Respiration
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
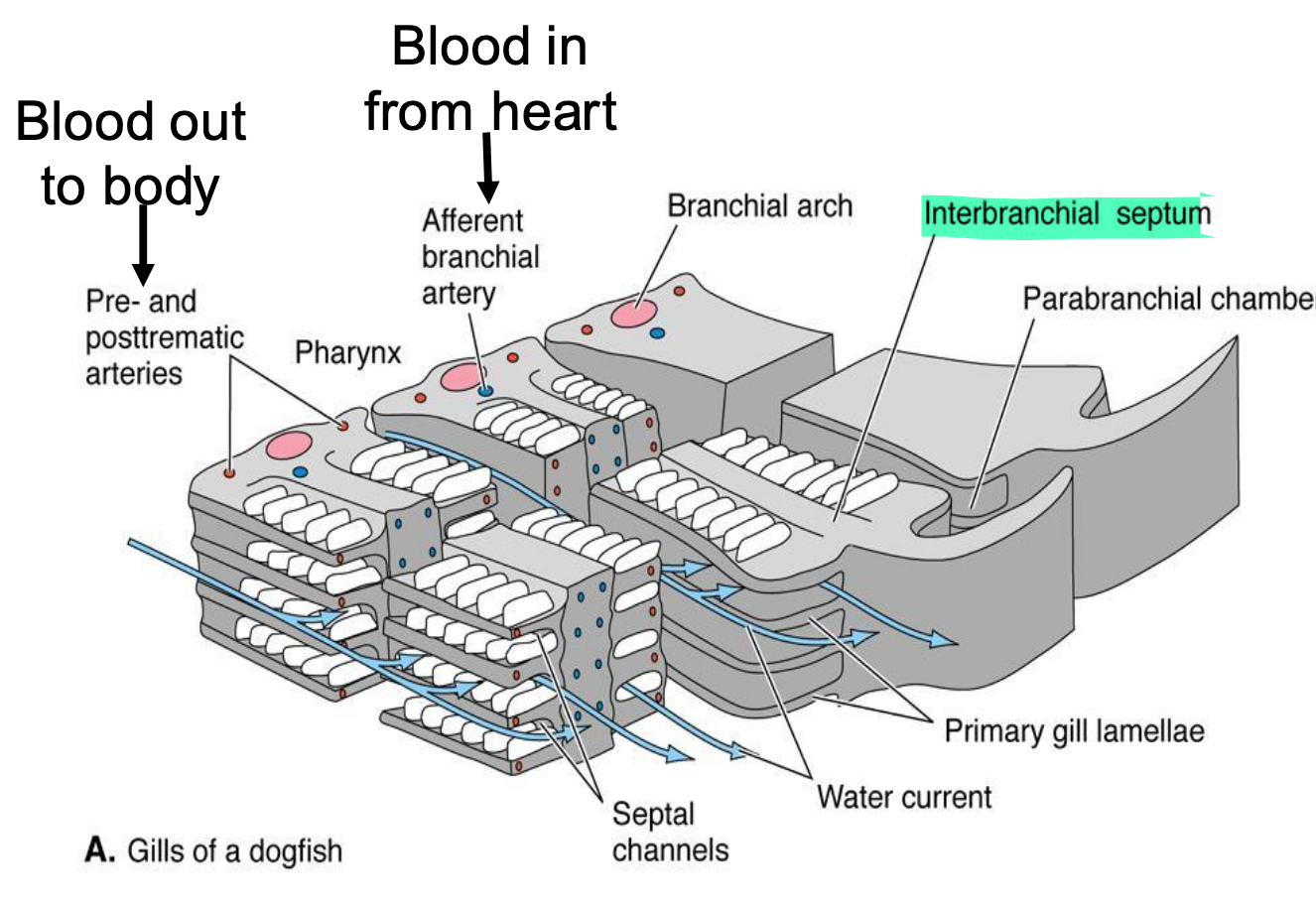
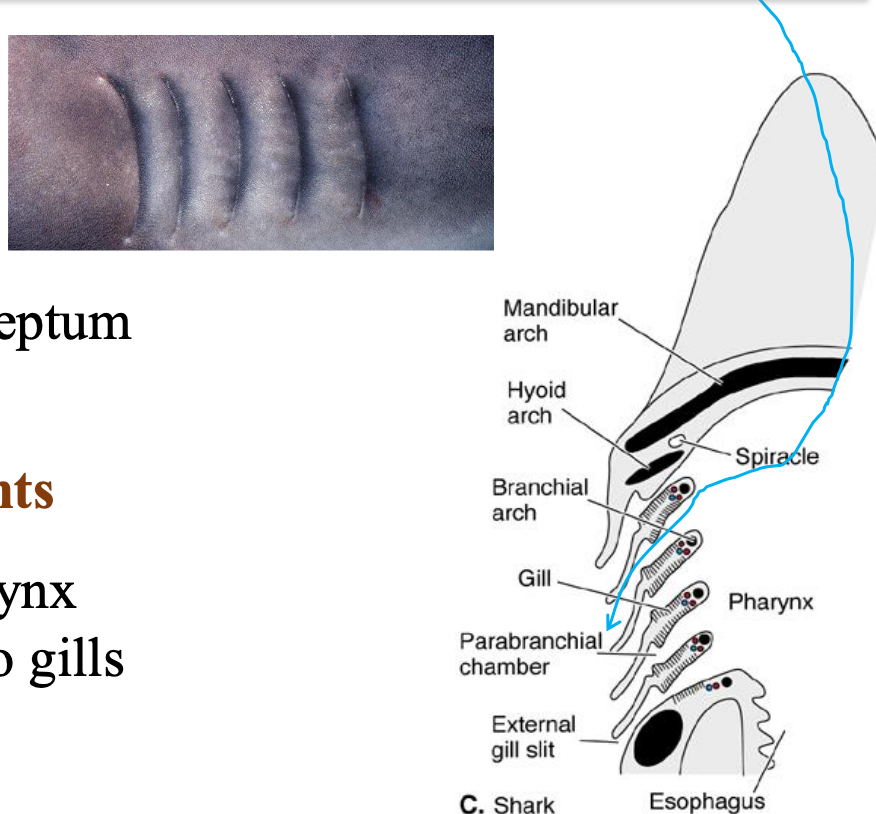
Gill arch
Bony (or cartilaginous)
curved bars along the pharynx, supporting the gills
Gill slits
Openings between gill arches, for H2O passage
Interbranchial septum
plates of tissue between pouches
Gill rays
skeletal, extend into interbranchial septum; support
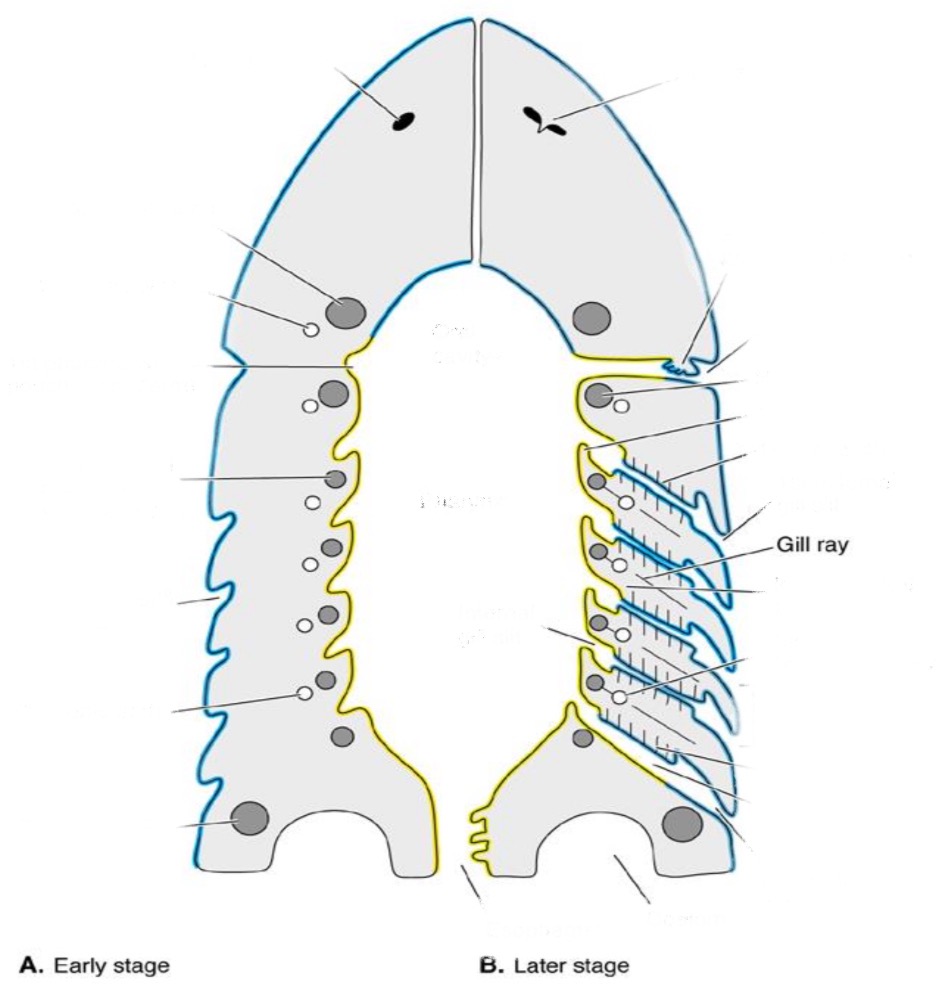
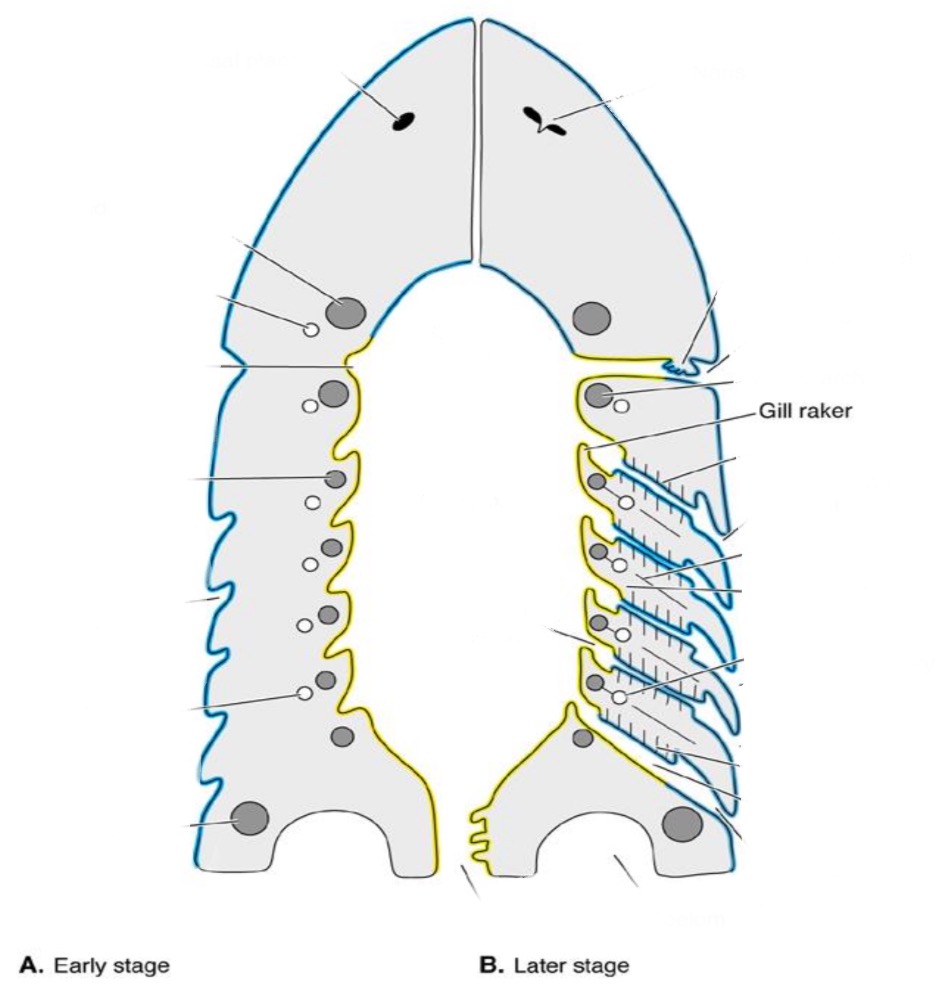
Gill raker
process at base of interbranchial septum
Primary gill lamellae (gill filaments)
red, fleshy vascularized plates, take O2 in blood; attach to walls of gill/branchial pouches or to the gill arches
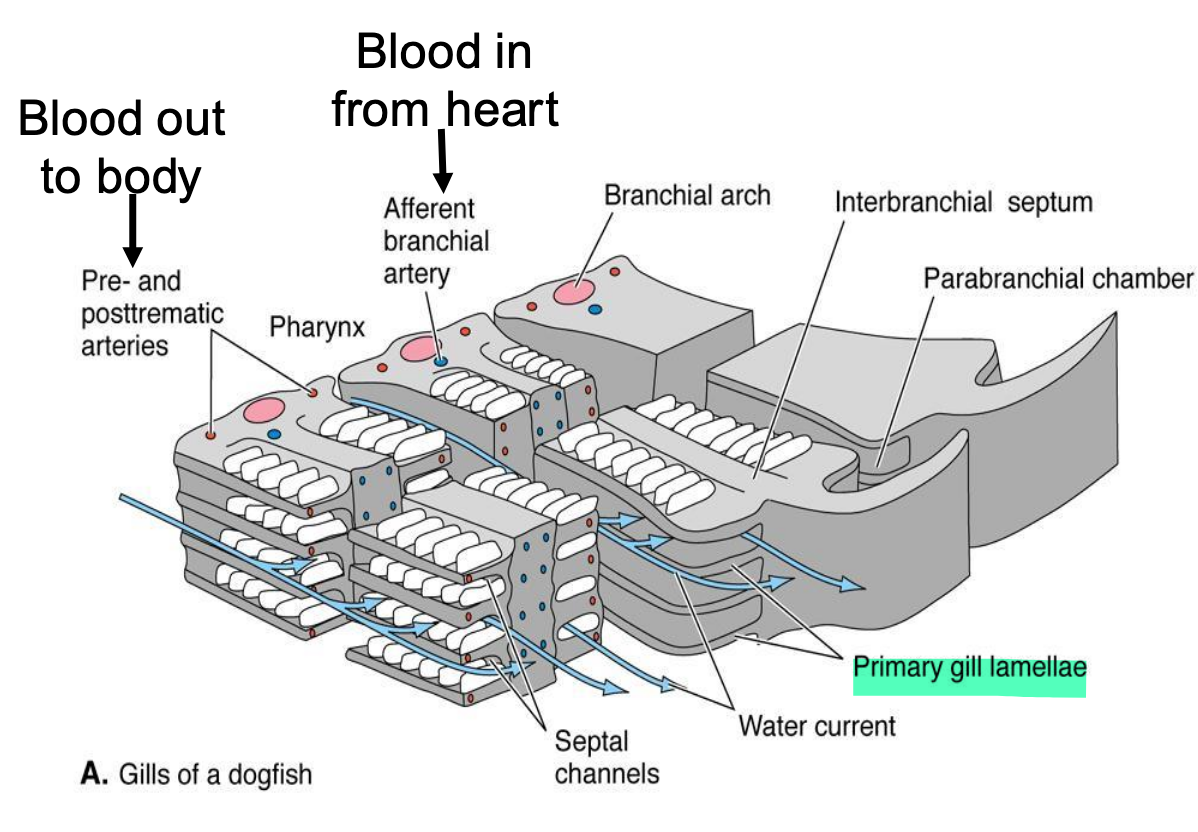
