Inline Assembly
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Why would we want to write Assembler within C?
Outsmart gcc logic
Specific optimisations
Close to the hardware programming (drivers)
Embed existing code fragments
Performance
Compilation Example

Breaking Down Function Execution
Caller stores arguments in registers or memory
Function call: caller transfers flow control to the callee
Callee acquires/allocates memory for doing work
Callee executes the function body
Callee stores the result in ‘some’ register
Callee deallocates memory
Function return: callee returns control the caller
Inline Assembly
GCC allows inline assembler
The compiler inserts assembler code in the code of its caller
This removes function call overheads (recall, function prolog)
The key word asm or asm is used to include code:
asm("assembly code");
Assembly is architecture-specific
You ARM assembly will not be transcoded into x86
You can also compile an assembly file into an obj file
Basic Inline Assembler

Extended Inline Assembler
The embedded assembler code must interact with C code
Parameters must be passed on to the assembler program
Results must be passed on to C code

Input/Output Operands
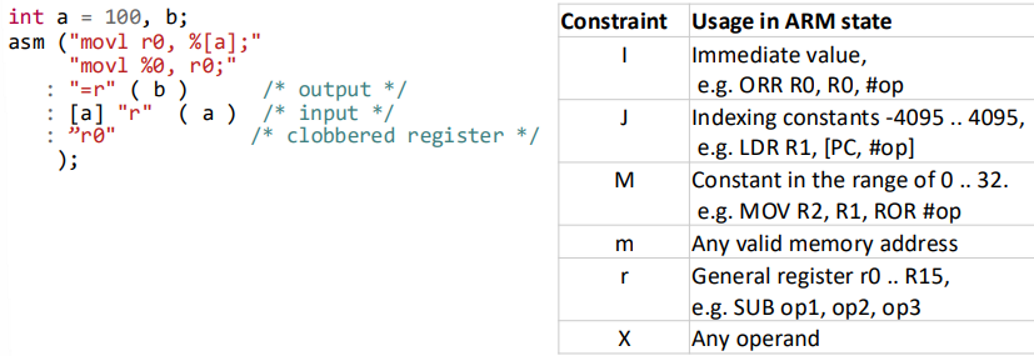
Register Allocation
A compiler must assign variables into processor register
Any two variable must not be assigned to the same register at any point
Use Spilling to store variable values
Coalescing will aim to optimize register allocation to reduce value copying
Graph colouring problem and liveness analysis
Volatile
Used for instructions with processor side-effects
Disable compiler optimizations, which might lead code block removal (compiling with flag -O1 or higher)
volatile asm("assemler");
__volatile__ asm(“assembler”);
Clobbered Register
r0 after the third colon tells GCC that the value of r0 is to be modified inside "asm", so GCC won’t use this register to store any other value
the list can also contain special arguments:
"cc": The instruction modifies the condition code flags (save psr)
"memory": The instruction accesses unknown memory addresses

Usage Example - MACRO
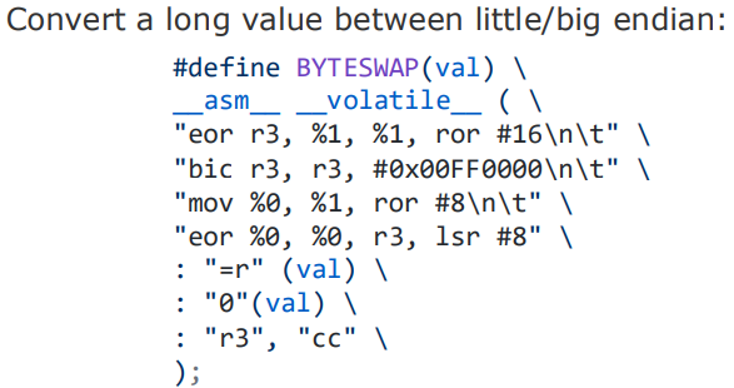
Usage Example - Interrupts
