Vaccines
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
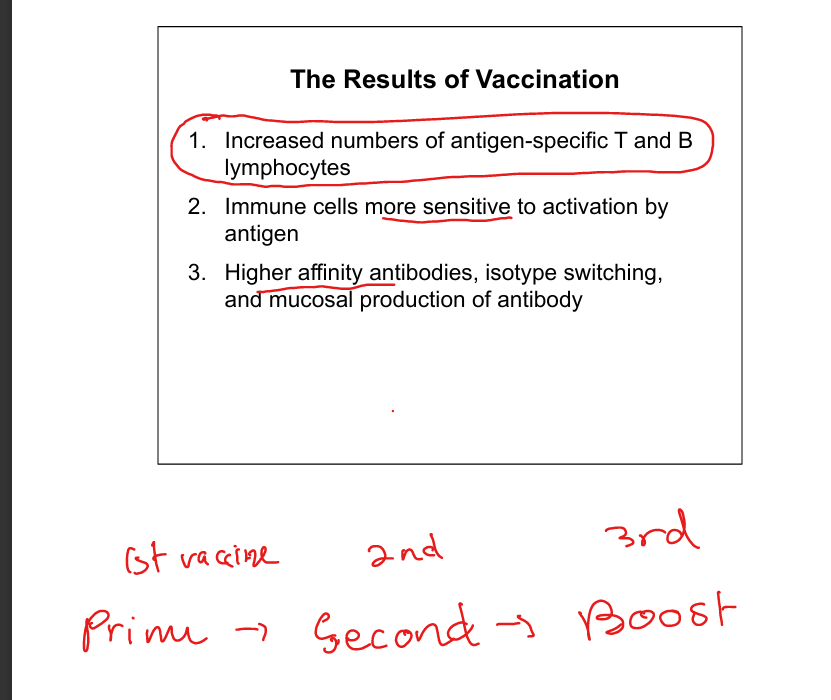
Results of vaccination
Increased antigen‑specific lymphocytes, heightened sensitivity to activation, higher‑affinity antibodies, isotype switching, and mucosal IgA.