Secondary gill lamellae
• thousands of fine branches that attach perpendicular to primary lamella
• where gas exchange occurs

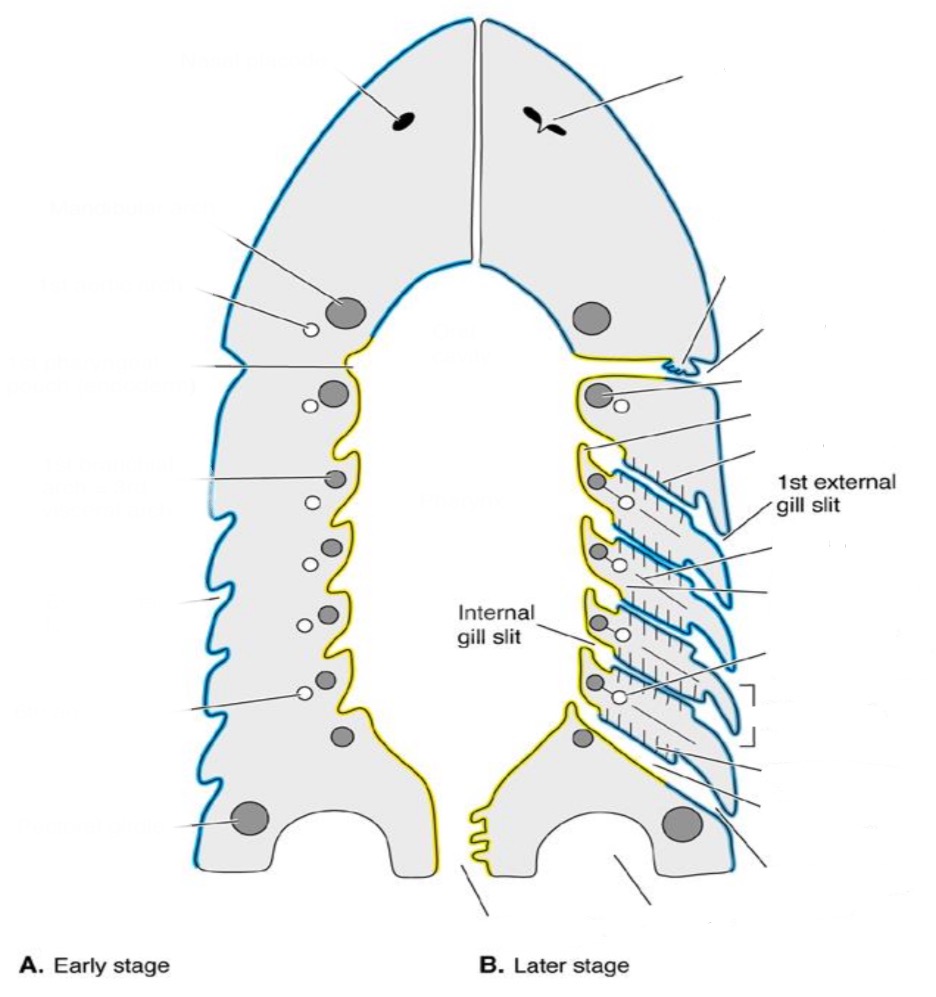
Branchial chamber (AKA pouches in early fish)
lined with gill lamellae
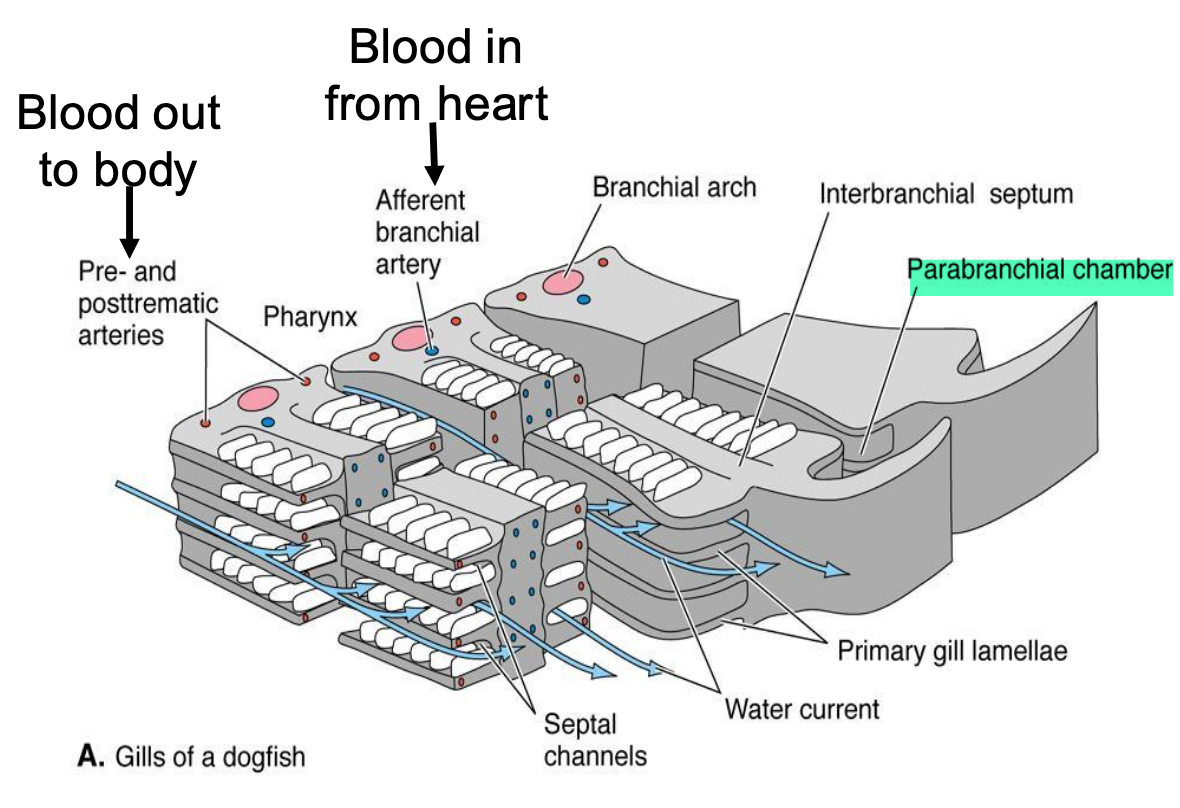
Parabranchial chamber
between branchial chamber and external gill slit;
early Osteichthyes & Chondrichthyes
• Distal tips of interbranchial septae extend into parabranchial chamber and act as valves for closing
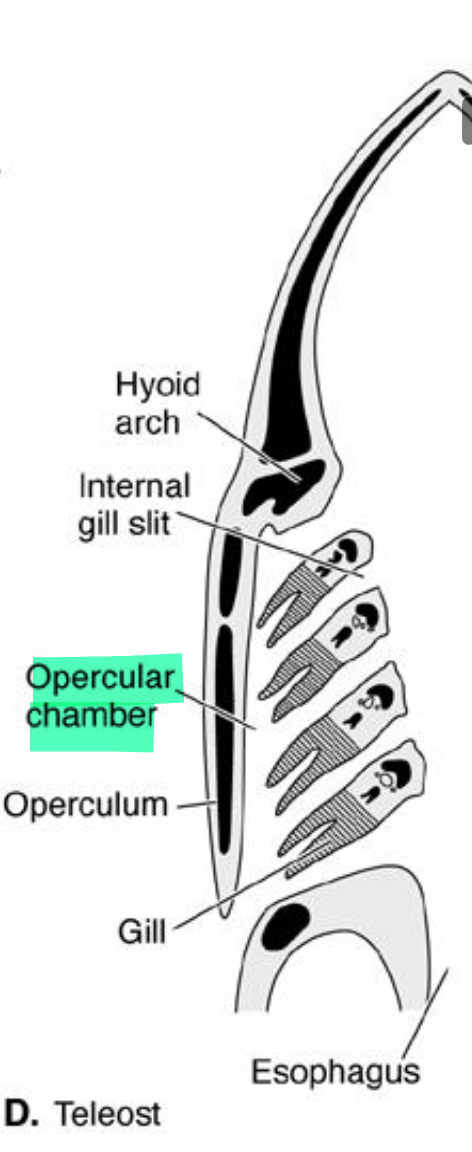
Opercular chamber
in extant bony fish
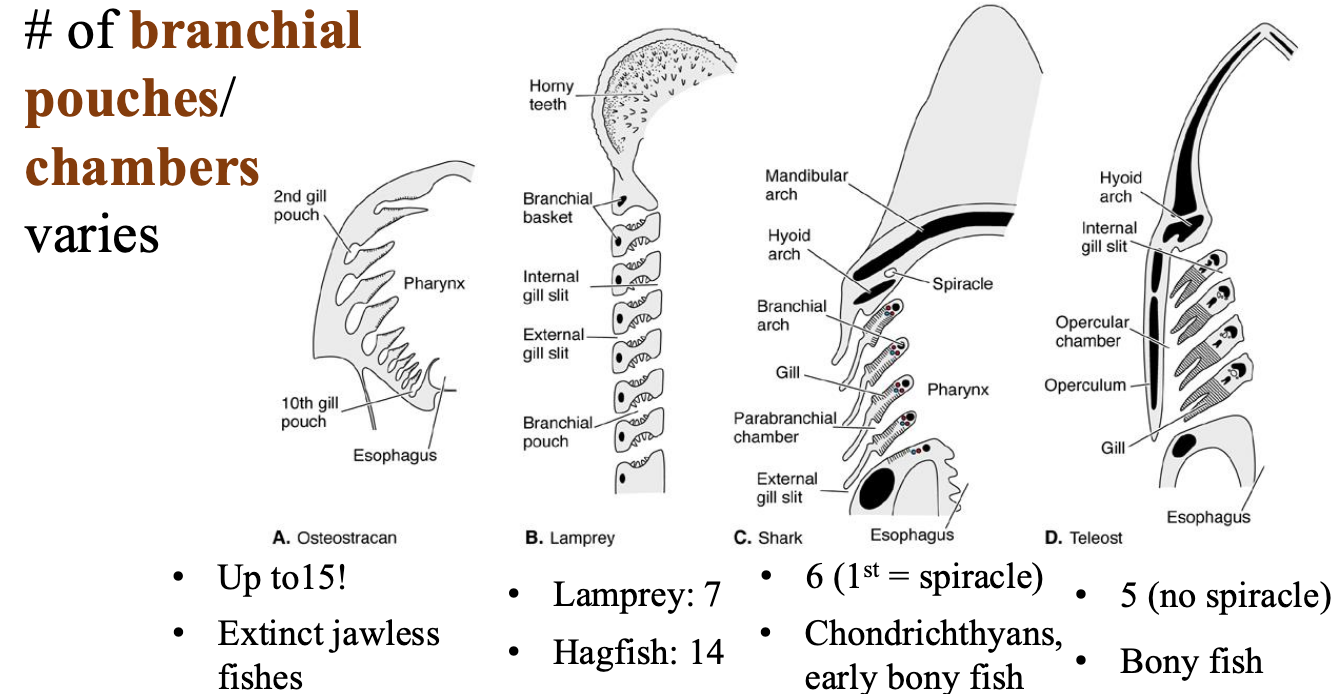
branchial pouches/ chambers
# of branchial pouches/ chambers varies
Septal Gills
Present all along the interbranchial septum (gills go all the way to the outside)
