Module 8: GI System (Part 1)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What are common S/S related to the GI System? (Part 1 - 4)
Abdominal pain (Acute and Chronic)
Indigestion, Nausea, Vomiting including blood
Loss of Appetite
Early Satiety (Eat small amount and be full right away)
What are common S/S related to the GI System? (Part 2 - 4)
Dysphagia and/or Odynophagia (Painfull Swallowing)
Change in bowel function
Diarrhea, Constipation
Jaundice
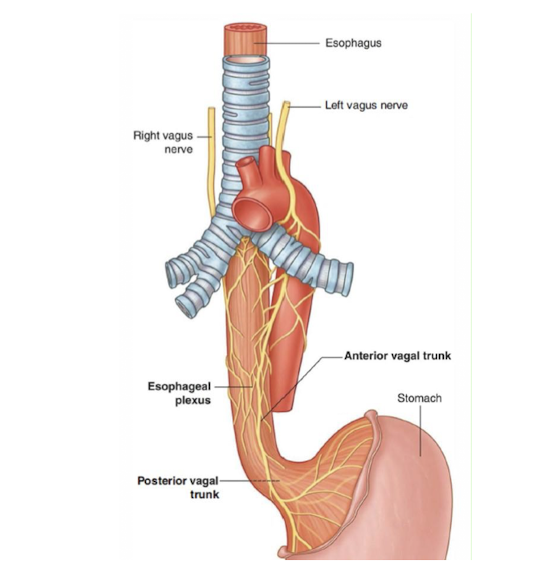
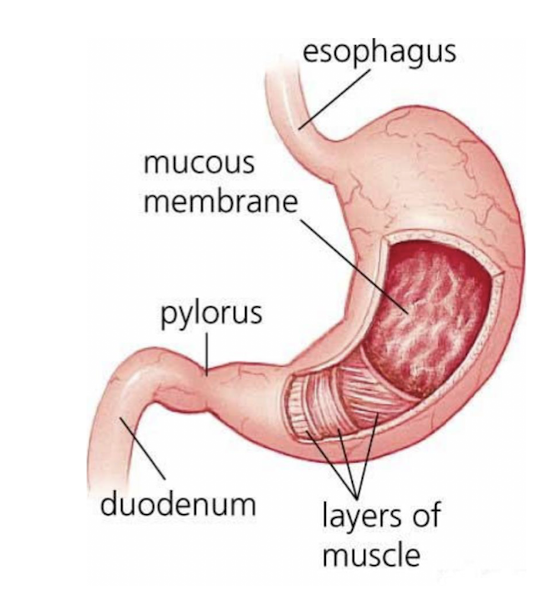
Mouth and Esophagus:
Pierces through what structure?
Innervated by what nerve?
Diaphragm
Vagus Nerve
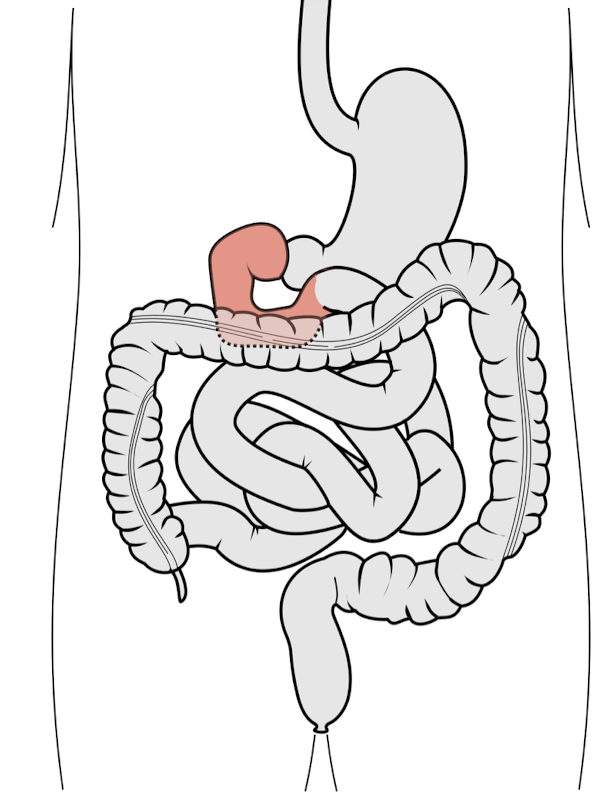
What structure is considered the BEGINNING of the Small Intestine?
What shape does this structure have?
Where is it located in the body?
What SC level is Umbilicus?
Duodenum
C Shaped Tube
Location:
Back Abdominal Wall of Abdomen
Posterior side of the body
L4
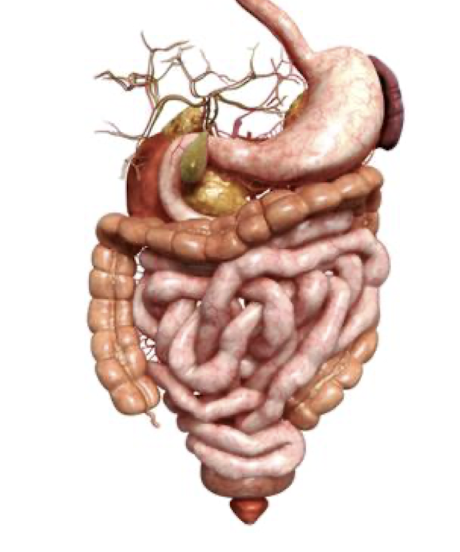
Small Intestine:
Small Intestine is composed of what 2 parts?
What is the Small Intestine connected to?
What body function occurs at the Small Intestine?
