Anatomy Practical 1
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
innervation and action of lateral rectus
abducens (VI); turn eye laterally
innervation and action of medial rectus
oculomotor (III); turn eye medially
innervation and action of superior rectus
oculomotor (III); turn eye superiorly
innervation and action of inferior rectus
oculomotor (III); turn eye inferiorly
innervation and action of inferior oblique
oculomotor (III); turn eye superiorly and laterally
innervation and action of superior oblique
trochlear (IV); turn eye inferiorly and laterally
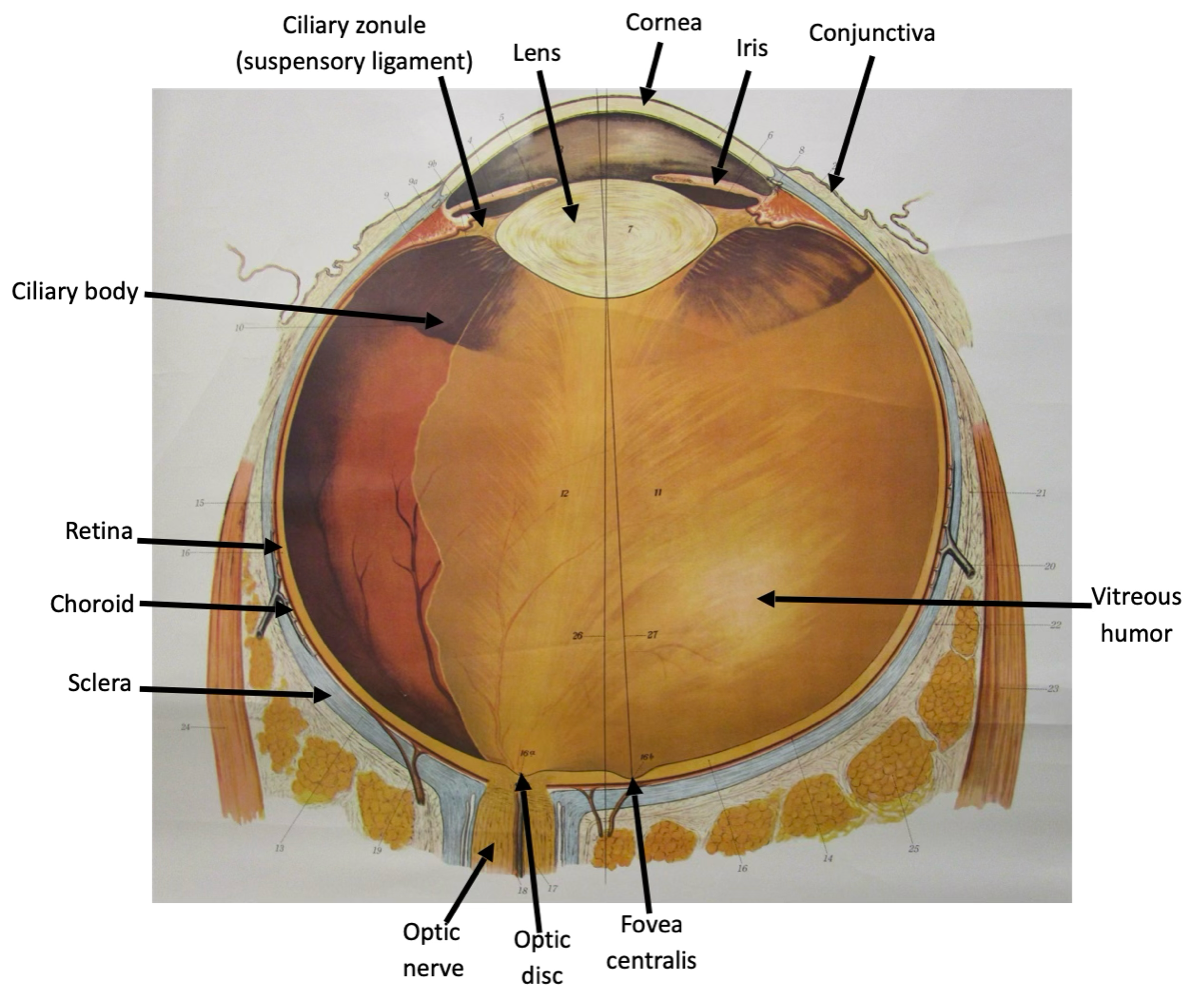
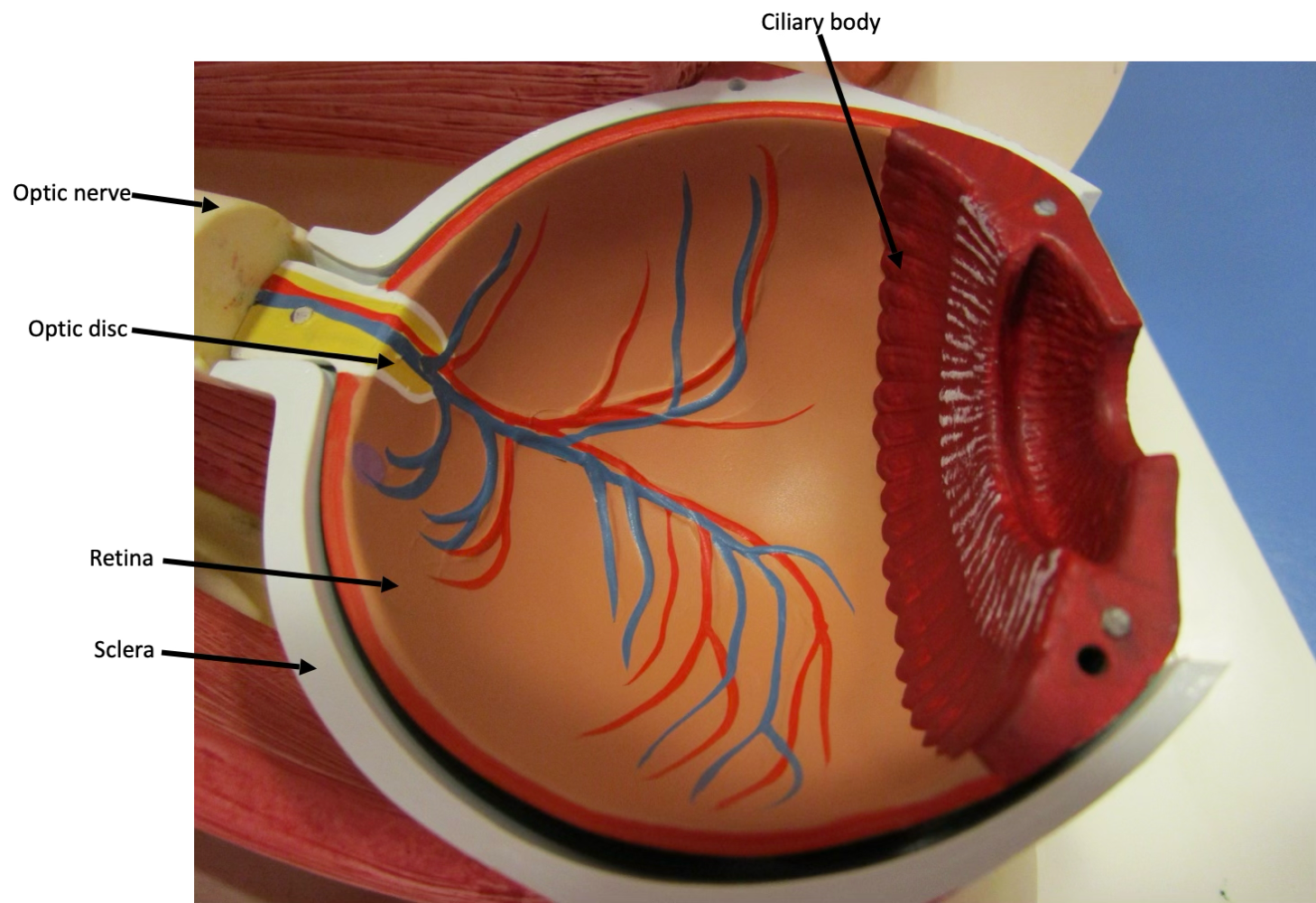
fibrous tunic
composed of sclera and cornea
vascular tunic
composed of iris, ciliary body, and choroid
retina
composed of pigmented and neural layer
blind spot visual test
-blind spot is due to absence of photoreceptors
-use of green bar with red dot and experience visual filling
near point of accomodation
-how close an object can be and still see it
-hold a paper at arms length, close one eye, and ove toward until blurry or you see 2 objects
-based on elasticity of lens
visual acuity (snellen test)
-read eye wall chart with one eye; smallest line with no errors is visual acuity
astigmatism
-due to cornea having irregular curvature
-hold astigmatism chart 20ft away and stare at center to see if any of the parallel lines are blurry
color blindness
-occurs to cone sensitivity
-use vision test kit of Ishihara color charts
depth perception
tested by trying to hold two pencils in line with eachother with one eye closed or placing pencil in test tube
photo pupillary reflex
in the dark pupils get larger; in the light pupils get smaller