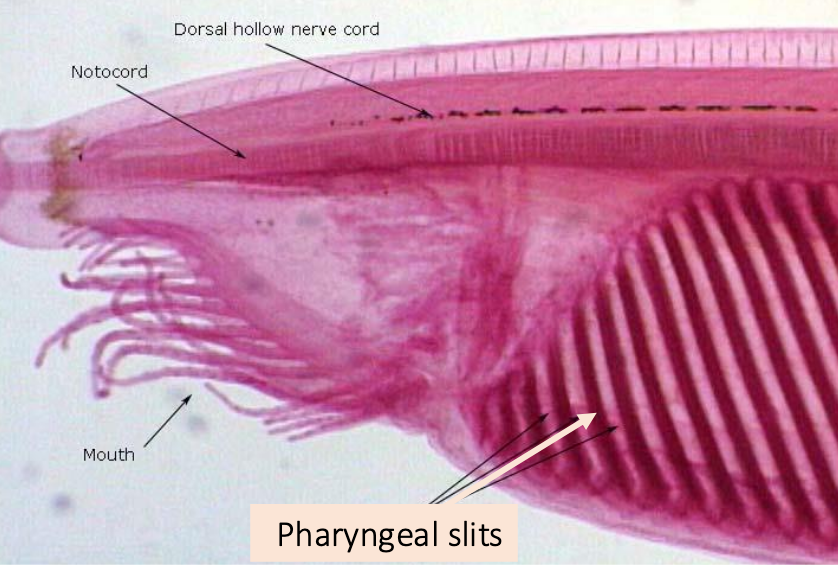
Gills: Tunicates & Cephalochordates
• Small and inactive (no gills; diffusion is enough)
• Body & pharynx wall serve as respiratory membranes
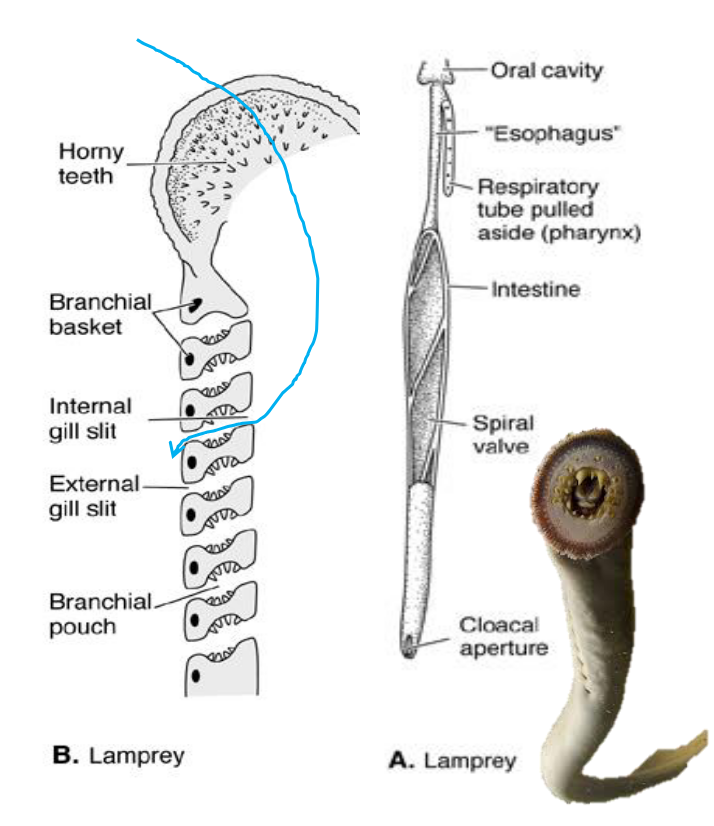
Gills: Lamprey
• Pouched gills (present in internal chambers)
• Gill lamellae in all pouches seen in the agnathans (thought to be ancestral)
• Separation of esophagus and respiratory tube so water pumped through gills while feeding
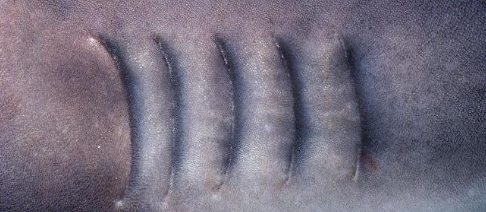
Gills: Elasmobranchs
• Septal Gills:Present all along the interbranchial septum
• Gill slits help support gill filaments
• Gill rakers in pharynx stop food going into gills
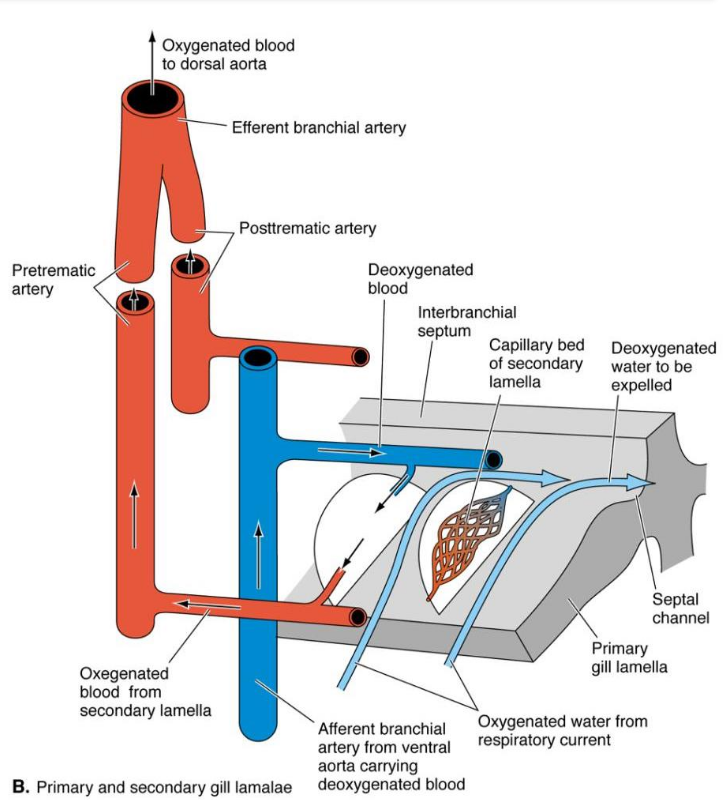
