Lecture 2: General Features of Bacteria
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Bacteria are prokaryotes that are small and simple, they have no _________ or _______-_____ nucleus
Organelles, membrane-bound
What are the 2 main ways that bacteria transfer genes?
Vertical gene transfer
Binary Fission (aka asexual reproduction)
Horizontal gene transfer
Via extrachromosomal and mobile genetic elements
What are some advantages of replication via binary fission?
Only one parent cell is needed to reproduce
Daughter cells are clones of the parent
Rapid Division
Produce great #s quickly
Define Generation Time
The average time it takes for one bacterium to divide and give rise to 2 daughter cells
A bacteria with a quick replication time that caused disease would likely be associated with ____ onset of symptoms, and vice versa
Acute
Why do we study bacterial structure and function?:
It aids in identifying the disease for diagnosis
Aids in our understanding of pathogenic mechanisms and pathogenesis of diseases caused by bacteria
Helps us to develop therapeutics and vaccines
What are the 3 broad categories that make up the structure of bacteria cells?
Cell envelope
Cytoplasmic structures
Nuclear body
ribosomes
inclusions
spores
Surface receptors
Capsule
Flagella
Fimbriae/pili
Which is larger prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes
What are the 3 main shapes of bacteria?
Coccus
Spherical
Rod
Bacilli
Spirochete
Spiral
Define staphylococcus
A clump of spherical shaped cells
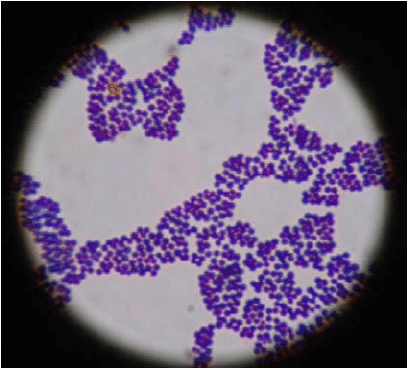
T/F: Both gram ± bacteria have peptidoglycans
True, Gram + has more peptidoglycans than Gram -
Which of these structures is only present in gram + bacteria?
Thin cell wall
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Layer
Thin single-layer of peptidoglycan
Teichoic Acids
Two periplasmic spaces
4
Which type of bacteria has a thick peptidoglycan layer?
Gram + Bacteria
What are teichoic acids? Where are they found?
Anionic polymers that form a significant part of the cell wall in most Gram-positive bacteria, serving structural and functional roles
LPS are only found in gram _ bacteria
-
The LPS makes up the ________ layer of Gram - bacteria, an example of an LPS in this layer is Lipid A, what does it do?
It is an endotoxin that induces fever
The cell envelope (cell wall+ associated structures) is made up of 4 components/categories, what are they? What is their function?
Structural support and protection
Maintains shape of the wall
Selective Barrier/Transport
Porins
In gram - only
Allow passage of small molecules
Teichoic Acids
In gram + only
Help regulate movement of cations
Enzymes in the cell wall
The enzymes help to..
Break down complex nutrients
Make nutrients easier to transport across the cell membrane
Virulence and Immune Evasion
Surface proteins in the wall
They adhere to host tissue
They resist phagocytosis or antibody attack
Which color does Gram + bacteria stain?
Purple
Which color does Gram - bacteria stain?
Pink
Why does Gram + bacteria stain purple? What causes them to retain that stain?
The highly cross-linked and thick layer of peptidoglycan
Why does Gram - bacteria stain pink? What causes them to retain that stain?
Since it lacks the thick peptidoglycan layer it can’t retain the stain when the decolorizer is added
So, when the pink (safarin) stain is added after then it takes it up
T/F: You cannot get false +s when using gram staining
False, you can due to human error
Examples
Over/under colorization
Thick smears
Excessive heat used to fix
Excessive washing
What is gram variable staining? Is it natural or human error?
Gram variable staining is when you get both gram ± cells
Natural, some species have ± versions of their bacteria
T/F: Gram + bacteria will always stain gram + IF there is no human error
False, some bacteria can be Gram + and just be resistant to stain
This would be things like thick lipid layers, etc.
Define Atrichous vs Peritrichous
Atrichous is bacteria that don’t have flagella
Peritrichous are bacteria that do have flagella
What are flagella?
