Dermatologic Neoplasms (PEARLS), Kaposi sarcoma, Melanoma, Squamous cell carcinoma (Smarty PANCE)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is it basal cell carcinoma?
Carcinoma arising in the germinating basal cell layer of epithelial cells
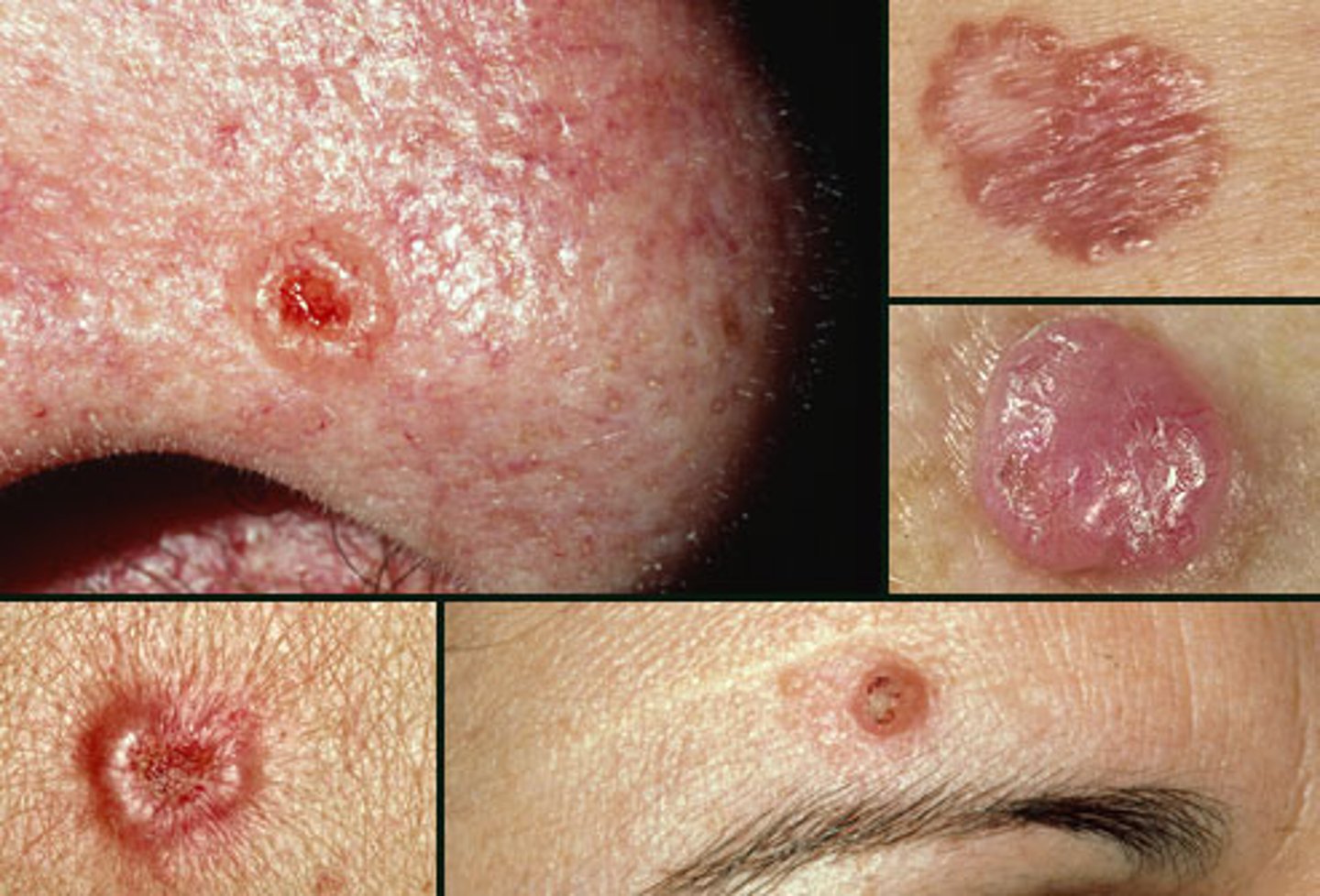
What are the risk factors for basal cell carcinoma?
Sun exposure, fair skin, radiation, chronic dermatitis, xeroderma pigmentosum
What are the most common sites of basal cell carcinoma?
Head, neck, and hands
What are the signs/symptoms of basal cell carcinoma?
Slow-growing skin mass (chronic, scaly); scab; ulceration, with or without pigmentation, often described as "pearl-like"
How is the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma made?
Excisional or incisional biopsy
What is the treatment of basal cell carcinoma?
Resection with 5-mm margins (2-mm margin in cosmetically sensitive areas)
What is the risk of metastasis of basal cell carcinoma??
Very low (recur locally)
What is Kaposi sarcoma?
Kaposi sarcoma is a violaceouspapular lesion associated with human herpesvirus 8 and is an AIDS-defining cancer
What are the clinical features of Kaposi sarcoma?
