W7 L1: Animal digestion feeding strategies
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Feeding
• Process of obtaining and ingesting food
• Must target food that meets nutritional needs
• Success depends on feeding mechanism
– Feeding apparatus and behaviour
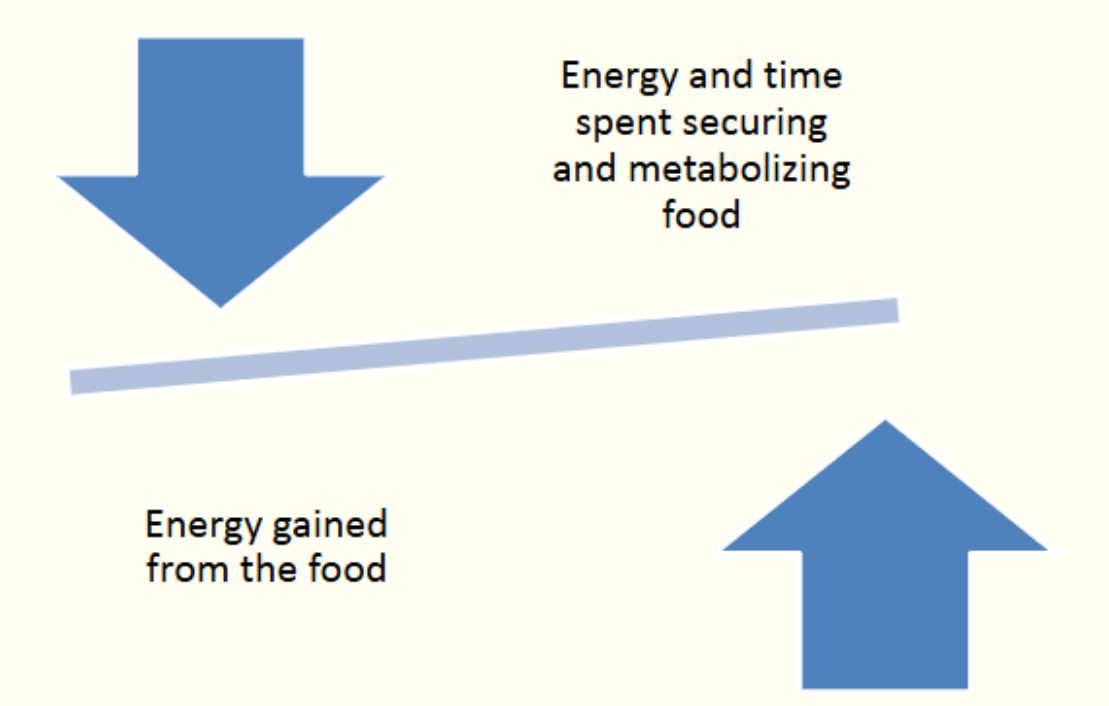
• Balance between energy expenditure and intake – evolutionary driver
Food sources
Sources of energy - Trophic levels, about 90% loss of energy via heat at each trophic level
Food availability can vary - E.g. seasonality
Feeding mechanisms
Feeding on organisms that are individually attacked and ingested
Suspension feeding
Symbioses
Feeding on organisms that are individually attacked and ingested