accomodation
focus on object at different distances
convergence
eyes point inward to focus on near object
myopia
nearsighted
hyperopia
farsightedness due to shape of eye
presbyopia
farsightedness due to loss of elasticity in the lens
chemoreceptor
chemical receptor that responses to chemicals in aqueous solution
5 types of taste receptors
salt, sour, bitter, sweet, umami
organ of smell and location
olfactory epithelium; covers superior nasal concha and involves cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
olfactory receptor cells
bipolar neurons that have cilia
gustatory cell
receptor of taste found in taste buds, tongue, pharynx, palate
4 types of papillae
filiform (NO taste cells), fungiform, foliate, vallate
foliate papillae histology
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
olfactory discrimination
vials of spice
olfactory adaptation
vials of oils
otoscope
used to asses condition of external auditory ear canal, tympanic membrane, and middle ear
cochlea
organ of hearing
organ of corti
organ of hearing
crista ampullaris
organ of equilibrium
Hearing Acuity Test
-how well someone can hear sounds at different pitches and volumes
-use audiometer but tuning fork in lab
sound localization
sit with eyes closed and have partner strike tuning fork around head and determine where sound was
weber test (hearing)
-used to test for conductive deafness to tympanic membrane
-place tuning fork on head and see if the sound is louder in one ear
Rinne test (hearing)
-used to test for conductive deafness to tympanic membrane or ossicles
-place tuning fork on mastoid process until sound disappears; sound reappears when move off mastoid
-sound travels better through air compared to bone