Clinical features of Kaposi sarcoma include macular, papular, nodules that are brown/pink/purple/red
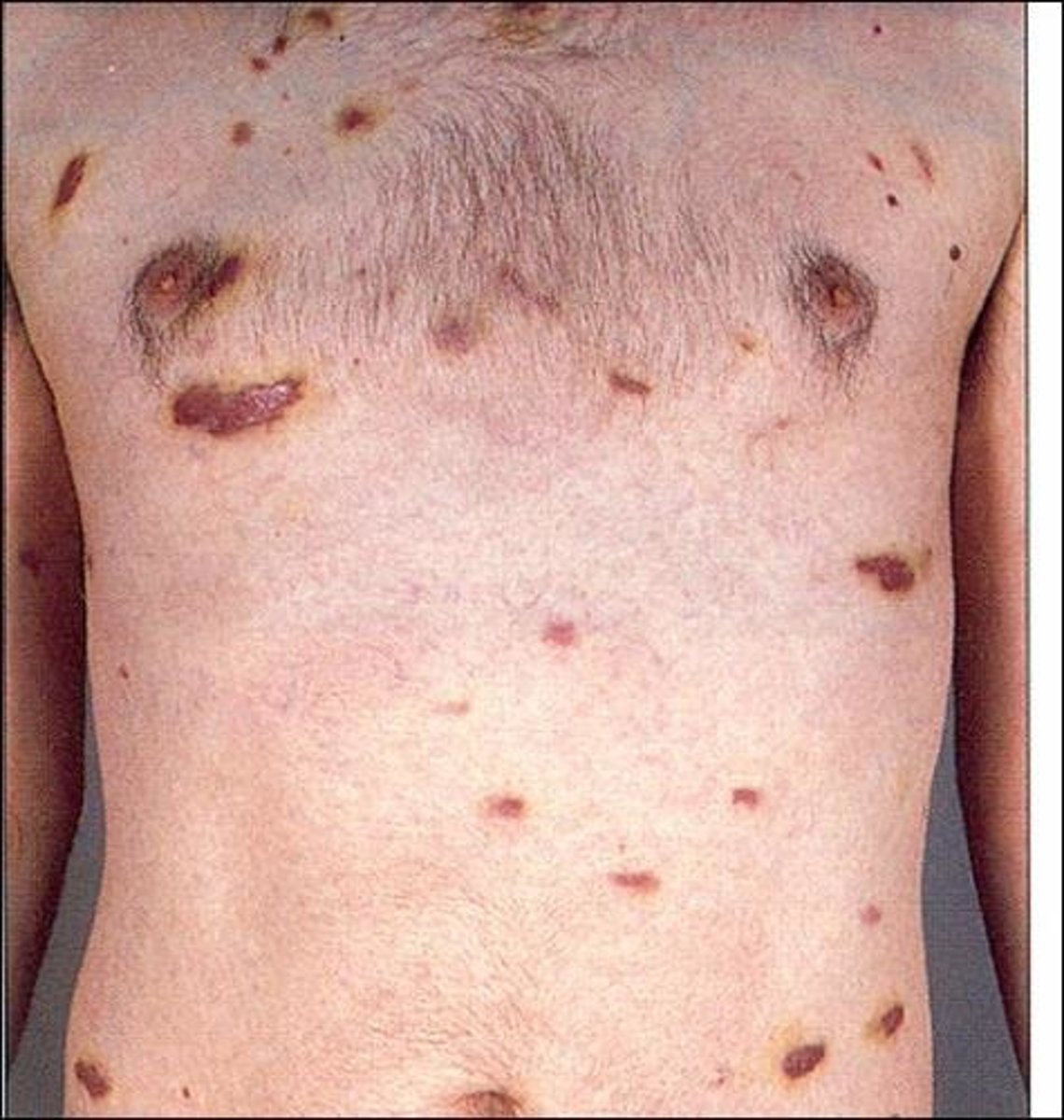
Kaposi sarcoma is most common when the CD4 count is below what in HIV patients?
Kaposi sarcoma is most common when the CD4 count is below 100 in HIV patients
How is Kaposi sarcoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis is by biopsy
Treatment of Kaposi Sarcoma includes...
HAART if the patient is HIV +
Treat widespread disease with systemic chemotherapy or radiation therapy
Define melanoma
Neoplastic disorder produced by malignant transformation of the melanocyte; melanocytes are derived from neural crest cells
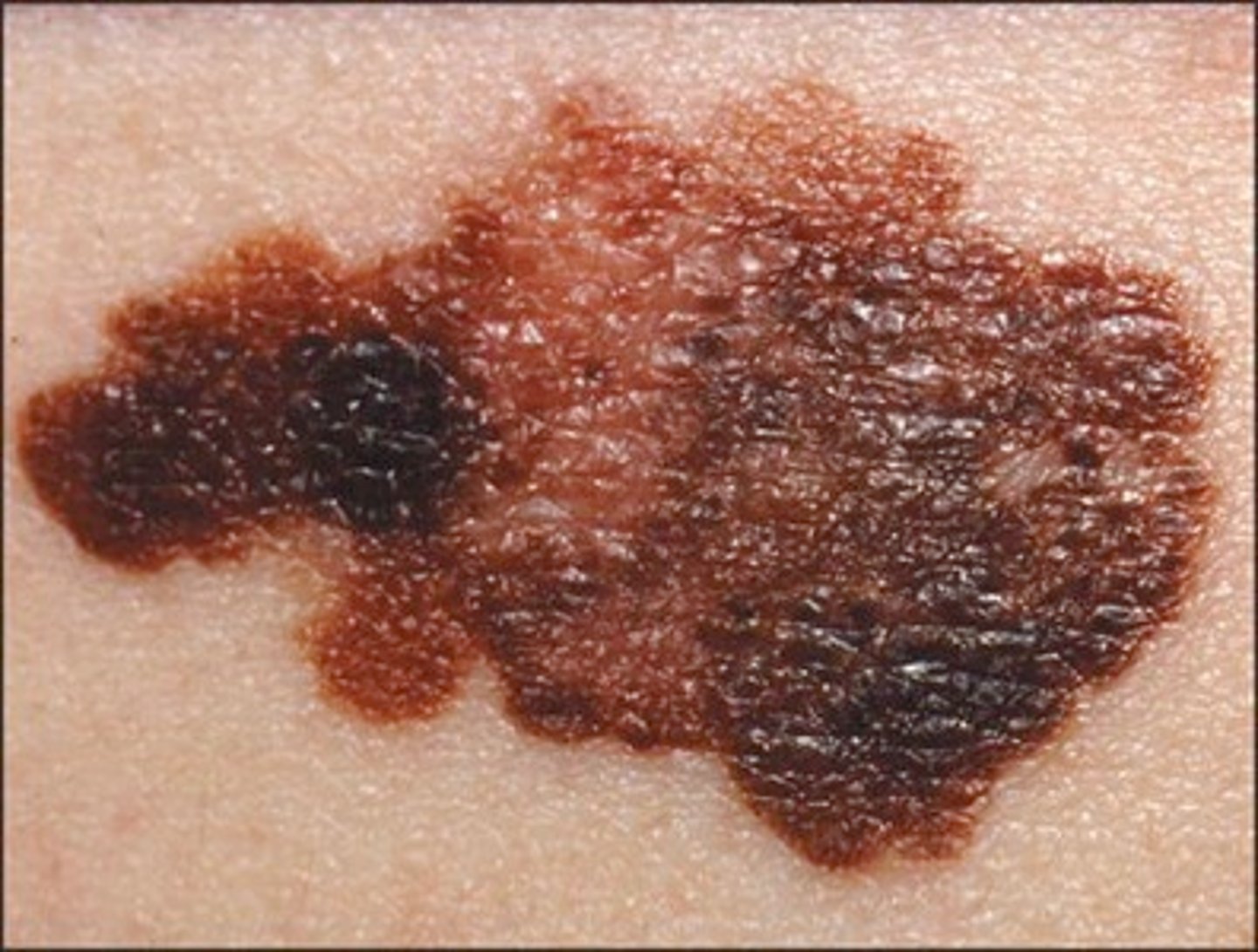
Which patients are at greatest risk for melanoma?