Jejunum and Ileum
Mesenteric Root
Nutrient Absorption
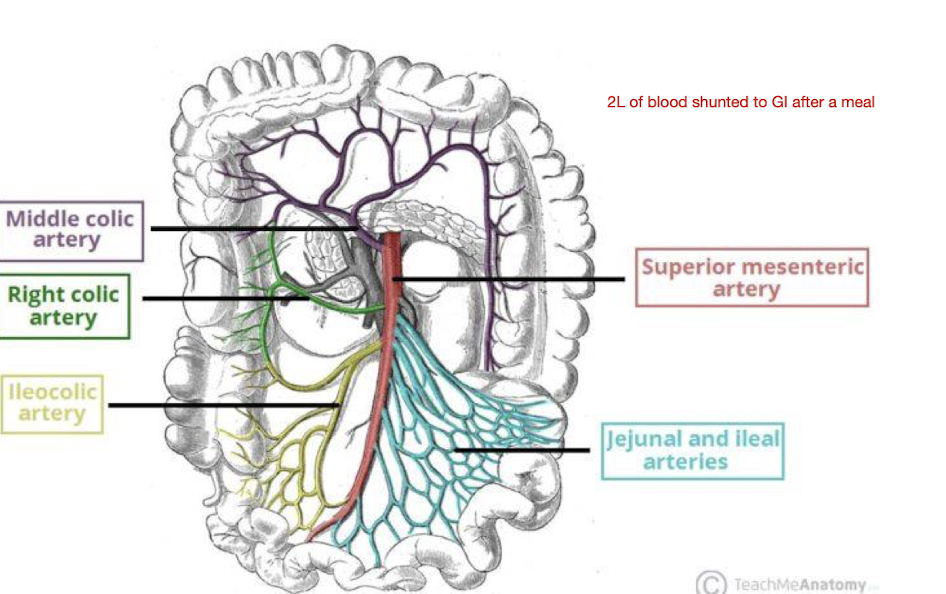
How much blood is shunted to the GI System after a meal for digestion?
2L
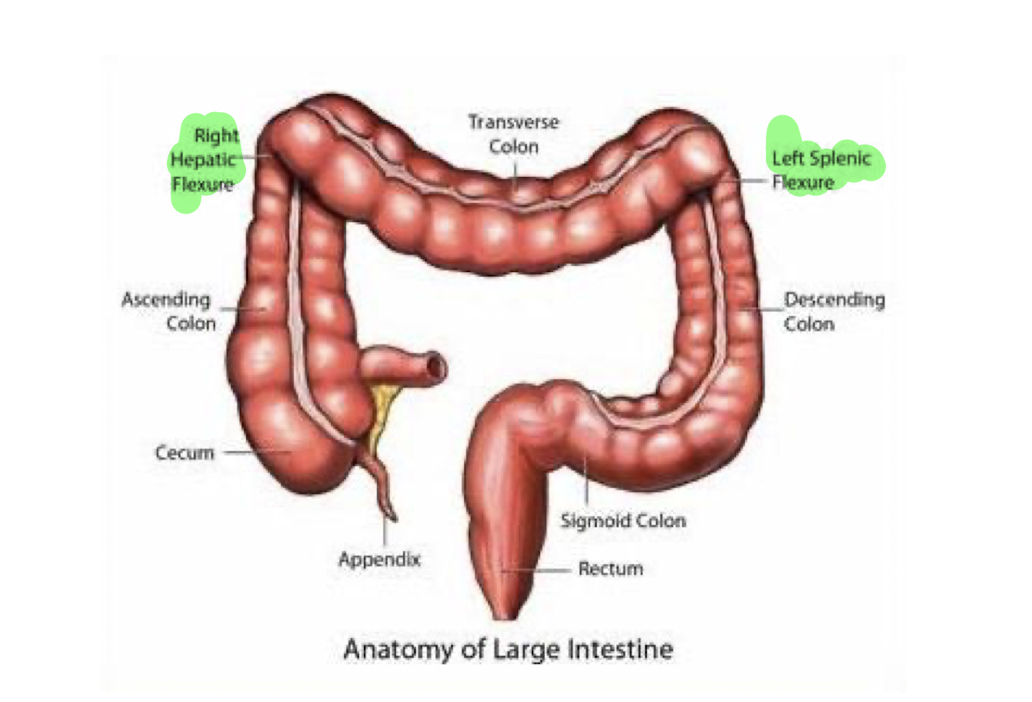
Large Intestine:
Trace the structures of the Large Intestine from R to L: (9)
Ileocecal Valve
Cecum
Ascending Colon
R Hepatic Flexure
Transverse Colon
L Splenic Flexure
Descending Colon
Sigmoid Colon
Rectum
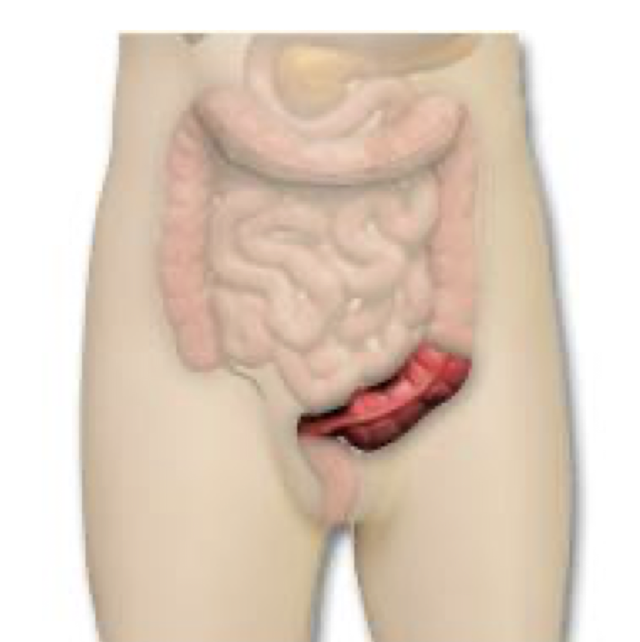
Sigmoid Colon and Rectum:
What structures are considered the LAST section of the Large Intestine?