bing test (hearing)
-tuning fork on mastoid process and close auditory canal
-positive: sound better with ear closed = normal/sensorineural hearing loss
-negative: no change in sound = conductive hearing loss
postural reflex
test balance and negative feedback mechanism
barany test (equilibrium)
-used to asses function of vestibular system
-spin in chair and observe eyes move in opposite direction of movement
-nystagmus: twitching of eyes due to endolymph flowing in semicircular ducts
romberg test (equilibrium)
-used to determine integrity of dorsal white column of spinal cord
-have pt stand feet together, eyes closed, and arms out for allotted period of time
vertigo
the sensation of dizziness
what are the 9 endocrine glands
thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, pituitary, adrenal, thymus, pineal, ovaries, testes
what hormones are released by the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone
what is the target of oxytocin
uterus and mammary gland
what is the target of antidiuretic hormone
kidney
what hormones are released by the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) and what are their targets
growth hormone --> muscle, bone, adipose tissue, liver
thyroid stimulating hormone --> thyroid
adrenocorticotropic hormone --> adrenal cortex
follicle stimulating hormone --> ovaries and testes
luteinizing hormone --ovaries and testes
prolactin --> mammary glands
what hormones are released by the thyroid gland
thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine, thyroxine, and calcitonin
what are the target/effect of TH, T3 and T4
target most cells; sets basal metabolic rate, thermoregulation, growth and development, synergist of sympathetic nervous system