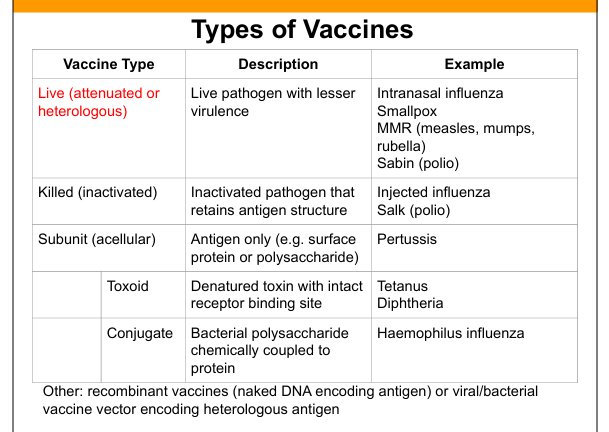
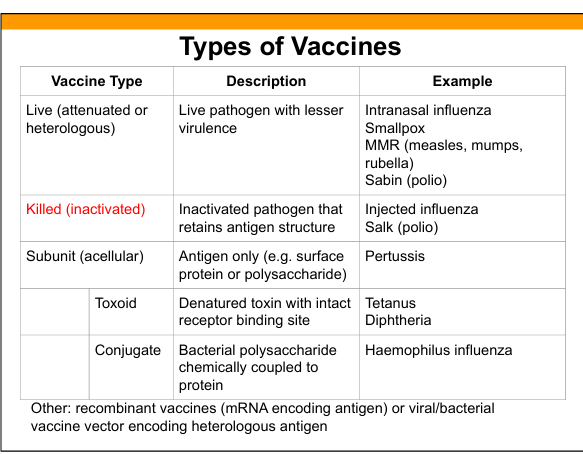
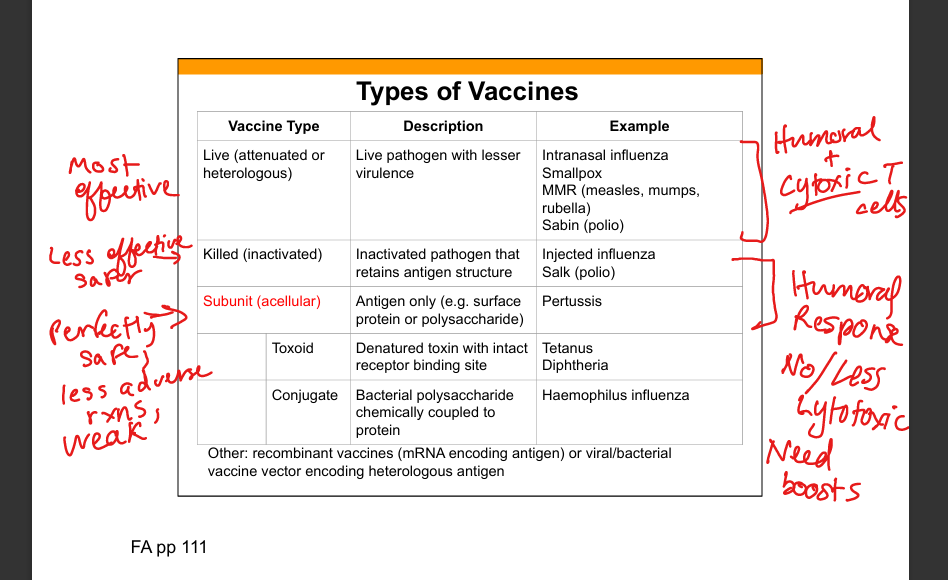
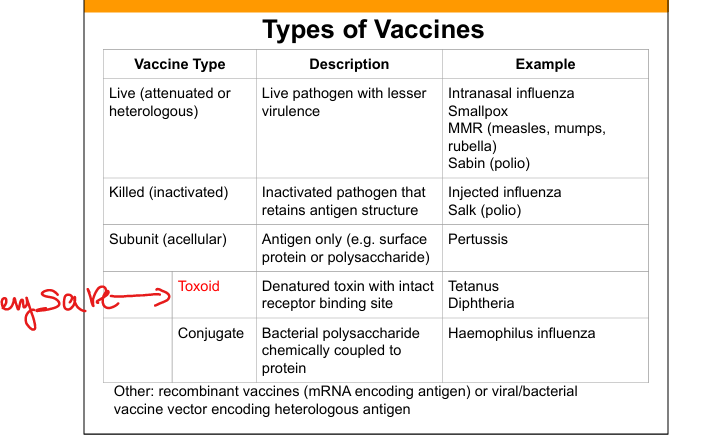
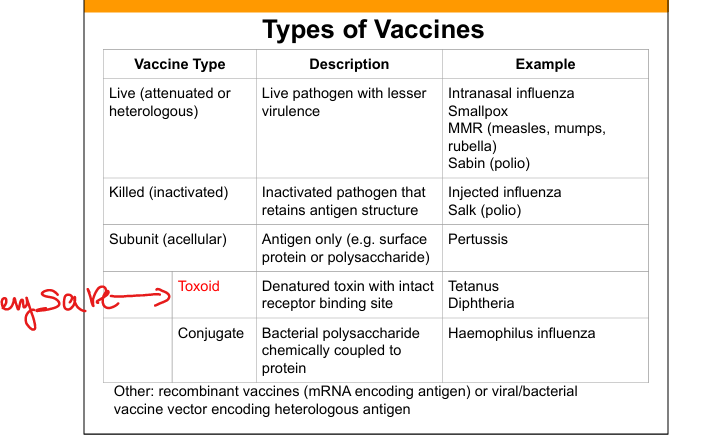
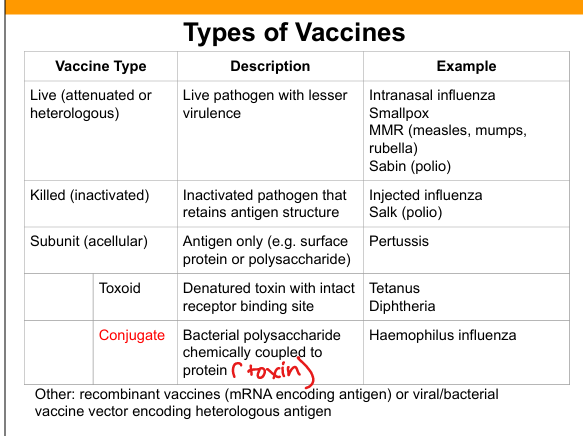
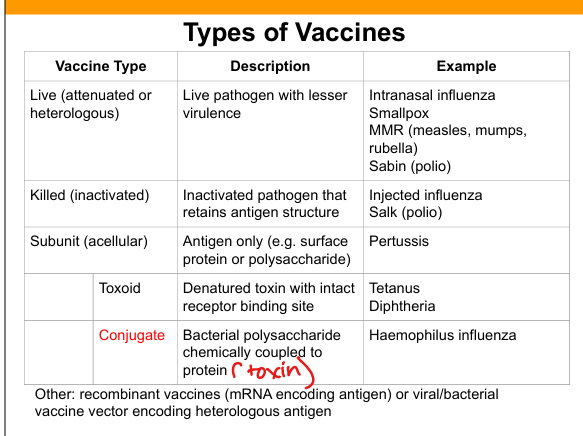
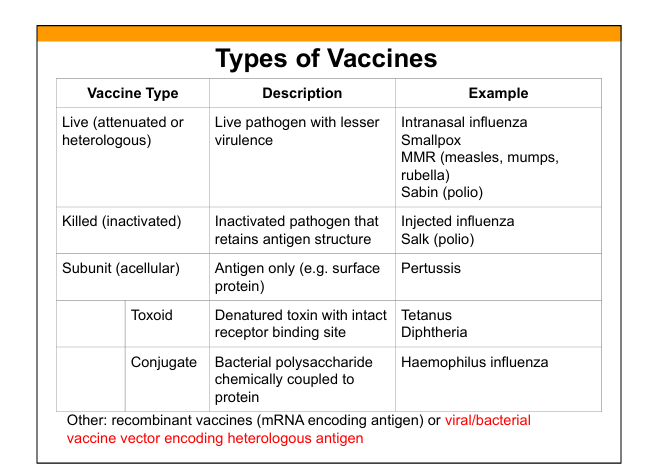
Live attenuated vaccine
Live pathogen with reduced virulence; induces strong humoral B-cells(IgG,IgA) and cellular immunity(T cells).
Examples of live attenuated vaccines
MMR, intranasal influenza, Sabin polio, smallpox, yellow fever.

