Econ
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
scarcity
exists where we desire more than what we can have
Tradeoff
You must give something up when we make a choice
opportunity cost
value of the next best option when you make a choice
Example: Watching GOT instead of Studying
resources
factors of production; basic elements of goods and services
Labor
people who do the work
Human Capital
knowledge to do the job
Physical Capital
the tool needed for a job
Rational Decision
benefit the decision maker; weighs all marginal costs and marginal benifits
Marginal Benefit
the area beyond where we are now and the effects of taking another step
example: more preparedness when you study for 1 more hour
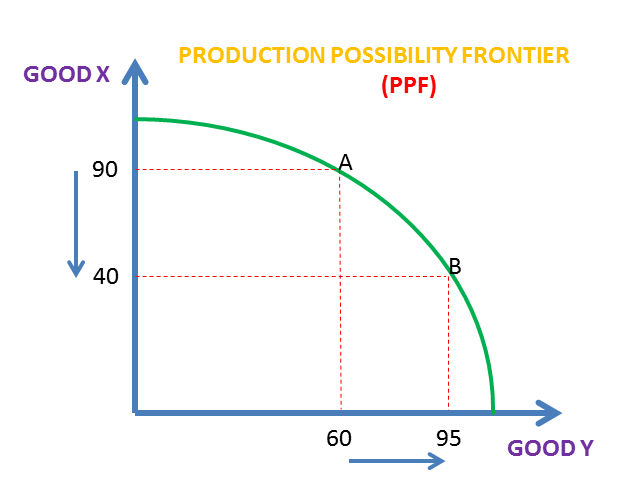
Production Possibilities Frotier
Helps a country/company determine their opportunity costs in production of 2 goods
3 Economic Decisions
What should be produced? (Choice & Tradeoff)
How should it be produced? (Resources)
For whom should it be produced? (Who get the supply)
Society’s Economic Goals
Economic Growth
Efficency
Equity
Economic Security
Economic Freedom
Net Benefit
Benefit of the Choice ($) - The Cost of the Choice
Bounded rationality
choices that are "good enough" rather than optimal, due to cognitive limitations and time constraints
Supply’s POV
Seller and Producer
Law of Supply
As price increases quantity supplied increases (Direct Relationship)
POV of Demand
Buyers and Consumers
Law of Demand
Price increace causes quantity to decrease (Indirect Relationship)
Change in Demand
The curve is picked up and moved
Change in Quantity Demanded
movment along current curve
Shifters of Demand
Taste
Price related of related goods
Income
Expectations
number of buyers
Shifters of Supply
Cost of Input
Gov. Policies
Tech
Number of Firms
Natural Disasters
Expectations
Shortage
excess demand
Surplus
excess supply
Command
Government oversees production and establishes wages
ex: North Korea
Traditional
Everyone has a role
ex: Amish Communites
Market
Decisions made by consumer and business owner
Monopoly
one seller market, seller has power, no innovation
Oligopoly
few sellers and some buyers, mostly power with seller, more innovation
Monopolist Competition
Many sellers with similar products, buyers have most power, brand loyalty, innovation
Perfect Competition
Sellers with the same product, buyers have all the power, A LOT of Innovation
Inflation
A rise in the price level of goods and the dollar depreciates in value
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
a measure of the overall price level faced by a typical consumer
Public Goods
goods/services that can be consumed by a group of people and cannot be prevented from using it
Private Good
A good that can be used by only one person at a time
Externality
affect felt beyond those whose decisions caused the effect
For the economy described by the production possibilities curve above, which of the following is true?