what is the target of calcitonin
bone
what hormones are released by the thymus
thymosin, thymopoeitin
what is the target/effect of thymosin and thymopoeitin
direct maturation and specialization of T cells
what hormone is released by the parathyroid gland
parathyroid hormone
what is the target of the parathyroid hormone
bone, kidney, intestines
what hormones are released from the adrenal cortex and what do they target
aldosterone --> kidney
cortisol --> liver, muscle, adipose, white blood cells
what hormones are released from the adrenal medulla and what do they target
epinephrine and norepinephrine --> many cell types; increase rate and force of heart contractions, dilate bronchioles, increase metabolic rate, dilate pupils, constrict blood vessels to digestive, urinary organ, and skin
what hormones are secreted by the pancreas and what do they target
glucagon --> liver
insulin --> muscle, fat
what hormone is secreted by the pineal gland and what does it target
melatonin --> brain
what hormone is secreted by the testes and what does it target
testosterone --> bone, muscles, testes; secondary sex characteristics
what hormones are secreted by the ovaries and what do they target
estrogen --> uterus; secondary sex characteristics
progesterone --> uterus
what parts of the heart are O2 rich
left atrium, left ventricle, pulmonary veins, aorta
what parts of the heart are O2 poor
right atrium, right ventricle, superior and inferior vena cava, pulmonary arteries
pathway of blood through the heart
superior and inferior vena cavae --> right atrium --> right atrioventricular (tricupsid) valve --> right ventricle --> pulmonary arteries --> lungs --> pulmonary veins --> left atrium --> left atrioventricular (bicupsid) valve -->left ventricle --> aortic valve --> aorta --> systemic circulation
