Microbial Genetics Ch.6 - 6.1 and 6.2
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Define terms –gene, genome, chromosome, plasmid
gene: A piece of DNA that codes for a characteristic —> A site on a chromosome that provides information for a certain cell function. A specific segment of DNA that contains the necessary code to make a protein or RNA molecule.
genome: Sum total of genetic material of an organism —> The complete set of chromosomes and genes in an organism
chromosome: tightly coiled bodies in the cell and is the primary sight of genes composed of neatly packaged DNA molecule
plasmid: extra pieces of DNA in bacteria (+ some fungi) —> small, circular pieces of DNA that contain their own origin of replication and replicate independently.
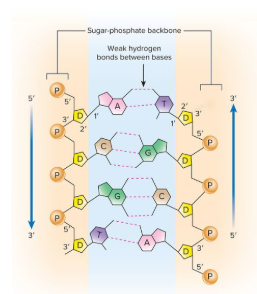
Thoroughly understand structure and characteristics (complementary, anti-parallel) of DNA
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acids - helical structure that has two complementary strands that run antiparallel from each other
It has Phospdiester bonds: bonds between nucleotides and hold them together—> seen as the backbone with the Deoxyribose sugar
Nucleotide (3 parts)
phosphate group (5’ end)
deoxyribose sugar (5-C) (3’ end)
nitrogenous bases - connected to each other via H-bonds (two for A-T and 3 for C-G)
2 types
Purines: Adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines: Cytosine and thymine, (uracil RNA only)
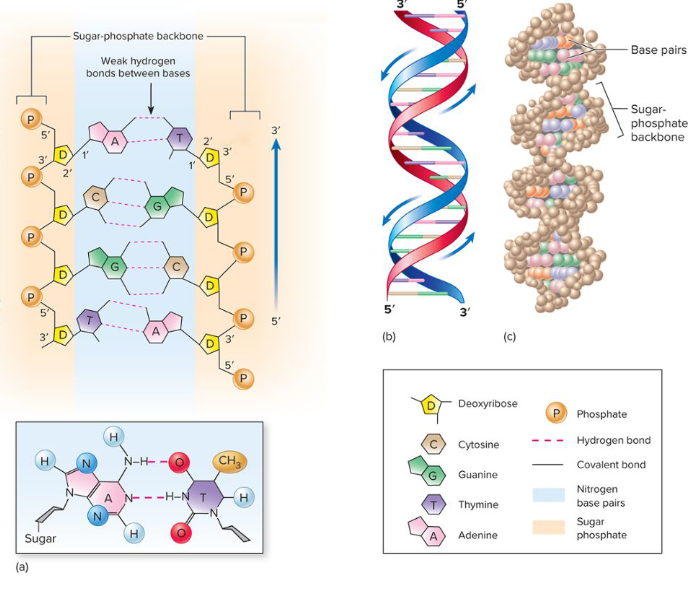
Antiparallel - one strand of helix runes opposite direction — A description of the two strands of DNA, which are parallel to each other, but the orientation of the deoxyribose and phosphate groups run in the opposite directions, with the 5′ carbon at the top of the leading strand and the 3′ carbon at the top of the lagging strand.
Complementary - where the nitrogenous bases compliment each other. One strand will have a guanine and that other stand will have a cytosine. (adenine with thymine (or uracil)

Know the parts of a nucleotide
phosphate group (5’ end)
deoxyribose sugar (5-C) (3’end)
nitrogenous bases
2 types
Purines: Adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines: Cytosine and thymine, (uracil RNA only)

MOLECULAR Processes of Gene Expression - transcription, translation
Fully understand this process: DNA --> RNA --> Protein – (more specifically -- Gene--> mRNA --> polypeptide)
3. What is transcription? Translation?
4. DNA vs. RNA structure. Know differences!
5. Where within eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells do these processes occur? What are some differences in the process in the two cell types?
6. What is the genetic code? It is a triplet code – what does this mean? KNOW and be able to explain the characteristics of the genetic code given in class. (Remember redundancy)
7. What is a codon (in mRNA)? What is an anti-codon (in tRNA)? Do all codons code for amino acids? Stop and start – know these codons!
8. Be able to use the dictionary of the genetic code (be able to determine amino acid coded for by any given codon using the code sheet). Understand the importance of complementary base pairing in DNA, between DNA and mRNA and between mRNA and tRNA. (Given any one of the above be able to determine the others).