Requires that food organisms are
Located - find the organism
Identified - find the correct organism
Subdued
Ingested
- Includes carnivores and herbivores e.g. Carnivorous mammals, Grazing mammals, Carnivorous fish, Birds of prey, sea stars, nectar feeding, gastropods
Some use toxic compounds
• Work by inflicting structural damage and/ or subdue prey
• Examples
Scorpions
Spiders
Jellyfish
Snakes - secretes a neurotoxins
Suspension feeding
• Common in aquatic organisms
• Feeding on organisms that are very small in comparison with the feeding animal
• Has evolved often
• Feeding on organisms lower on food chain
• Increase of energy available
E.g. Bivales - filter ingested water that contains food particles (planktons), Basking/Whale sharks, Baleen whales, Humpback whale
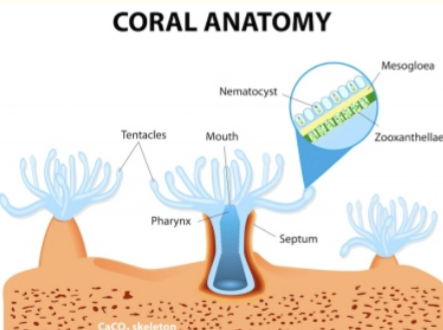
Symbioses
– With autotrophic microbes - use inorganic compounds
– With heterotrophic microbes - use organic compounds, e.g. Gut microbiome
Reef corals
photoautotrophic microbes - algae use light to produce food for the coral
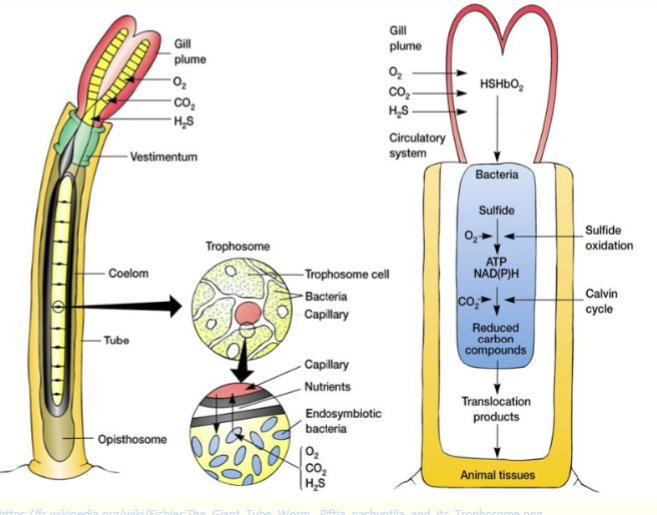
Hydrothermal vent species
chemoautotrophic microbes
No photosynthesis as there is no light
Chemoautotrophic bacteria ensures oxidation of chemicals similar to photosynthesis to produce organic compounds
E.g.Giant tube worm
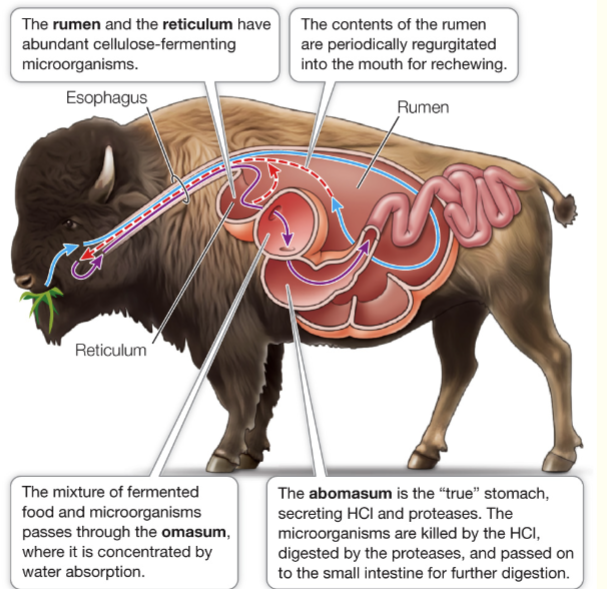
Ruminants
Fermenters
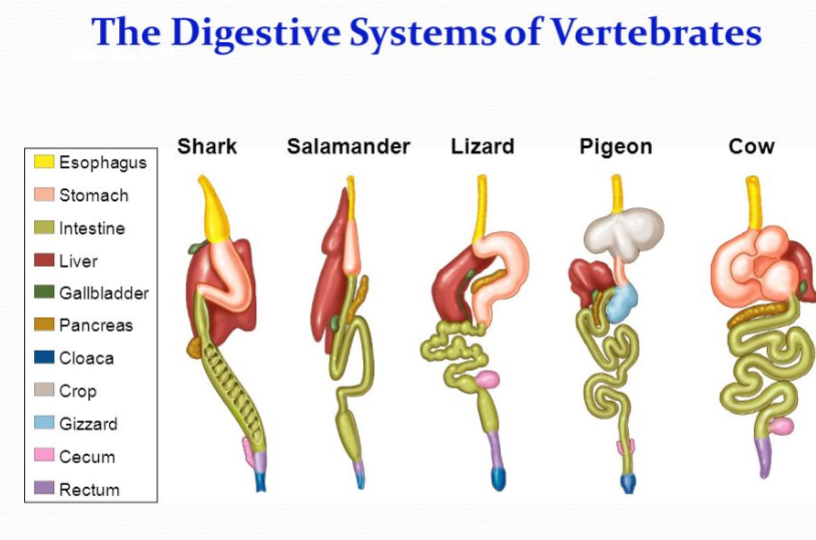
Diversity in digestive structures
