component 3 plant transport
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
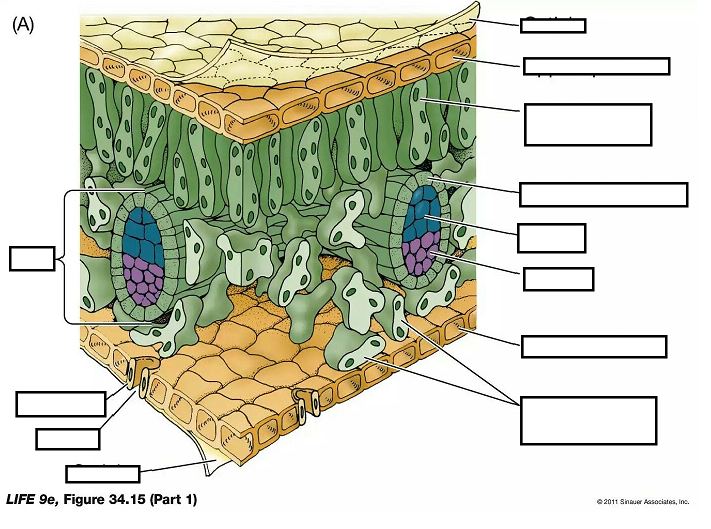
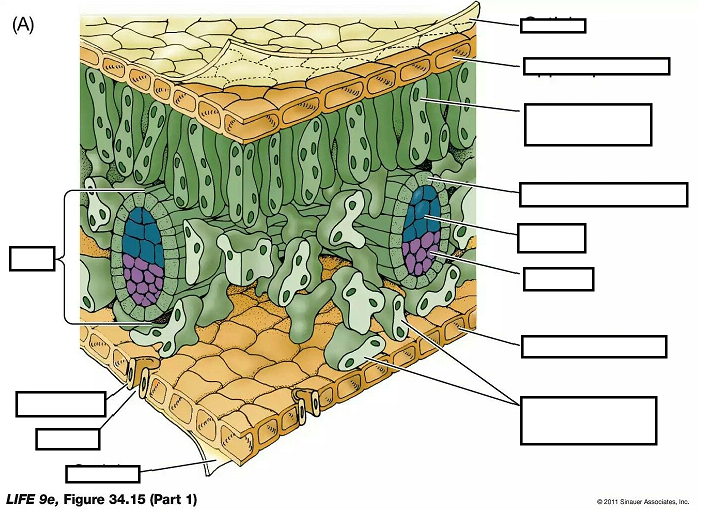
what does a large surface area of leaf allow for gas exchange and photosynthesis
allows for more stomata for gas exchange allows more light to be absorbed as there are more chloroplasts for photosynphesis
what does a thin leaf allow for gas exchange and for photosynthesis
gas exchange: short diffusion pathway
photosynthesis: allows light to penetrate leaf so absorbed by all cells
what does a transparent leaf allow for in photosynthesis
can pass into leaf for photosynthesis
what does long palasade cells full of chloroplast allow for in photosythesis
maximise the light absorbed packed cells together with as many chloroplasts as possible
what does airspaces in leaf allow for in photosynthesis and gas exchange
gas exchange: allow free diffusion of gasses between stomata and cell
photosynthesis: allow co2 to diffuse to photosythesising cell
what does stomata in leaf allow for in gas exchange and photosynthesis
gas exchange: allows gases to enter and leave leaf
photosynthesis:allow co2 in leaf
what is primarily happening in leaf in day
photosynthesis
what is primarily happening in night in leaf and why
respiration no light for photosynthesis
in the day what is relation ship between o2 and co2 in leaf
as more photosynthesis than respiration so co2 is taken in and o2 is given out
in the night what is the relationship between co2 and o2
in night more respiration than photosynphesis so o2 in co2 out
what is the function of the waxy cuticle and what is it made off
stops water being lost made of lipid
what is the function of guard cell
used to controll water loss and gas exchange in stomata
how do guard cells open
need a lower waterpotential so k+ ions activly transported in guard cell with atp from photosynthesis and insoluble starch converted into soluble sugar
so water moves into guard cell down a water potential gradient by osmosis
guard cell becomes turgid so stomata opens because cellulose is thicker next to stomata causing the guard cell to bend
how do guard cells close
need a higher water potential so k+ ions facilitated diffusion out of cell down conc gradient soluble matate converted into starch
so water moves out of cell by osmosis
guard cell becomes flacid so stomata closes
how can a practicle to find stomatal density be done
add a thin layer of nail varnish in a half cm squared section on the bottom of leaf
place piece of tape over the varnish and peel away
place tape on a slide then on a microscope stage count stomata in the highest power then use pi r squared to find area of eye pieve and use stomata to find density
what should be controlled in stomata density practicle
humidity
airflow
what does standard deviation show
the spread of data around the mean the lower the standard deviation the more reliable the result
what are the features of a mesophyte
few stomata on upper surface
many stomata on lower surface to reduce water loss
waxy cuticle on upper surface to avoid water loss
no cuticle on lower surface
air spaces present to allow diffusion
no hairs
what are features of a xerophyte
many stomata on upper surface
no stomata on lower surface
thick waxy cuticle on upper surface
thick waxy cuticle on rolled leaves lower surface
air spaces present
hairs present
sunken stomata
rolled leaves
what are features of a hydrophyte
stomata present only on upper surface
little to no waxy cuticle on upper none on lower as water loss not needed to be prevented
large airspaces for boyency
no hair
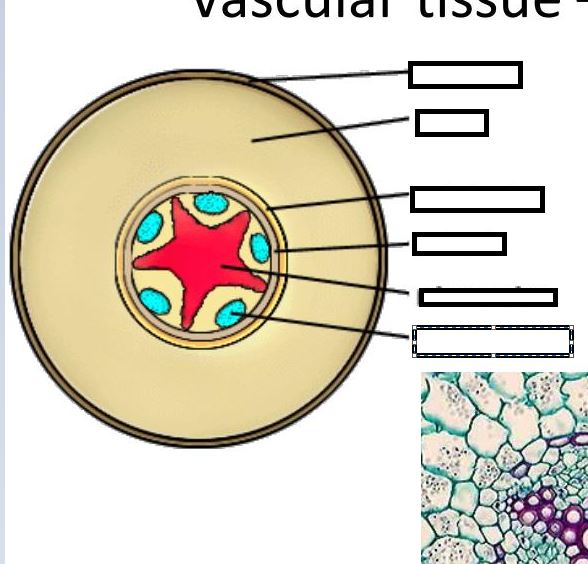

what is the symplast pathway
water moves through the cytoplasm and plasmodensmata
what is the apoplast pathway
water moves through cellulose cell walls through
what is the vascuolar pathway
water moves through vacoules cytoplasm and plasmodensmata
what is the casparian strip
surronds cells of endodermis prevents water and minerals from seeping between cells to get into vascualr cylinder water must pass through cell membranes
why does cohesion cause water to enter leaves
water molecules are attracted to each other so trasnpiration at leaf causes a transpitarion stream
why does adhesion cause water to enter leaves
due to attraction water will move upwards when tubes are narrow like xylem
how does root pressure cause water to enter leaves
nitrate ions are activly transported into cell of endodermis this lowers the water potential in that area causing water to move in via osmosis this created hydrostatic pressure forcing water in the xylem up
what is parenchyma
living tissue
what is the xylem made off
tracheids and vessels
what is the function of trachieds