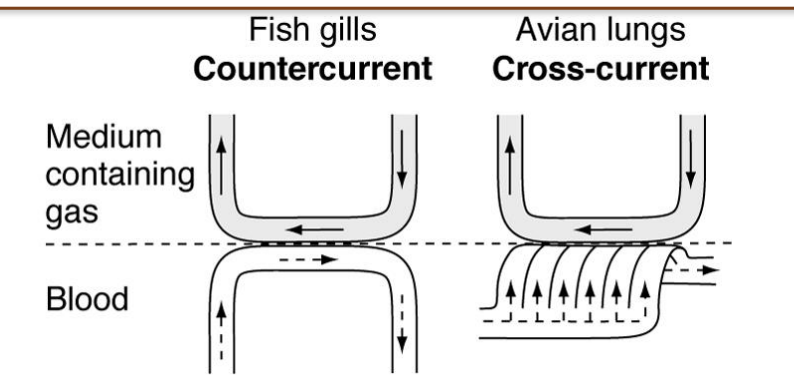
Countercurrent
• Water flows opposite direction to blood = countercurrent
• Far more efficient than both flowing in same direction (up to 95% of O2 taken up)
• Aerated blood leaving the 2º lamellae also encounters water that has not yet crossed 2º lamellae (contains more O2 than the blood)
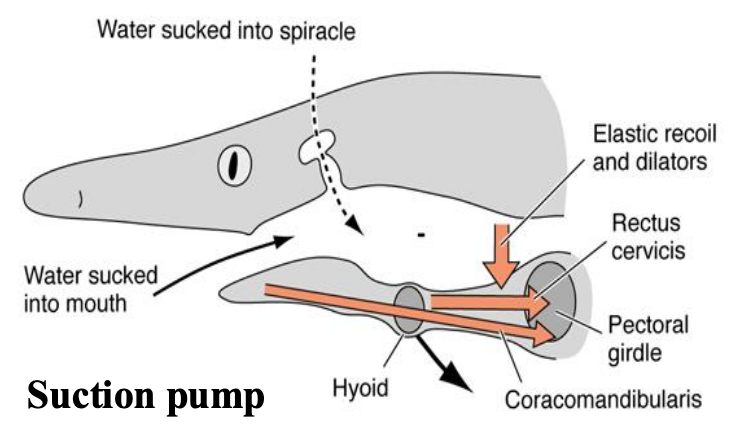
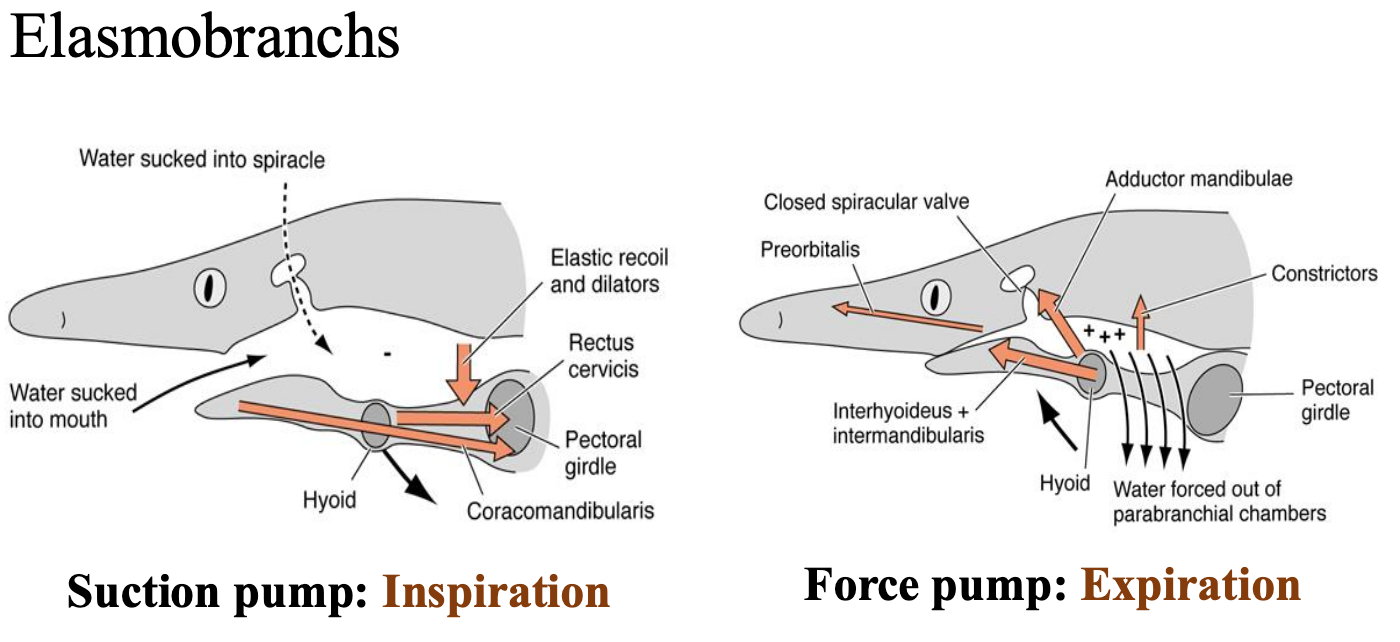
Elasmobranchs: Inspiration
• Mouth and spiracle open(abducting muscles); valves that close gills shut
• Pharynx expands: Reduces pressure relative to water
Suction pump (Elasmobranchs)
Outward bowing of parabranchial chambers also reduces pressure, together they form a suction pump
• Mouth and spiracle open(abducting muscles); valves that close gills shut