• Invertebrates
– Blind guts (incomplete digestive tract)
– Complete digestive tract
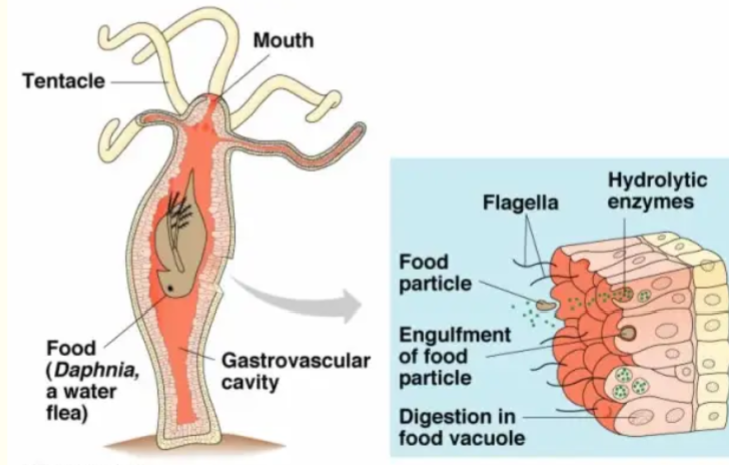
Hydra
Blind guts, one opening that works as a mouth and an anus
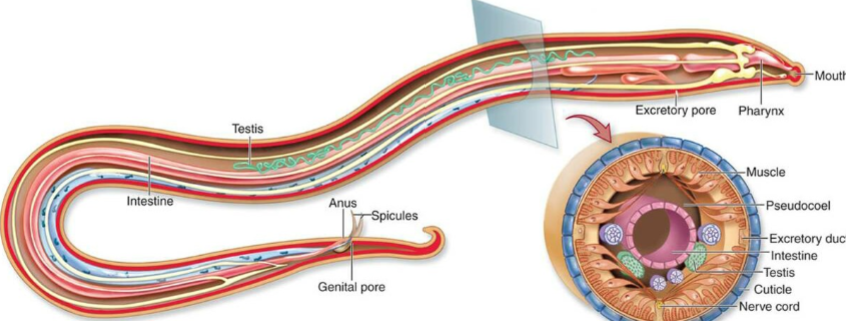
Nematode
complete digestive tract
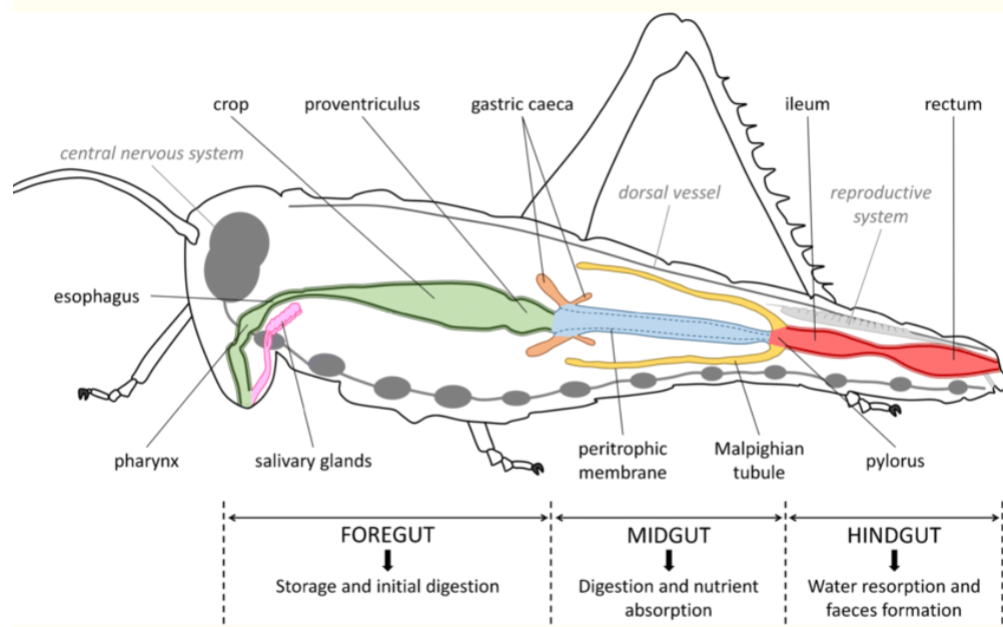
Insect digestive system
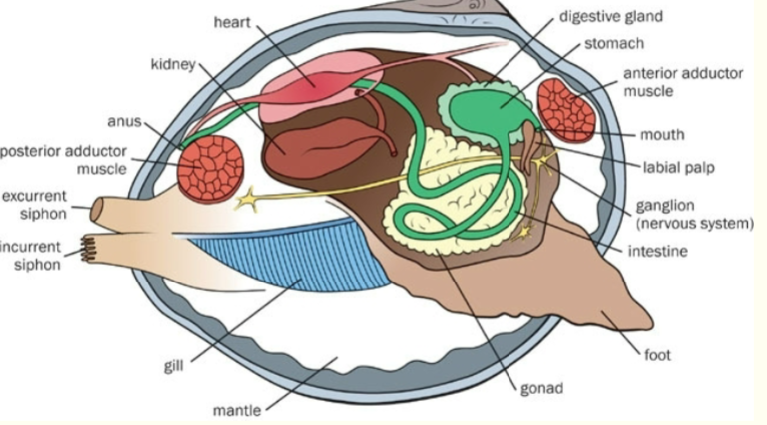
Bivalve digestive system
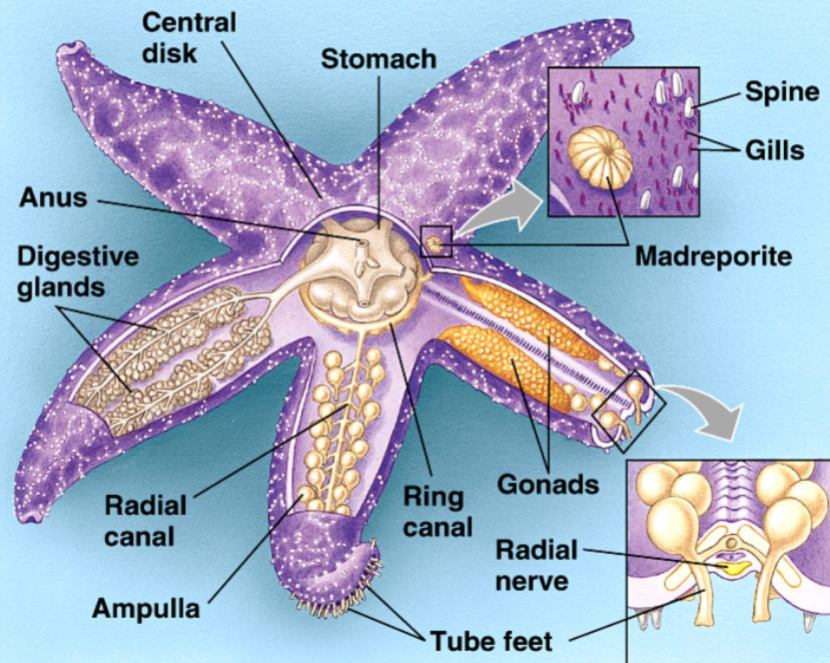
Starfish digestive system
everted stomach
Mouth - Tongues
Present in almost all vertebrates
Used to gather food, speech development
Mouth - Teeth
Makes food more accessible for the digestive system
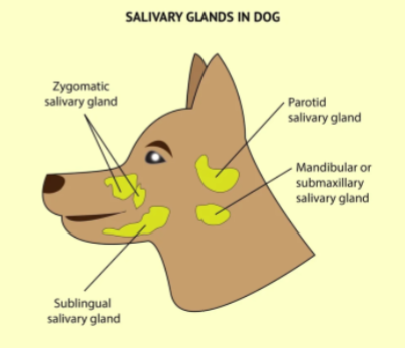
Mouth - Salivary glands