What structures is the Sigmoid Colon and Rectum POSTERIOR to in:
Men:
Women:
Sigmoid Colon and Rectum
Posterior to:
M: Prostate and Bladder
W: Uterus and Bladder
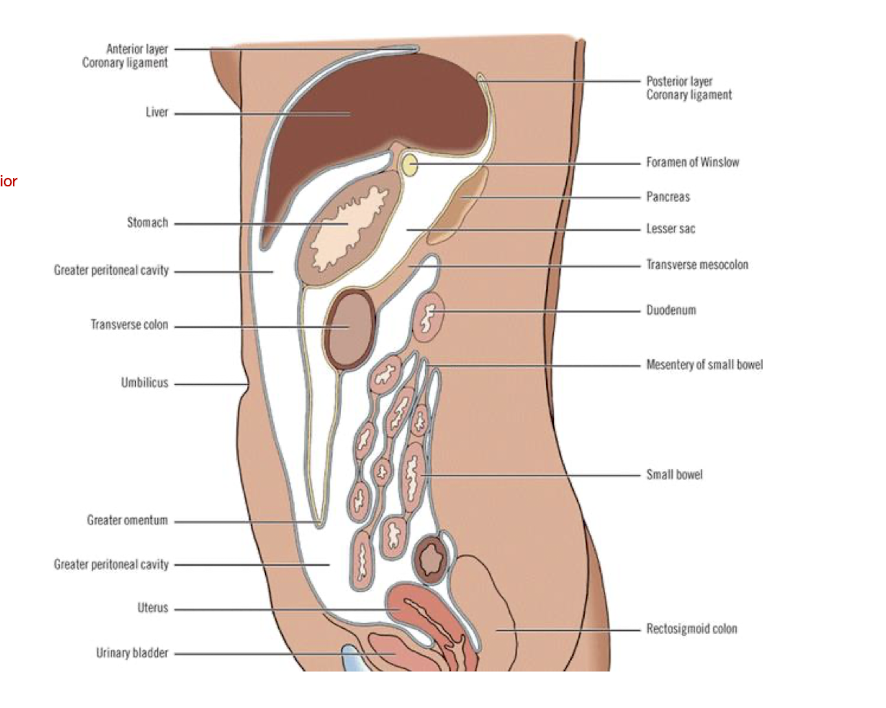
GI System (Lateral View)
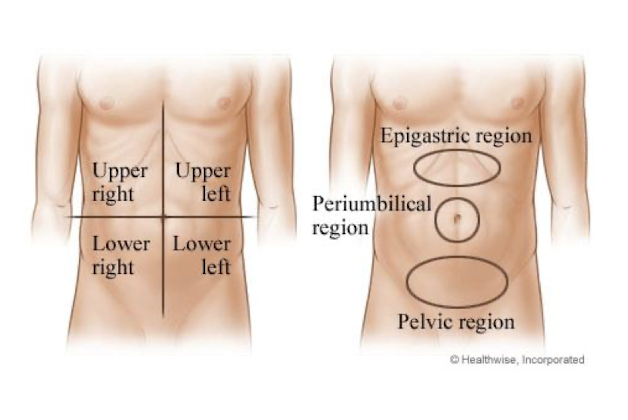
Areas of Pain:
Imaginary lines crossing what structure?
Can give clues about what?
Crossing Umbilicus
Which structures are involved
Visceral Pain in Abdomen:
Visceral Pain in Abdomen occurs when the abdominal muscles do what? (3)
Prolonged can causes what?
Often difficult to ____:
Abdominal Organs:
Contract in forceful manner
Stretched or Distended
Tissue Inflamed
CNS Changes
Localize
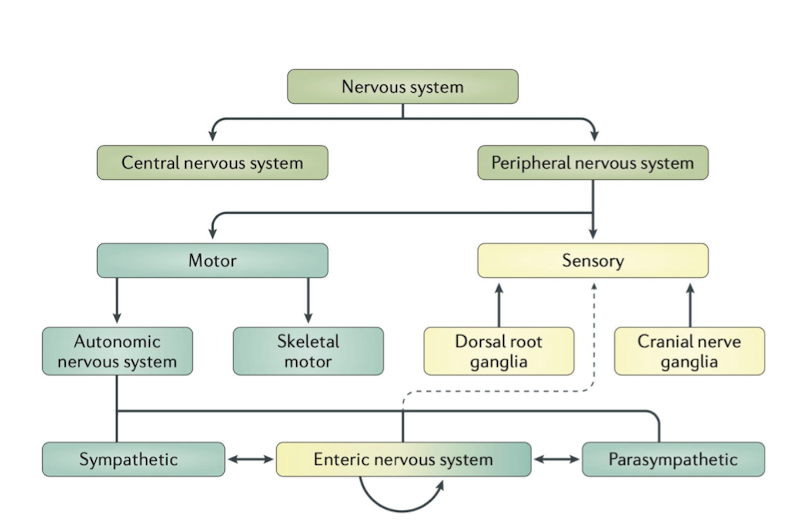
Enteric NS:
Enteric NS sits at the intersection of what?
