tissue
sieve cells
helps roots separate nutrients and minerals from the absorbed water
pith made of
parenchyma with rings of xylem and phloem
inner bark
made of cells that transport sap and nutrients
how is heartwood different from sapwood
xylem cells are modified to be harder and more rot-resistant
xylem combines to form _, phloem combines to form
vessel elements, sieve tubes
xylem can transport water ____ while phloem can transport sugar solutions ____
only up tree, up and down tree
parenchyma cell function
soft and spongy cells that surround and nourish phloem and xylem cells. Make up most of tree’s volume
Fiber bundles
mostly made of cellulose, long slender cells usually found in bundles
optimal temp for photosynthesis
65-85F
how does photosynthesis change with light intensity
positive correlation until a certain point where it plateaus, different for every spcies
what % of water absorbed by roots used by transpiration
90%
If photosynthesis rate much higher than respiration rate
photosynthesis slows down or stops bc photosynthates cant be broken down
hardwood traits
angiosperm, have vascular tubes throughout wood which increase workability and density, more expensive bc grows slowly. Used for furniture and flooring
softwood traits
gymnosperm, usually completely changes its needles every 2 years. Wood is less dense due to tracheids instead of pores transporting nutrients. Used for cheap construction materials (plywood, particleboard) and pulpwood
when did the first gymnosperms emerge? Angiosperms?
319 mya, 150 mya
angiosperm vs gymnosperm species number
300-500k, 1k