anatomy exam 3 iupui
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
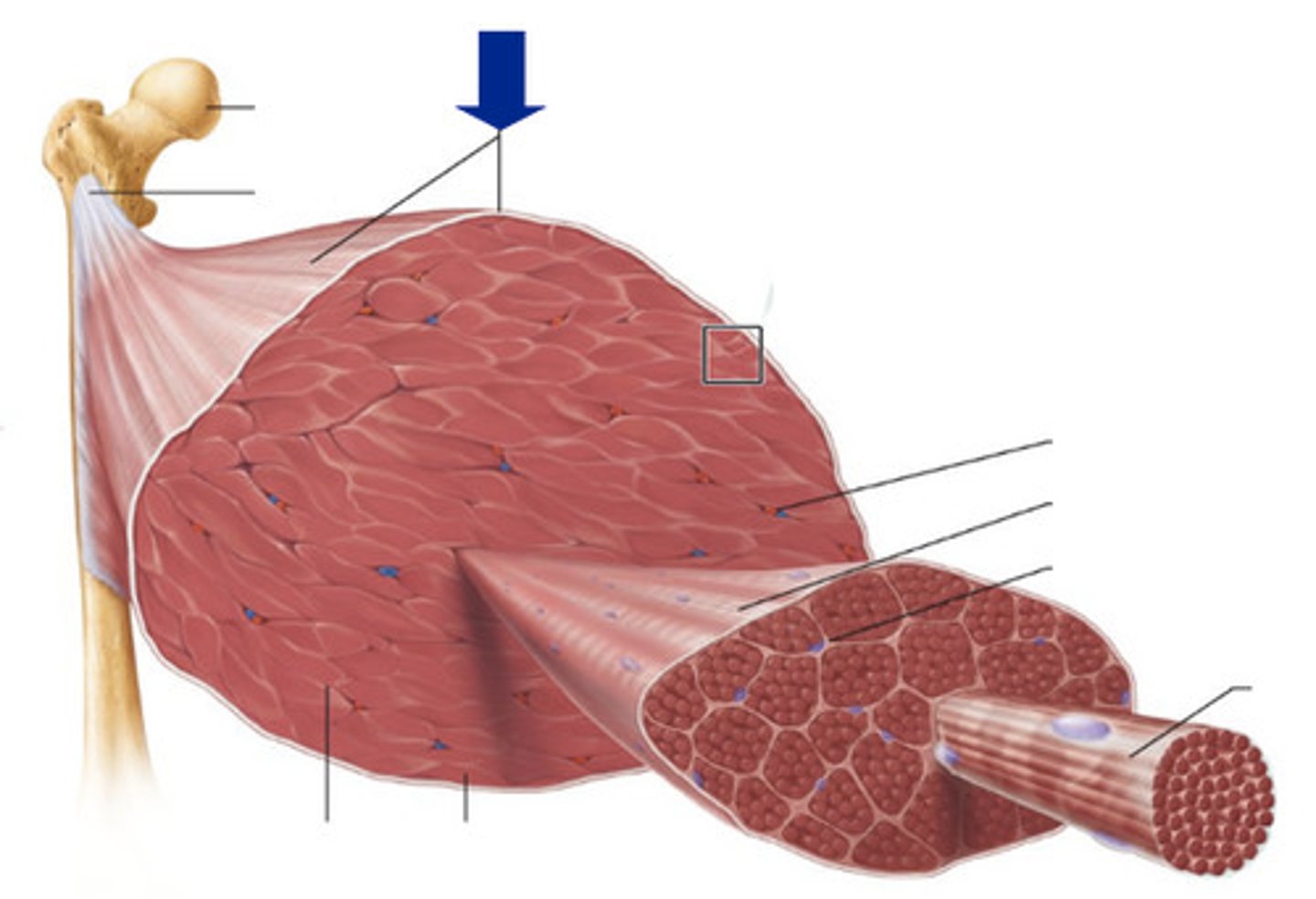
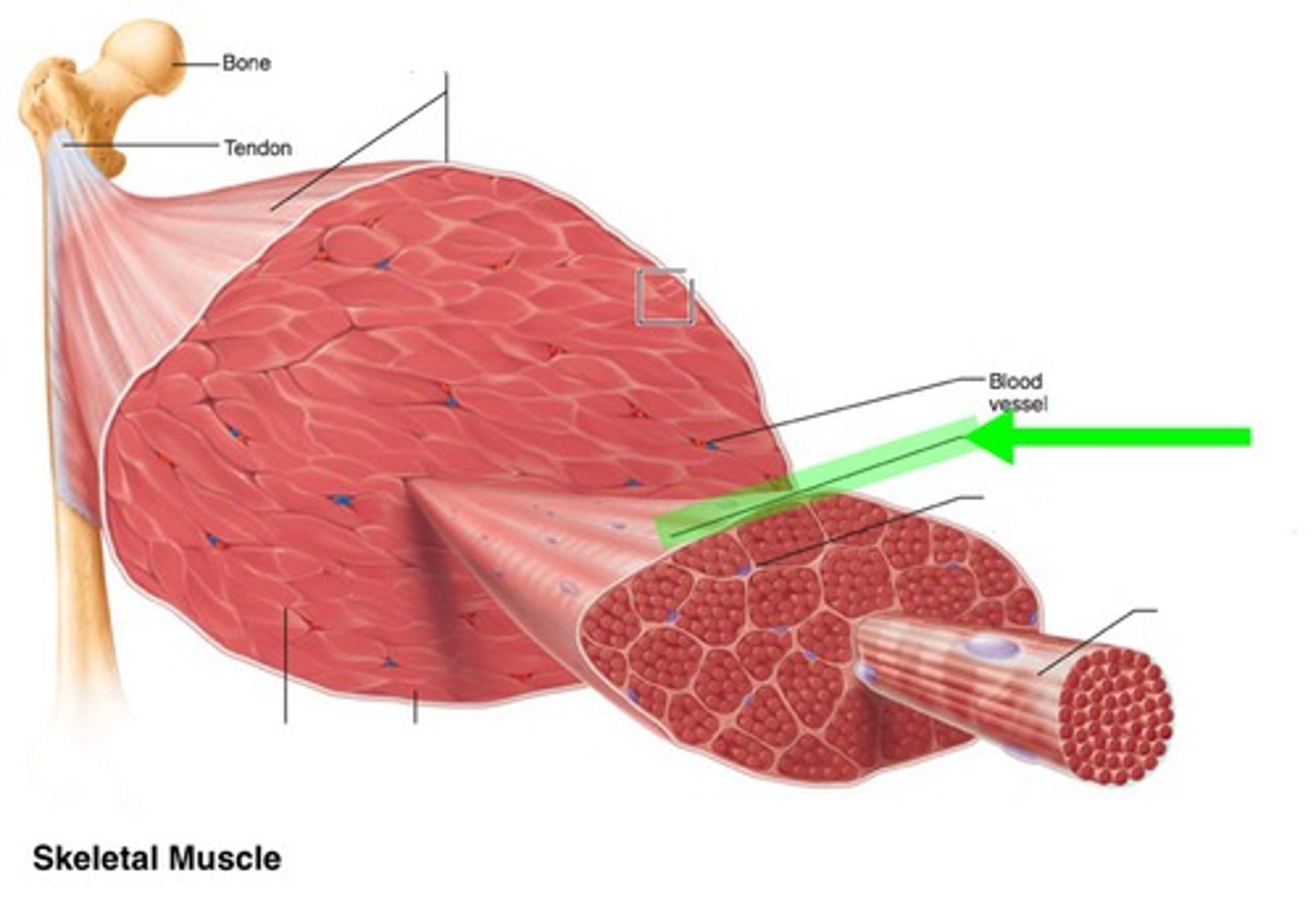
muscle fiber
muscle cell
epimysium
surrounds entire muscle
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
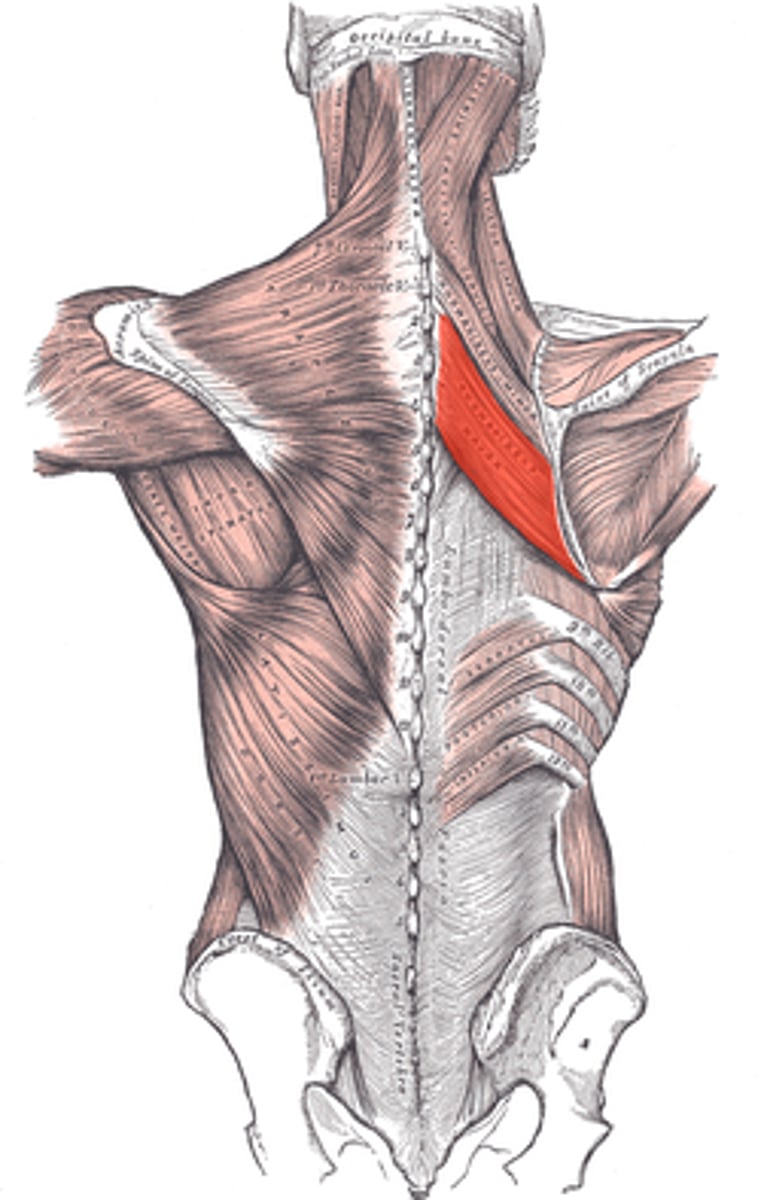
epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
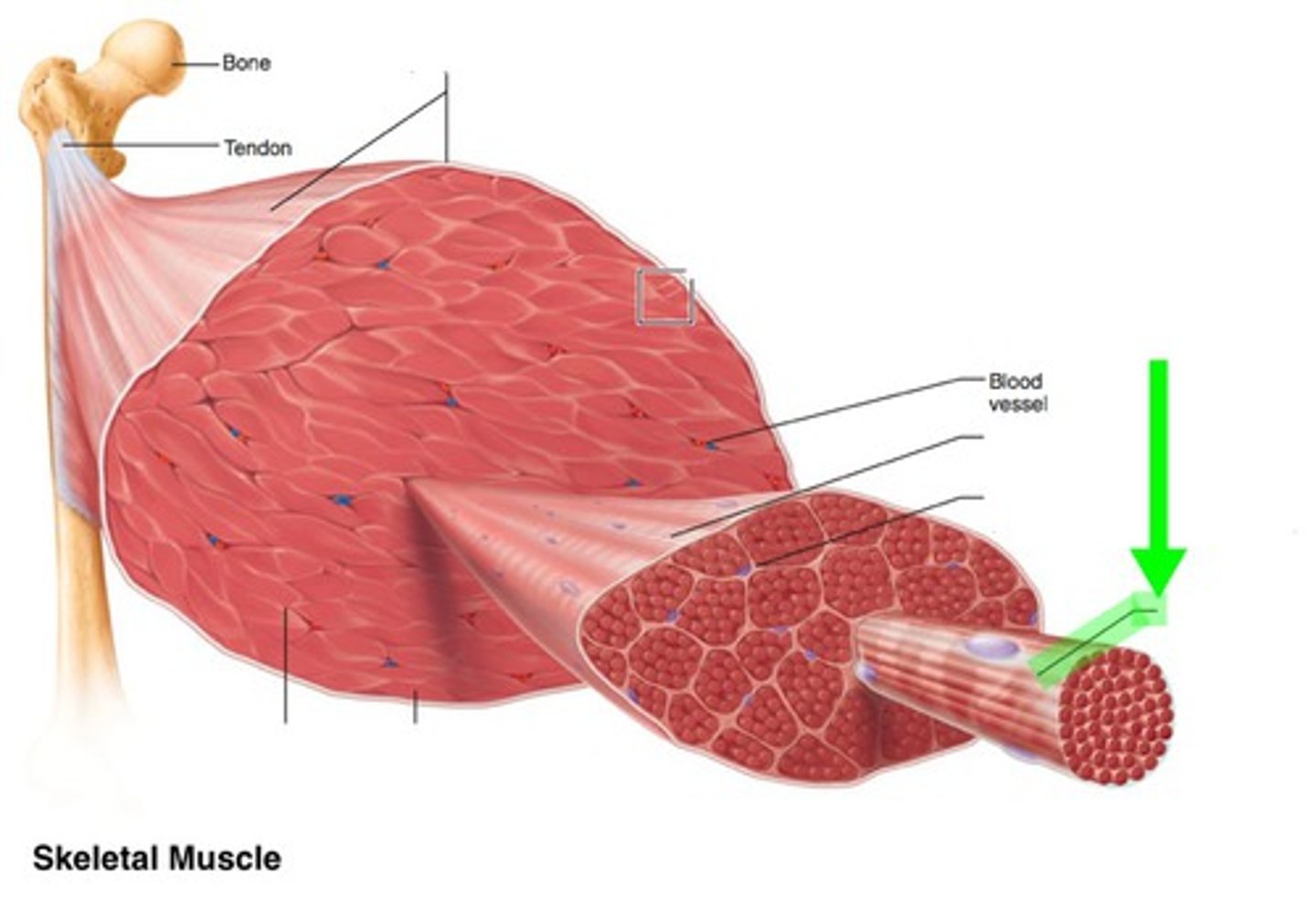
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle cell
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium.