T/F: The GI System had more nerve connections than the Spinal Nerves/Cord due to interneurons
CNS (Fight or Flight) AND PNS (Rest and Digest)
True
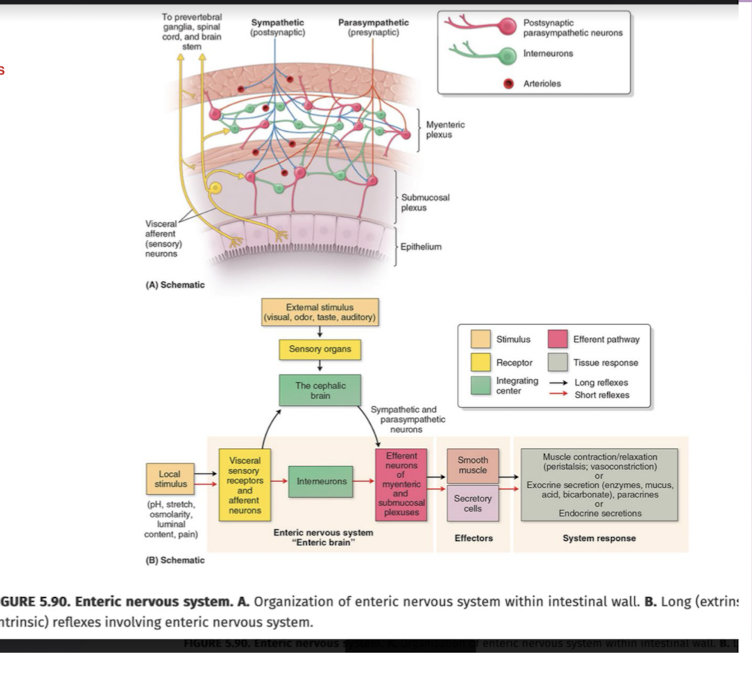
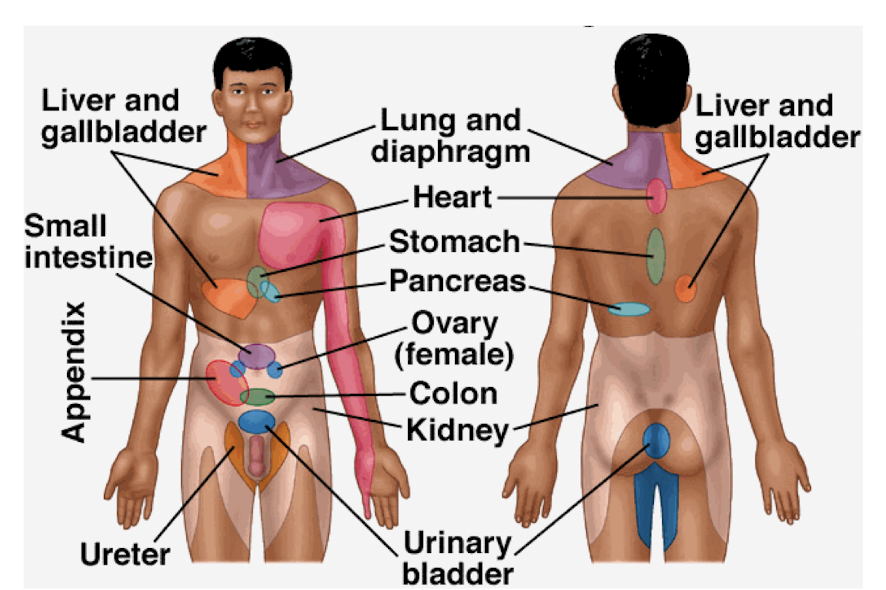
Referred Pain in Abdomen:
Referred pain in the abdomen is usually felt where?
Which are innervated at approximately where?
T/F: Often NOT the same as the initial site of pain
Referred pain in abdomen becomes more ____ and travels as the ___ ___ gets worse.
May be referred to the abdomen from what 3 structures?
Distant Sites
Innervated at approximately the SAME level as dysfunctional structures
True
Intense; Original Site
Chest, Spine, Pelvis
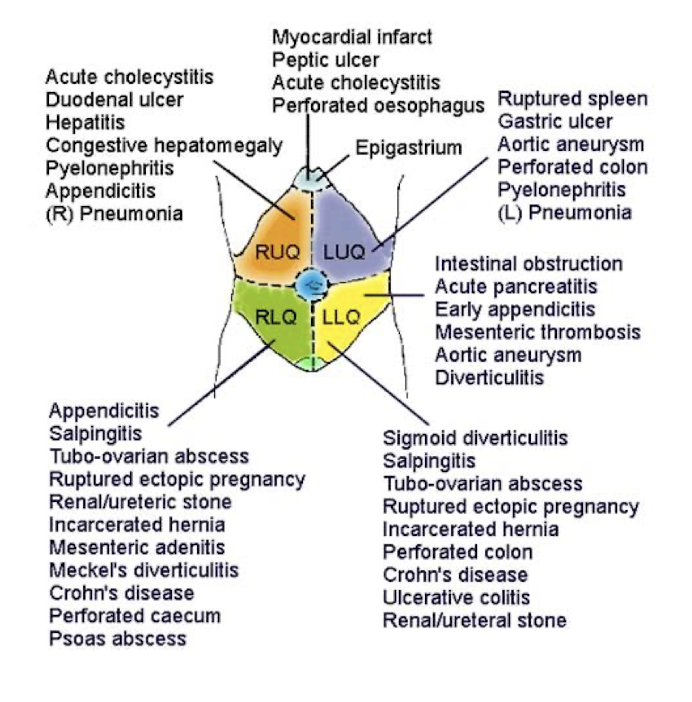
4 Quadrant Division (More Commonly Used)
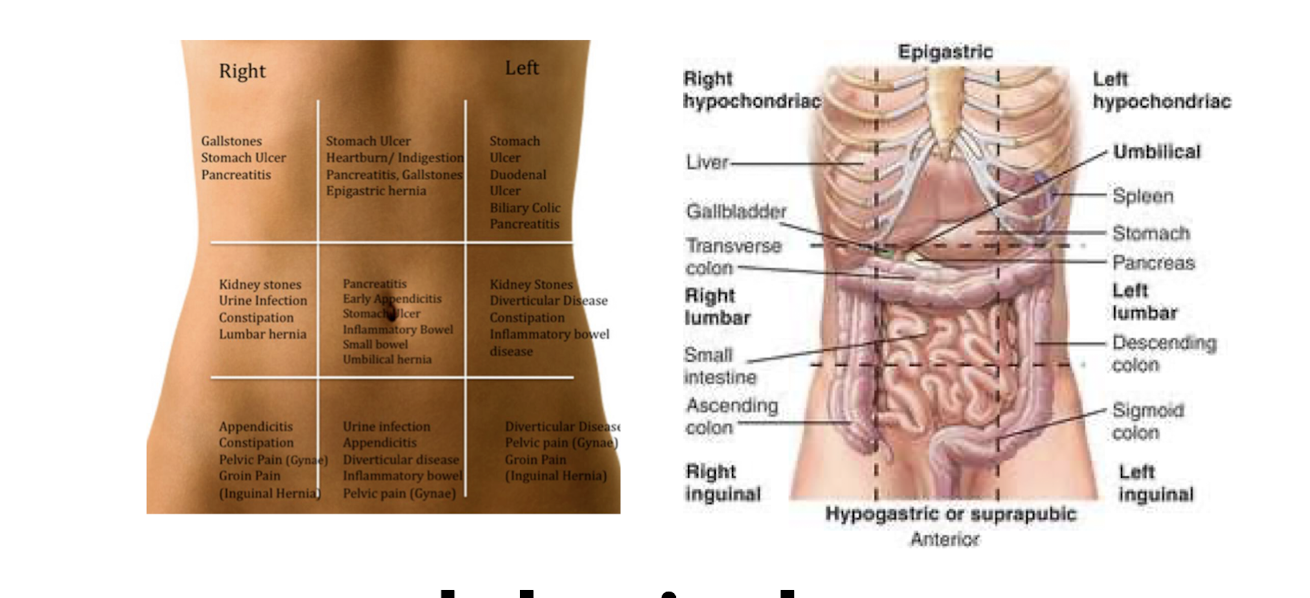
9 Abdominal Areas/Divisions (Less Commonly Used)
Abdominal Pain Subjective Questions:
What are common GI Subjective questions to ask? (Part 1 - 5)
Can you describe the pain in your own words?
Where is it?
Where did it start?
Where did it travel to?
Timing of pain?
Abdominal Pain Subjective Questions:
What are common GI Subjective questions to ask? (Part 2 - 5)
How did it begin?
How gradually did it come on?
24 hr pain pattern?
Are you acutely ill?
Is this a chronic problem and something that you have had before?
What type of pain is common for GI issues? (5)
Cramping
Sharp
Colicky
Knifelike
Burning
Esophageal Pain
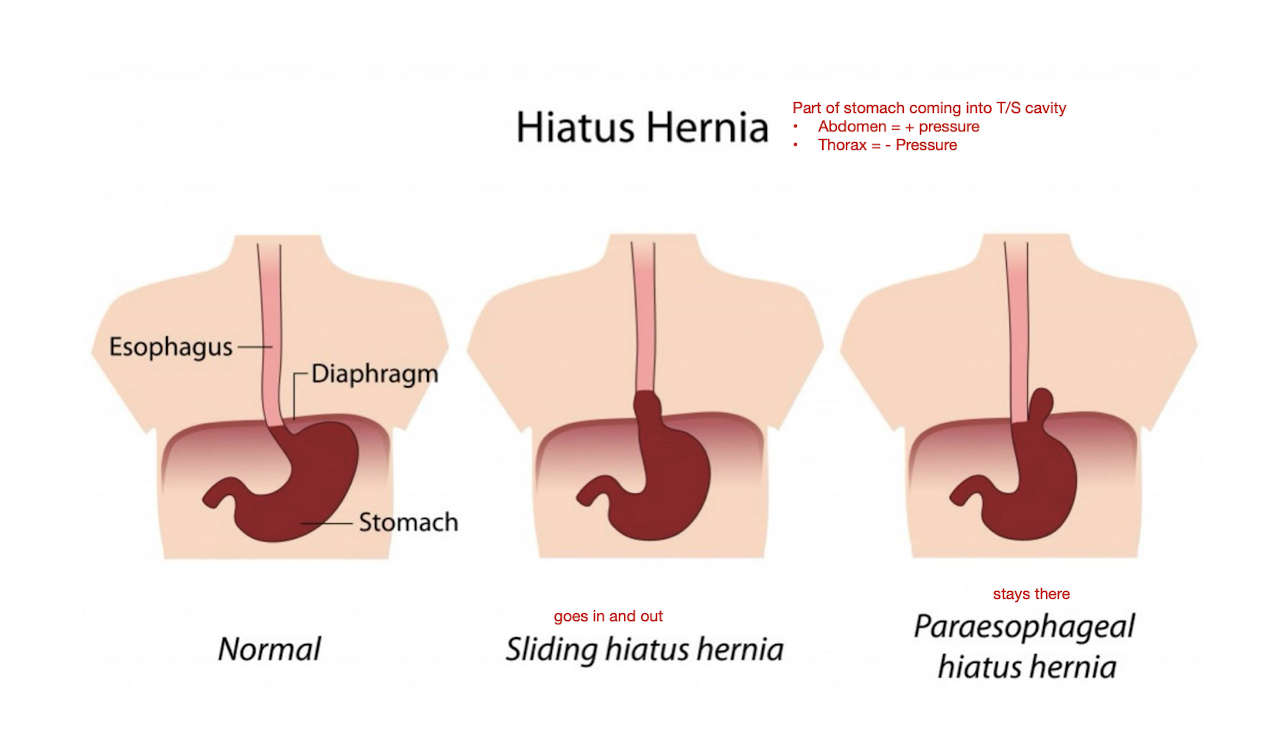
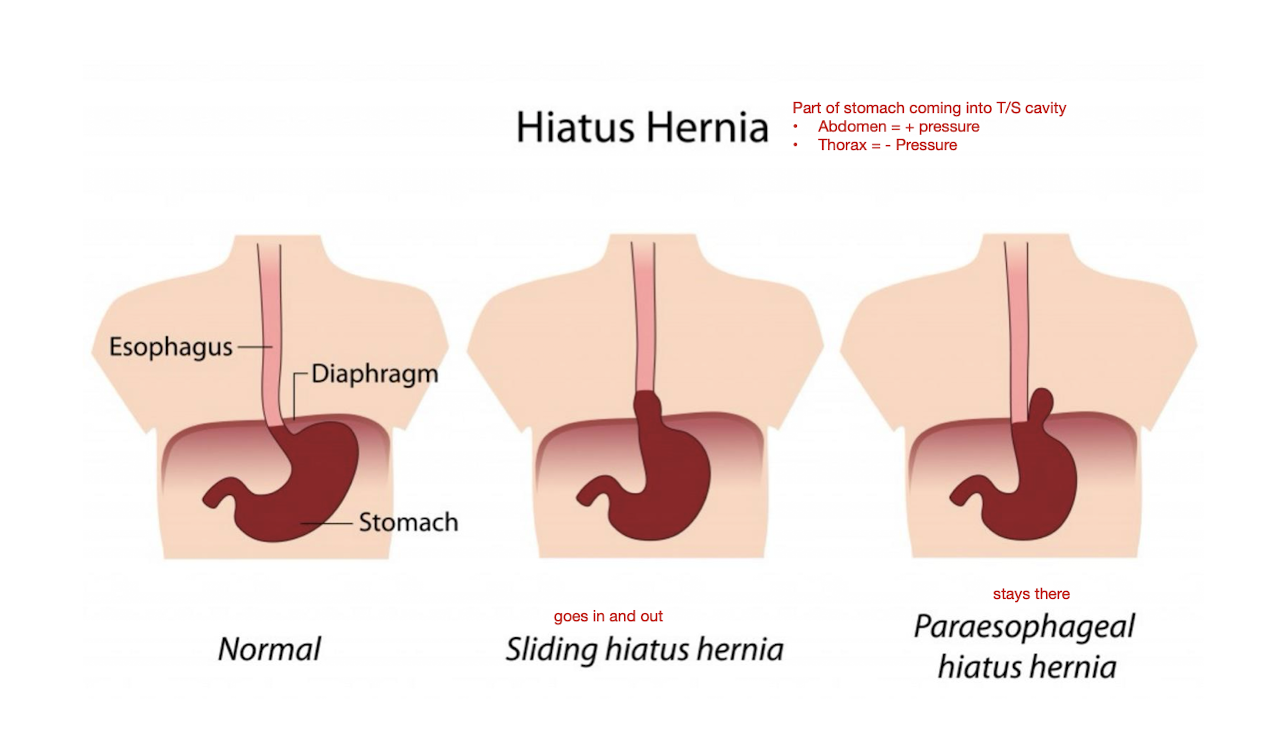
Esophageal Pain: Hiatal Hernia
How does an Hiatal Hernia occur?
Prevalence rate:
Increased w age:
Occurs where the cardiac (lower esophageal) spinchter becomes WEAK allowing the stomach to pass through the diaphragm into the thoracic cavity
Prevalence: 20%
Age:
50% over 50yo
60% over 60yo
70% over 70%
Esophageal Pain: Hiatal Hernia
What are the 2 types of Hiatal Hernia?
Sliding Hiatus Hernia
Stomach goes in and out
Paraesophageal Hiatus Hernia
Stomach is stuck and stays there