Makes food more accessible for the digestive system
Mouth - Salivary glands
Contains enzymes that digest carbohydrates in the mouth
Not all vertebrates E.g.fish have salivary glands
Esophagus
• Esophagus: moving food to stomach
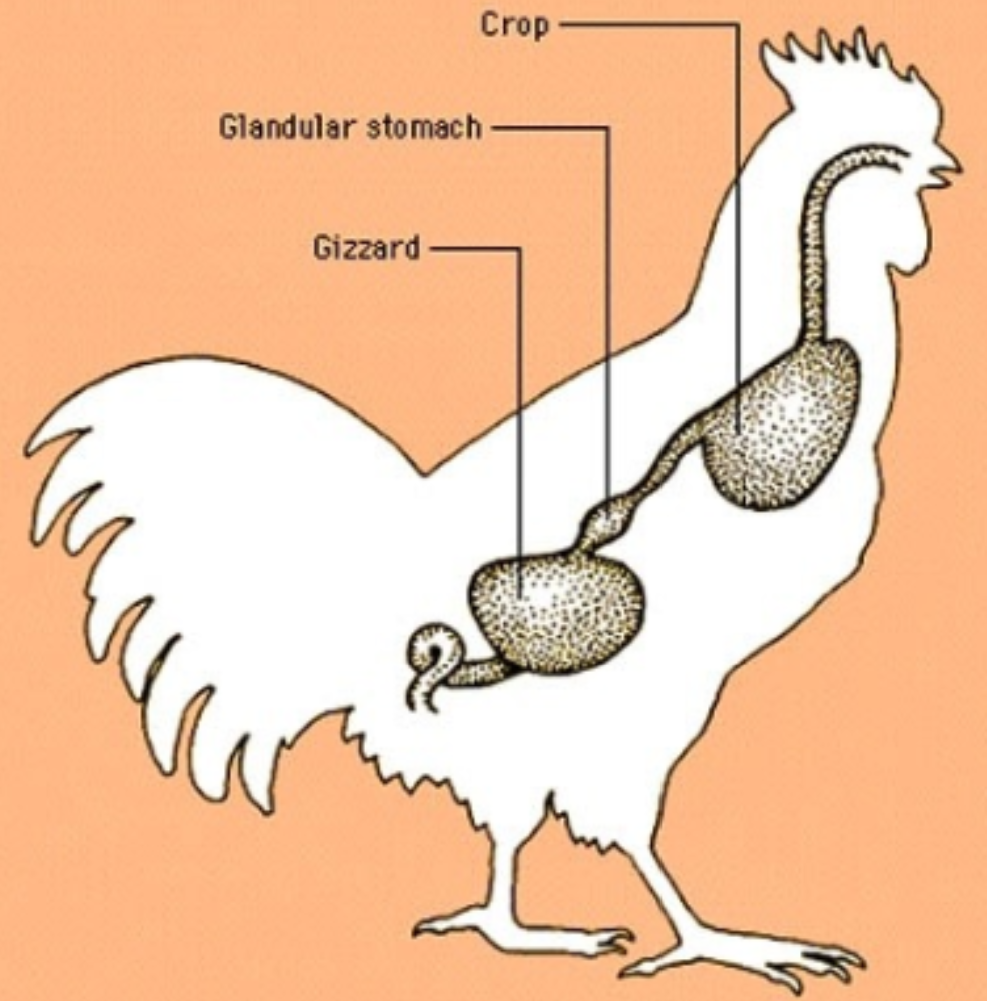
• Crop: food storage in birds
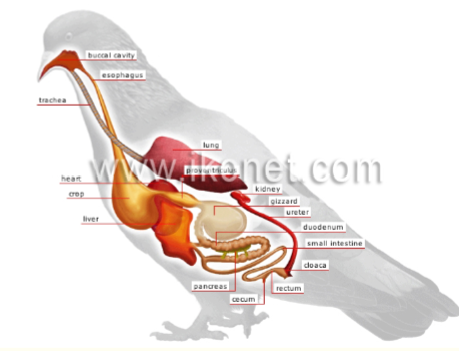
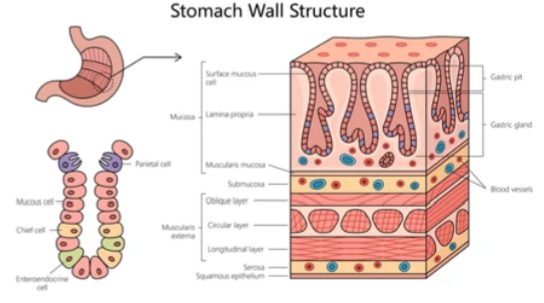
Stomach
HCl
Pepsinogen - protein digestion
Gizzard
Mechanical grinder
Used to grind grains and seeds
Seen in some birds
Rumen
multichambered stomach that holds microorganisms
Ceca
Binding pouches
– Important in non-ruminant herbivores
– House microorganisms, cellulose digestion
Intestines
Used for breakdown and absorption of food with less energy