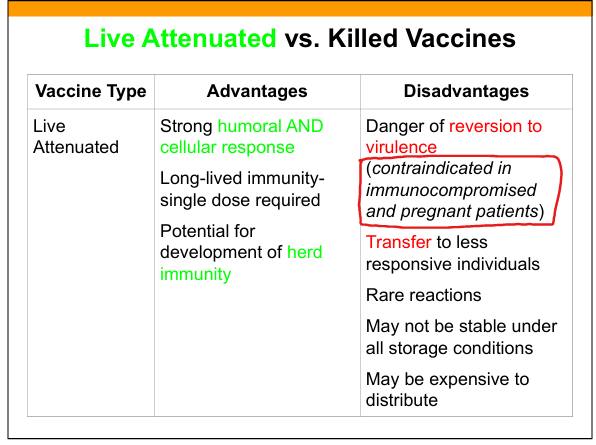
Advantages of live attenuated vaccines
Strong humoral + cellular immunity, long‑lasting, single dose, herd immunity.
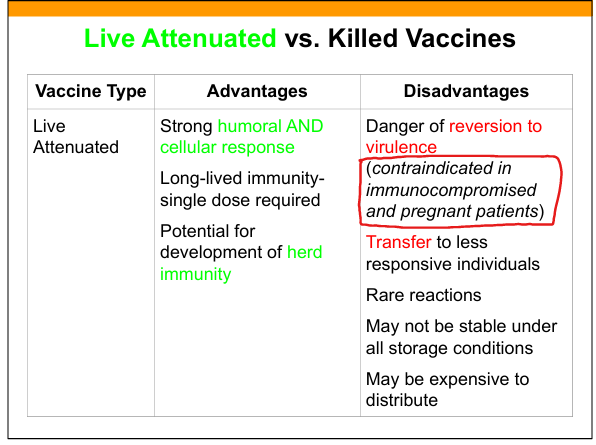