White patients with blonde/red hair, fair skin, freckling, a history of blistering sunburns, blue/green eyes, actinic keratosis Male > female
What are the three most common sites for melanoma?
1. Skin 2. Eyes 3. Anus
(Think: SEA - Skin, Eyes, Anus)
What is the most common skin site of melanoma in African Americans?
Palms of the hands, soles of the feet (acral lentiginous melanoma)
What characteristics are suggestive of melanoma?
Usually a pigmented lesion with an irregular border, irregular surface, or irregular coloration. Other clues: darkening of a pigmented lesion, development of pigmented satellite lesions, irregular margins or surface elevations, notching, recent or rapid enlargement, erosion or ulceration of surface, pruritus
What are the "ABCDEs" of melanoma?
ABCDE: A symmetry, B order is irregular, C olor variability (blue, red, white), D iameter (increasing or > 6 mm), E volving (changing in size, shape, or color)

What are the associated risk factors for melanoma?
Severe sunburn before age 18, giant congenital nevi, family history, race (White), ultraviolet radiation (sun), multiple dysplastic nevi
How does the location of melanoma differ in men and women?
Men get more lesions on the trunk; women on the extremities
Which locations are unusual for melanoma?
Noncutaneous regions, such as mucous membranes of the vulva/vagina, anorectum, esophagus, and choroidal layer of the eye
What is the most common site of melanoma in men?
Back (33%)
What is the most common site of melanoma in women?
Legs (33%)
What are the four major histologic types of melanoma?
1. Superficial spreading 2. Lentigo maligna 3. Acral lentiginous 4. Nodular
What is the most common type of melanoma?
Superficial spreading ( 75%) (Think: SUPERficial SUPERior)
What are the common sites of metastasis of melanoma?
Nodes (local) Distant: lung, liver, bone, heart, and brain. Melanoma has a specific attraction for small bowel mucosa and distant cutaneous sites. Brain metastases are a common cause of death
What are the metastatic routes of melanoma?
Both lymphatic and hematogenous
How is the diagnosis of melanoma made?
Excisional biopsy (complete removal leaving only normal tissue) or incisional biopsy for very large lesions (Note: Early diagnosis is crucial)
What is the role of shave biopsy for diagnosing melanoma?
No role
What is the "sentinel node" biopsy?
Inject Lymphazurin® blue dye, colloid with a radiolabel, or both around the melanoma; the first LN in the draining chain is identified as the "sentinel lymph node" and reflects the metastatic status of the group of lymph nodes
When is elective lymph node dissection recommended?
Controversial—possible advantage in melanomas 1 to 2 mm in depth but jury still out; sentinel node biopsy if 1 mm is becoming very common
Melanoma tumor marker
S-100 tumor marker
What is the recommended size of the surgical margin for depth of invasion:
Melanoma in situ? 0.5-cm margin
1 mm thick? 1-cm margin
1-4 mm thick? 2-cm margin
4 mm thick? 3-cm margin
What is the treatment for digital melanoma?
Amputation
What is the treatment of palpable lymph node metastasis?
Lymphadenectomy
What factors determine the prognosis of melanoma?
Depth of invasion and metastasis are the most important factors (Superficial spreading and lentigo maligna have a better prognosis because they have a longer horizontal phase of growth and are thus diagnosed at an earlier stage; nodular has the worst prognosis because it grows predominantly vertically and metastasizes earlier)
What is the work up to survey for metastasis in the patient with melanoma?
Physical exam, LFTs, CXR (bone scan/CT/ MRI reserved for symptoms)
What is the treatment of intestinal metastasis?
Surgical resection to prevent bleeding/ obstruction
Which malignancy is most likely to metastasize to the bowel?
Melanoma
What is the surgical treatment of nodal metastasis?
Lymphadenectomy
What is FDA-approved adjuvant therapy?
Interferon alpha-2b (for stages IIB/III)
What is the treatment of unresectable brain metastasis?
Radiation
What is the treatment of isolated adrenal metastasis?
Surgical resection
What is the treatment of isolated lung metastasis?
Surgical resection
What is the most common symptom of anal melanoma?
Bleeding
What is the treatment of anal melanoma?
APR or wide excision (no survival benefit from APR, but better local control)
What other experimental therapy is available for metastatic disease?
1. Monoclonal antibodies 2. Chemotherapy (e.g., dacarbazine) 3. Vaccinations
What is the median survival with distant metastasis?