voluntary, striated
skeletal muscle
striated, involuntary
cardiac muscle
involuntary, non-striated
smooth muscle
sarcomere
Contractile unit of muscle
sarcomere
Z disc to Z disc
myosin
thick filament
actin
thin filaments
I band
light band
zone of overlap
the densest, darkest area on a light micrograph
where thick and thin filaments overlap
h band
middle of A band; thick filaments only
m line
middle of sarcomere
a band
dark area; extends length of the thick filaments, anisoprophic
move closer together
Z-lines _____ during contraction
doesn't change
during contraction the A band ____
Contractility
ability to shorten forcibly when stimulated
Extensibility
ability to be stretched
Elasticity
The ability of a material to bounce back after being disturbed
skeletal muscle
sentitial or multinucleated
cardiac muscle
mono or binucleated
triad
group of three, pouching in of the sarcolemma
t tubule
projection of the sarcolemma into the interior of the cell
muscle, fascicle, fiber/cell, myofibril, sarcomere
organization of muscle to sarcomere 5
troponin
what holds tropomyosin in place
actin filaments
myosin binding heads will turn towards _____
calcium ions
atp occurs with ______
get smaller
in the sliding filament theory, H and I band ______
gets larger
in the sliding filament theory, the zone of overlap ____
red fibers
"Slow Twitch"
Fatigue resistant, aerobic metabolism
Myoglobin: slow to contract, darker color, smaller
white fibers
