NURS
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
emotional and social intelligence (ESI)
vital components of effective communication and leadership
professional communication
empathy, equality, openness, positivity, supportiveness, respect, dignity
past experiences, context, precipitating events, environment, preconceptions
how do we interpret nonverbal communication?
verbal communication
talking, listening, tone of voice, inflection, attitude
T
temperature
BP
blood pressure
HR
heart rate
VS (VSS)
vital signs (vital signs stable)
RR
respiratory rate
Ht
height
Wt
weight
I/O
intake/output
Dx
diagnosis
communication process
message sent, message interpreted, information filtered, response
message interpreted
the receivers belief about what the message means and influenced by context, environment, precipitating event, transmission, past experiences
information filtered
can lose valuable information during filtration
response
feedback loop
each message is interpreted
what is the biggest and most important thing about the communication process
therapeutic communication
develop trust (clear communication in words they understand, keep promises, protect privacy, avoid negative communication, be available, eye contact, sit down, express empathy, open communication with open-ended questions, clarifying information, be aware of body language, use touch)
we do not listen to understand. we listen to reply
what is the biggest communication problem?
active listening
paraphrase, reflect, open questioning, acknowledging, summarizing, framing, reframing
look interested (be interested)
L in LISTEN mean?
involve yourself by responding
what does I stand for in LISTEN?
Stay on target
what does the S mean in LISTEN?
test your understanding
what does the T mean in LISTEN?
evaluate the message
what does the E mean in LISTEN?
neutralize the feelings
what does the N mean in LISTEN?
nonverbal communication
facial expressions, eye contact, posture, body movement, how one dresses, lifestyle, material possessions
conflict resolution styles
avoidance, accommodation, force, compromise, collaboration
actively listen, dont take it personal, work together, dont make it personal
active listening
improves the likelihood of receiving the correct message
written communication
accuracy, attention to detail, thoroughness, conciseness
documentation, white boards, emails, texts
forms of written communication
accuracy
concise, descriptive, truthful. no judgement or perceptions
clear and accurate documentation
essential to safe, quality nursing care
negative communication
yes or no questions (closed communication), blocking, false assurances/false hope, conflicting messages
negative communication: blocking
•“Nurse, I’ve never had surgery before. I’m afraid I might not ever wake up.” Mr. Clayton is twisting the bed sheet as he speaks.——-NEVER respond like this: “Oh, Mr. Clayton, many people feel that way. It’ll be okay.” Makayla Butler, RN, smiles brightly, pats his hand, picks up the dirty line bag, and bounces out of the room
information and perception
what causes conflict?
misunderstandings and emotions
what makes conflict worse?
passive, passive aggressive, aggressive, and assertive
four basic communication styles
decubitus ulcer
pressure wound or bed sore
staged by order of severity
only those with specialty training stage…otherwise describe!
passive
emotionally dishonest, indirect, inhibited, self-denying, blaming, apologetic
passive aggressive
emotionally dishonest, indirect. self-denying at first. self enhancing at expense of others later
aggressive
inappropriately honest, direct, expressive, attacking, blaming, controlling, self enhancing expense of others
assertive
where we should be as a nurse; appropriately honest, direct self enhancing, expressive, self confident, empathic to emotions of all involved
handoff report
transfer and acceptance of patient care; vital for effective communication; poor handoff reports can result in medical errors; standardized methods; use of SBAR
situation, background, assessment, recommendation
SBAR stands for? p. 347
always use when calling the doctor
closed loop communication
sender initiates message to receiver repeats message back to sender verifies the message REPEATS
used in an emergency situation especially
subjective and objective
what is described when you explain the assessment information to the doctor?
example of SBAR

integumentary system
skin (epidermis, dermis), hair, nails, nerves, glands (sweat, sebaceous)
adip/o
fat
lip/o
fat
steat/o
fat
cutane/o
skin
derm/o
skin
dermat/o
skin
hidr/o
sweat
seb/o
oil
sebace/o
oil
-rrhea
drainage
pil/o
hair
trich/o
hair
nails
clubbing of the fingernail
kerato-
hard
xero-
dryness
crypto-
hidden
leuko-
white
erythro-
red
xantho-
yellow
melano-
black
cyan/o-
blue
pruritus
an itch
urticaria
hives (raised/splotchy areas of skin, could be d/t allergic reaction)
dermatalgia/dermatodynia
rash
diaphoresis
sweating
hyperhidrosis
excess…
anhidrosis
lack of…
depigmentation
loss of pigmentation
vitiligo
disease causes loss of skin color
hypermelanosis
a darkening area of the skin
alopecia
hair loss
hypertrichosis
too much hair
comedo
white head or blackhead
macerate
very wet, soggy to the touch (exposed to moisture, poor wound healing)
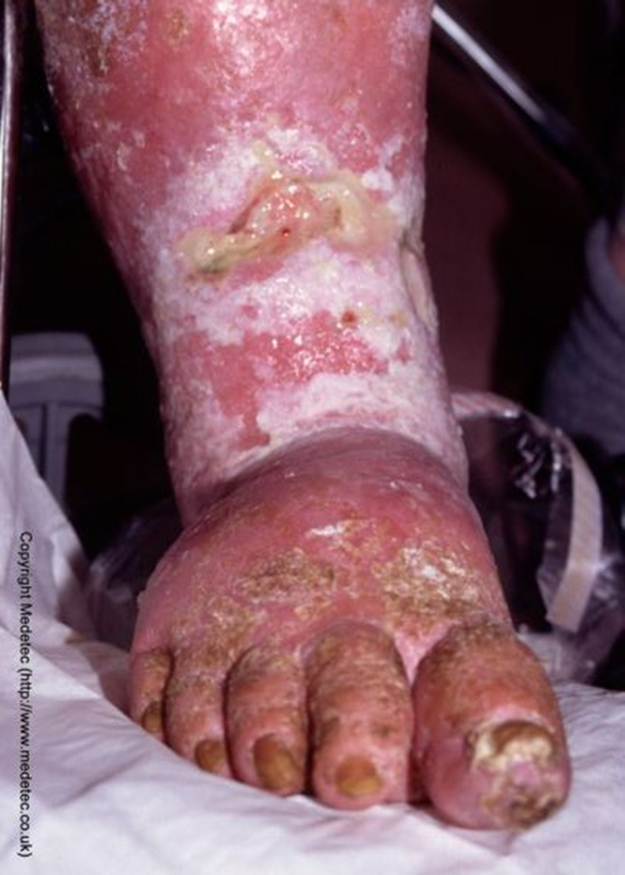
urticaria
swollen raised, itchy area
dermatolysis
skin broken away from the body
location, size, color, texture, filling of the rash (pustules)
what is apart of the description of a rash?
generalized or spreading
location of rash?
papules
< 1 cm
nodules
> 1 cm
true
plaques are large and flat
vesicles
< 1cm and filled with clear fluid
bulla
> 1cm and filled with clear fluid
pustules
filled with pus
abscesses
large pustules
macules
freckles; small flat spots
nevi
mole is a what?
patches
large macules (freckles)
burn
exposure to a harmful agent; heat, radiation, chemicals, electricity, or friction
first degree burn
affects only the epidermis (outer layer) of the skin