Disadvantages of live attenuated vaccines
Risk of reversion, contraindicated in immunocompromised/pregnant, unstable, rare adverse reactions.

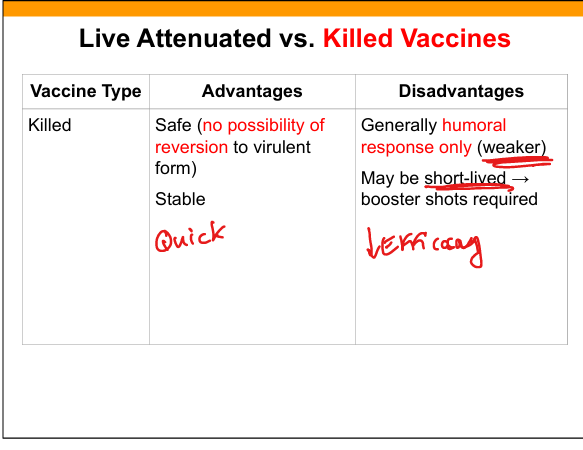
Killed (inactivated) vaccine
Pathogen is inactivated but antigenic structure preserved.
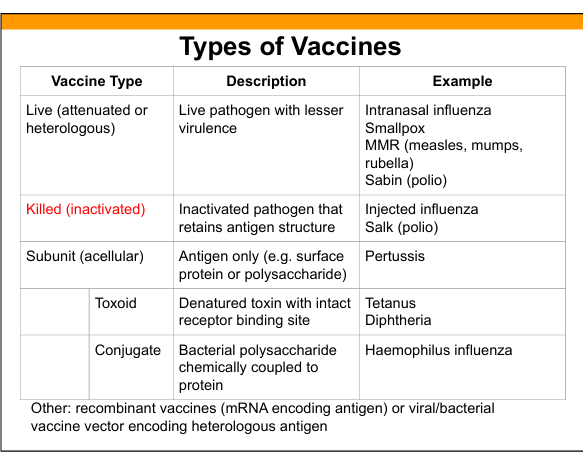

Examples of killed vaccines
Injected influenza, Salk polio.

Advantages of killed vaccines
Safe, no reversion, stable.
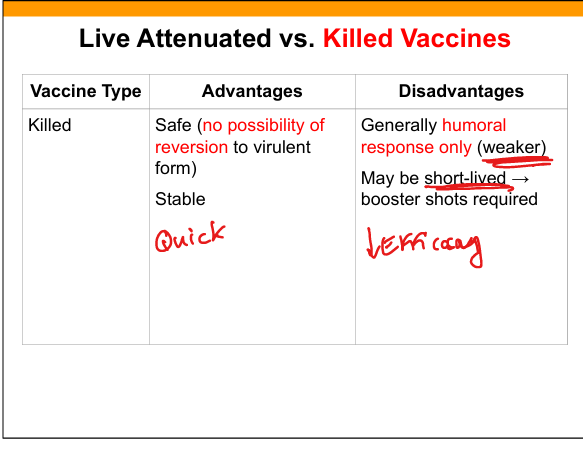

Disadvantages of killed vaccines
Primarily humoral response(B cells), weaker, boosters required.