> 6 months
Define squamous cell carcinoma
Carcinoma arising from epidermal cells
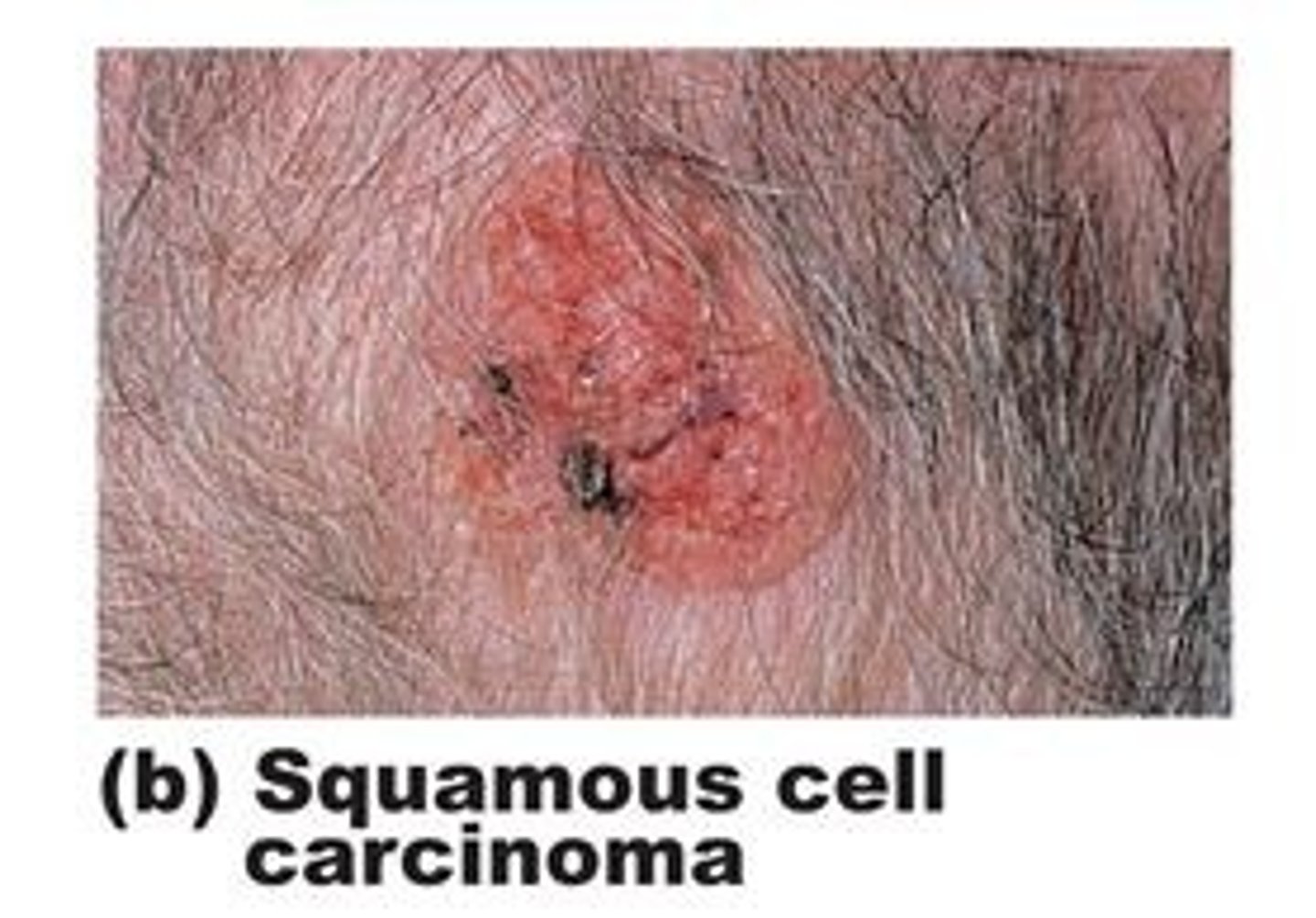
What are the most common sites of squamous cell carcinoma?
Head, neck, and hands
What are risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma?
Sun exposure, pale skin, chronic inflammatory process, immunosuppression, xeroderma pigmentosum, arsenic
Squamous cell carcinoma is often preceded by what skin lesion?
Actinic keratosis is a skin lesion that serves as a risk factor for the development of squamous cell carcinoma. It often presents as rough, scaly patches on sun-exposed areas of the skin and can potentially progress to squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent malignant transformation.
