experimental methods in molecular bio
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Common features of cloning vectors
origin of replication
selectable marker
insertion site for cloned DNA (aka multiple cloning site/polylinker)
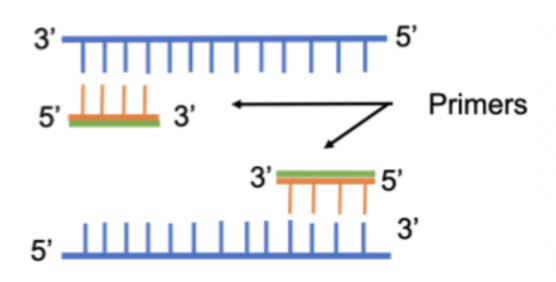
what strands are the forward and reverse primers added to?
Forward primer: binds to template (antisense) strand (3’ → 5’)
Reverse primer: binds to complementary (sense) strand (5’ → 3’)
what are sticky ends?
short, single-stranded DNA overhangs created by restriction enzymes that cut DNA in a staggered way
what is the purpose of sticky ends?
they base-pair with complementary sticky ends to hold the fragments together temporarily, allowing for permanent covalent bonds to form and to create recombinant DNA
importance of poly-A tail in cDNA synthesis
to act as a binding site for an oligo(dT) primer, which is necessary to initiate the reverse transcription of mRNA into cDNA
what are the two enzymatic activities of T4 DNA polymerase?
5’ → 3’ polymerase activity (restores chain using dNTPs and complementary strand as template)
3’ → 5’ exonuclease activity (removes nucleotides from 3’ ends of DNA)
what is bacterial transformation?
process where bacteria take up and incorporate foreign DNA into their genome
how many strand(s) are sequenced simultaneously in next-generation sequencing?
billions of strands
how many strand(s) are sequenced simultaneously in next-generation sequencing?
only one strand at a time
in next-gen sequencing, what are the adapters and why are they used?
they contain info needed for sequencing and contain an index; this is done during the library prep
what is sequencing by synthesis (SBS)?
DNA template is prepared: The DNA you want to sequence is attached to a solid surface.
Add nucleotides one at a time: The DNA polymerase enzyme adds complementary nucleotides to the growing strand.
Detect the added base: Each nucleotide has a label (like a fluorescent tag) so a machine can detect which base was just incorporated.
Repeat: The process continues step by step, and a computer records the sequence as the strand grows.
what is the basic process of sanger sequencing?
DNA copying: You start with the DNA you want to sequence and use an enzyme called DNA polymerase to make new DNA strands.
Special “stop” nucleotides: Some nucleotides are modified (called dideoxynucleotides or ddNTPs) that stop DNA copying when they are incorporated. Each type of stop nucleotide is labeled with a different color.
Resulting fragments: You end up with many DNA fragments of different lengths, each ending with a colored ddNTP.
Read the sequence: A machine separates the fragments by size and detects the color of the last nucleotide in each fragment. This tells you the order of the bases in the DNA.