Esophageal Pain: Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal Hernias can be caused by what 2 things?
Weakening of Diaphragm
Increased Intra-Abdominal Pressure
Ex: Tight Clothing and Preg
Esophageal Pain: Hiatal Hernia
3 Common S/S:
Common location of pain:
S/S:
Burning pain in Chest and Throat
Belching
N/V
Site:
Back Pain
Chest Tightness
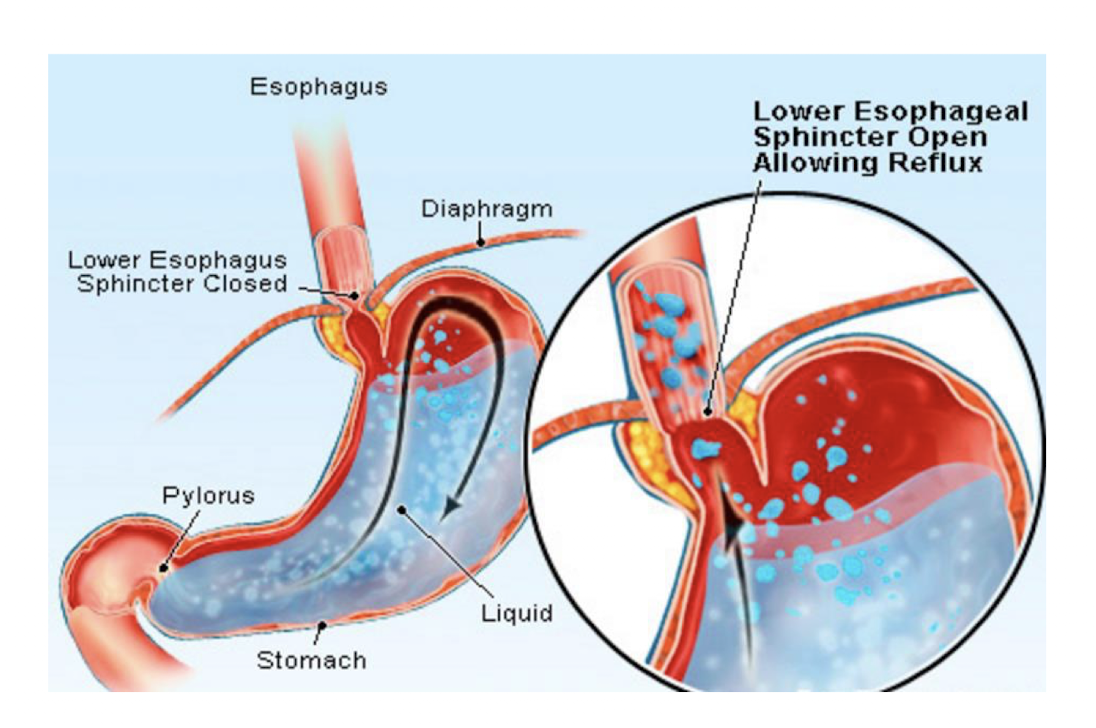
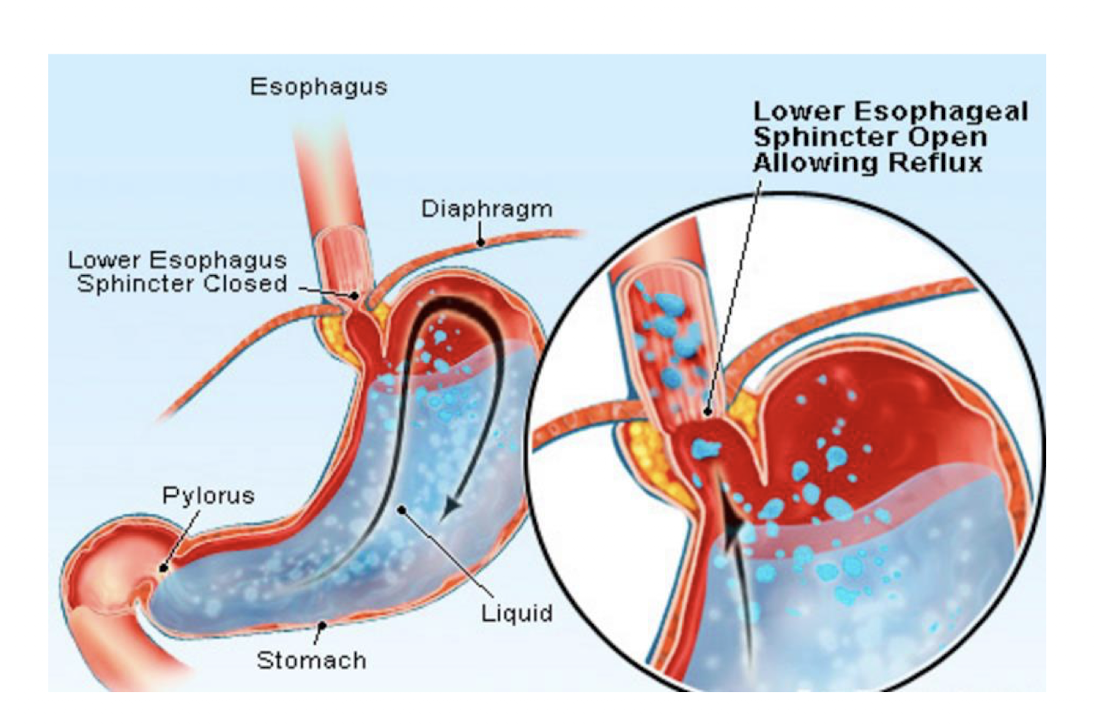
Esophageal Pain: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a consequence of what?
Consequence:
Backward flow of gastric contents into the esophagus
Esophageal Pain: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
How does GERD occur?
Occurs:
Transient relaxation of the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) not related to swallowing that allows the stomach acid to pass into the esophagus
Esophageal Pain: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
4 main GERD Complications:
Esophagitis
Necrosis of the esophageal epithelial lining that leads to erosions and ulcers
Strictures that narrow the esophagus secondary to scar tissue formation
Barret Esophagus
Precancerous Condition
Adenocarinoma
Esophageal Pain: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Which GERD complication presents the MOST CONCERN?
Strictures
Esophageal Pain: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
4 main Clinical Manifestations
Heartburn that may irradiate to where?
Esophageal symptoms can include what 3?
Pt may demonstrate what?
Heartburn that may irradiate to the stomach, chest, back
Esophageal symptoms can include:
Cough
Asthma
Laryngitis
Demonstrate:
Decreased mobility of L Lower Rib Cage and L Shoulder
What are 4 things to consider when treating a pt w UPPER GI Diagnosis?
Timing tx away from meals (esp if doing intense exercise)
Avoid lying flat after meals
Avoid exercise that increase IAP in supine position
Assess diaphragm mobility (L Side)
What are 4 common MSK structure considerations for pts w Upper GI Diagnosis?
Diaphragm
Shoulder Mobility/Strength
T/S
C/S
Where to palpate LES?