• Pharynx expands: Reduces pressure relative to water
Elasmobranchs: Expiration
Mouth and spiracle close (adducting muscles); external gill slits open
Force pump (Elasmobranchs)
Muscular compression of pharynx and branchial chambers act as a force pump

Inspiration =? and Expiraction =?
suction pump and force pump
Ram ventilation
Fast moving sharks also use open mouths to drive water (into their mouths)

Operculum
covers gills, so only one external gill slit
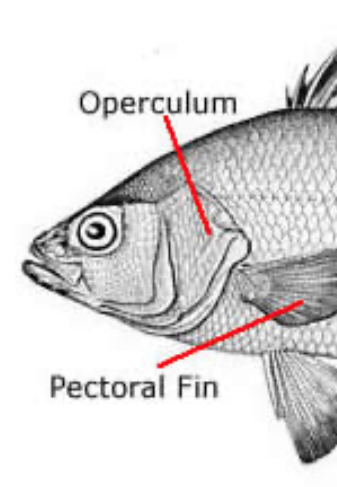
Aseptal Gills
• Interbranchial septa are reduced; gill lamellae extend freely in opercular chamber • Operculum covers gills, so only one external gill slit
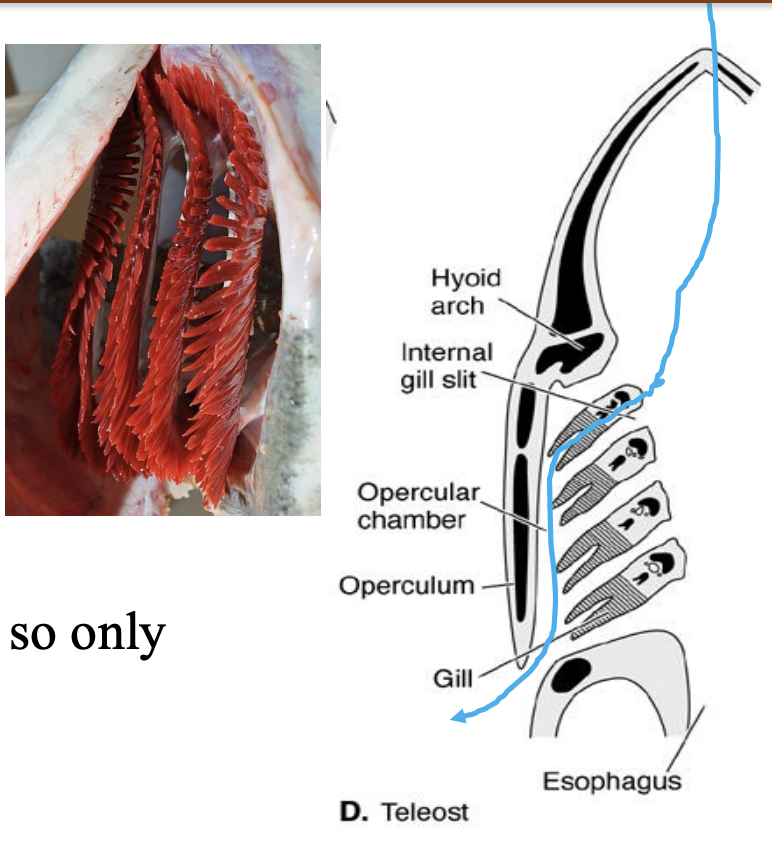
Gills: Bony Fish
• Principles of flow same as sharks, but because of opercular cavity water flow across gills during suction as well!
• Result is a continuous flow of water across gills
• Active fish have up to 10x greater surface area of gills compared to sluggish, bottom dwellers
• Good diffusion because water to blood interface is only one cell thick
Air + water breathers: Found where?
Found in water
with low O2 content (shallow warm pools)

3 Accessory respiratory organs (Lungs:Bony Fish)
1. Vascular skin: Freshwater eels migrating over land; also mudskippers
2. Modified gut: Gulp air and keep it for 30 minutes (mud eel)
3. Arborescent organs protrude into suprabranchial air chamber making a ‘lung’ (climbing perch, walking catfish)
Respiratory lungs found in which fishes?