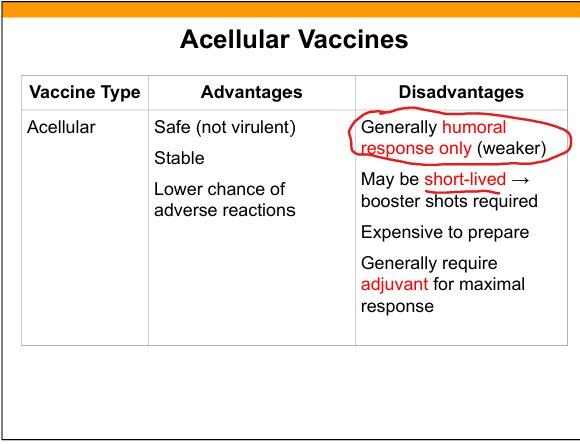
Subunit (acellular) vaccine
Contains purified antigen only (protein or polysaccharide).
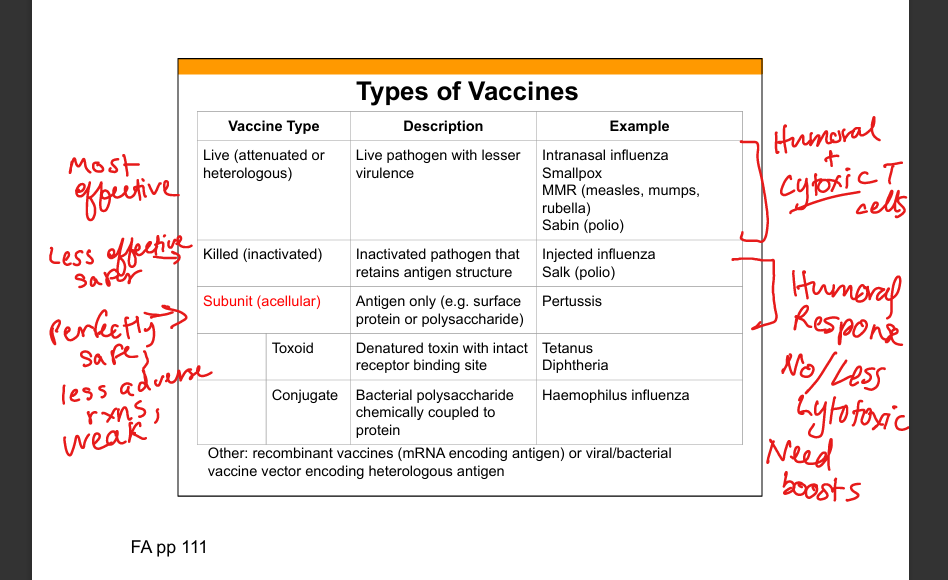

Examples of subunit vaccines
Pertussis, hepatitis B surface antigen.

Advantages of subunit(acellular) vaccines
Safe, stable, fewer adverse reactions.
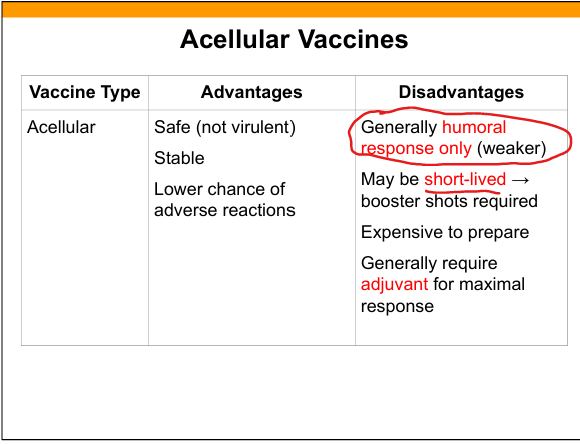

Disadvantages of subunit vaccines
Weaker immunity(Humoral), short‑lived, expensive, often require adjuvants.