Just LEFT of the Sternum on 6-7 costal cartilage
Xiphoid Process
Stomach Pain
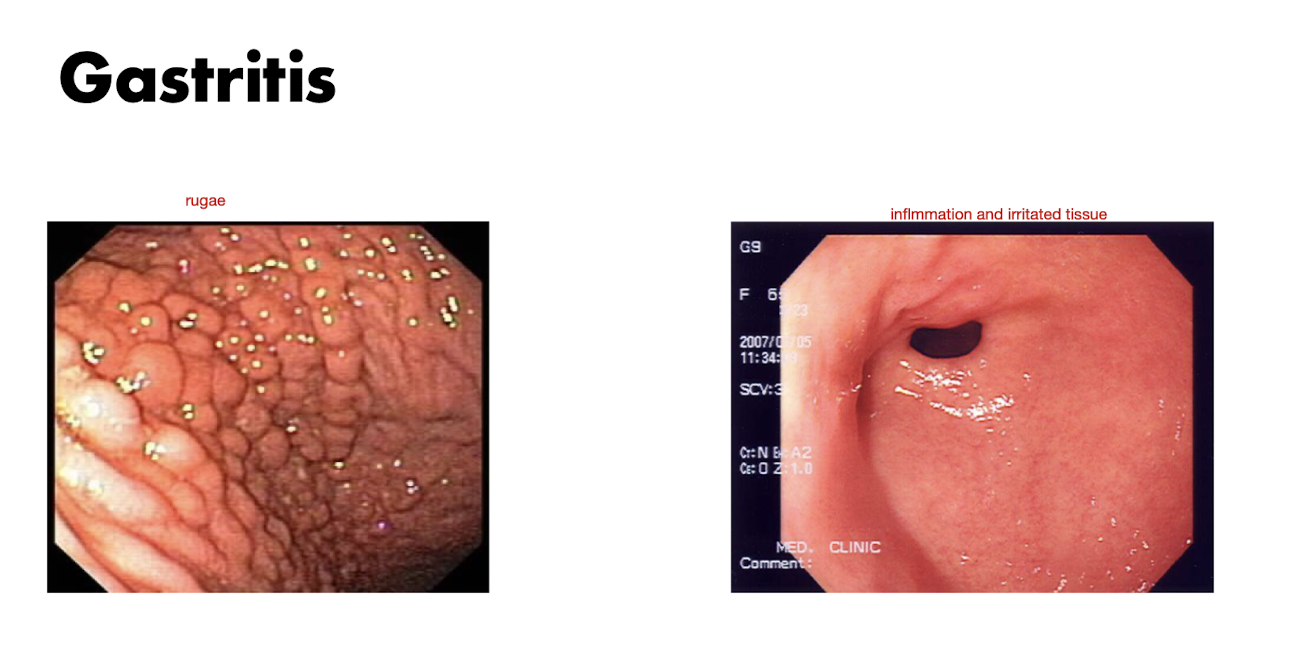
Stomach Pain: Gastritis
Gastritis is a condition that affects what?
Acute Gastritis = (2)
Chronic Gastritis = (3)
Condition affecting the mucosa of the stomach
Acute:
Hemorrhagic
Erosive
Chronic:
H Pylori Gastritis
Multifocal Atrophic Gastritis
Autoimmune Metaplastic Gastritis
Stomach Pain: Gastritis
S/S of Gastritis include what? (3)
How is diagnosis made?
Can be caused by what?
S/S:
Feeling of Abdominal Distention
Loss of Appetite
Nausea
Endoscopy
Long Term use of NSAIDS
Stomach Pains: Peptic Ulcer Disease
What does Peptic Ulcer Disease involve?
Erosion (Do not extend through muscularis mucosae)
OR
Ulcer of the stomach or duodenum
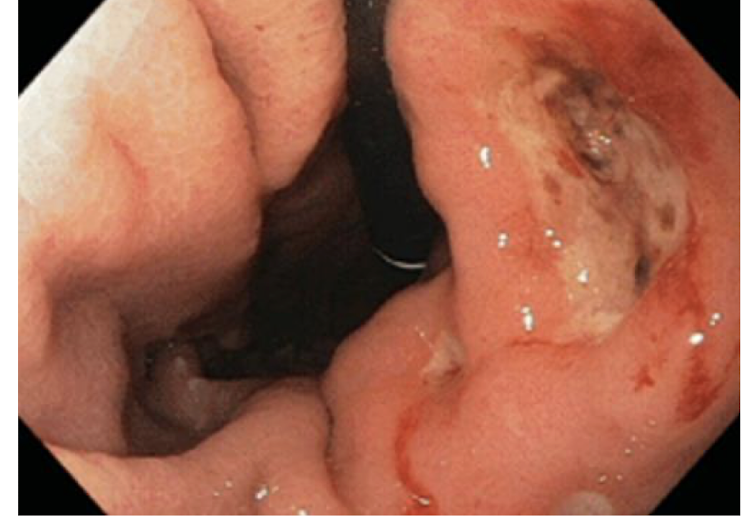
Stomach Pains: Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic Ulcer Disease extends into where?
Replaces what?
Potential for damage to what?
Could lead to what?
Extends to muscle layer
Replaced w Scar Tissue
Blood Vessels
Bleeding Risk (Hemorrhage)
Stomach Pains: Peptic Ulcer Disease
What type of ulcer is it?
Response to what?
3 Common Causes:
Stress Ulcer
Physiologic Stress
Causes:
Long Term use of NSAIDS
Low Dose Aspirin
H Pylori Bacteria Infection
Stomach Pains: Peptic Ulcer Disease
What are the 2 Peptic Ulcer Complications?
Bleeding
Requires Hospitalization
Perforation of stomach or duodenum may occur presenting w severe sudden pain
T/S from T6-T10 w radiation to RUQ
Stomach Pains: Peptic Ulcer Disease
What is the 3 main Tx for Peptic Ulcer Disease?
Reduce H Pylori Bacteria
Stop use of NSAIDS
Bleeding can be treated endoscopically
Stomach Pains: Peptic Ulcer Disease
What are 3 pt conditions for stomach pathology?
Acute changes in fatigue level
Discuss changes in stool
Monitor for signs of bleeding
How to palpate for Pyloric Sphincter?
6-7 cm above umbilicus
May be slightly L or R of midline
4 finger
Size fo quarter
At level of L1