gar, reed fish, bowfin (Actinopterygians; Neopterygii)
Also found in lungfish (Sarcopterygians)

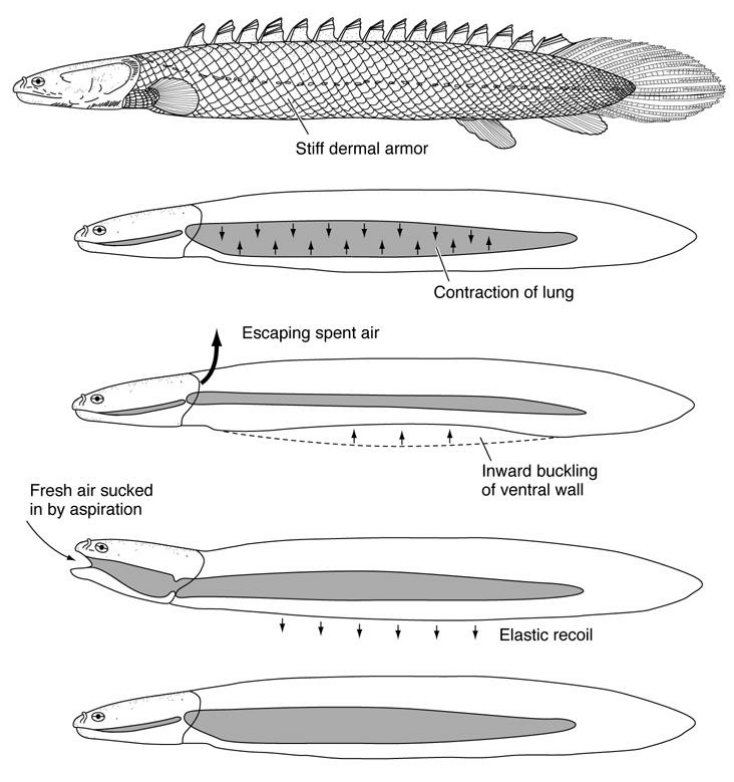
Pulse-pump system
Bony Fish: Neopterygii
Lungs expand due to force of pushing air into them from the oral cavity
Lungfish (Sarcopterygians) use as well but with mixed air
Surfactant
Bony Fish: Lungfish (Sarcopterygii; Dipnoi)
Surfactant (lipoprotein) present; acts like an anti-glue to prevent cells sticking together

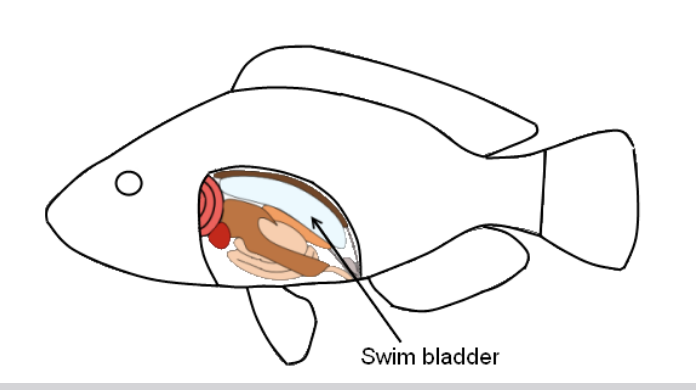
Swim Bladder
• Arises from the ancestral Actinopyterygian lung
• In O2 rich water lungs are converted into a buoyancy organ that can also take up O2 (so still a lung as well)
• Contains 80% O2: Secreted into swim bladder from gas gland, against pressure gradient
• Walls prevent diffusion
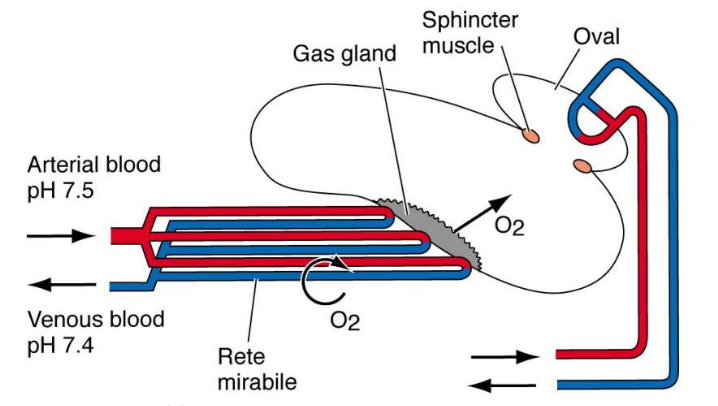
Rete mirabile
acts as a countercurrent system to prevent O2 leaving
Problems: Terrestrial (3 of them)
1. Lots of O2 but needs to be in solution to diffuse
2. Need to keep lungs moist with no excessive loss of water
• Air saturated with water vapor, mucous conditions air first, not a full exchange of air in a cycle
3. Prevent collapse of lung
• Lots of internal septae
• Surfactant
• ‘Inherited’ lungs from fishes
laryngotrachael chamber
Amphibians : Vocalization
• Vocal cords in the laryngotrachael chamber
• Vibrate when air passes across
• Only males have resonating vocal sacs
• Can be filled with air

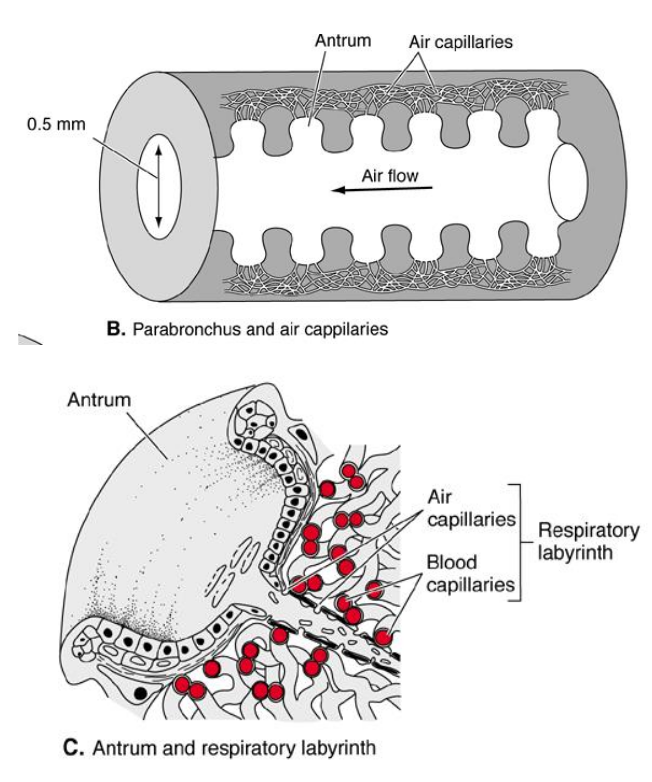