They are filamentous appendages that allow bacteria to move in liquid environments
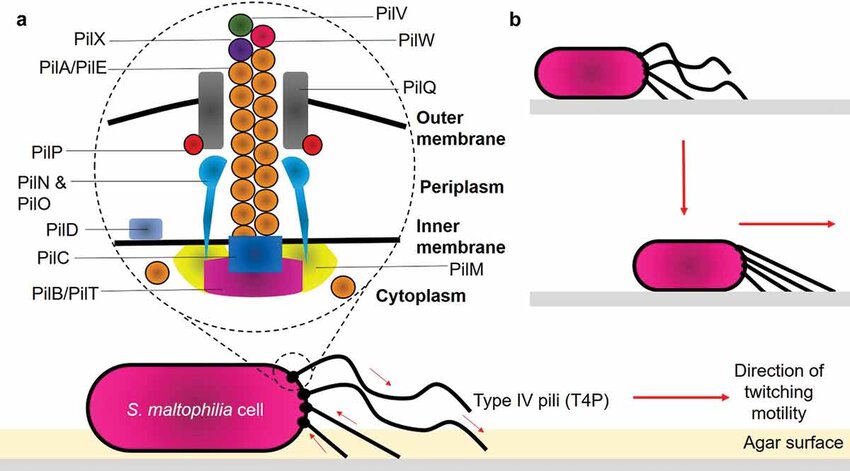
What are Pili?
Thread like appendages, smaller than flagella
Mainly found in Gram -
They are used for adhesion and conjugation
Short attachment pili (aka fimbriae)
Long conjugation Pili (Sex pili)
What is the difference between Pili and Flagella
Flagella are used for movement in liquids, Pili are used to adhesion and conjugation (and for gliding/twitching motility)
Type _ Pili provide bacteria with motility on solid surfaces
Type IV Pili
They provide twitching and gliding motility
Act like a grappling hook
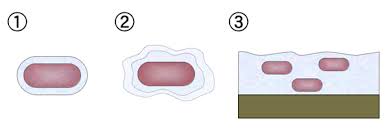
Define these 3 similar terms
Capsule
Slime Layer
Biofilm
A well organized thick, gelatinous outer covering that is outside of the bacterial cell wall
Loose, unorganized, easily removable gel-coating outside of the bacterial cell wall
Structured community of bacteria enclosed in a self-produced slime matrix attached to the surface
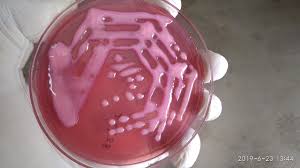
Encapsulated bacteria produce ______ colonies
Mucoid
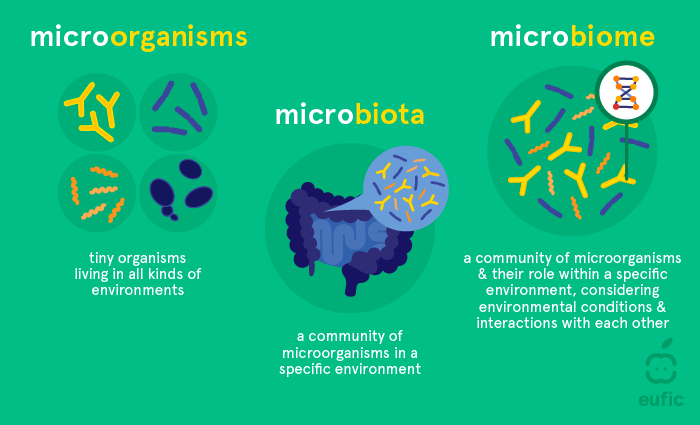
Describe the difference between Microbiota and Microbiome
Microbiota
The community of living microorganisms in a specific environment
Microbiome
The entire ecosystem of the microorganisms, the genetic material and the surrounding environment
T/F: Microbiomes are important to all animals health
True
What is the term that goes with this definition?
Highly resistant, dormant structures formed inside certain bacteria that allow the bacteria to survive extreme conditions
Endospores
T/F: The structure of the bacterial cell envelope determines whether the organism is gram-positive or gram-negative
True
T/F: Gram + bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall and an extra outer membrane
False, This is Gram -
T/F: The outermost layer of the gram + cell envelope is LPS
False, this is Gram -
T/F: Bacteria use flagella and pili for movement in different environments
True
T/F: Microbiome is a monomicrobial community
False
T/F: Endospores can germinate into vegetative cells when conditions become favorable
True
T/F: Bacterial capsule facilitate host immune recognition and phagocytic killing
False