Fast-twitch muscle fibers. They are primarily anaerobic and fatigue more easily, bigger, pale, few mitochondria
slow (red) fibers
a marathoner would have more _____
fast (white) fibers
a sprinter would have more_____
stationary
origin , multiple
insertion
attachment to movable bone, single
prime movers, agonist
responsible for producing a particular movement
synergist
muscle that aids a prime mover in a movement and helps prevent rotation
antagonist
muscles whose actions oppose agonist
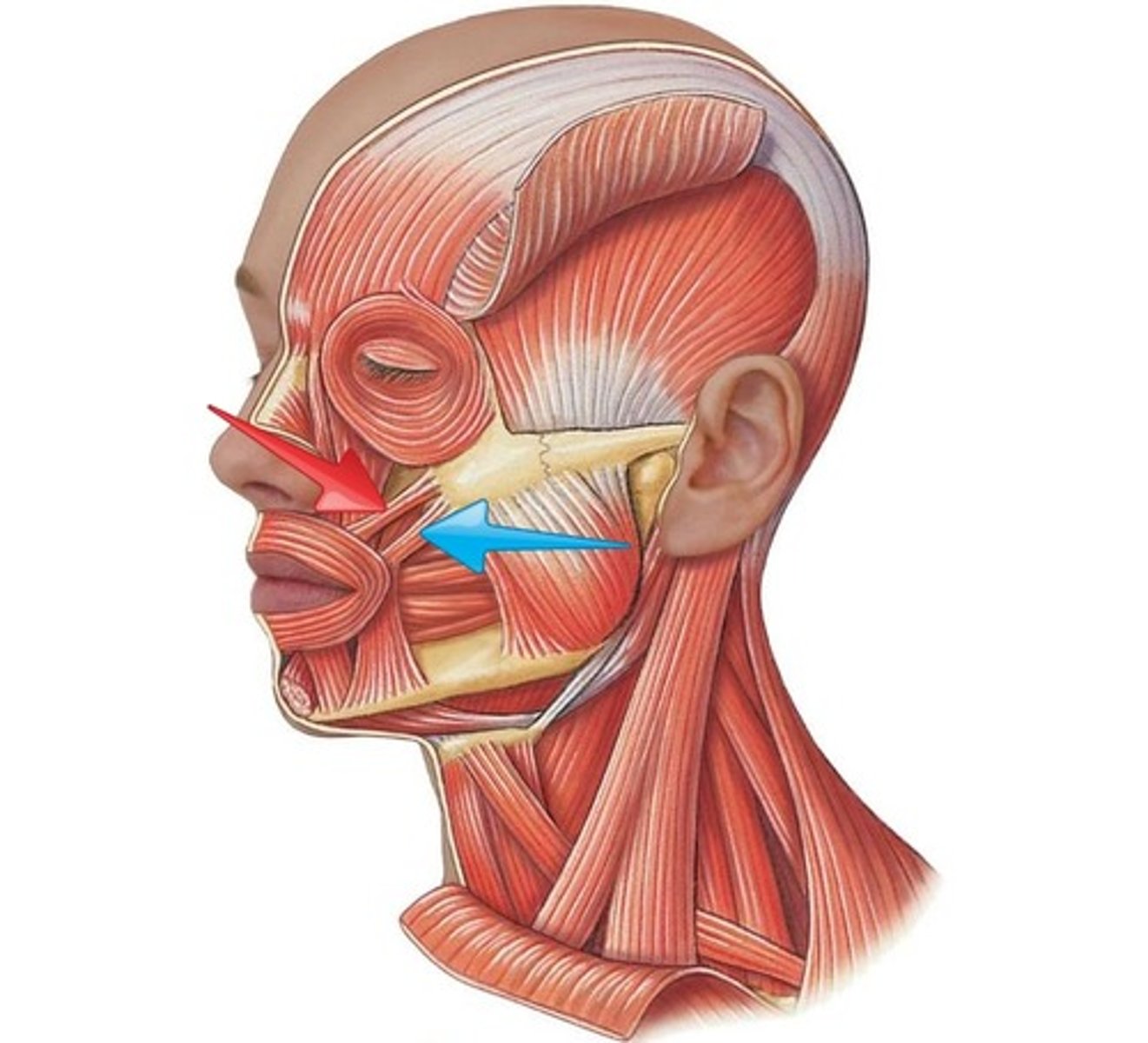
buccinator
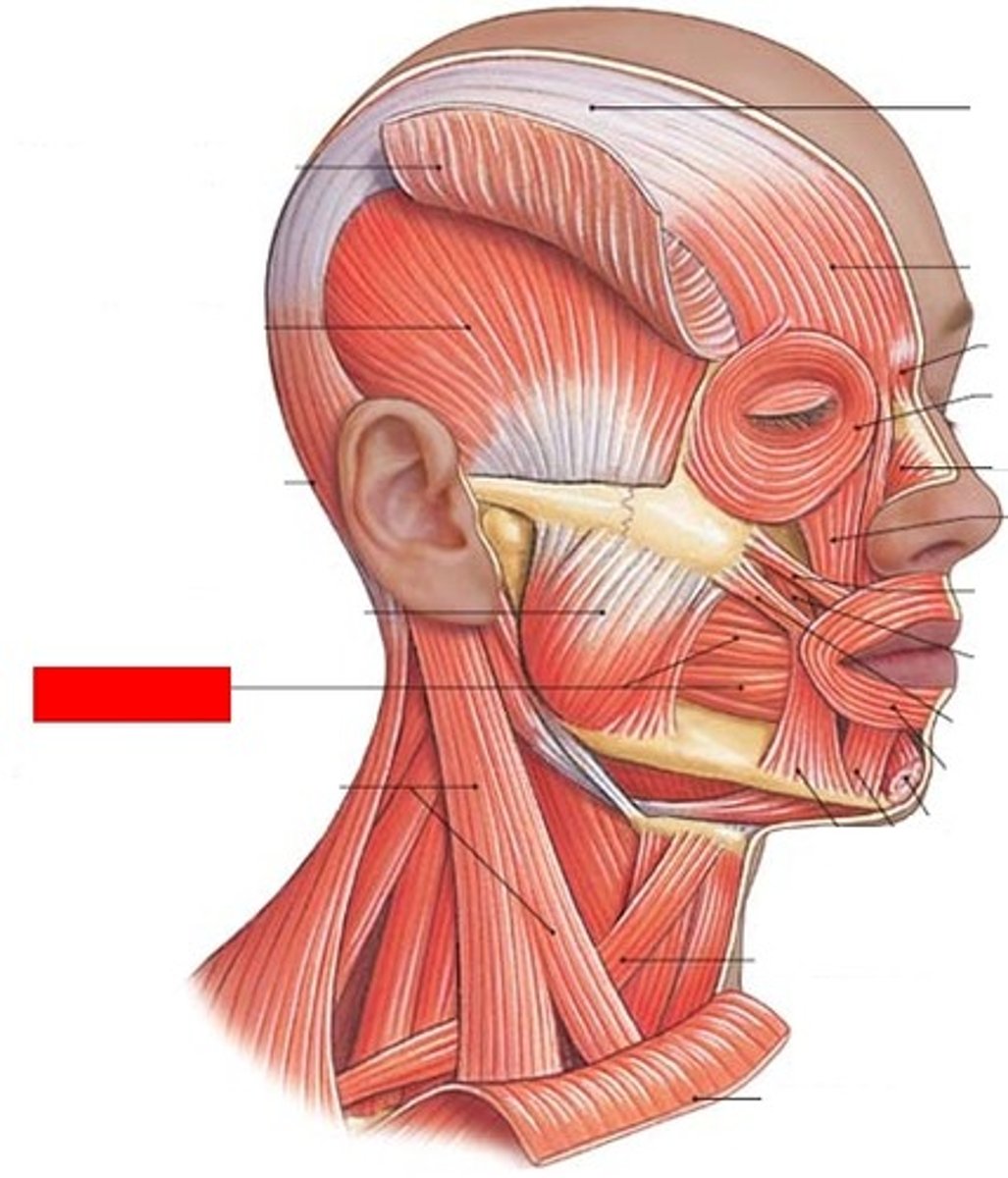
buccinator
compresses cheek
mentalis
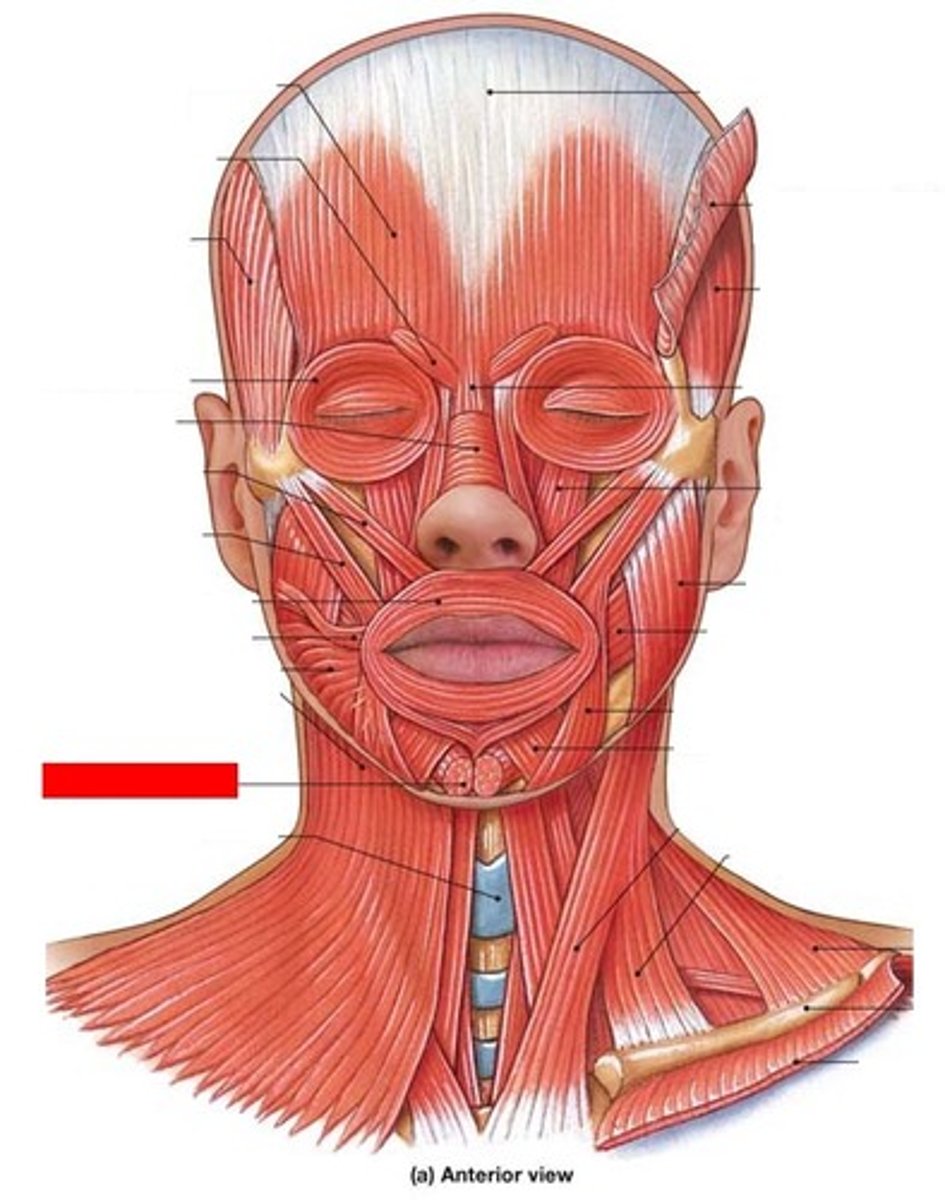
mentalis
Elevates and protrudes lower lip, pouting
orbicularis oris
