BIOL 2111-02 Chapter 12: Central Nervous System (CNS)
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Brain and Spinal Cord
The CNS is composed of which 2 structures?
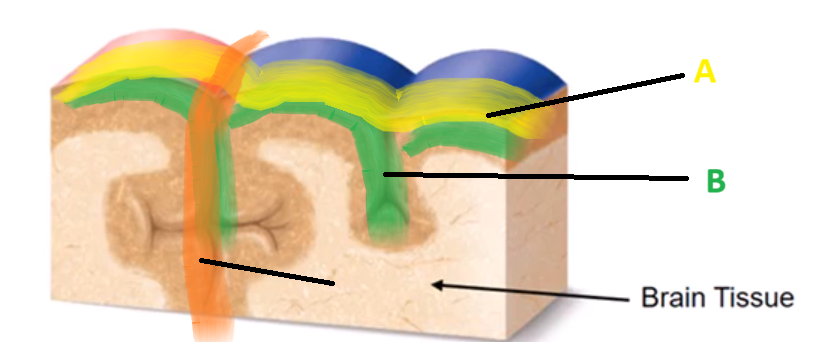
Convolutions
(definition) The folds and ridges on the surface of the brain (cerebral cortex), which increases the brain’s surface area to accommodate neurons within a limited amount of space in the skull.
Gyrus, Sulcus, Fissure
List the THREE Convolutions…
Gyrus
A
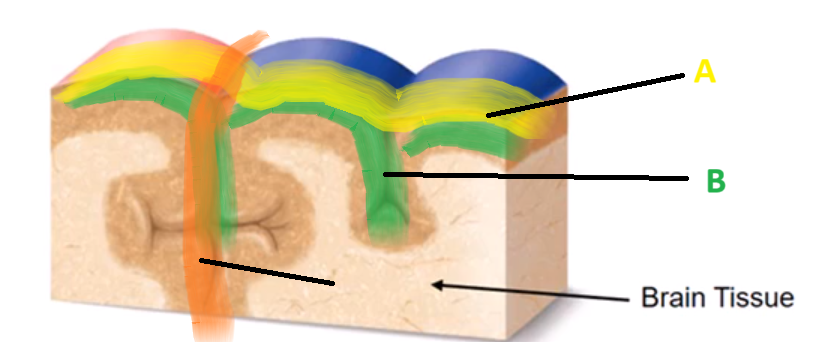
Sulcus
B
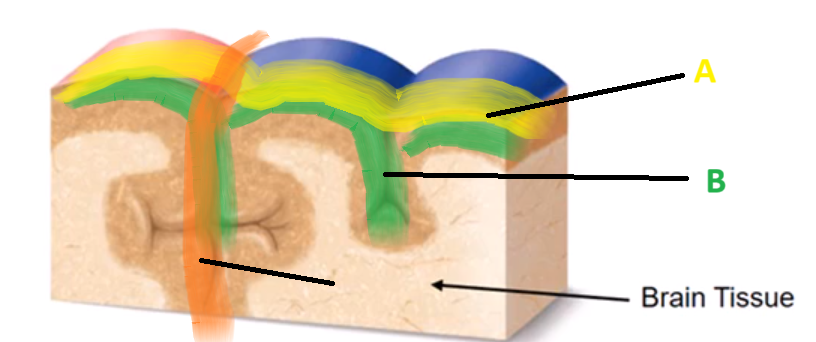
Fissure
C
Gyrus
(definition) Elevated tissue (aka the RIDGES of the brain)
Sulcus
(definition) GROOVES or SPACES between the Gyri of the brain
Fissure
(definition) a DEEP SULCI which SEPERATES the brain regions…
White Matter
(definition) Composed of lipids and fats (MYELINATED), WHITE in color, and contains mainly the AXONS of a neuron
White Matter
Between the TWO TYPES OF MATTER found in the CNS, which one contains AXONS?
Gray Matter
(definition) Contains mainly the CELL BODIES and DENDRITES of a neuron.
Gray Matter
Between the TWO TYPES OF MATTER found in the CNS, which one contains CELL BODIES and DENDRITES?
Brain
(matter arrangement) The INSIDE contains WHITE MATTER, and the OUTSIDE is covered in GRAY MATTER
Spinal Cord
(matter arrangement) The INSIDE contains GRAY MATTER, and the OUTLINE is covered in WHITE MATTER
Nerve
(definition) Is a bundle of AXONS in the Peripheral Nervous System (ALL STRUCTURES BESIDES THE BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD)
Tract
(definition) is a bundle of AXONS in the Central Nervous System (Inside the BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD)
Ganglion
(definition) is a collection of CELL BODIES and DENDRITES in the Peripheral Nervous System
Nucleus
(definition) Is a collection of CELL BODIES and DENDRITES in the Central Nervous System
Nucleus and Tract
Which TWO STRUCTURES are found in the CNS?