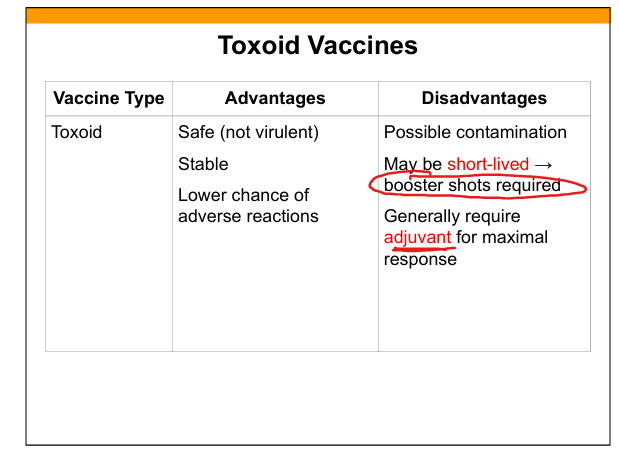
Toxoid vaccine
Denatured toxin retaining receptor‑binding site to induce antitoxin antibodies.

Examples of toxoid vaccines
Tetanus, diphtheria.

Advantages of toxoid vaccines
Safe, stable, low adverse reactions.
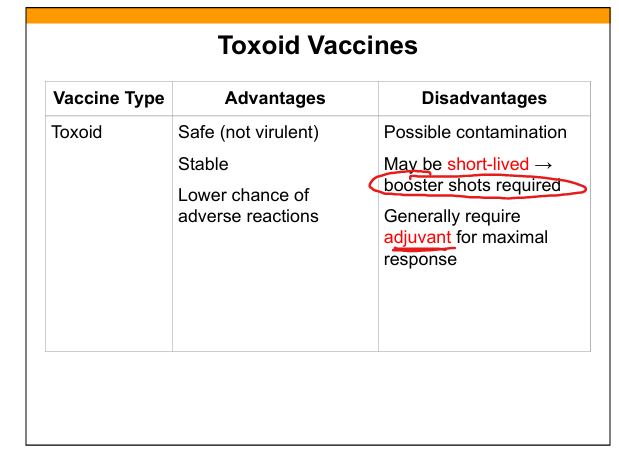

Disadvantages of toxoid vaccines
Short‑lived, require boosters, may need adjuvants.

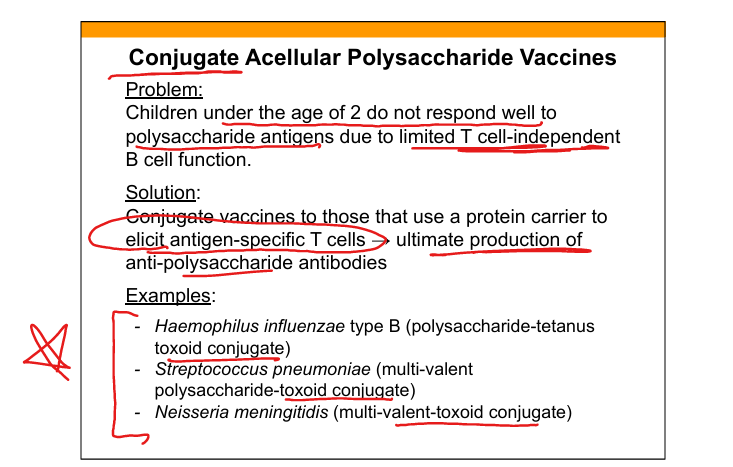
Conjugate vaccine
Polysaccharide antigen chemically linked to protein carrier to induce T‑dependent response.

Examples of conjugate vaccines
Hib, pneumococcal conjugate, meningococcal conjugate.

Purpose of conjugate vaccines
Convert T‑independent polysaccharide antigens into T‑dependent forms for infants.