What are the signs/symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma?
Raised, slightly pigmented skin lesion; ulceration/exudate; chronic scab; itching
How is the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma made?
Small lesion—excisional biopsy Large lesions—incisional biopsy
What is the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma?
Small lesion ( <1 cm): Excise with 0.5-cm margin Large lesion (>1 cm): Resect with 1- to 2-cm margins of normal tissue (large lesions may require skin graft/flap
What is the dreaded sign of metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma?
Palpable lymph nodes (remove involved lymph node basin)
What is Marjolin's ulcer?
Squamous cell carcinoma that arises in an area of chronic inflammation (e.g., chronic fistula, burn wound, osteomyelitis)
What is the prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma?
Excellent if totally excised (95% cure rate); most patients with positive lymph node metastasis eventually die from metastatic disease
What is the treatment for solitary metastasis related to squamous cell carcinoma?
Surgical resection
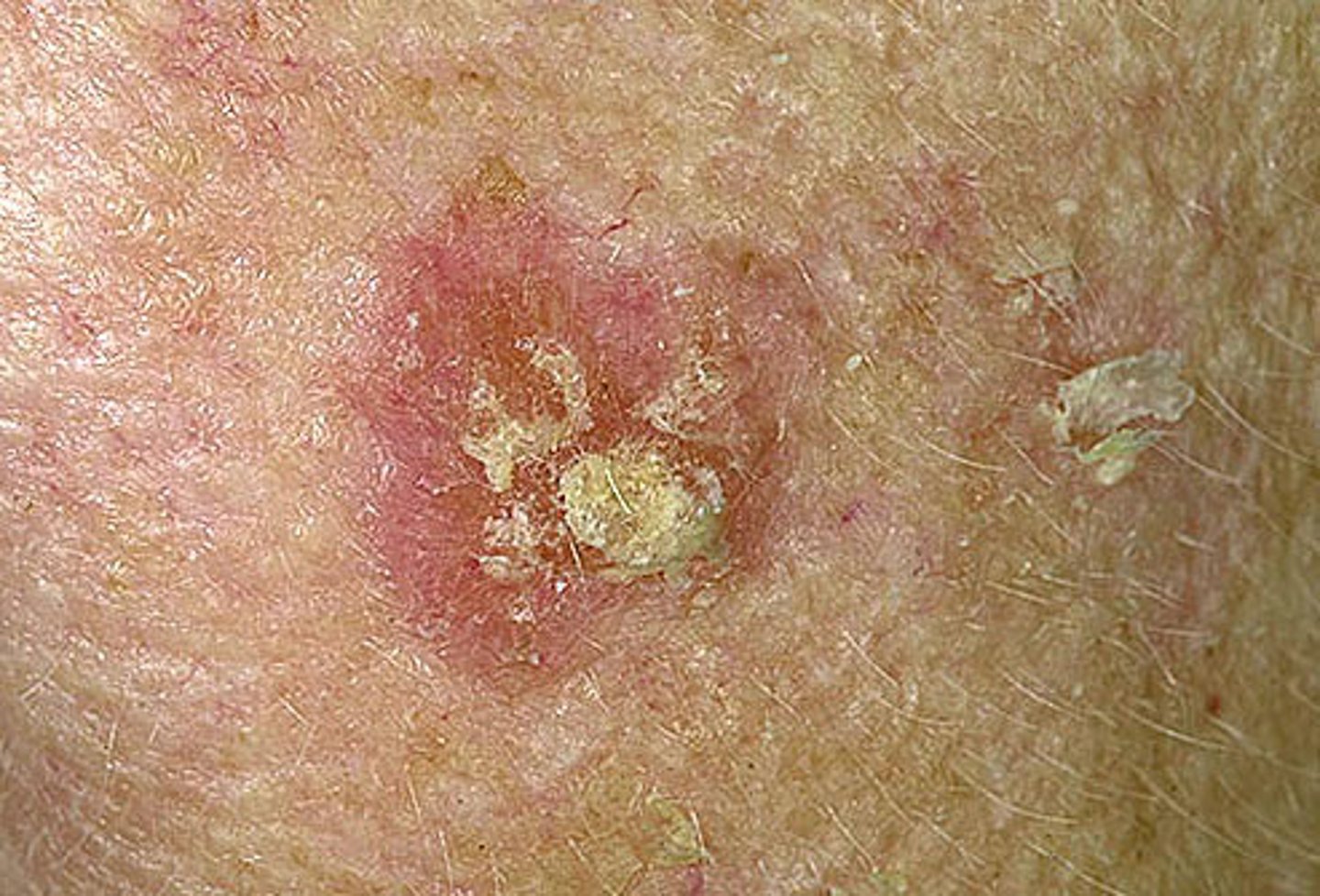
Pearly, raised borders with telangiectasia and a central ulcer that may crust. Sun-exposed areas are most commonly affected
Basal cell carcinoma
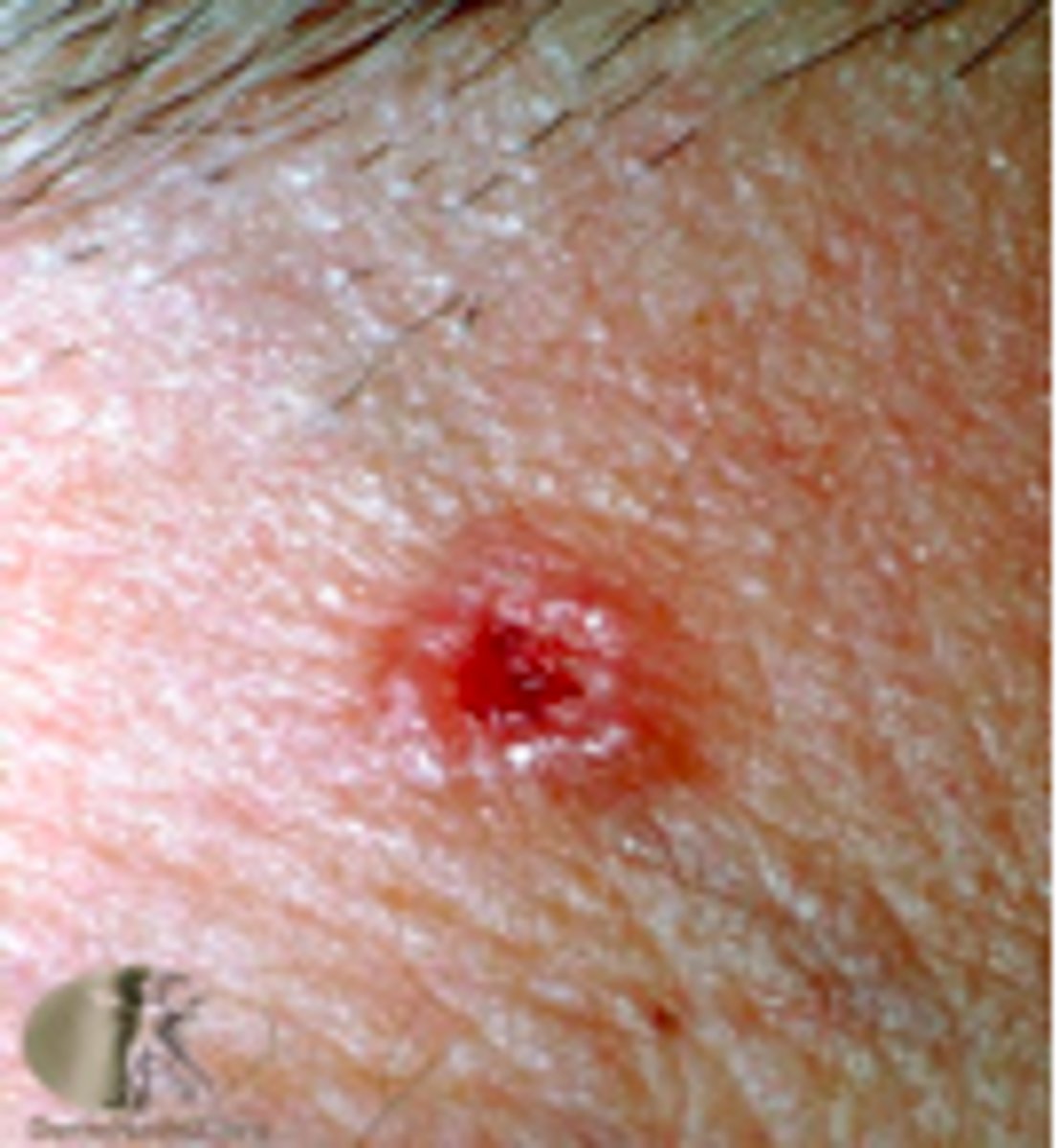
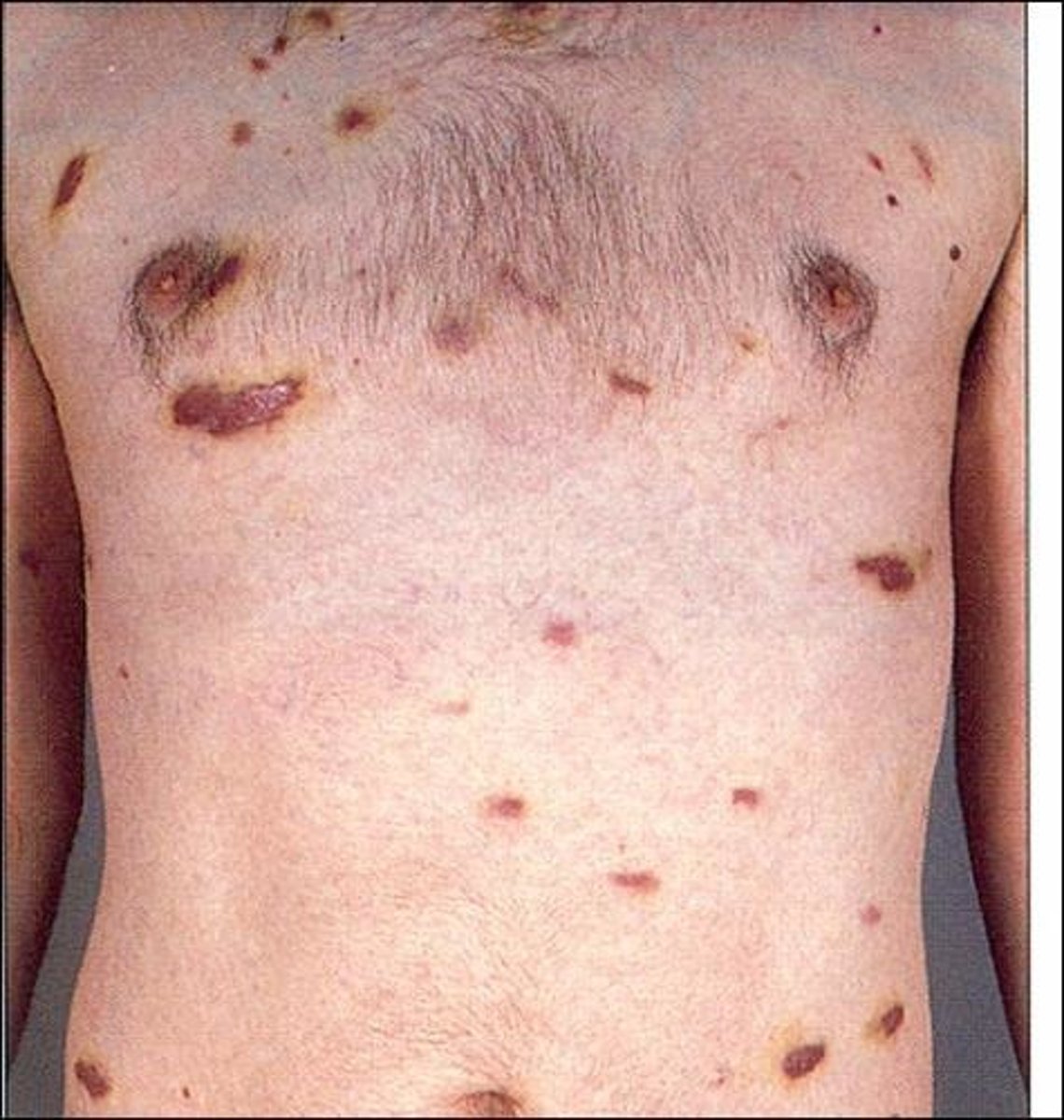
Asymptomatic, purplish, infiltrative, firm nodules and plaques on the head, neck and mouth in an HIV positive patients.
Kaposi sarcoma