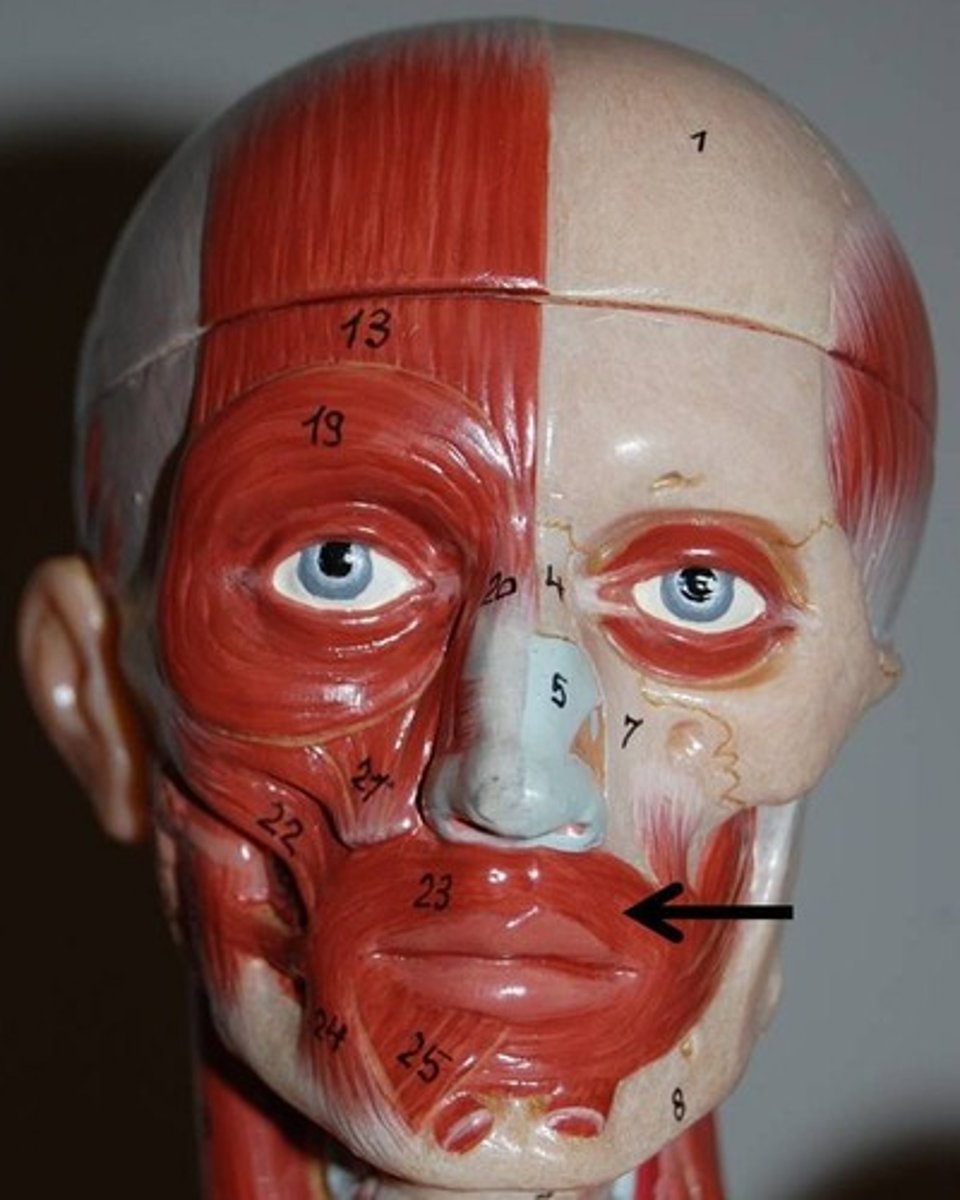
orbicularis oris
compresses, purses lips
Risorius
Draws corner of mouth laterally
risorius
zygomaticus major
retracts and elevates corner of mouth
zygomaticus major
bottom
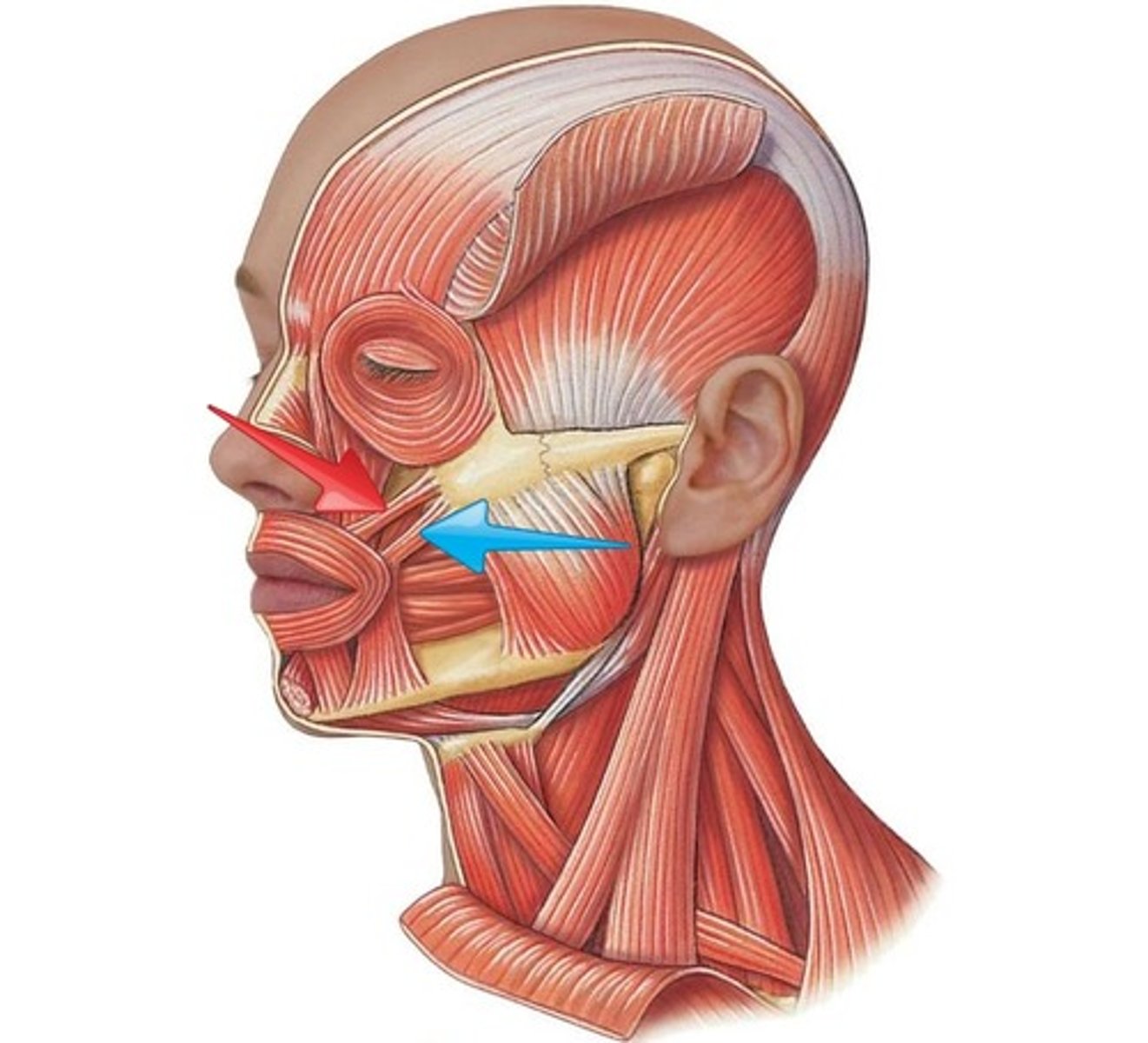
zygomaticus minor
retracts and elevates upper lip
zygomaticus minor
top
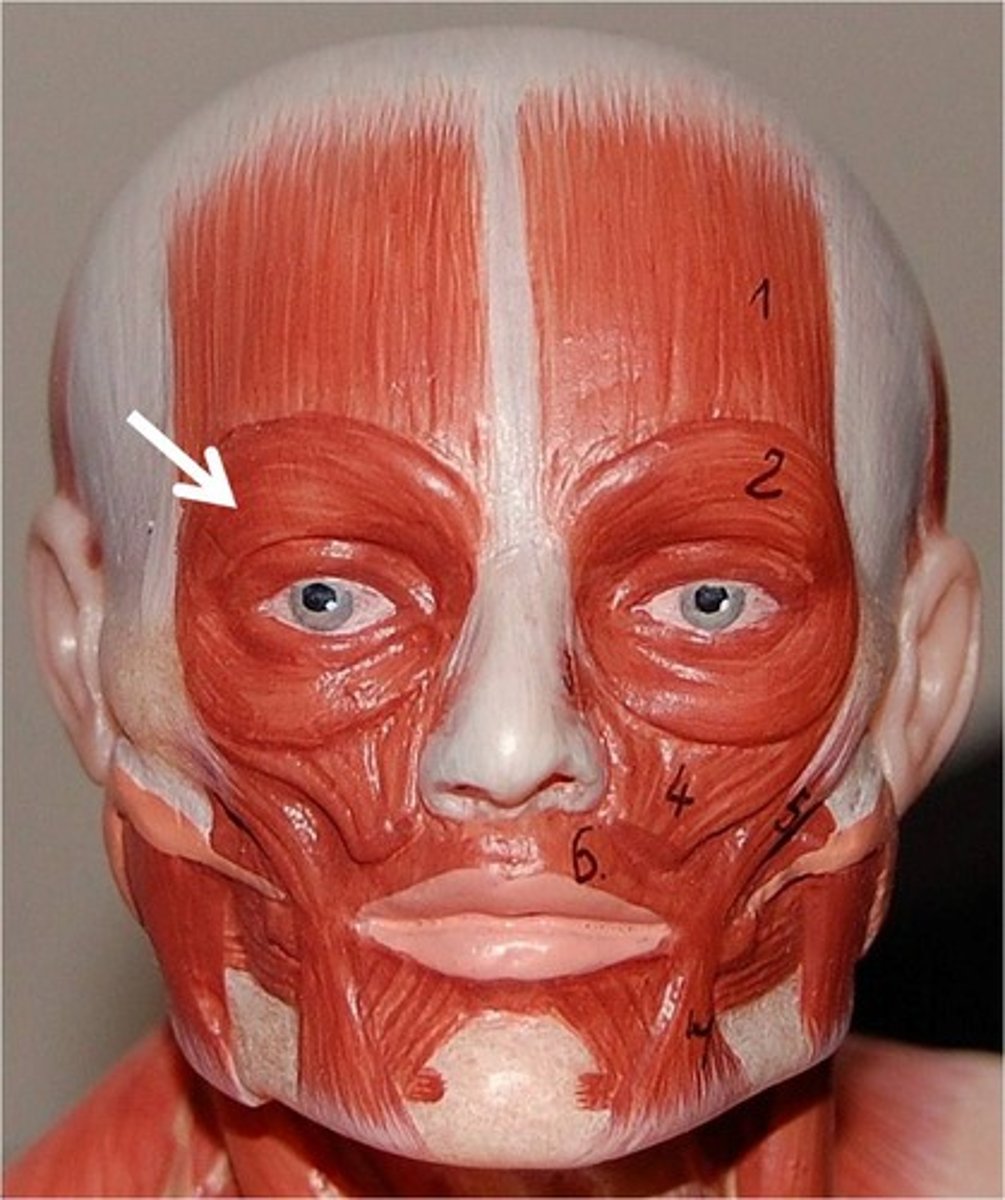
orbicularis oculi
closes eye
orbicularis oculi
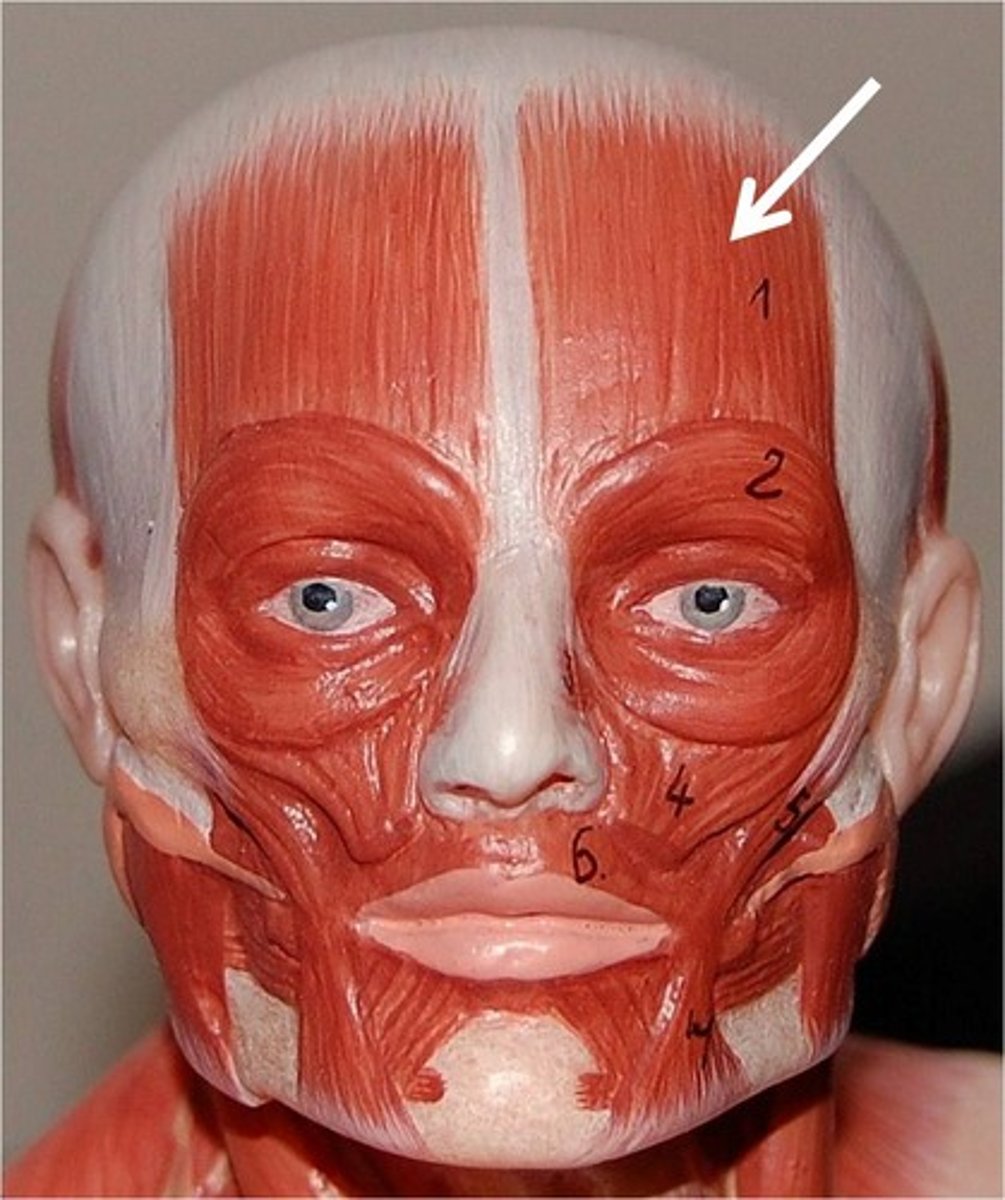
frontal belly
raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
frontal belly
occipital belly
tenses and retracts scalp
occipital belly
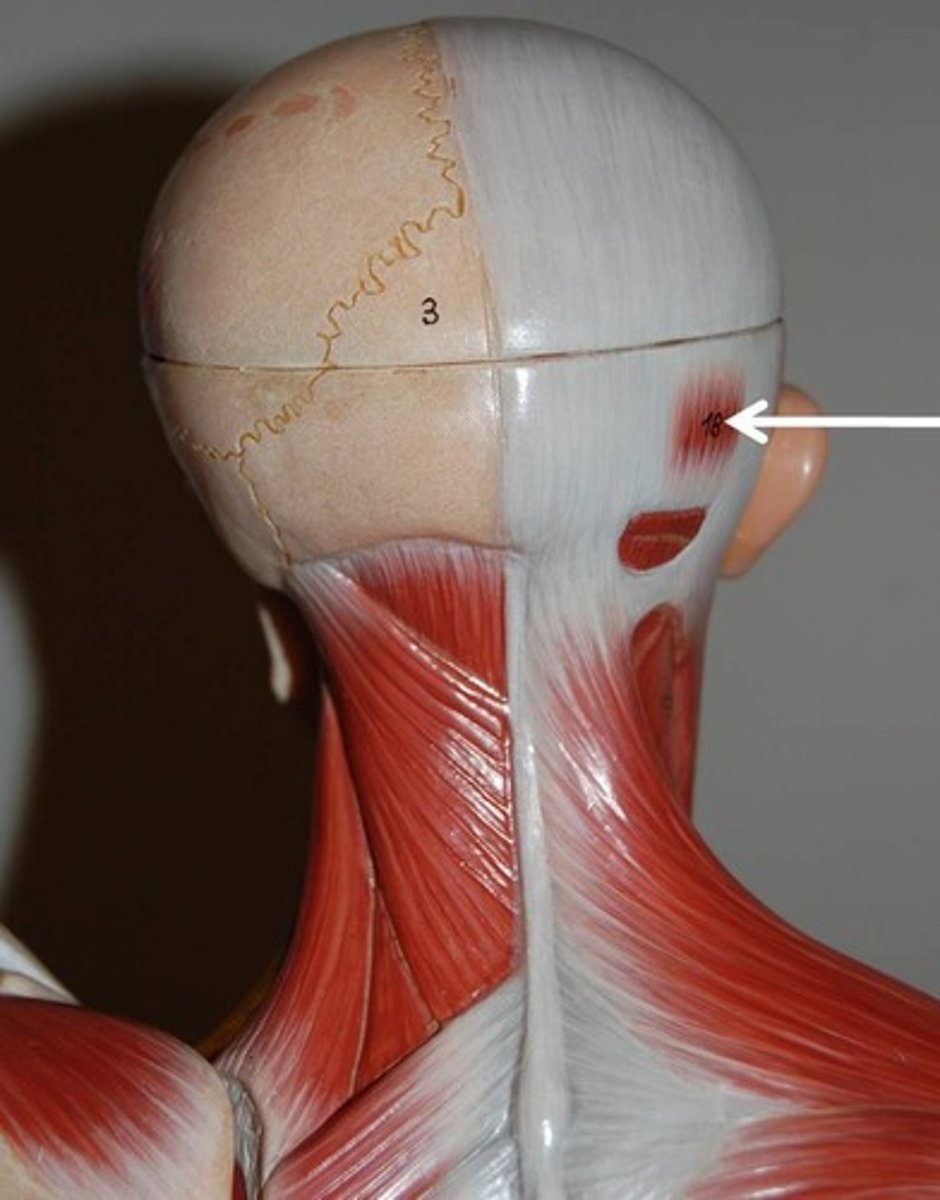
platysma
tenses skin of neck, depresses mandible
platysma
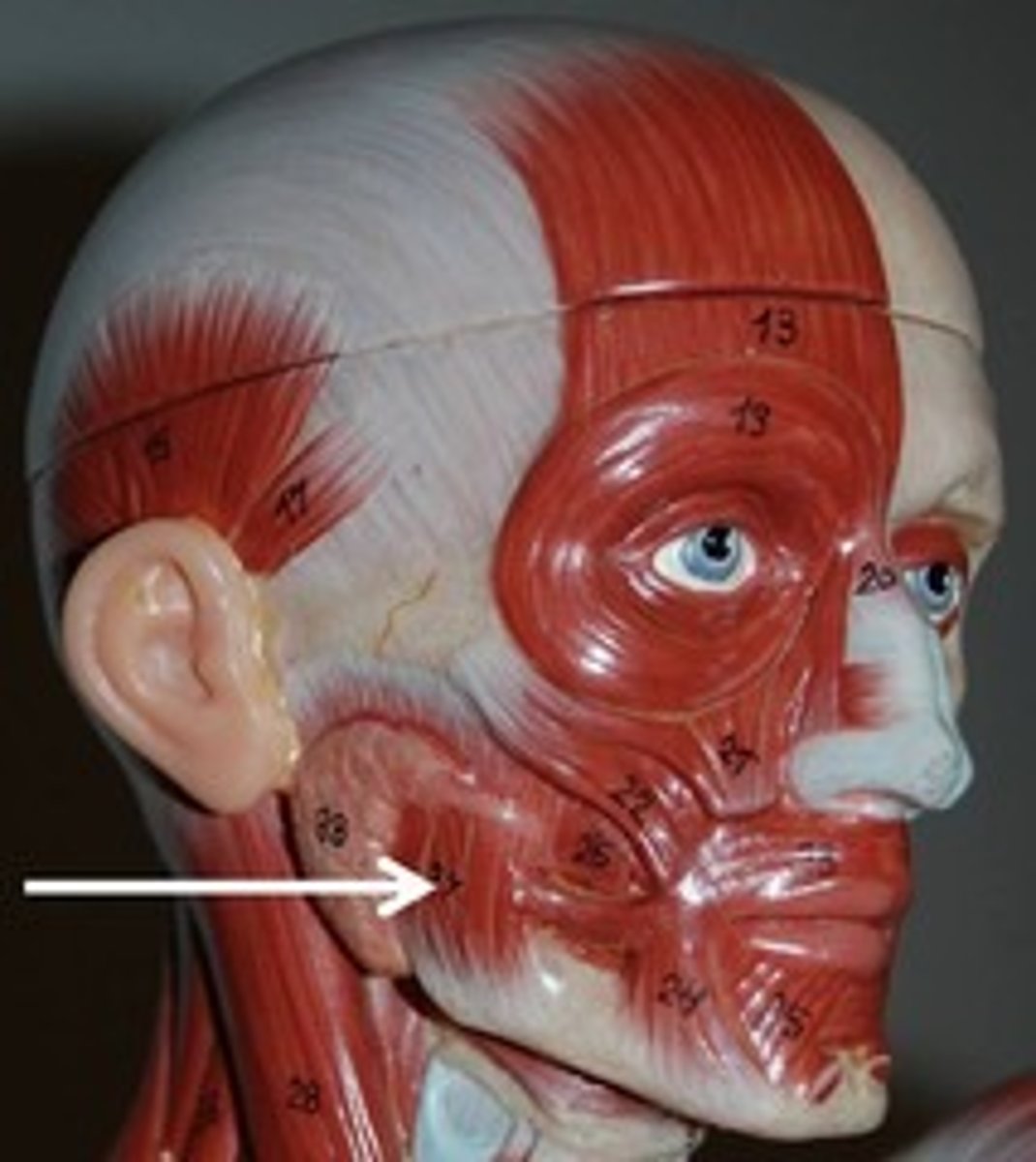
masseter, temporal
what are the muscles of mastification
masseter
elevates mandible and closes jaw
masseter
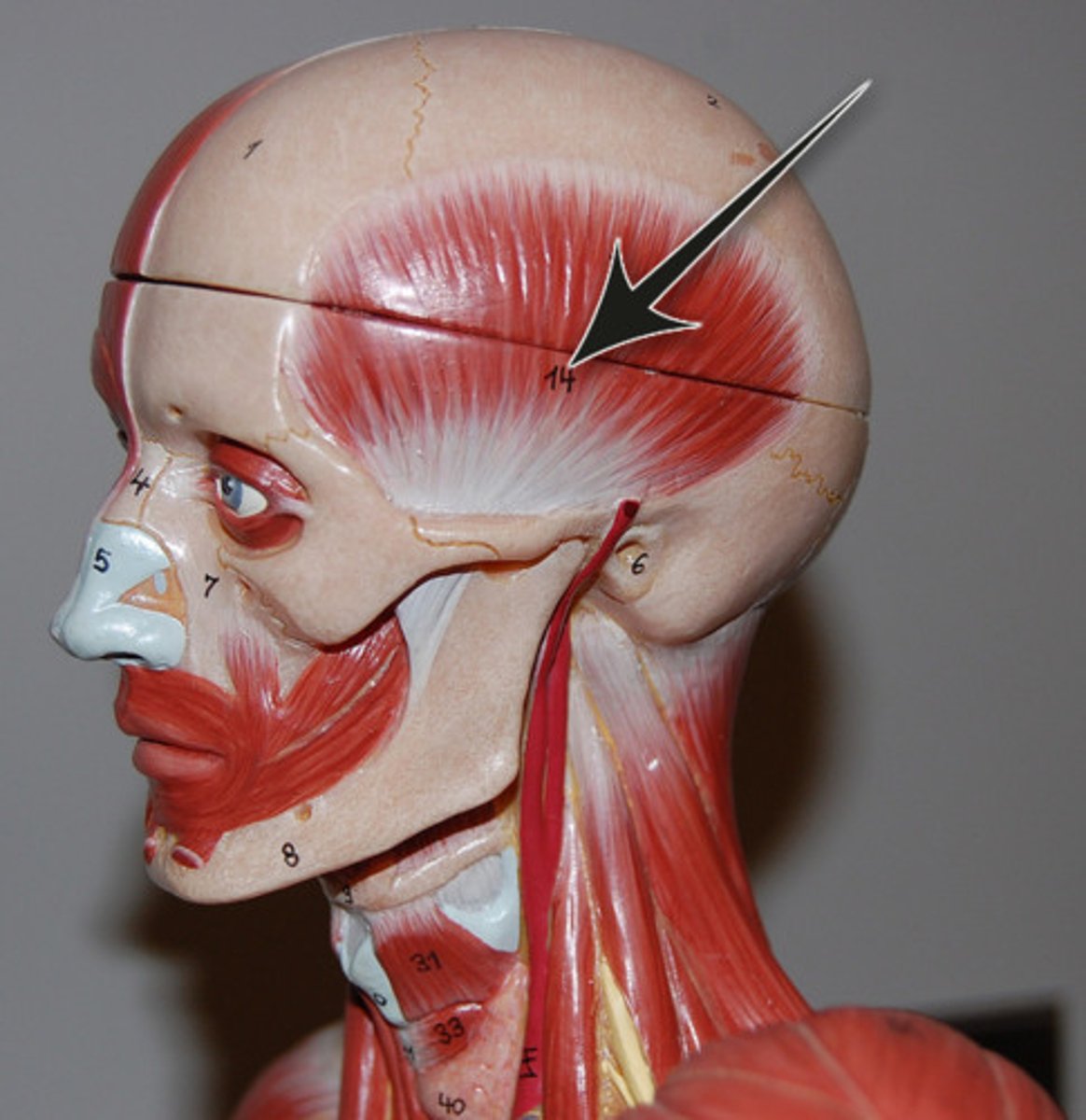
temporalis
elevates mandible
retracts jaw
temporalis
digastric
depresses mandible, opening mouth, swallowing, elevates larynx
digastric
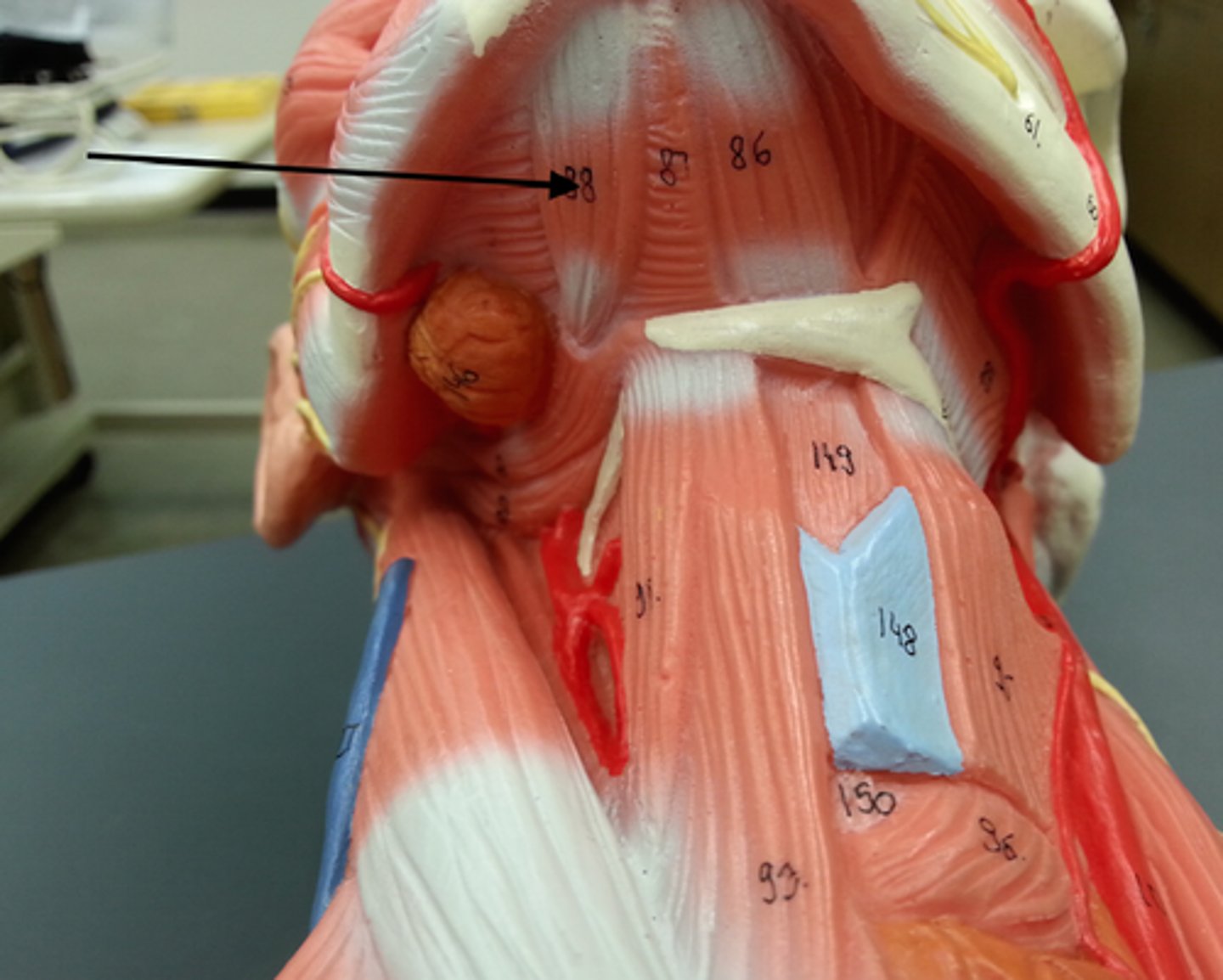
omohyoid
depresses hyoid bone and larynx o
omohyoid
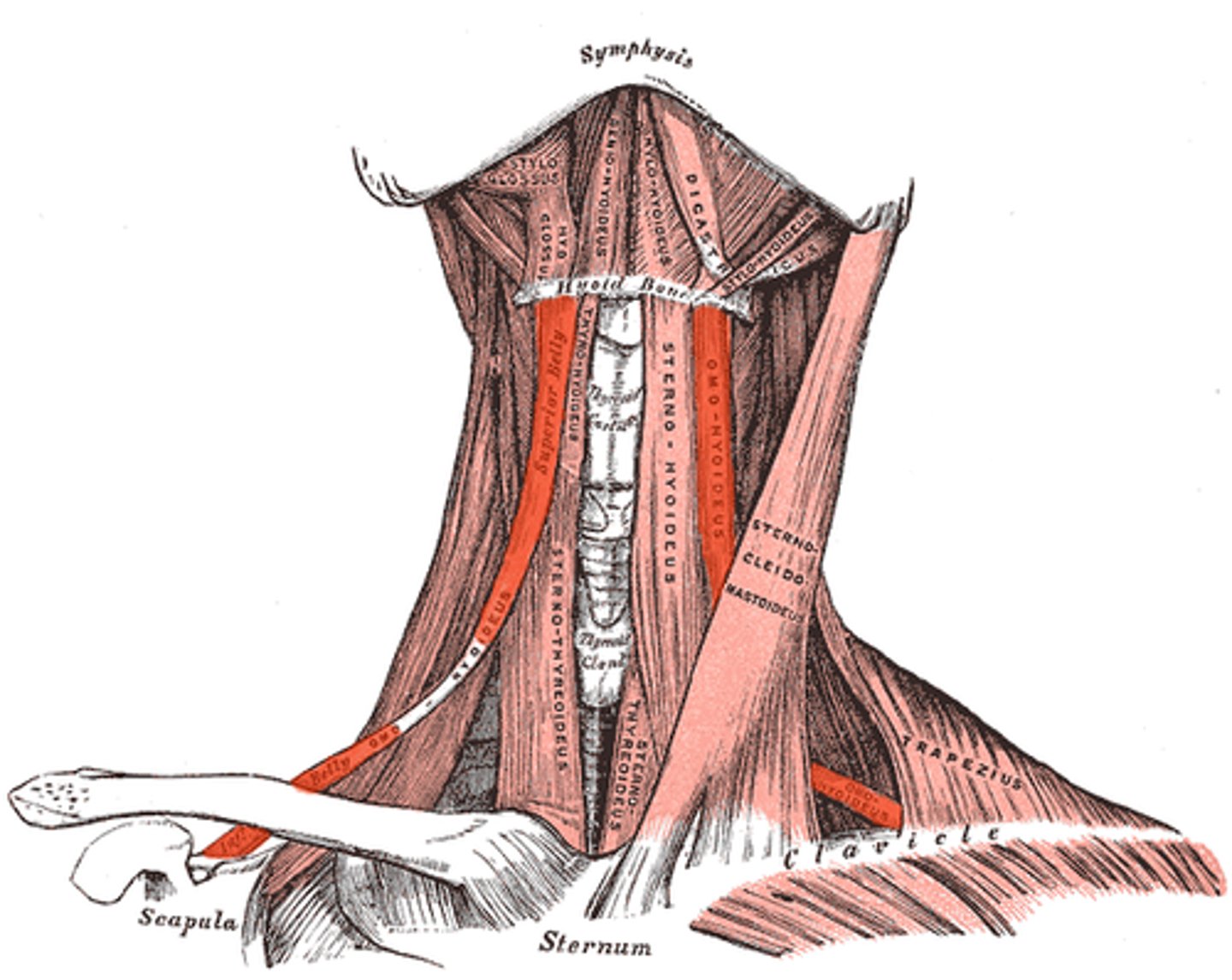
sternohyoid
depresses hyoid bone and larynx s
sternohyoid
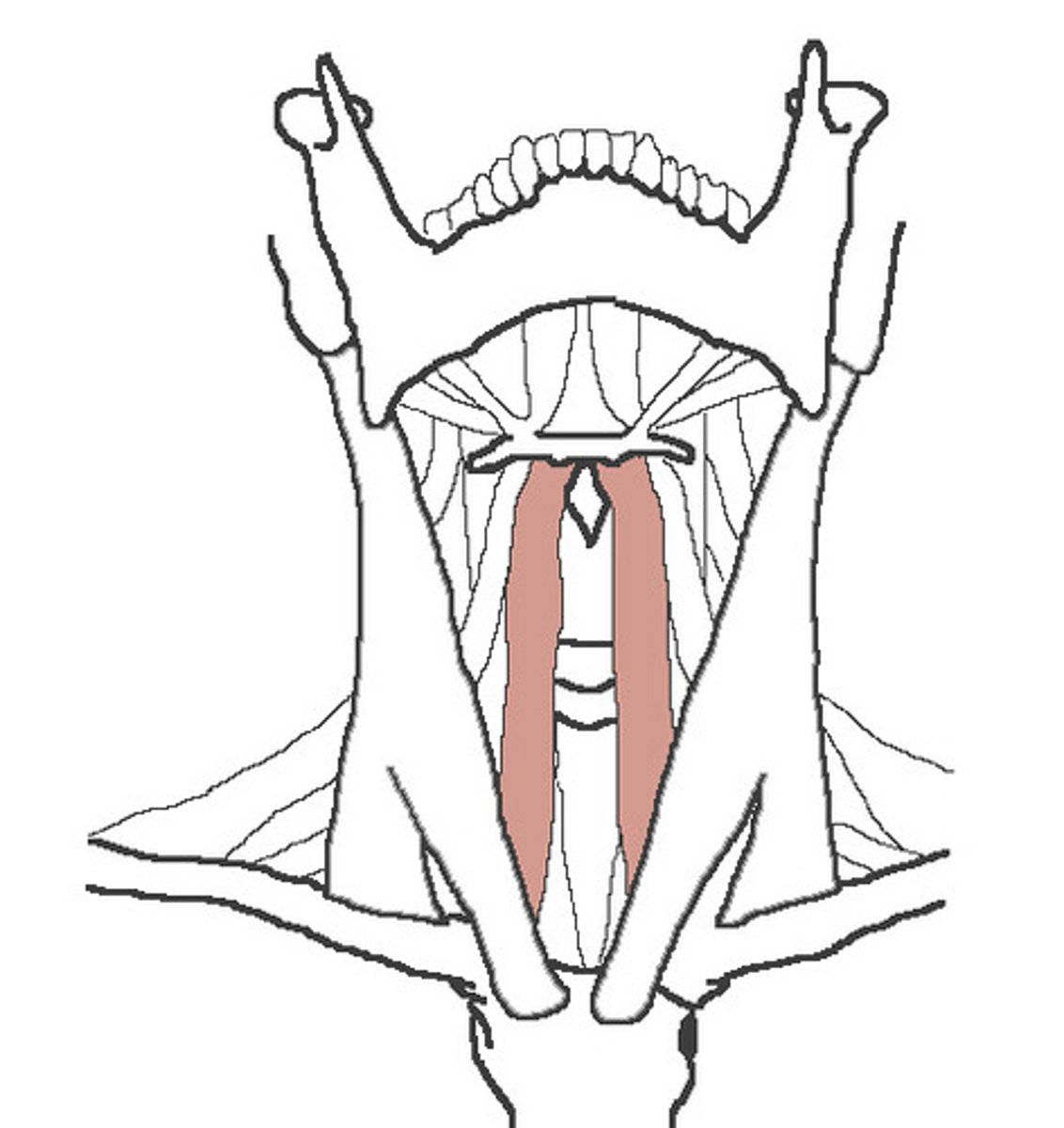
sternothyroid
depresses hyoid bone and larynx th
sternothyroid
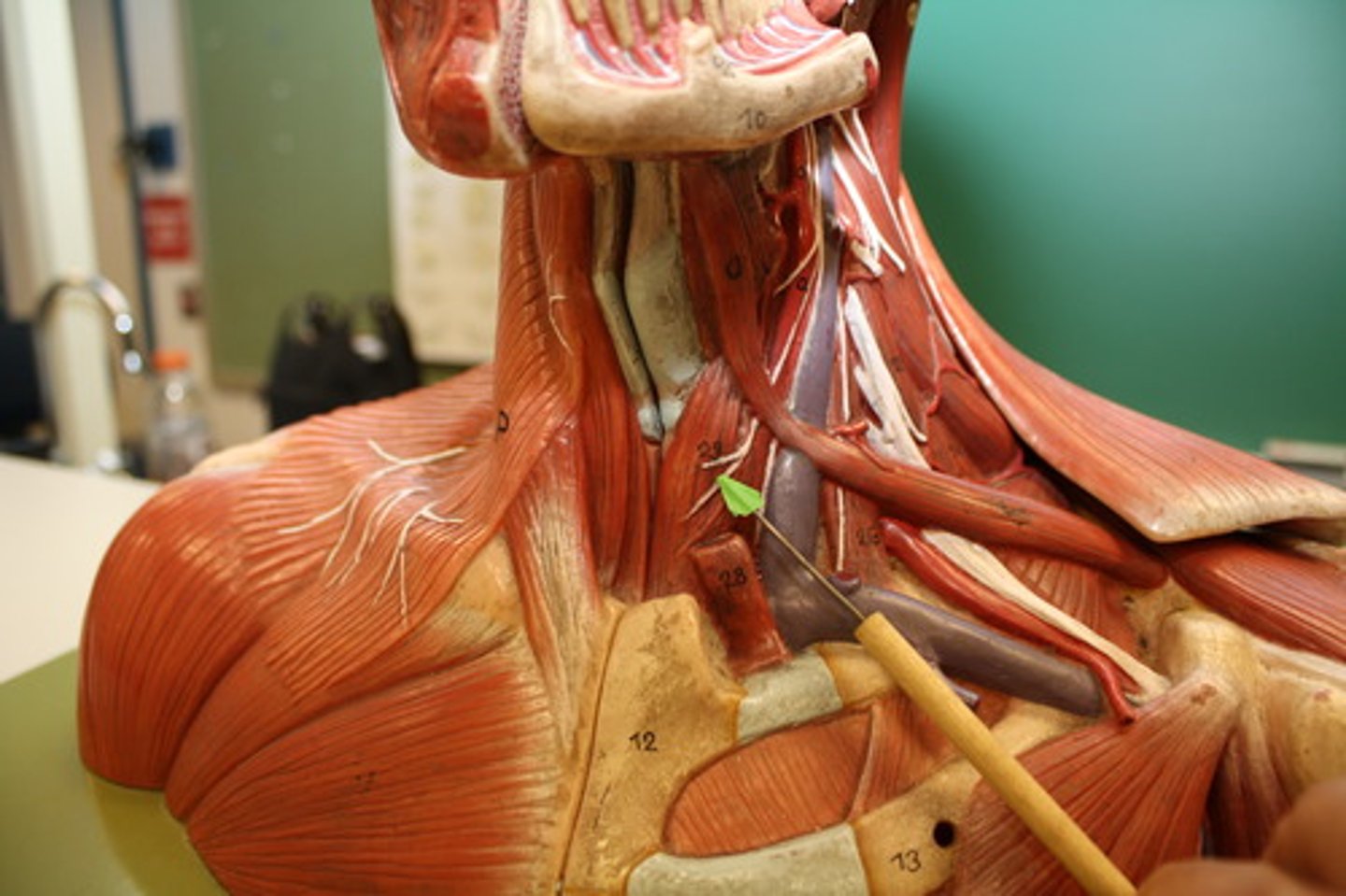
Sternocleidomastoid
Contraction of one side: laterally flexes neck, rotates head to opposite side; Contraction of both sides together: flexes neck
Sternocleidomastoid
iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis
order of erector spinae group that extend neck
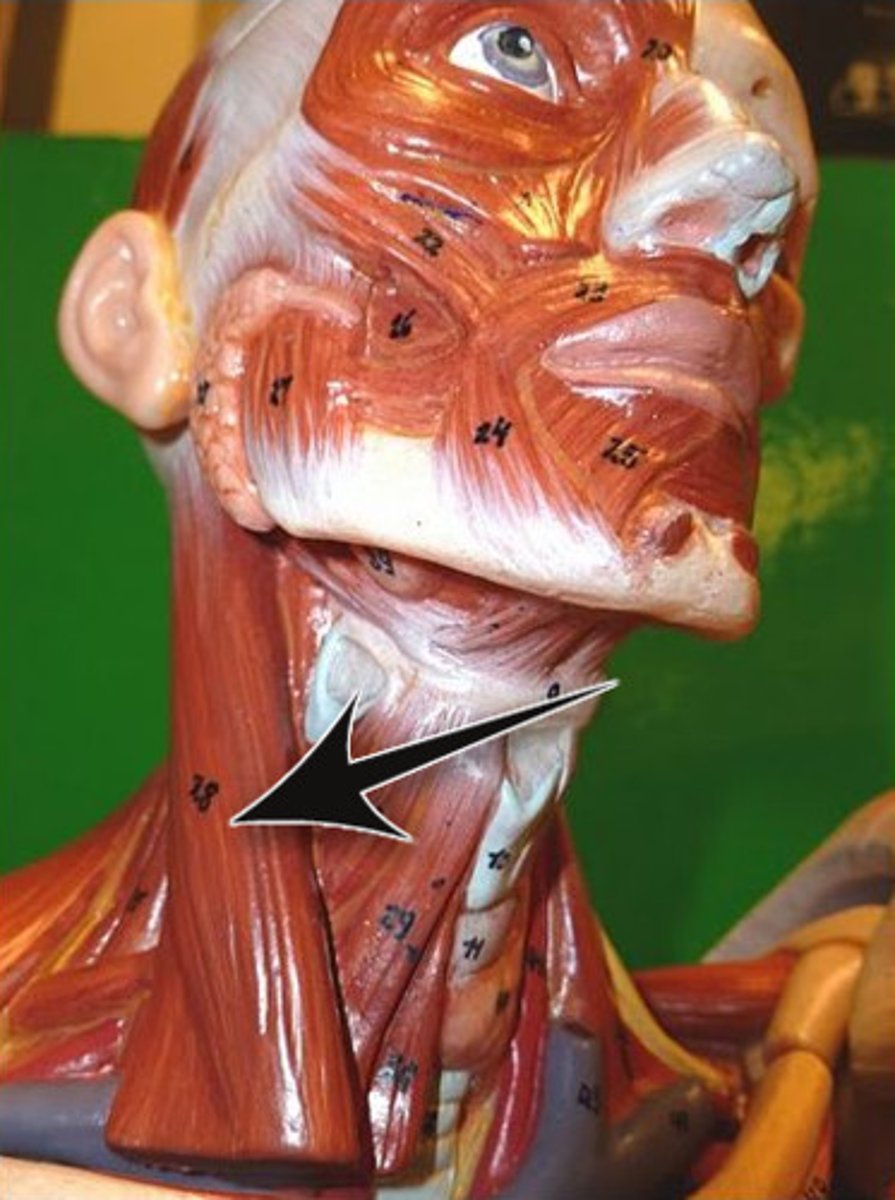
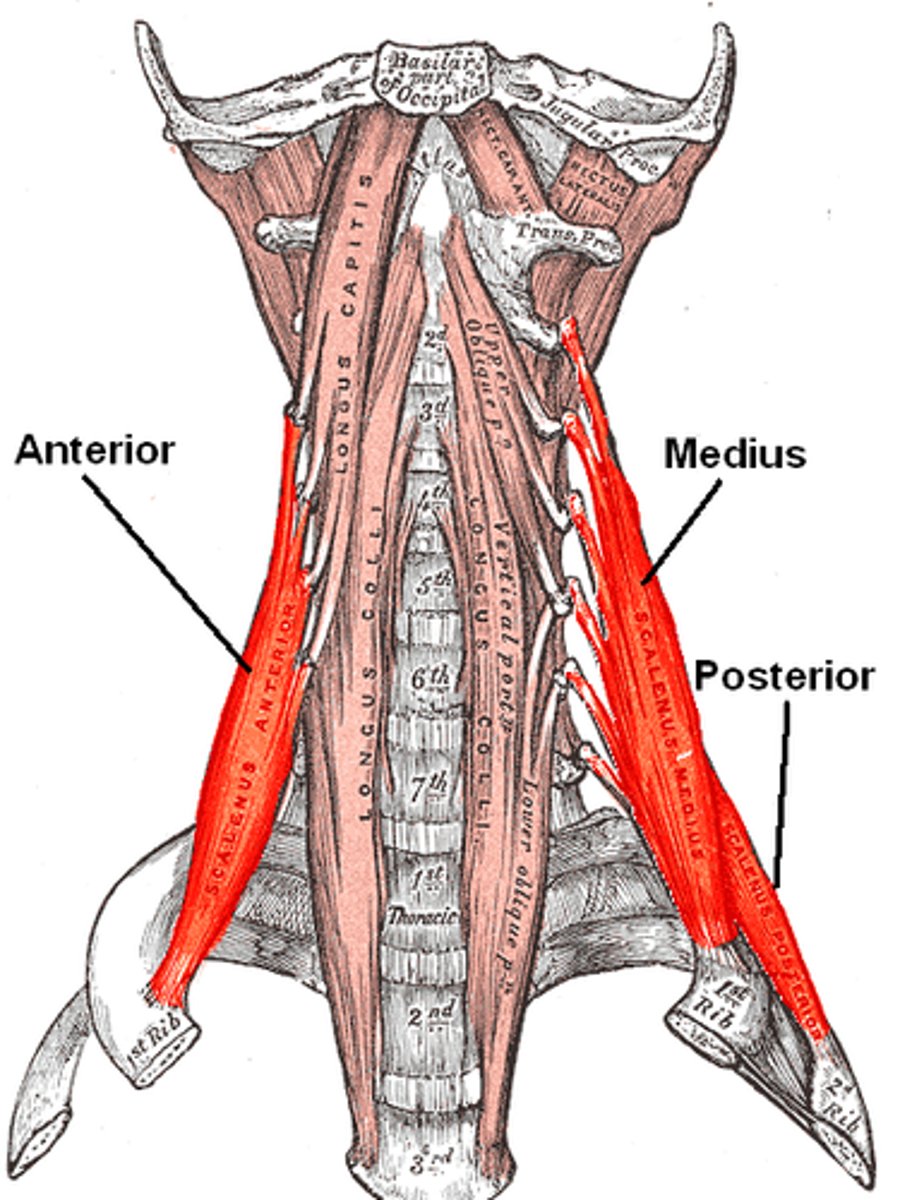
scalenes
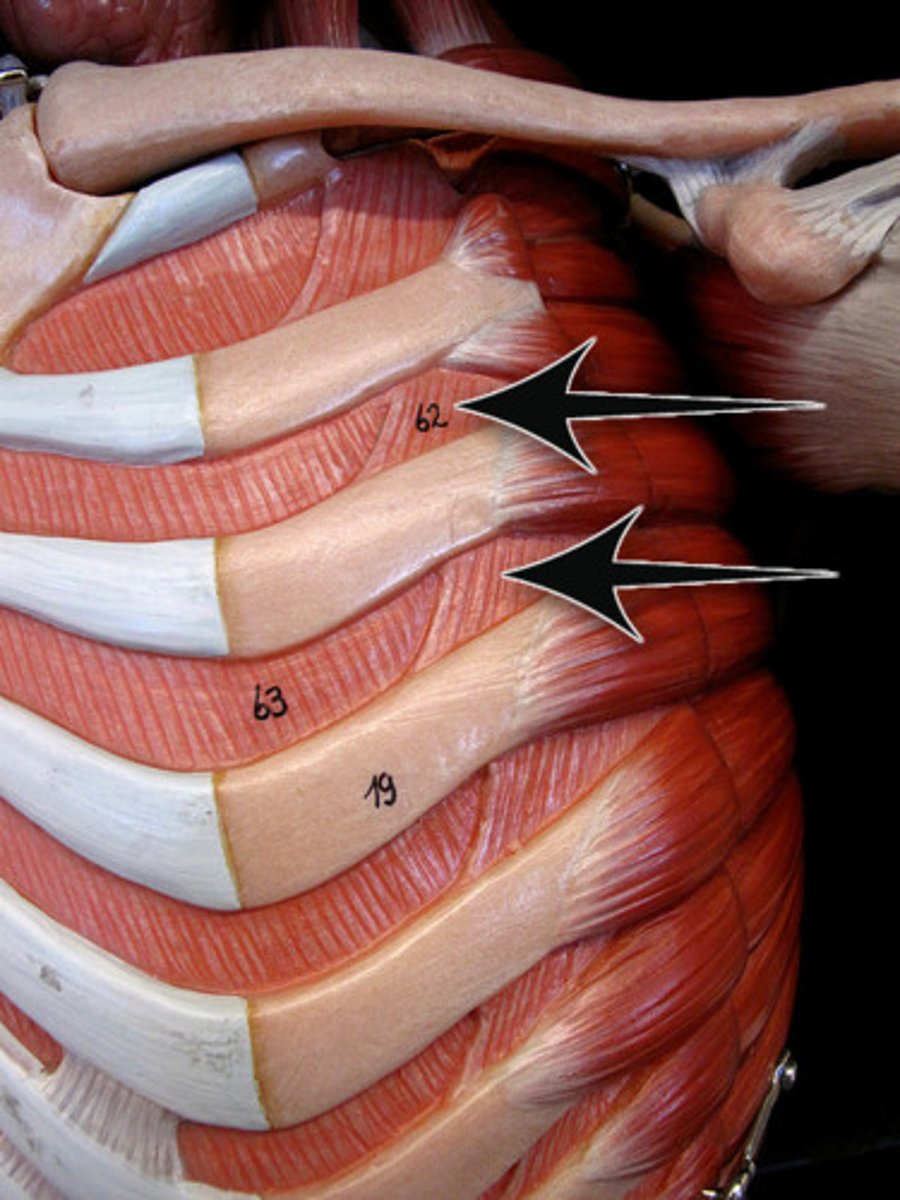
external intercostals
elevates ribs
external intercostals
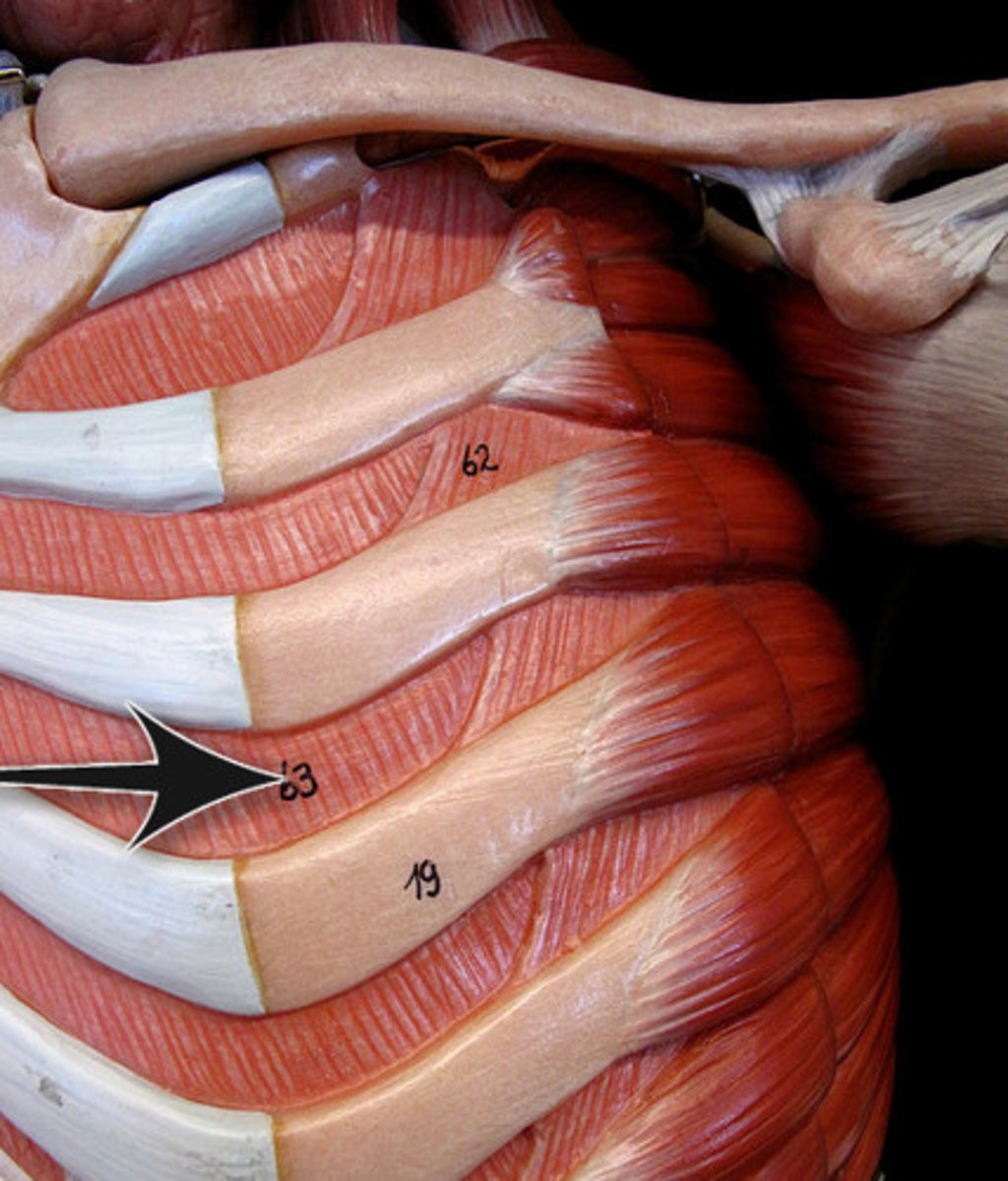
internal intercostals
depress ribs
internal intercostals
linea alba
The "white line:" the tendinous median line on the ventral abdominal wall between the two rectus muscles
tendinous inscriptions
The Rectus abdominis is crossed by fibrous bands, three in number, which are named the
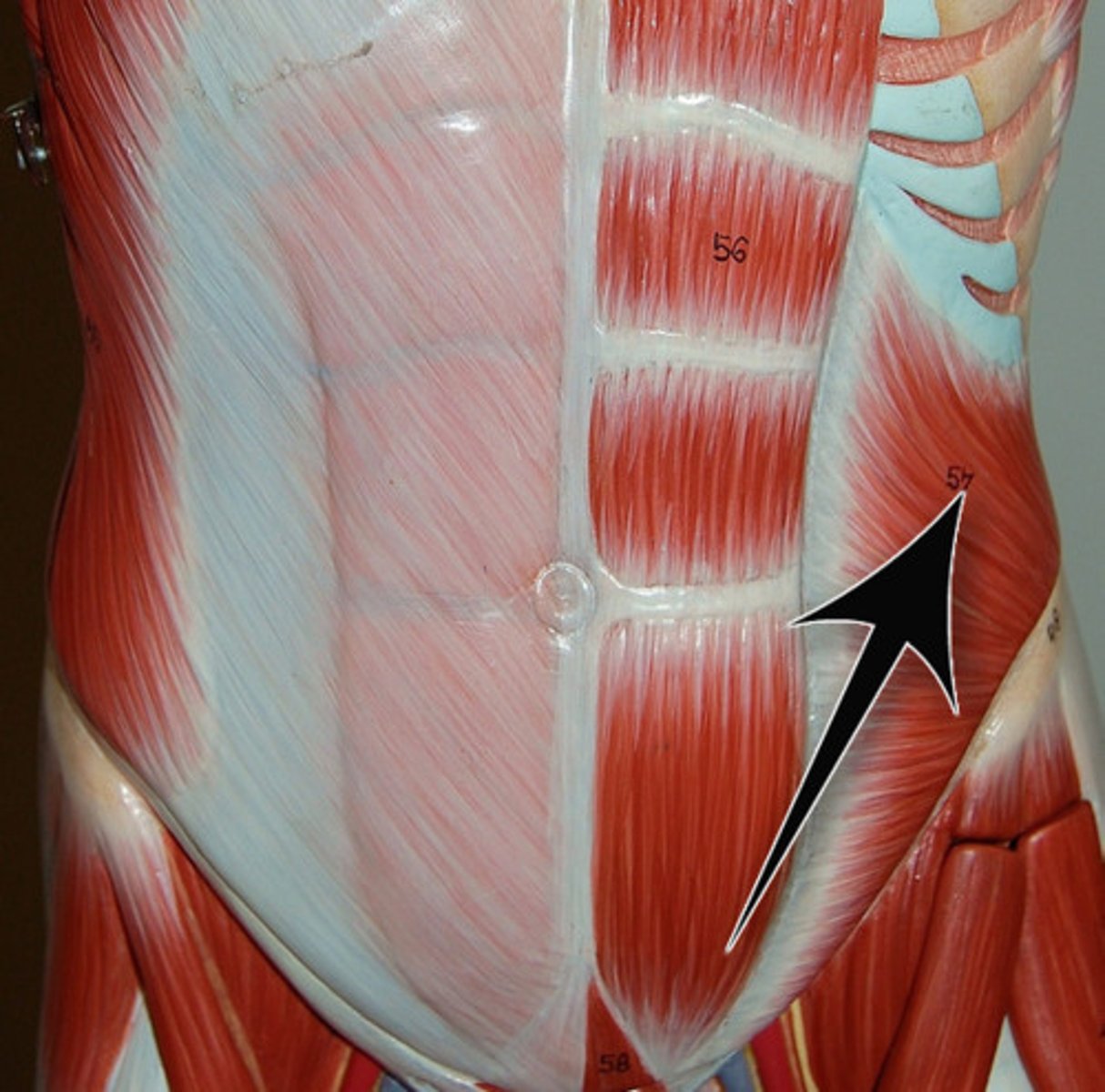
external oblique
Compresses abdomen; laterally flexes and rotates vertebral column to opposite sides
external oblique
internal oblique
flexes and rotates vertebral column to same side
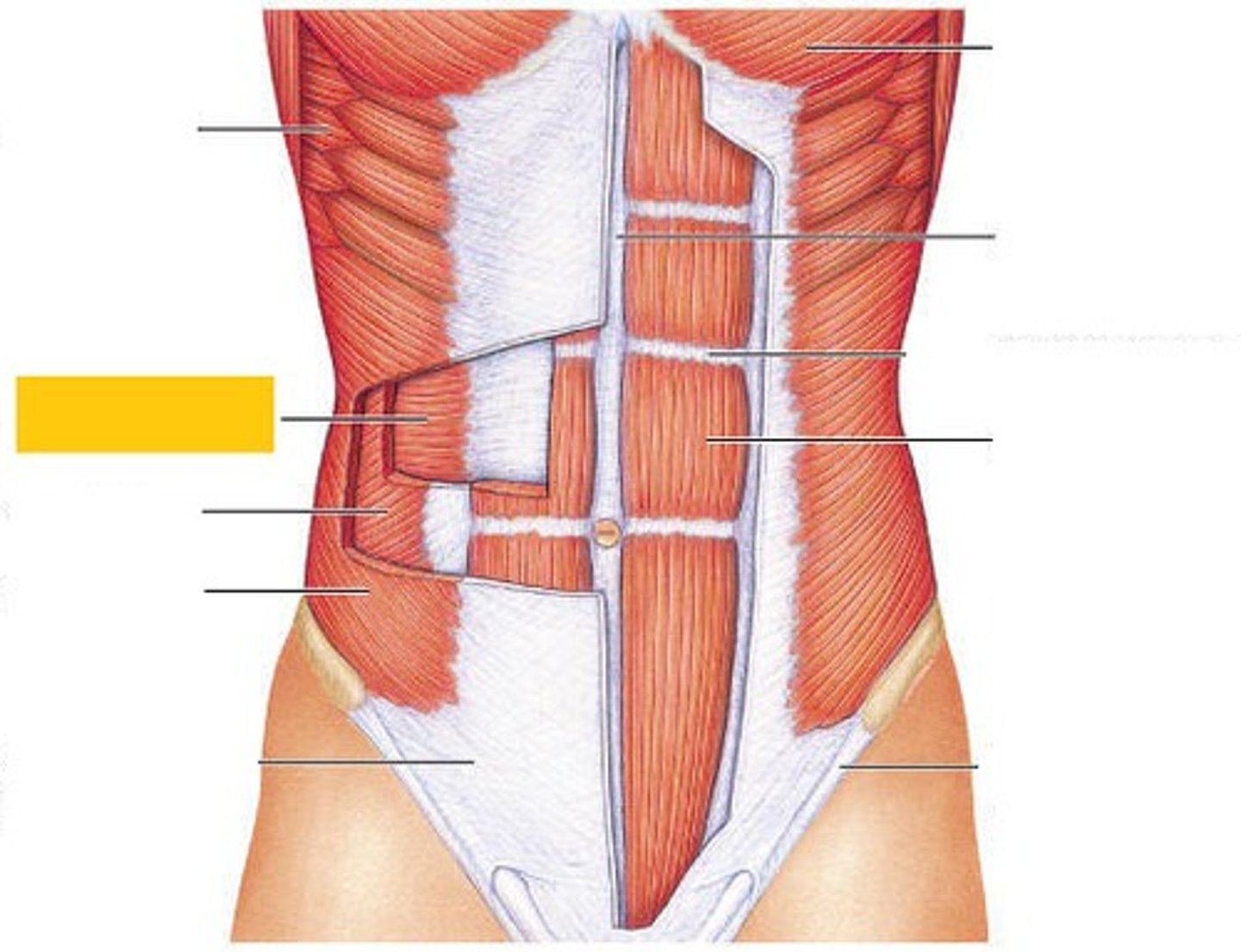
internal oblique
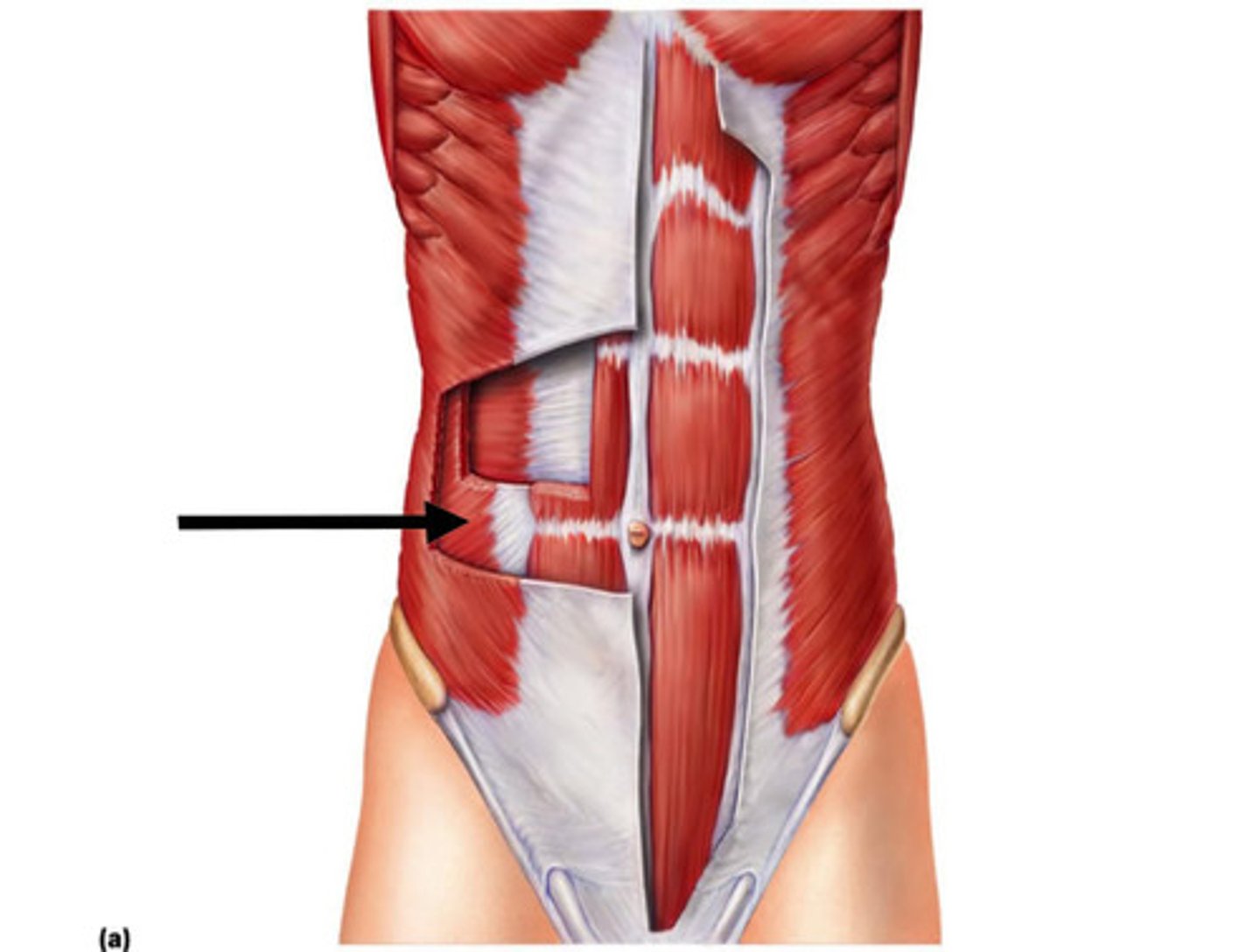
transverse abdominis
compresses abdominal contents
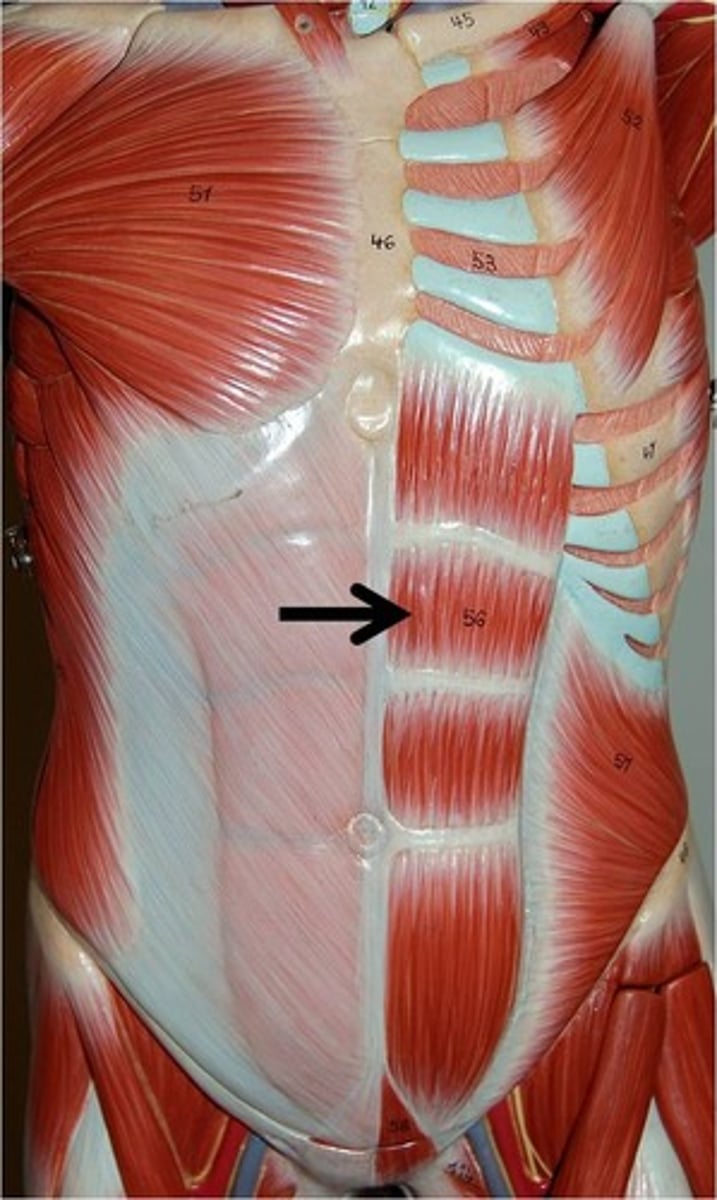
rectus abdominis
depresses ribs, flexes vertebral column, compresses abdomen
levator scapulae
elevates scapula
levator scapulae
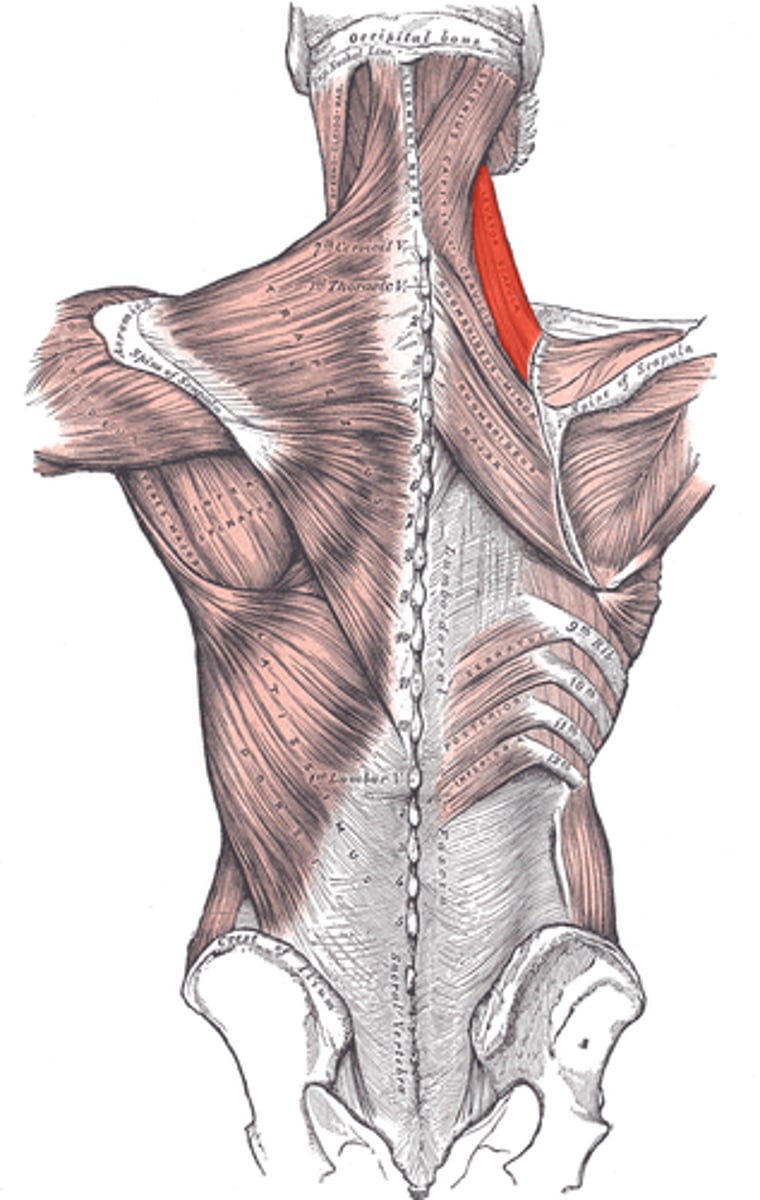
pectoralis minor
protracts and depresses shoulder, rotates scapula, elevates ribs if scapula is stationary
pectoralis minor
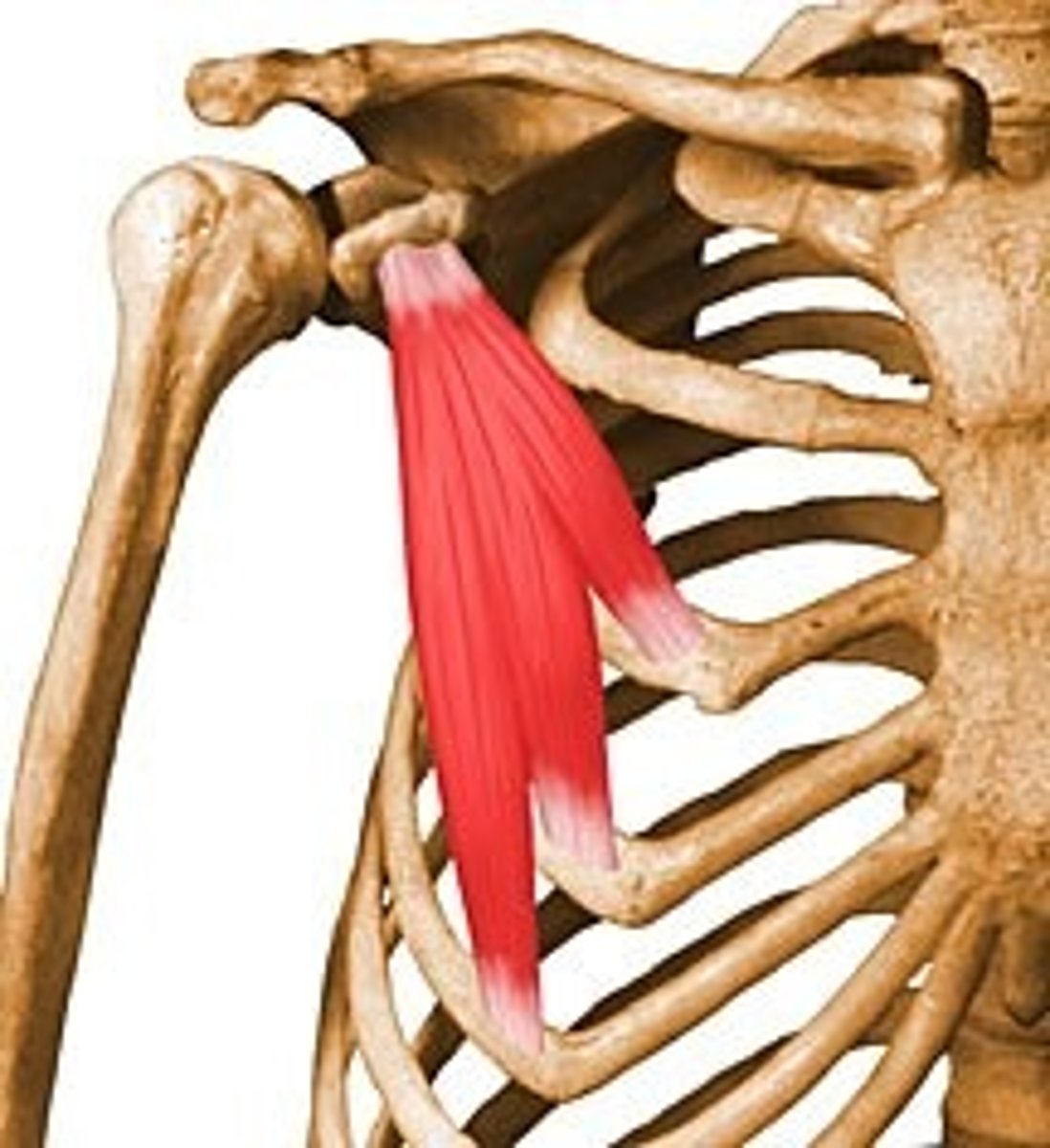
rhomboid major
adducts scapula
rhomboid major