The economy cannot produce at point X using currently available resources and technology
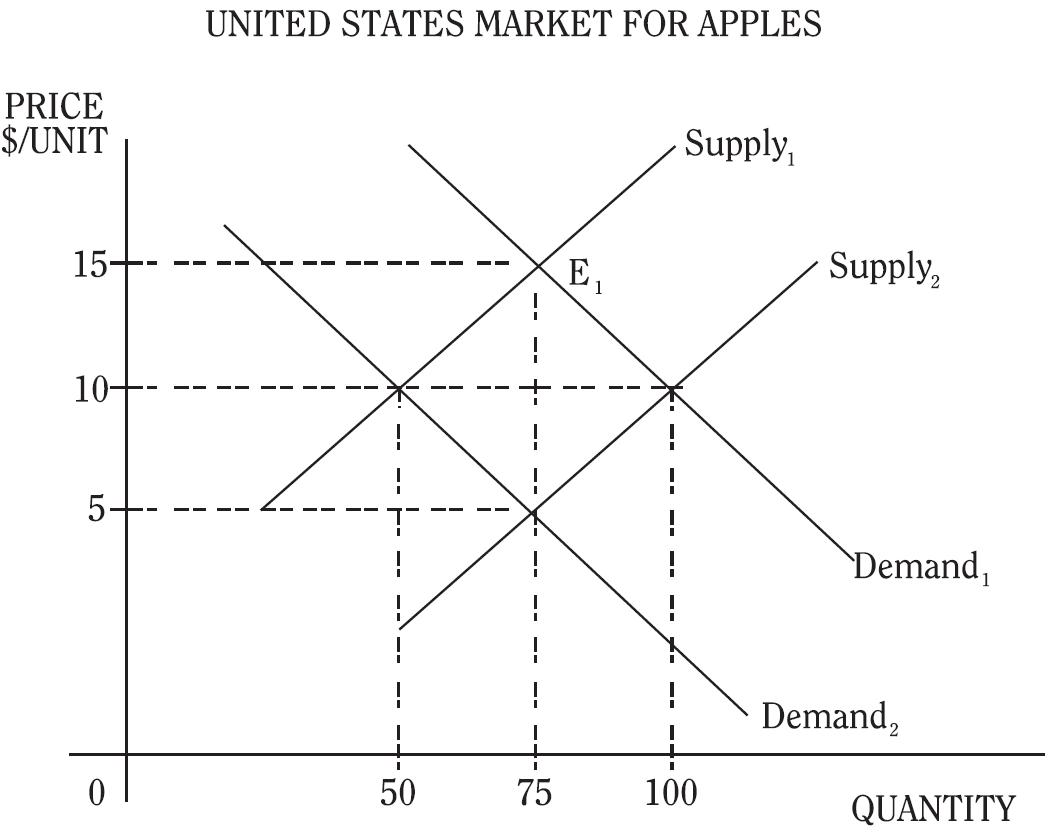
The United States market for apples is in equilibrium at E1, where 75 units are sold at a price of $15 per unit. If consumers' per capita disposable income decreases, the equilibrium price and quantity of apples sold can be which of the following?
$10 | 50
Which of the following economic policies is likely to result in the greatest reduction in aggregate demand?
A $5 billion decrease in government purchases accompanied by a $5 billion increase in personal income taxes
Which of the following would increase the demand for workers in the short run?
An increase in the price of the product
Which of the following would shift the supply curve for gasoline rightward?
A decrease in the price of a resource used to produce gasoline, such as crude oil
Oil is used by many firms for production. Political instability in oil-producing countries has decreased the oil supply and increased the price of a barrel of oil.
As a result, the short-run aggregate supply curve would:
Shift to the left
Which of the following is an example of a tertiary economic activity?
Development of ecotourism in Costa Rica
Primary economic activities include which of the following?
Mining and mineral extraction
In a market characterized by pure monopoly control, which of the following is a limit on the power of monopoly?
the elasticity of the demand curve
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the sum of:
Personal consumption, gross private investment, government spending, and net exports
The required reserves ratio for banks is set by who?
the Fed
Which of the following is an example of a countercyclical monetary policy?
reducing interest rates to stimulate economic activity
Over a 12-month period the purchasing power of the United States dollar dropped by 10 percent and interest rates increased from 5 percent to 15 percent. This is an example of:
Inflation