pathway of conduction in heart
1. SA node
2. atrial myocardium
3. AV node
4. atrioventricular bundle
5. ventricular myocardium
what does the P wave represent
atrium depolarization
what does the QRS wave represent
ventricular depolarization and contraction while atrium is repolarizing
what does the T wave represent
ventricular repolarization
normal heart rate
60-100 bpm
bradycardia
slow heart rate (less than 60 bpm)
tachychardia
heart rate > 100 bpm
fibrilation
a rapid, uncoordinated shuddering of the heart muscle (100-200bpm)
myocardial infarction
heart attack
projection pathway of smell from the olfactory receptors to the temporal lobes of brain
olfactory receptors —→ olfactory nerves ——> primary olfactory cortex and other regions in temporal lobe
what structures are involved in taking the sense of taste from buds to brain
facial and glossoparyngeal nerve
sclera
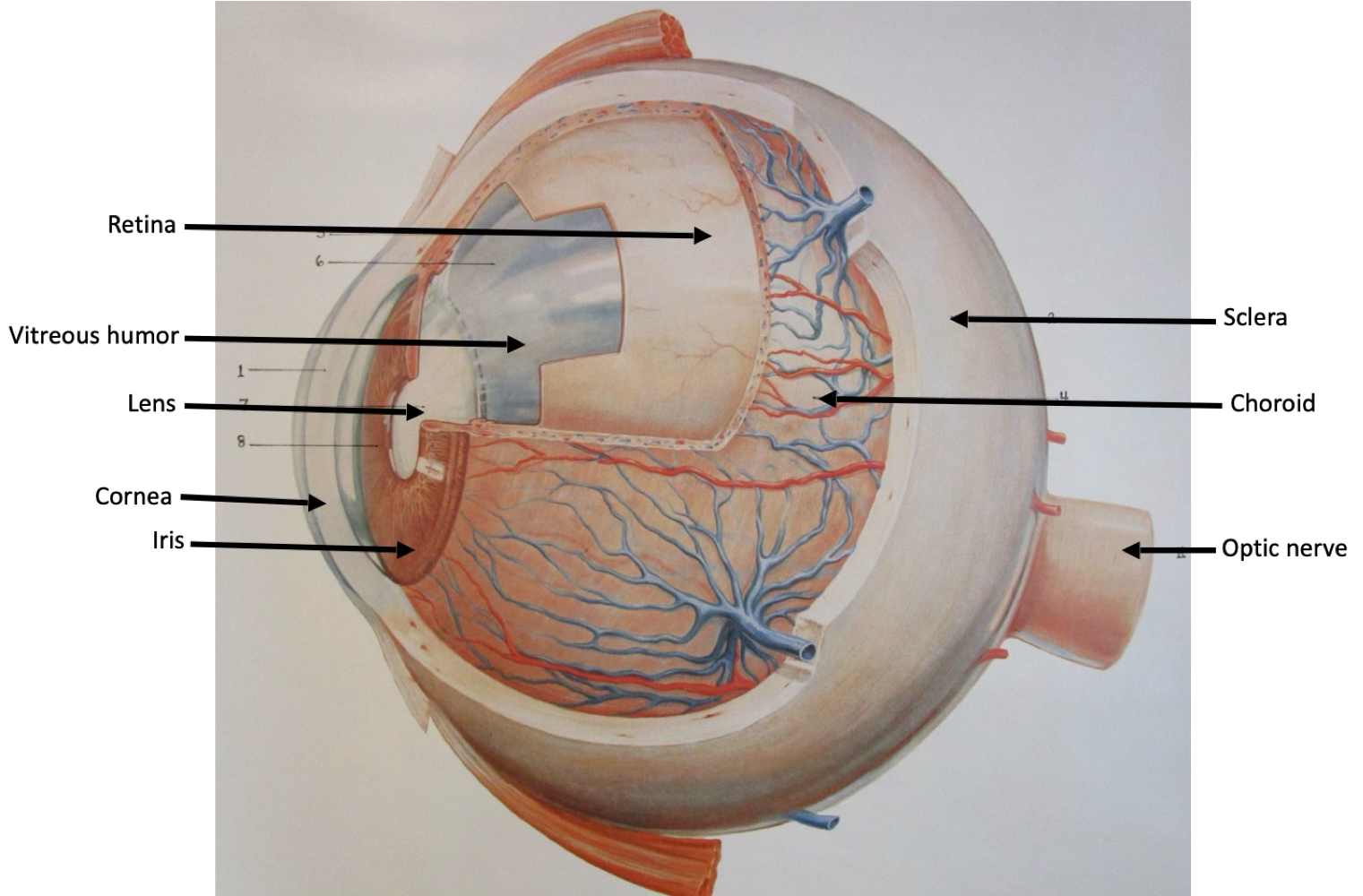
choroid
retina
suspensory ligament
a fibrous connective tissue structure that supports and suspends an organ or body part
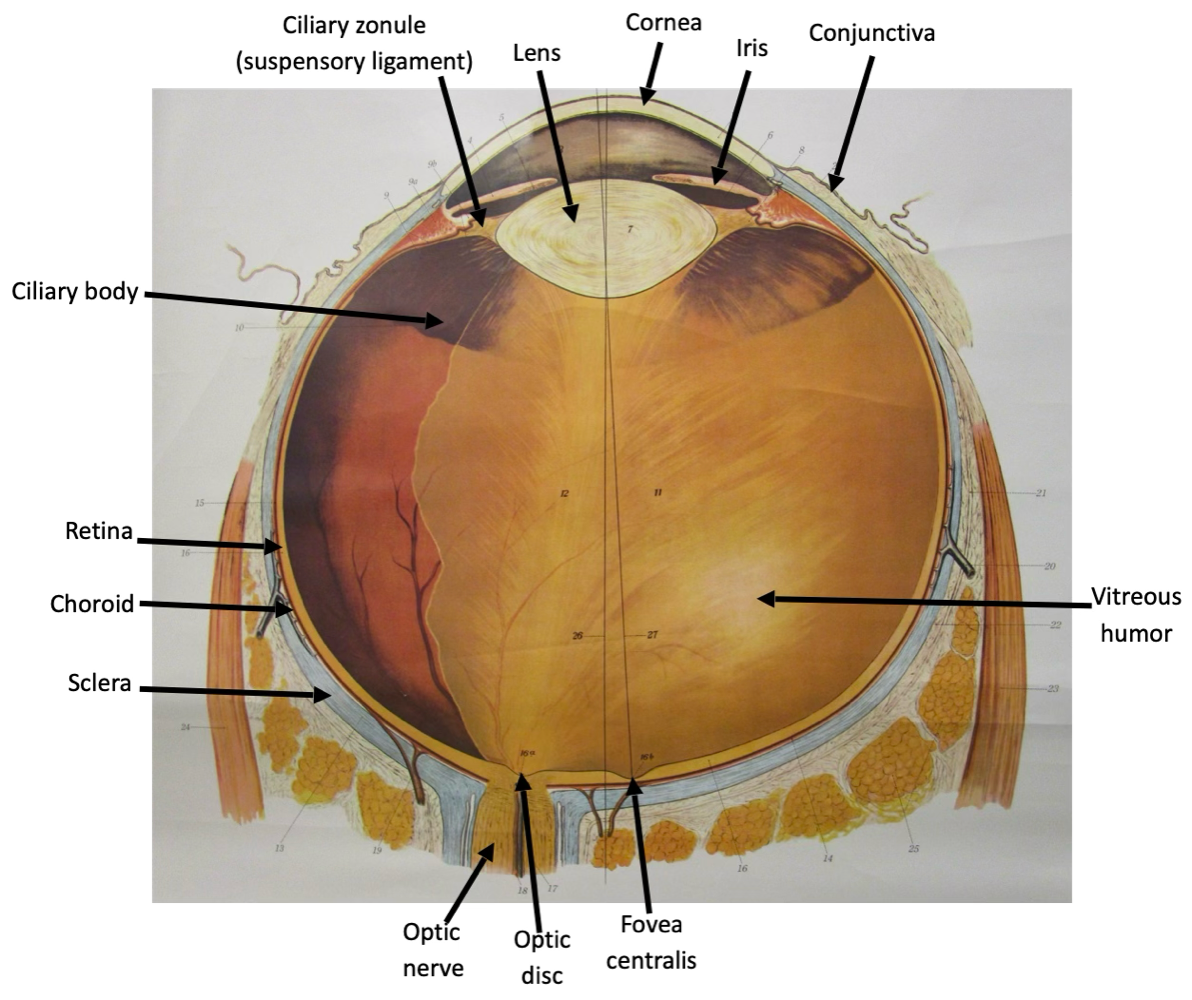
What is the consensual reflex of the pupil?
The consensual reflex is the decreased diameter of one pupil when the other pupil is
exposed to an increase in light.
What gland produces tears?
lacrimal gland
11. What part of the inner ear is involved in conducting signals of static equilibrium?
vestibule
what is the name of the canal that runs from the auricle to the tympanic membrane?
auditory canal
19. Name all the parts of the inner ear.
cochlea, vestibule, semicircular ducts