lab med test 3 lecture 14
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
- pt with complaints of a sore throat
- fever of unknown cause
what are indications to do a throat culture
polymicrobial colonization. culture only identifies a few particule pathogens
throat culture explanation
- streptococci
- meningococci
- gonococci
-bordetella pertussis
- corynebacterium diphtheria
- candida
what pathogens are identified in a throat culture
- complete destruction of RBCs
- group a and b strep
beta hemolysis is
- partial destruction of RBC
- steptococcus pneumoniae
alpha hemolysis is
- no damage to RBC
- s. mutans and group d strep
gamma hemolysis is
hemolysis
Strep further speciated by _______
true
T/F all cultures must be performed before antibiotics initiated
empiric
cultures take 24-72 hrs to result; can consider ______ abx while waiting on culture results
identify acute nasal and/or sinus infections and to identify carriers of pathogenic bacteria
what are nasal cultures used for
- Staphylococcus aureaus (MRSA)
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Neisseria meningitidis
- RSV
what are the various organisms can colonize the nares without causing clinical infection
- Screen patients in ICU, neonatal patients, preoperative patients
- Screen healthcare workers in operating rooms or newborn nursery
what is the preventative transmission in healthcare settings (test patients and providers)
C)A MRSA nasal swab being negative
A 23-year-old female with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus is admitted to the ICU with sepsis due to pneumonia. She was recently admitted to the hospital for an episode of diabetic ketoacidosis and was discharged home roughly three weeks ago in good health. Her healthcare team initiates broad spectrum antibiotic therapy with Vancomycin and Zosyn. Which of the following tests would prompt her medical team to discontinue vancomycin?
A)A Complete Blood Count (CBC) showing leukopenia
B)A Complete metabolic panel showing elevated LFTs
C)A MRSA nasal swab being negative
D)A negative rapid strep test
- Wound or soft tissue has signs of infection
- Postoperative patient with fever of unknown origin
- Spontaneous drainage from a wound
- Delayed wound healing
- To determine appropriate wound isolation precautions
indications on when to do wound culture
Used to determine the presence of pathogenic bacteria in patients with suspected urinary tract infections
when is it indicated to do a urine culture
•+ White Blood Cells
•+ Nitrites
•+ Leukocyte Esterase
what will you find in a urinalysis
skin flora
Urine samples require special collection procedure to avoid contamination with _____ ______
1)Use a sterile container
2)Clean urinary meatus with antiseptic prep
3)Collect sample mid-stream
how to get a clean urine sample
- Negative: <10,000 bacteria/mL urine
- Positive: > 100,000 bacteria/mL urine
results for a urine culture
sensitivity
If _________ is performed, susceptibility to antibiotics will also be provided
Can take 24 hrs to grow and up to 48-72 hrs to identify species and sometimes longer for susceptibility
- Pathogen species found in urine
- Sensitivity and resistance of this organism to common antibiotics
what will urine cultures demonstrate
A.A urine culture is indicated to evaluate for causative organism of UTI
A 23-year-old female presents to the clinic for evaluation of urinary frequency. She reports that she feels the need to urinate ~10 times per day but when she goes she only produces a small amount of urine. She also notes an urgency to urinate even right after having gone to the bathroom. She also reports that her urine appears cloudy and is foul smelling. She has mild pelvic pain which is non-radiating. She reports no recent medication changes. A post-void residual is ordered and is normal. Labs, including a CBC, CMP, and HgA1c are normal. A urinalysis obtained which is seen below. Which of the following is true?
A.A urine culture is indicated to evaluate for causative organism of UTI
B.The patient should be treated for a UTI and needs no further testing given these UA results
C.The patient likely does not have a UTI; no urine culture is indicated
D.A CT with IV contrast of the abdomen is the next best step in evaluating the patient
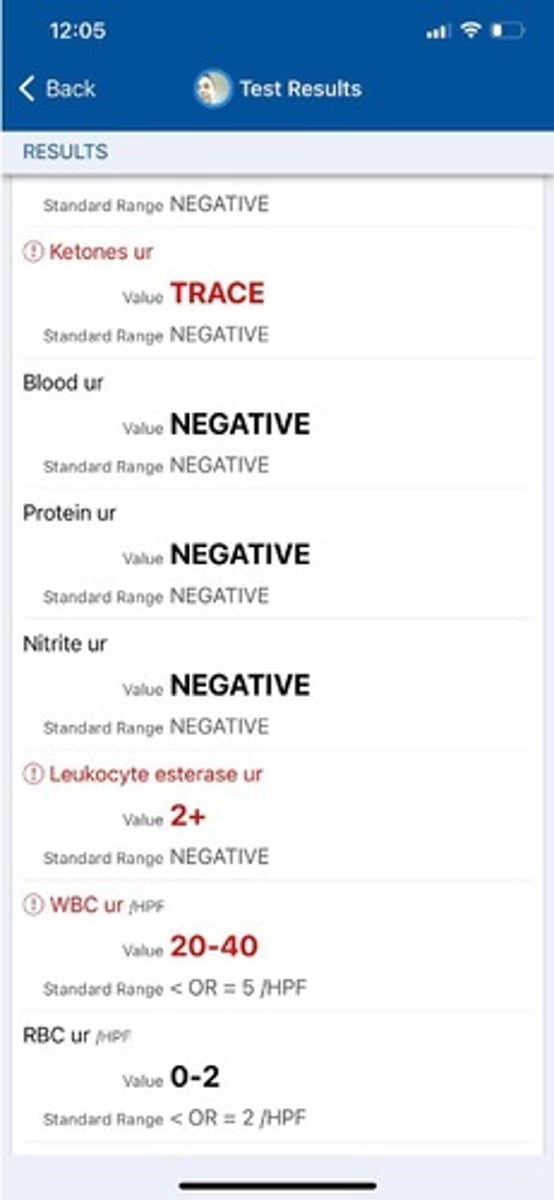
C.The patient likely does not have a UTI; no urine culture is indicated
A 23-year-old female presents to the clinic for evaluation of urinary frequency. She reports that she feels the need to urinate ~20 times per day but when she goes she only produces a small amount of urine. She also notes an urgency to urinate even right after having gone to the bathroom. She notes that her symptoms are slightly worse when she consumes alcohol or caffeine. She denies dysuria, hematuria, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, abdominal or pelvic pain, flank pain, fever, or chills. She reports no recent medication changes. A post-void residual is ordered and is normal. Labs, including a CBC, CMP, and HgA1C are all normal. A urinalysis obtained which is seen below. Which of the following is true?
A.A urine culture is indicated to more definitively rule out urinary tract infection
B.The patient should be treated for a UTI and needs no further testing given these UA results
C.The patient likely does not have a UTI; no urine culture is indicated
D.The patient likely has Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus

narrow antibiotic coverage
Once the urine culture comes in it allows the practitioners to direct antibiotic to what kind of coverage
- Provider selects the most effective and targeted antibiotic
- Reduces risk of antimicrobial resistance
- Informs decision-making if patient has recurrent urinary tract infection
- Guides treatment in non-resolving infections
- Monitors for local and global resistance trends
After getting the results for a urine culture what needs to be considered