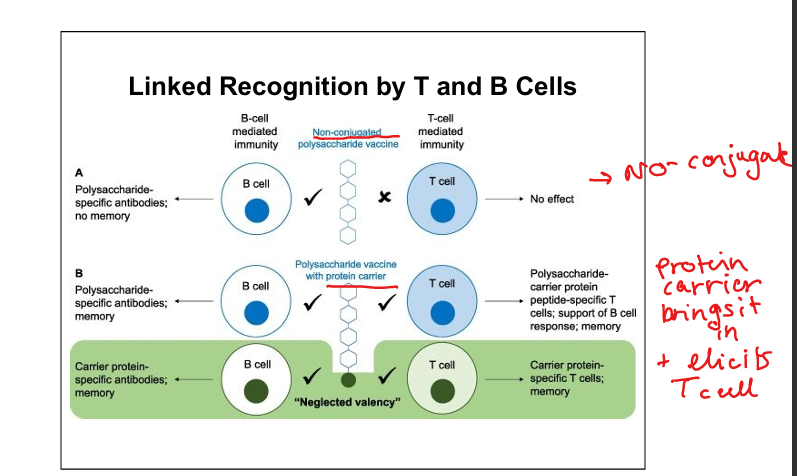
Linked recognition
B cell binds polysaccharide; presents carrier protein peptide to CD4 T cells; T cells help B cells produce anti‑polysaccharide antibodies.

Recombinant vaccines
Vaccines using mRNA or viral/bacterial vectors encoding antigen.

Examples of recombinant vaccines
mRNA COVID‑19 vaccines, adenovirus‑based vaccines.
Targeting vaccines: required immune response
Depends on pathogen: neutralizing antibody (polio), Cytotoxic T cells (HIV), mucosal IgA (respiratory/enteric pathogens).


TLR agonists in vaccines
Promote dendritic cell maturation and shift Th1/Th2 balance.


Adjuvant definition
Substances that enhance immune responses by activating innate immunity and dendritic cells.


Purpose of adjuvants
Increase immunogenicity of weak antigens and promote dendritic cell maturation.
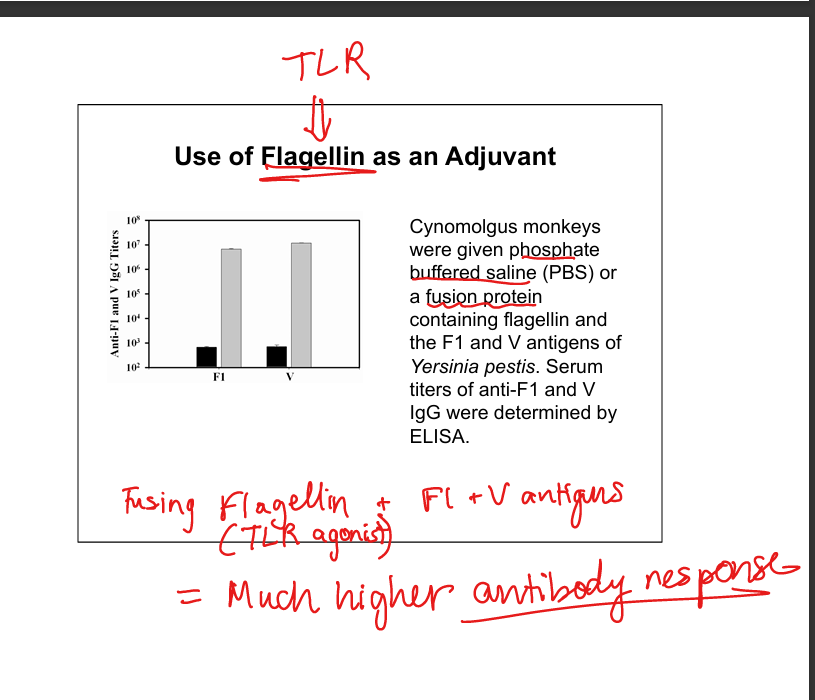
Flagellin as adjuvant
TLR5 agonist that enhances antibody responses and protection.