chapter 6: reaction pathways to ATP hydrolysis
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
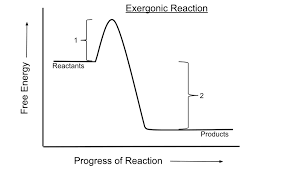
catabolic reaction
increases entropy by taking complex molecules and breaking them down into simpler ones. they are exergonic and occur spontaneously. there is negative gibbs free energy.
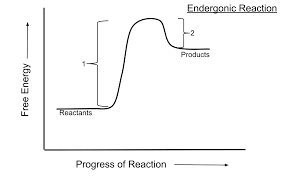
anabolic pathways
consumes energy to build complex molecules from simple ones. endergonic reactions that are nonspontaneous and have positive gibbs free energy.
for a spontaneous change to occur, a system must:
give up enthalpy/total energy ( - delta h) and which increases entropy ( + delta s)
catabolic pathway, exergonic reaction, entropy mnemonic
the cat exits through the window.
anabolic pathway, endergonic reaction, less entropy mnemonic
the analytical bodybuilder ended her workout.
metabolism is the
totality of an organisms chemical reactions that manage the material and energy resources of the cell. it is essential to life!
cells are at
dynamic disequilibrium, constantly exchanging materials and energy with their surroundings. cells are open systems. closed systems results in equilibrium, which means cell/system death.
what is energy coupling?
the use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one. for example, the breakdown of ATP to power cellular functions.
describe the structure of ATP molecules
ATP is an unstable molecule consisting of 3 phosphate groups, a nitrogenous base, and a ribose sugar. its phosphate groups are extremely negative and repel each other, which contributes to its high-energy nature and ability to release energy when hydrolyzed.
how is mechanical, transport, and chemical work powered?
by the hydrolysis of of ATP.