Nerves and Ganglions
Which TWO STRUCTURES are found in the PNS?
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, Brain Stem
List the FOUR REGIONS of the BRAIN
Cerebrum
(definition) Superior, highly convoluted area of the brain that is 83% of the brain mass…
Cerebral Cortex
(definition) Thin SUPERFICIAL layer of GRAY MATTER of the CEREBRUM, which consists of SIX LAYERS of neurons.
Cerebral Cortex
This structure is also known for their FUNCTION of being the “site of conscious mind," processing and understanding,,,
Contralateral
(definition) Something occurring on or affecting the opposite side of the body (in reference to the brain…)
False
True or False: Each HEMISPHERE of the CEREBRUM is NOT CONTRALATERAL…
Ipsilateral
(definition) Something occurring on or affecting the same side of the body (in reference to the brain…)
Lateralization
(definition) The term used to describe SPECIALIZED FUNCTIONS within each HEMISPHERE of the CEREBRUM…
Frontal Lobe
(definition) LOBE is considered the “home” of our PERSONALITY, the EMOTIONAL control center, and MOTOR FUNCTION!
Prefrontal Cortex
(definition) Involved in intellect, cognition, personality, memory, problem solving, judgement, planning, etc…
Prefrontal Cortex
Which structure of the FRONTAL LOBE acts as the GO and BRAKE system when it comes to PROCESSING…
Prefrontal Cortex
Which STRUCTURE of the FRONTAL LOBE is connected with the LIMBIC SYSTEM…
Prefrontal Cortex
FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURE known to develop slowly, and does not reach full development until early 20s or 30s…
Primary Motor Cortex
(definition) Found on the PRECENTRAL GYRUS, controls VOLUNTARY MOVEMENT (talking or moving)
Primary Motor Cortex
This FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURE can be represented spatially on a HOMUNCULUS map, with NEURONS projected to the SPINAL CORD’S VENTRAL HORN…
Premotor Cortex
(definition) Region controls learned, repetitious, SKILLED MOTOR MOVEMENTS → HELPS PLAN MOVEMENTS
Premotor Cortex
FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURE also known for being the MEMORY of MOTOR ACTIVITY…
Sports, Texting, Typing
Examples of ACTIVITIES which use Premotor Cortex
Frontal Eye Field
FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURE which Controls VOLUNTARY EYE MOVEMENT…
Broca’s Area
FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURE Found usually only on one side of the Hemisphere’s (Left), and involved in MOTOR SPEECH PRODUCTION
Broca’s Area
Disruption in this FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURE results in being able to UNDERSTAND LANGUAGE, MOUTH WORDS, but SPEECH IS IMPAIRED…
Parietal Lobe
(definition) Integrates our SENSORY experiences…
2 Structures
How many STRUCTURES are found in the PARTIETAL LOBE…
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
PARIETAL LOBE STRUCTURE found on the POST-CENTRAL GYRUS, responsible for SENSATION received from SKIN and PROPRICEPTORS, and the entire body can be represented on a HOMUNCULUS MAP…
Somatosensory Association Cortex
PARIETAL LOBE STRUCTURE involved in the MEMORY OF SENSATION, and produces an understanding of stimuli (sharp v.s. dull)
Temporal Lobe
(definition) Lobe which functions in HEARING…
Primary Auditory Cortex
TEMPORAL LOBE STRUCTURE responsible for conscious PERCEPTION of SOUND…
Auditory Assocation Cortex
TEMPORAL LOBE STRUCTURE responsible for the MEMORY and INTERPETATION of SOUND
Association
Another WORD which hints to MEMORY…
Wernicke’s Area
TEMPROAL LOBE STRUCTURE which allows us to understand the SPOKEN LANGUAGE and sounding out words…
Wernicke’s Area
Disruption in this TEMPORAL LOBE STRUCTURE results in WORDS COMING OUT AS GIBBERISH…
Olfactory Cortex
TEMPORAL LOBE STRUCTURE which receives SENSORY INPUTS from the NOSE for SMELL
Occipital Lobe
(definition) Functions in VISION
2 Structures
How many structures are found in the OCCIPITAL LOBE?
Primary Visual Cortex
OCCIPITAL LOBE STRUCTURE which receives information from the RETINA for SIGHT and contains a map of contralateral field of view,
Visual Association Cortex
OCCIPITAL LOBE STRUCTURE responsible for the MEMORY of VISION.
Primary Visual Cortex
Damage in this OCCIPITAL LOBE STRUCTURE results from FALLING ON THE BACK OF THE HEAD which causes damage and BLINDNESS…
Visual Association Cortex
Damage in this OCCIPITAL LOBE STRUCTURE results in being able to see, but NOT being able to COMPREHEND what is being SEEN.