Respiratory Labyrinth
Reptiles
• Air capillaries interwoven by dense vascular capillary beds
• Short diffusion distance
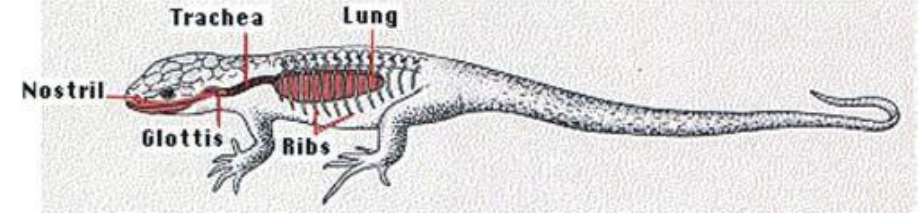
Aspiration Pump
• Draw air in
• Intercostal muscles abduct ribs & expand ribcage, pressure drops, & air drawn in, glottis is closed, and air is held in
• Long periods of apnea (temporary cessation of breathing)
• Air expelled by adduction of ribs & smooth muscle in lung wall
• More efficient than buccal pump (air transferred to lungs in one movement)
diaphragmatic muscle (crocs)
Aspiration Pump
• Crocs have an unusual system involving a diaphragmatic muscle which pulls liver down
• Air expulsion by contraction of abdominal flank muscles

Steps of breathing cycle for birds
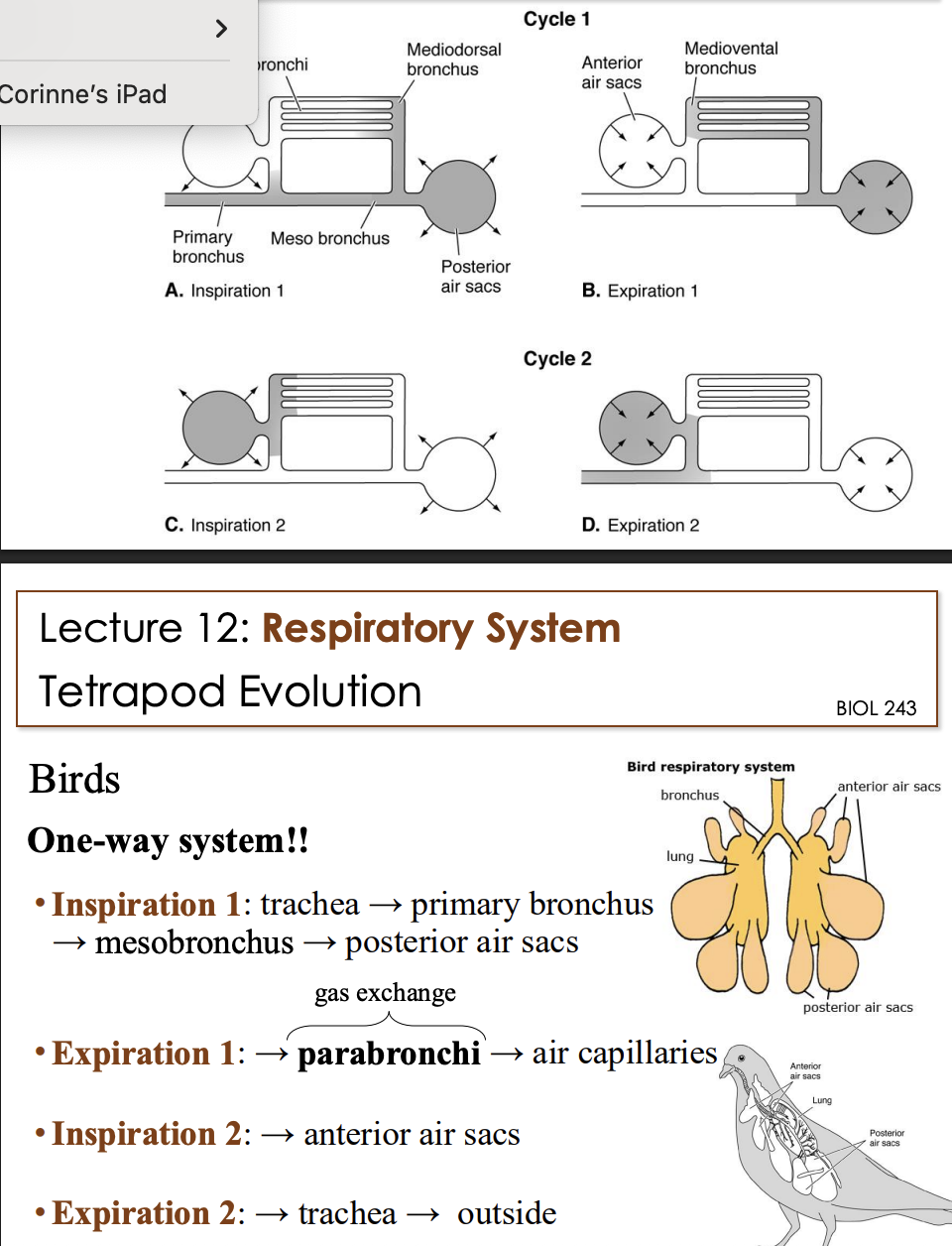
Cross-current flow
Birds
Air flows L to R and loses oxygen to blood; blood flowing across the air gains oxygen
• Creates gradient for oxygen transfer
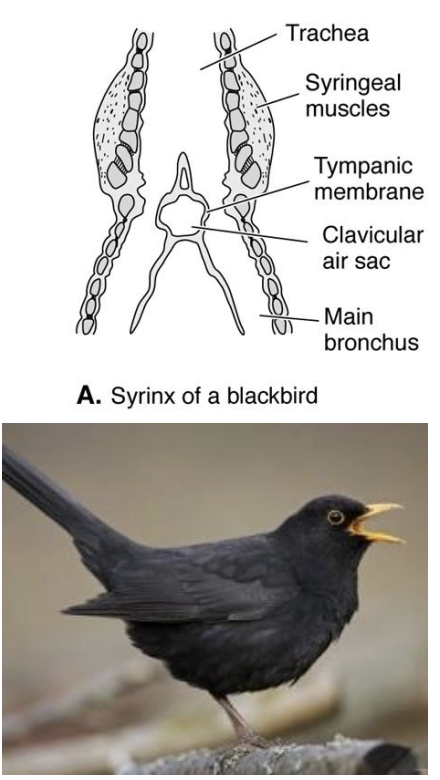
Syrinx
Birds: Vocalization
• Syrinx: lower larynx or voice organ
• Found at the junction of the trachea and bronchi
secondary palate
Mammals
soft palate, breathing
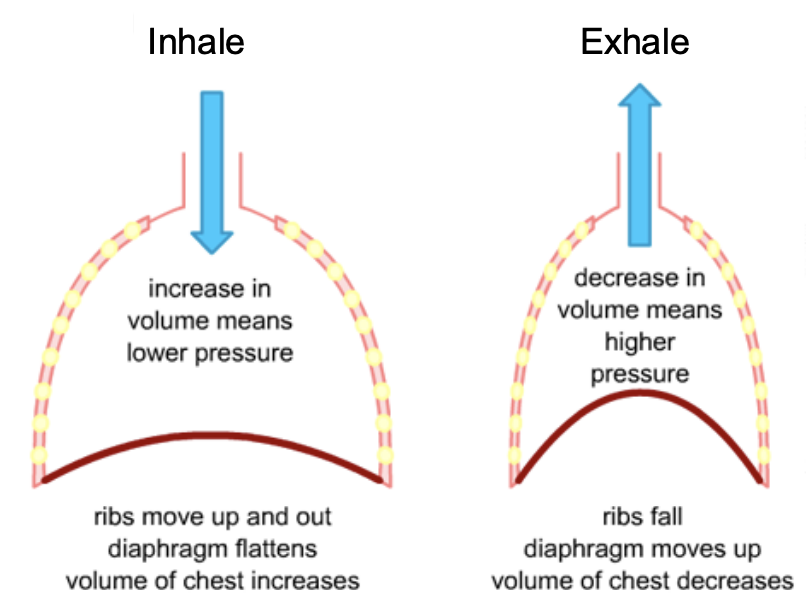
costal aspiration pump
mammals
rib based
• Air moves in & out by changes in size of pleural cavity
• Increase by contraction of diaphragm and intercostal muscles, and clavicle and neck
• Diaphragm contracts to increase pleural cavity size
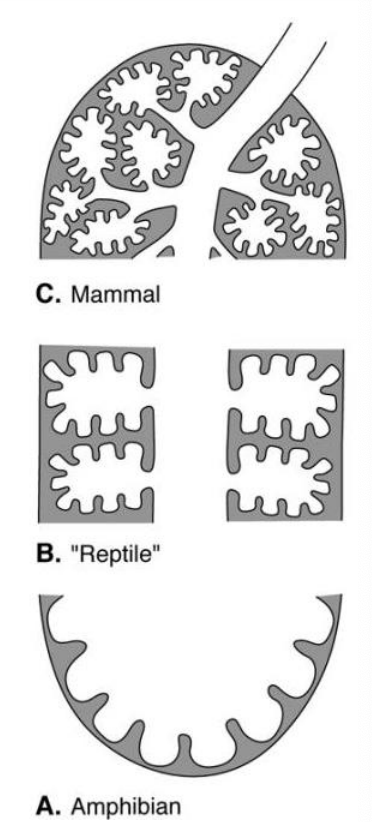
respiratory tree
c. mammals (in image)