provide support as narrow
what are pits in xylem
gaps in lignin allowing water to leave tube
why is xylem imperiable
made of dead material called lignin
what are the factors that affect transpiration
humidity as humidity inc trans dec
temp as temp inc trans inc
airflow as airflow inc trans inc
light intensity as light inc trans inc
why does water uptake not equal water used in traspiration
water could be used in photosynthesis
some stays in cell to make turgid
used in hydrolysis
made by respiration
what are the 9 steps of transpiration
water evaporates from surface of epidermal cell
water diffuses from sub stomatal chamber into atmosphere
water evapotates from cellulose cell wall of palaside and spongy mesophyll into sub stomatal chamber
water moves through leaf tissues via apoplast symplast and vascuolar pathway into leaf
water leaves xylem via vessels with little ligninification moves into apoplast due to cohesion and other pathways by osmosis
water is drawn up xylem as transpiration causes neg pressure in xylem so water forms a continous stream due to cohesion and adhesion
water enters xylem through porly ligninfied cell walls due to cohesion from apoplast and osmosis from other pathways
casparian strip prevents water enetering between cells water must go though a cell membrane
water is uptaken by ososis along a water into root hair cells
why does inc temp inc transpiration
higher temp inc ke of water so they diffuse more quickly
warm air also has more ke and holds more water
why does inc in humidity dec transpiration
dry air outside creates a steeper diffusion gradient
why does inc in air movment in transpiration
blows air maintaining conc gradient allowing more transpiration
why does inc in light intenstity inc transpiration
affects degree of opening and closing of stomata
how can tranpiration of a plant be messured
use a potometer
1.cut shoot underwater to stop air entering xylem
cut shoot at a slant to inc surface area
check apperatus is full of water
insert shoot into apparatus under water
shut screw clip
remove potometer from water and ensure airtight joints around shoot use vaseline
dry leaves and leave in constant conditions
messure how far air bubble moves
what is an example of a source in a plant
leaves (where sugar is made)
what is an example of a sink in plants
growing areas (where sugar is stored)
explain mass flow and how it is used to transport materials
source contains lots of material so low water potential water enters source by osmosis inc hydrostatic pressure
fluid is pushed from an area of high hydrostatic pressure to and area of low hydrostatic pressure
fluid enters sink material is used to water potential increases and h20 leves dec hydrostatic pressure
what are the 6 steps of translocation
h+ is activly transported from companion cell into source cell
h+ ions move back into compaion cell when combined with sucrose in co transport down dif grad
sucrose diffuses into sieve tube element by diffusion through paslmodensmata
low water potential in sieve tube so water moves into sieve tube by osmosis inc hydrostatic presussure
at sink sucrose is removed and stored raising water potential water moves into xylem out of sink dec hydro static pressure
phloem sap is pushed from source to sink down a pressure gradient
what is the experimental evidence for translocation ( mass flow)
ringning expermiment (removal of phloem) shows accumulation of sucrose products on leaf side of ring but none on root. therfore sucrose was blocked by removal of phloem. so phloem is route of transport
using aphids to sample sap. aphid stylus extends into sieve tube laser is used to remove stylus sap drips out can be analysed to show that succrose is carried in phloem both above and below leaves and high pressure in phloem
radioactive labelling of co2 which will become incorporated into sucrose can be used in conjunction with aphids to determin rate of transpiration
source and sinks can be determined by autoadiogrpahy using radioacitve co2
what is the evidence against mass flow
sieve plates impede flow
traslocation is faster than expected with diffusion
this theory doesnt explain bidrectional flow or diffrent rates of flow of sucrose and amino acids
does not explain companion cell mitochondria high o2 intake or stopping of translocation by cyanide but not transpiration
what is alternative theory to mass flow
streaming in cytoplasm of sieve tubes could be resposible for bidirectional movment
what is translocation
Sugars produced in photosynthesis are transported from the leaves (source) to other parts of the plant (sink) for respiration and other processes.
what is transpiration
the process of water movment through the plant