Insula Lobe
(definition) DEEP to the TEMPORAL LOBE. Associated with visceral functions and feeling of DISGUST…
Visceral Sensory Area
INSULA LOBE STRUCTURE responsible for conscious perception of VISCERAL SENSATION
Upset Stomach, Full Bladder
TWO examples of the VISCERAL SENSORY AREA…
Gustatory Cortex
INSULA LOBE STRUCTURE responsible for TASTE
Vestibular Cortex
INSULA LOBE STRUCTURE responsible for BALANCE, especially the position of the HEAD in space…
Basal Nuclei
(definition) Consist of a group of subcortical nuclei → Located in the DEPTHS of each Hemisphere of the CEREBRUM, functions to REGULATE INTESNITY and the START/STOP of stereotypical movements…
Basal Nuclei
People with Parkinson’s Disease is a result of DISRUPTION in the…
Limbic System
(definition) A group of structures located in the DEEP CEREBRUM, functions as a key role in MOOD and EMOTIONS (FEAR)
Hypothalamus and Prefrontal Cortex
TWO STRUCTURES which help with OUTPUT and REGULATION in the LIMBIC SYSTEM…
Hippocampus
(definition) a DEEP CEREBRAL STRUCTURE within the LIMBIC SYSTEM, important for LEARNING/MEMORY…
Alsheimer’s Disease
(definition) Those with a DISRUPTED HIPPOCAMPUS are diagnosed with…
Reticular Formation
(definition) A DEEP CEREBRAL STRUCTURE which extends to the central core of the BRAIN STEM, helps keep CONCIOUS AND ALERT, and filters out REPTITIVE, FAMILIAR, or WEAK STIMULI…
Cerebral White Matter
(definition) Responsible for COMMUNICATION between different parts of the CNS, consists of largely MYELINATED AXON FIBERS bundled together in TRACTS…
Association Fibers, Commissural Fibers, Projection Fibers
List the THREE types of CEREBRAL WHITE MATTER within the CNS…
Association Fibers
(definition) HORIZONTAL running fibers which connect different parts of the SAME HEMISPHERE
Commissural Fibers
(definition) HORIZONTAL fibers that connect GRAY MATTER of TWO HEMISPHERES…
Different Lobes
An example of Association Fibers within the Brain…
Corpus Callosum
An example of Commissural Fibers within the Brain…
Projection Fibers
(definition) VERTICAL fibers that connect HEMISPHERES with the LOWER BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD…
Fornix
An example of Projection Fibers within the Brain…
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus (Pineal Gland)
The THREE structures which compose the DIENCEPHALON…
Diencephalon
(definition) GRAY MATTER STRUCTURE forming the BRAIN’S CENTRAL CORE and surrounds the THIRD VENTRICLE…
Thalamus
(definition) STRUCTURE WITHIN THE DIENCEPHALON, functions as the ORGANIZATION of SENSORY inputs, BESIDES SMELL, to the cortex.
Hypothalamus
(definition) MAIN VISCERAL and REGULATING CENTER for HOMEOSTASIS…
Hypothalamus
(function) Regulates Body Temperature
Hypothalamus
(function) Regulates Hunger and Fullness
Hypothalamus
(function) Regulates Water-intake
Hypothalamus
(function) Regulates Sleep-wake Cycle → BIOLOGICAL CLOCK…
Hypothalamus
(function) Controls the ANS (blood pressure, heart rate)
Hypothalamus
(function) Controls the ENDOCRINE (hormone) SYSTEM via the PITUITARY GLAND…
Hypothalamus
(function) Initiates PHYSICAL RESPONSES to EMOTIONS
Epithalamus
(definition) aka the Pineal Gland, secretes melatonin (regulates the sleep-wake cycle), and stimulates sleep…
Epithalamus
Another word for the “Pineal Gland”
Brain Stem
(definition) Contains fiber tracts, controls AUTOMATIC behaviors necessary for SURVIVAL → Sneezing, Vomiting, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure
Midbrain, Pons, Medulla
The THREE regions of the BRAIN STEM…
Copra Quadrigemina
(definition) Contains VISUAL/AUDITORY REFLEX CENTERS that coordinates HEAD AND EYE MOVEMETS
Spinal Cord
(definition) Provides TWO-WAY COMMUNICATION to and from the brain, WHITE MATTER contains PROJECTION TRACTS, known as the MAJOR REFLEX CENTER, and contains a FUNCTIONAL VENTRAL AND DORSAL portion…
Projection Tracts
What structure is found with WHITE MATTER within the SPINAL CORD?
Ventral Portion of the Spinal Cord
(ventral/dorsal) Contains MOTOR information…
Dorsal Portion of the Spinal Cord
(ventral/dorsal) Contains SENSORY information…
Skull and Vertebrae
Which BONES function to PROTECT the BRAIN and SPINAL CORD?