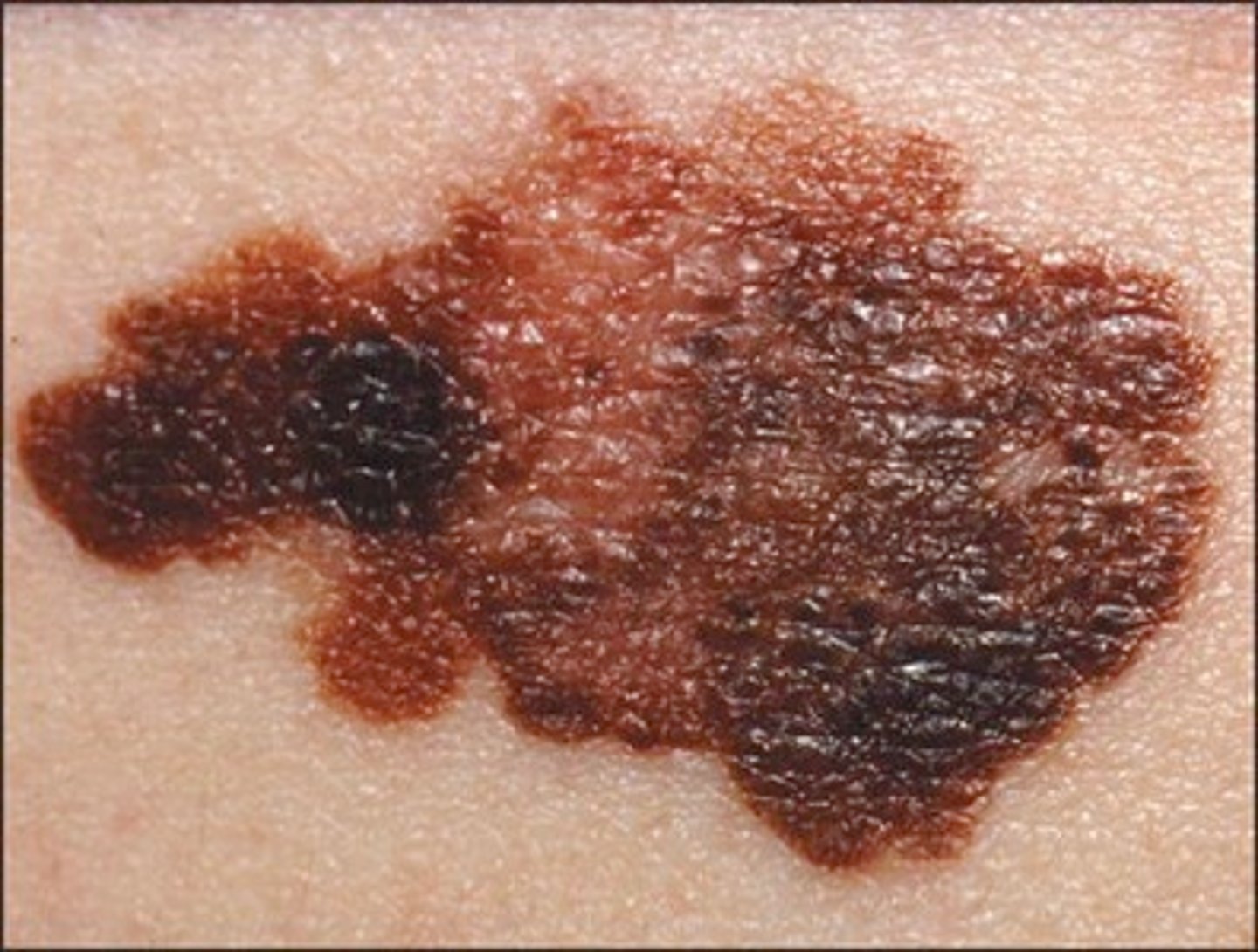
Asymmetrical, unevenly pigmented patch/plaque with a nodule and an irregular border
Melanoma
May appear as firm indurated papule, nodule or plaque with adherent rough scale
Squamous cell carcinoma
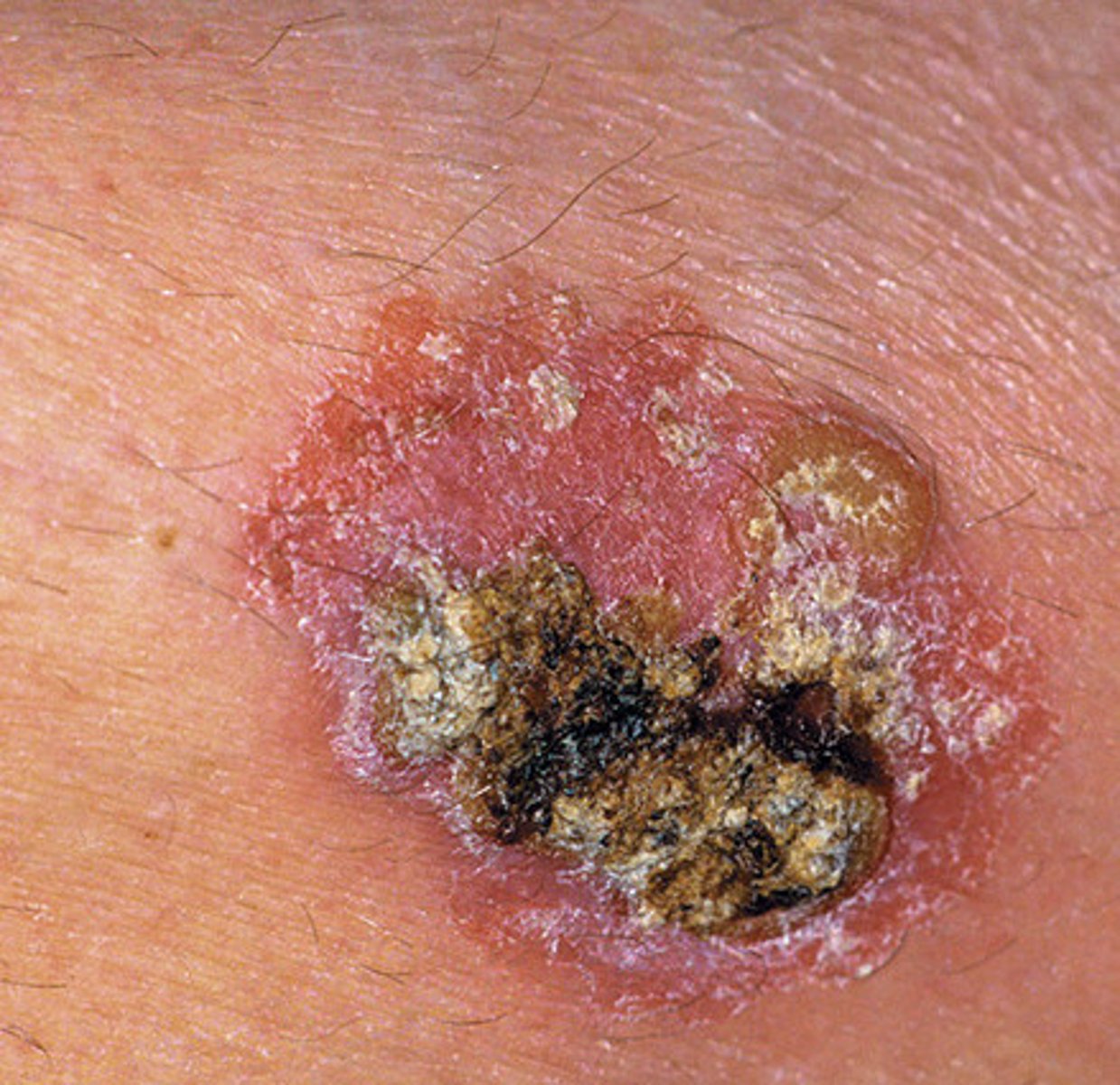
SWhat is the treatment for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma skin cancers?
Surgical excision +/- MOH
What is the AIDS defining skin cancer that appears as purplish lesions?
Kaposi Sarcoma
Malignant melanoma
A 74 year old male with a cardiac tumor history presents with a lesion on his chest. Examination reveals an asymmetric, multi pigmented, 8 cm lesion. What do you suspect?
Basal cell carcinoma
Raised pearly borders telangiectasia central ulcer?
