Anatomy and Physiology: Lab 10 Brain, Spinal Cord, Peripheral Nerves & Motor Nervous System (lecture)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Phrenic Nerve
Diaphram
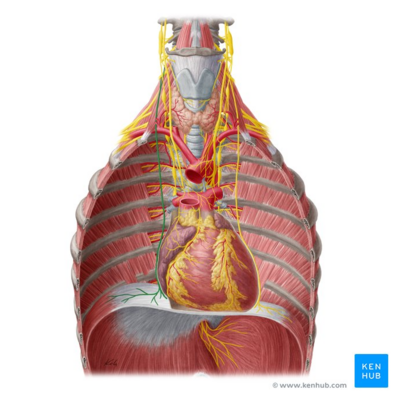
Anatomical marker of Phrenic Nerve?
Lateral to heart
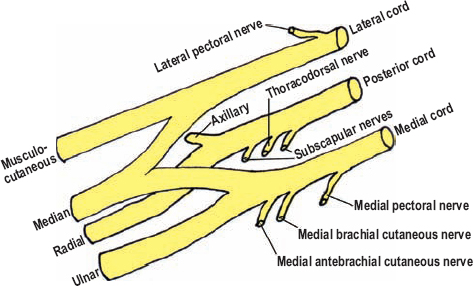
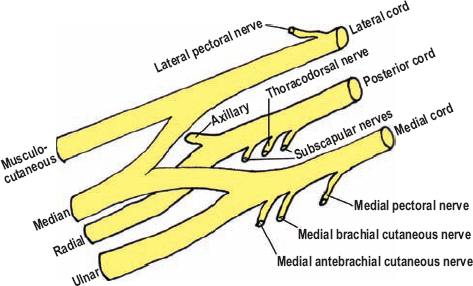
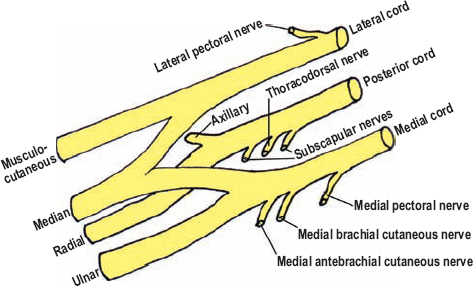
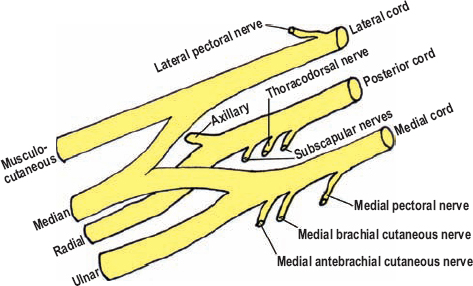
What nerves make up the Brachial Plexus?
musculocutaneous
median
ulnar
radial
axillary
What nerves make up the Lumbar Plexus?
Femoral
Obturator
What nerves make up the Sacral Plexus?
Sciatic
*Tibial
*Common Fibular
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Musculocutaneous Nerve
Sensory: lateral forearm
Motor: all anterior arm muscles; forearm flexion, forearm supination
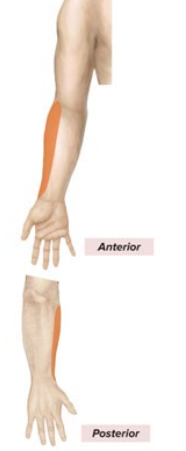
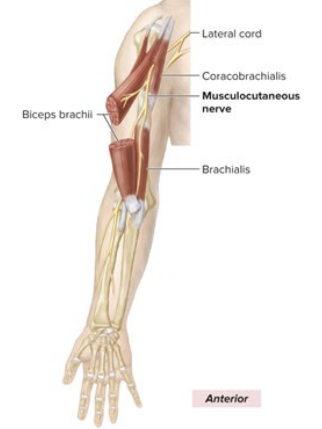
Anatomical marker of Musculocutaneous Nerve
pierces coracobrachialis
stays in upper arm
lateral-most nerve in the “M”
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Median nerve
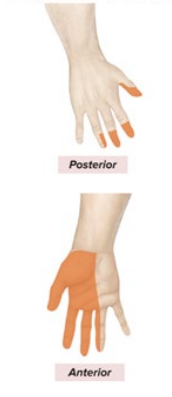
Sensory: lateral palm, anterior digits 1-3
Motor: anterior forearm muscles (NOT Flexor Carpi Ulnaris), Thenar muscle
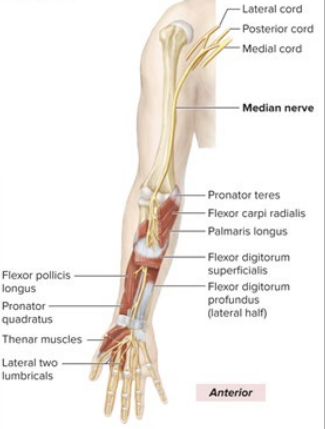
What is the anatomical marker for the Median Nerve?
innervates anterior forearm
innervates thenar muscle
middle nerve of the “M”
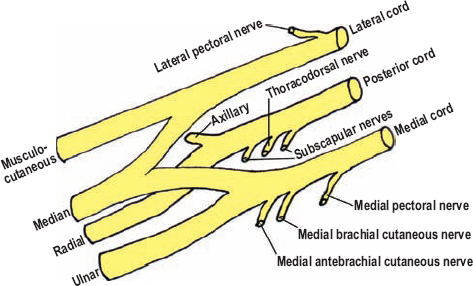
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Ulnar nerve
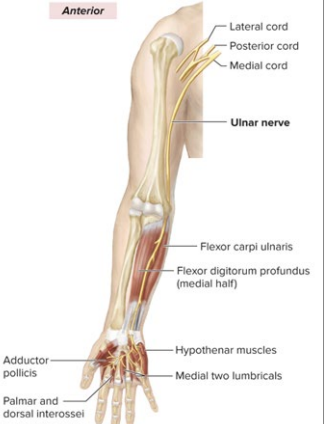
Sensory: Digits 4-5
Motor: Flexor Carpi Ulnaris; flex wrist, adduct/abduct fingers
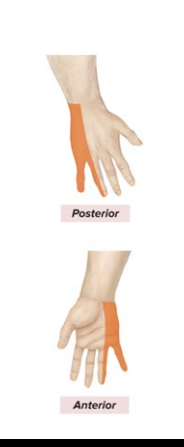
What is the anatomical marker of the Ulnar nerve?
innervates medial forearm
innervates hypothenar
innervates flexor carpi ulnaris
most medial nerve of the “M”
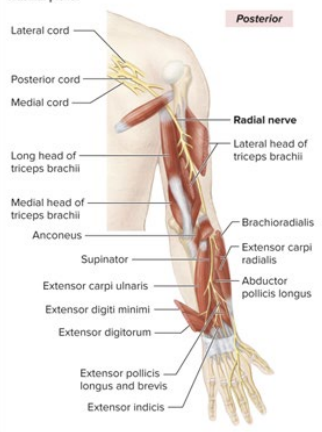
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Radial nerve
Sensory: Posterior arm and forearm, back of hand, posterior digits 1-3
Motor: all posterior arm and forearm muscles
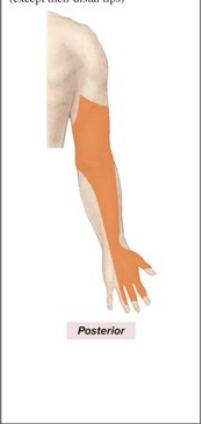
What is the anatomical marker of the Radial nerve?
all posterior arm muscles (extends length of entire arm)
lateral part of the “Y”
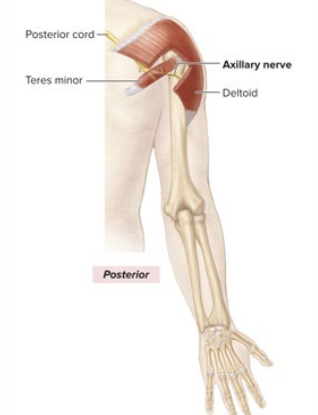
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Axillary nerve
Sensory: upper, lateral arm
Motor: Deltoid and Teres Minor; shoulder abduction, outward rotation
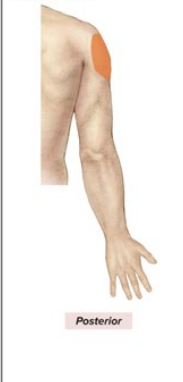
What is the anatomical marker for the axillary nerve?
STAYS within armpit
innervates deltoid and teres minor
medial part of the “Y”
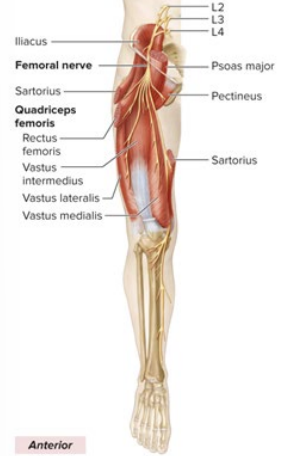
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Femoral nerve
Sensory: anterior thigh, medial leg, foot
Motor: anterior thigh muscles; extend knee, flex hip
What is the anatomical marker of the the Femoral nerve?
innervates inguinal ligament
all anterior thigh muscles, medial leg, foot
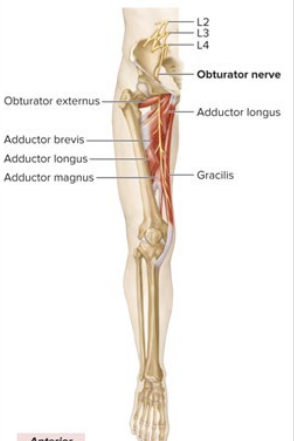
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Obturator nerve
Sensory: Upper, medial thigh
Motor: Medial thigh muscles
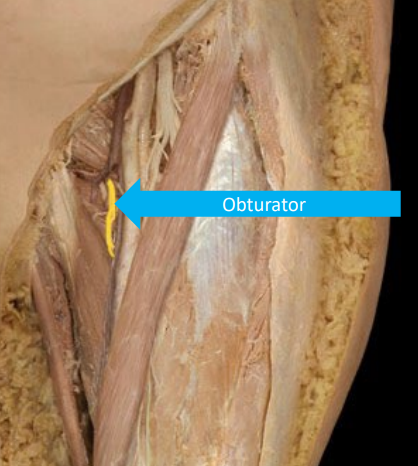
What is the anatomical marker of the Obturator nerve?
innervates inner thigh (addductors: gracilis, aductor longus, pectineus)
on top of adductor brevis
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Sciatic nerve
Sensory: NONE
Motor: Posterior thigh muscles
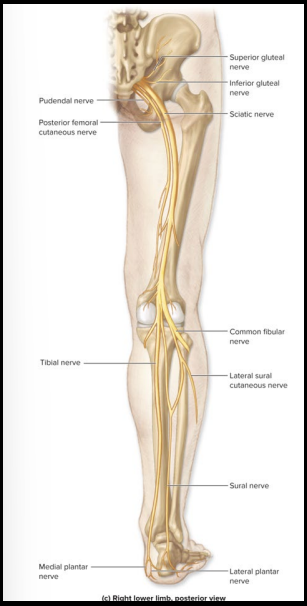
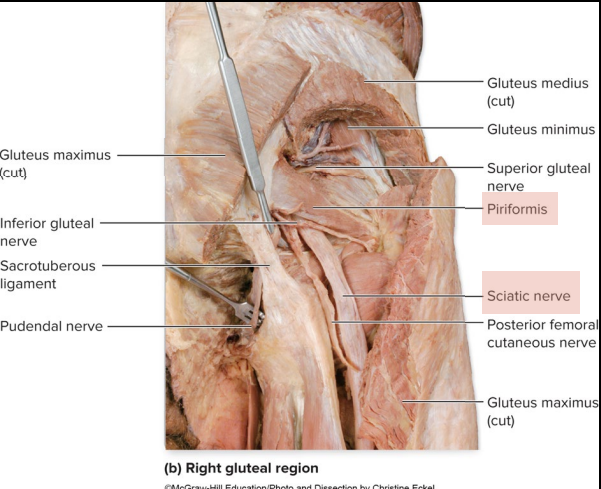
What is the anatomical marker of the Sciatic nerve?
posterior thigh
controls Tibial and common Fibular nerve
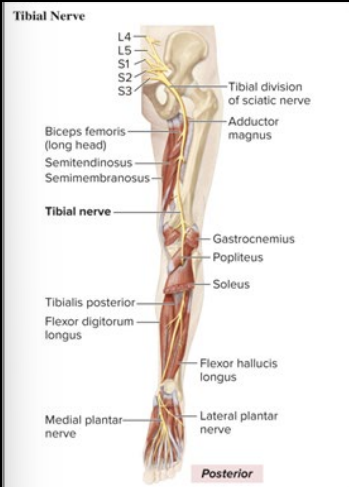
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Tibial nerve
Sensory: Heel, plantar foot
Motor: all posterior leg muscles; plantar flexion, inversion, flex digits
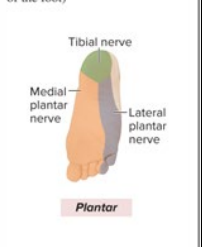
What is the anatomical marker for the Tibial nerve?
calves, bottom of foot, branches from sciatic nerve in lower leg
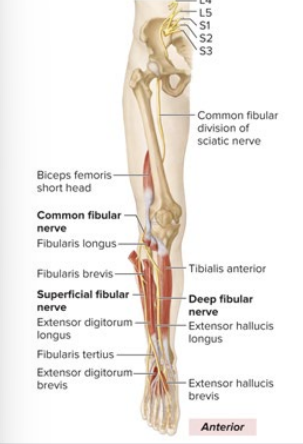
Sensory and Motor Innervation of Common Fibular
Sensory: bit of skin between toes 1 and 2, lateral leg, dorsum foot
Motor: all anterior and lateral leg muscles, dorsiflexion
What is the anatomical marker for the Common Fibular muscle?
parallel to tibial nerve
wraps around the lower leg to the front
What are spinal nerves?
exits thru intervertebral foramen
mixed motor and sensory (two way street)
branch into ventral and dorsal ramus (like highway exists)
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
8 cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Sacral
1 Coccygeal
How are spinal nerves named?
Cervical: nerve named for vertebra below; C5 nerve is between C4 and C5 (C8 nerve is between C7 and T1)
Everything else: nerve names for the vertebra above; T6 nerve is between T6-T7 vertebra
What are ganglia?
cell bodies in the PNS. Can be apart of sensory or autonomic pathways (no motor!)
What are the divisions of the Peripheral nervous system?
Autonomic nervous system
sympathetic (homeostasis during stress/emergency; fight or flight)
parasympathetic (rest and digest; homeostasis during rest)
somatic nervous system
sensory afferent
motor efferent
What is Bell’s Palsy?
paralyze facial nerve (CN 7)
one side of the face droops (there is one facial nerve for each half of the face and usually only one is damaged)
some cases are idiopathic
most cases follow viral infections
What are characteristics of somatic/descending motor pathways?
consciously controlled
signals come from CNS and move to skeletal muscles, to move those muscles
What are the types of neurons utilized in somatic/descending pathways?
upper motor neuron (UMN) go from the brain down the spinal cord
lower motor neuron (LMN) go from a UMN or an interneuron to a skeletal muscles
What are the types of somatic/descending motor pathways?
Direct: conscious skeletal muscle movement; UMN communicates directly with LMN (no interneuron)
Indirect: reflex like knee jerk; interneurons used between UMN and LMN
What are the steps to a direct/pyramidal pathway?
1.) primary motor cortex in the brain connects to UMN
2.) UMN synapses with LMN in the anterior horn of the vertebra
3.) LMN connects to skeletal muscle
What are the types of direct/ pyramidal pathways?
lateral corticospinal tract
innervates limbs
decussate at midline at the medulla (goes from L to R side…L side of the brain controls the R side of the body)
anterior corticospinal tract
innervates axial skeletal muscles
posture, stability
decussate (cross midline) at spinal cord (L to R)
corticobulbar tract
innervates face and neck
doesn’t go thru spinal cord; cranial nerves instead
decussate UMN to LMN at brainstem
What are the characteristics of Indirect/extrapyramidal pathways?
modifies somatic motor pathways
more than one UMN
What are the types of indirect pathways?
Rubrospinal tract:
precise movements
moves hand way from hot stove
Reticulospinal tract:
posture, balance
goes from midbrain to spinal cord
Tectospinal tract:
looking in the direction of sound or light
Vestibulospinal tract:
coordinates head and body position when we are sitting, standing or walking
works together with direct pathways
Preganglionic and Postganglionic neurons
Preganglionic neurons are PNS presynaptic neurons. They are the first UMN that send the signals. Postganglionic neurons are PNS postsynaptic neurons. They are the second LMN connected to the first LMN through a ganglion that recieve the signals.
What are the types of acetylcholine (cholinergic) receptors?
Nicotinic: found in postganglionic parasympathetic and sympathetic NS. Causes excitation
Muscarinic: cell response by G protein. Excitatory OR inhibitory (??)
Ach receptors are found in the sympathetic AND parasympathetic systems
What are the types of norepinephrine/epinephrine (adrenergic) receptors?
*receptors found in the CNS and throughout the body
alpha (excitatory)
a1: constricts blood vessels, dilates eyes
a2: CNS, sedation, stops insulin secretion in pancreas
beta
b1: hear rate increase
b2: blood vessels dilate (increase blood flow)
What are the categories of reflexes?
Intrinsic/learned: born with the reflex vs. learned
somatic/visceral: skeletal muscles vs. smooth/ cardiac muscles (ex. peeing)
Monosynaptic/Polysynaptic: poly uses interneurons
Ipsilateral/ Contralateral: starts and finishes on one side of the body vs. starts on one side and ends on the opposite side