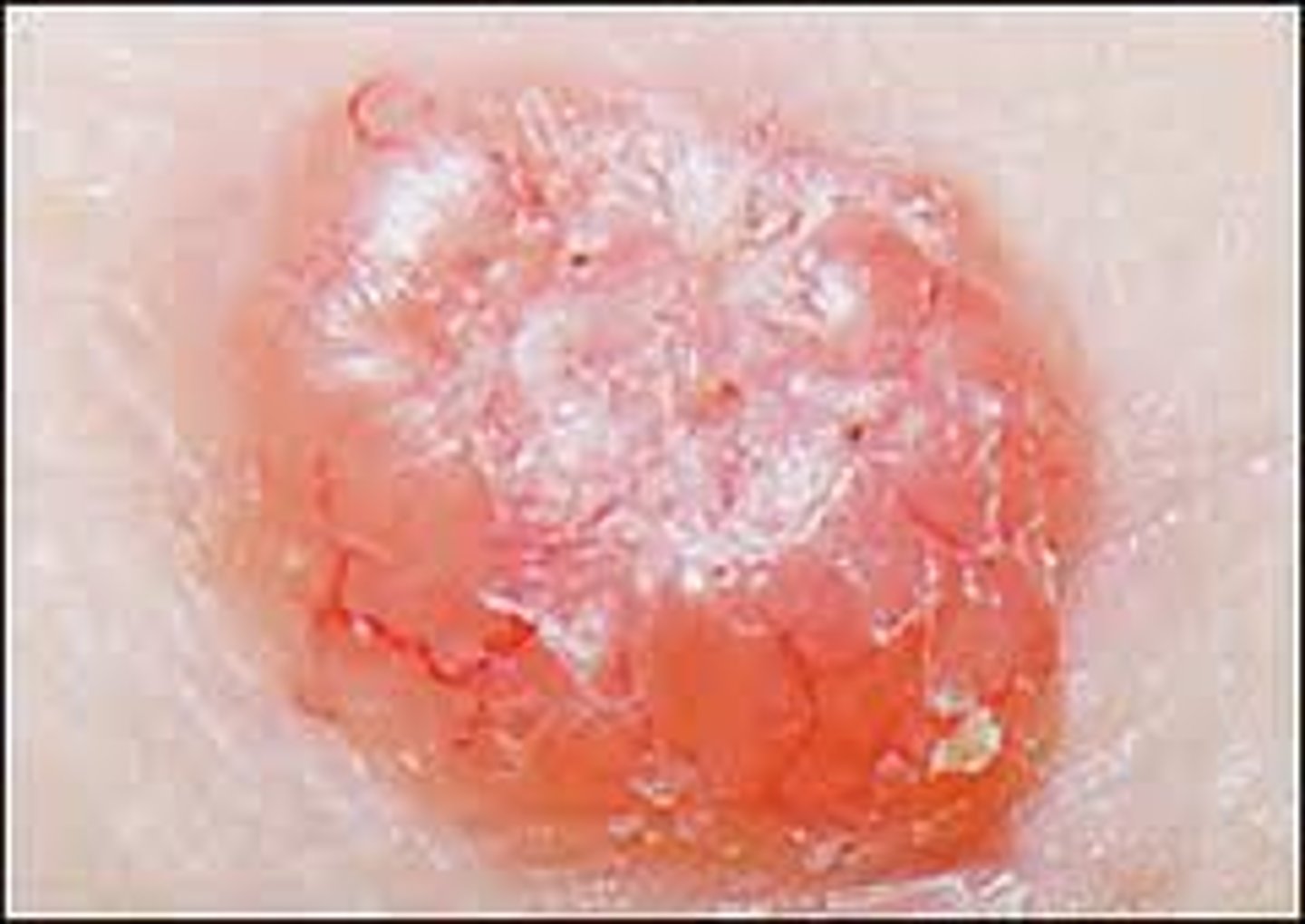
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Scaly papules
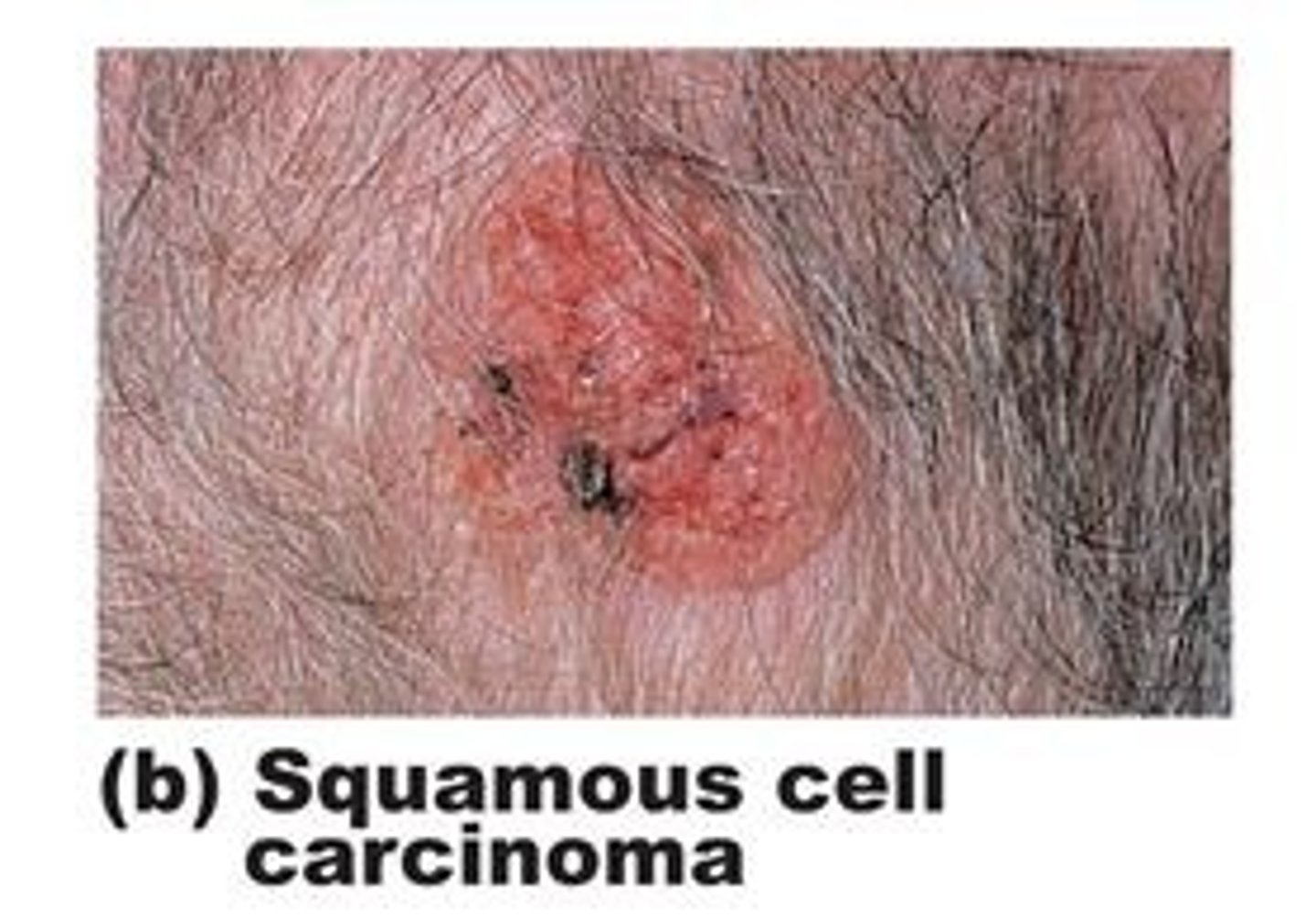
A 75 year old male presents with a centrally ulcerated, translucent/pearly papule with a rolled border and fine telangiectasia on his forehead. What do you suspect?
Basal cell carcinoma
A 65 year old man from Florida presents with an erythematous, indurated, scaly slightly ulcerated papule on his left chest. What do you suspect?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma