newtonian world and astrophysics (fill in gaps in astrophysics)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
absolute zero
the temperature at which a substance has minimum internal energy and kinetic energy of the particles is zero - 0K and -273.15C
thermal equilibrium
objects in contact with each other at the same temperature
particles in a solid
vibrate about a fixed position - strong forces between them
particles in a liquid
can slide past each other - weaker attractive forces
particles in a gas
particles move quickly in random directions very weak forces of attraction
equation of density for molecules
density = mass of one molecule x number of molecules per cubic meter
internal energy
the sum of the randomly distributed kinetic and potential energies of the atoms or molecules within a system
Brownian motion
The random movement of small visible particles suspended in a fluid
specific heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of the substance by 1 K
specific latent heat of fusion
the amount of energy required to change the phase of 1 kg of a substance from solid to liquid
specific latent heat of vaporisation
the amount of energy required to change the phase of 1 kg of a substance from a liquid to a gas
n
number of moles
N
number of particles
number of particles from the number of moles
N=n x NA
ideal gas
a gas that has internal energy only in the form of random kinetic energy
the 6 assumptions when modelling ideal gases
the gas contains a large number of particles
the particles move rapidly and randomly
all collisions are perfectly elastic
there are negligible forces between particles except during collisions
the time for collisions is negligible compared to the time between collisions
particles have a negligible volume compared to the volume of gas in the container
Boyles law
the volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure exerted on the gas, under conditions of constant temperature - pV = constant
pressure temperature law
at constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. P/T= constant
Charles’ law
at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature - V/T = constant
when will a real gas act like an ideal gas
temperature is high, well above the boiling point of the gas
pressure is low, so that the particles are far apart
k=
R/NA
angular velocity
the rate of angular rotation, measured in radians per second, symbol (omega)
centripetal acceleration
the acceleration of an object moving with uniform circular motion
centripetal force
the resultant force on an object, acting towards the centre of the circle, causing it to move in a circular path
displacement (SHM)
the distance an object moves from its equilibrium position
Amplitude (SHM)
the maximum displacement
SHM
a body oscillating in such a way that its acceleration is directly proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position and always directed towards that point
a use for damping
shock absorbers in car suspension
natural frequency
the frequency at which a system will oscillate when undergoing free oscillations
resonance
when the driving frequency is equal to the natural frequency of a system resulting in it oscillating at maximum amplitude
the two effects of increasing the amount of damping on an object undergoing resonance
reduces amplitude
reduces the frequency that coresponds to the maximum amplitude of the oscillation
a practical use of resonance
microwave ovens
a harmful effect of resonance
dangers in buildings or bridges caused by wind or earthquakes
gravitational field
the region around a body in which other bodies will feel a force due to the mass of the body
newtons law of gravitation
the gravitational force between two masses is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation
keplers first law
planets travel around the sun in elliptical orbits
keplers second law
a line joining the sun to a planet will sweep out equal areas in equal times
keplers third law
the time period of the orbit squared is proportional to the mean of the radius of cubed
geostationary orbit
an orbit that has the same time period and orbital rotatdirection as the rotation of the earth and is in the orbital plane
one use for geostationary satellites
broadcasting tv signals
Monitoring the weather
Monitoring air traffic
gravitational potential
the work done in moving a mass in a gravitational field to the point it is at from infinity
escape velocity
the minimum launch velocity required to move a object from that point to infinity
nuclear fusion
the process of two nuclei joining together and releasing energy
comet
a large rocky ice ball that travel in highly elliptical orbits around the sun
gravitational collapse
the inward movement of a star due to the gravitational force caused by its own mass
radiation pressure
an outward acting force caused by fusion reaction
gas pressure
outward acting force caused by the kinetic energy of the gas particles
features of a white dwarf
very dense with high surface temperature an low luminosity
electron degeneracy pressure
the pressure that stops the gravitational collapse of a low mass star
Chandrasekhar limit
the maximum possible mass for a stable white dwarf
luminosity
the total energy a star produces per second
basic initial stages for formation of any star
nebula (giant cloud of hydrogen gas)
protostar (hotter and glowing)
Main sequence star (inward and outward forces in equilibrium)
evolution of a low mass star
red giant (expanded and cooled)
Planetary nebula (outer layers of gas that have been ejected)
white dwarf (hot, dense core)
Black dwarf ( no longer emiting heat or light)
evolution of high mass stars
Red super giant (expanded and cooled)
supernova (High temperatures fusing heavy nuclei beyond iron)
neutron star (the neutron core has remained intact)
black hole (escape velocity is so high that photons are unable to escape, dense singularity)
3 and 4 both evolve from supernova not in order
HR diagram
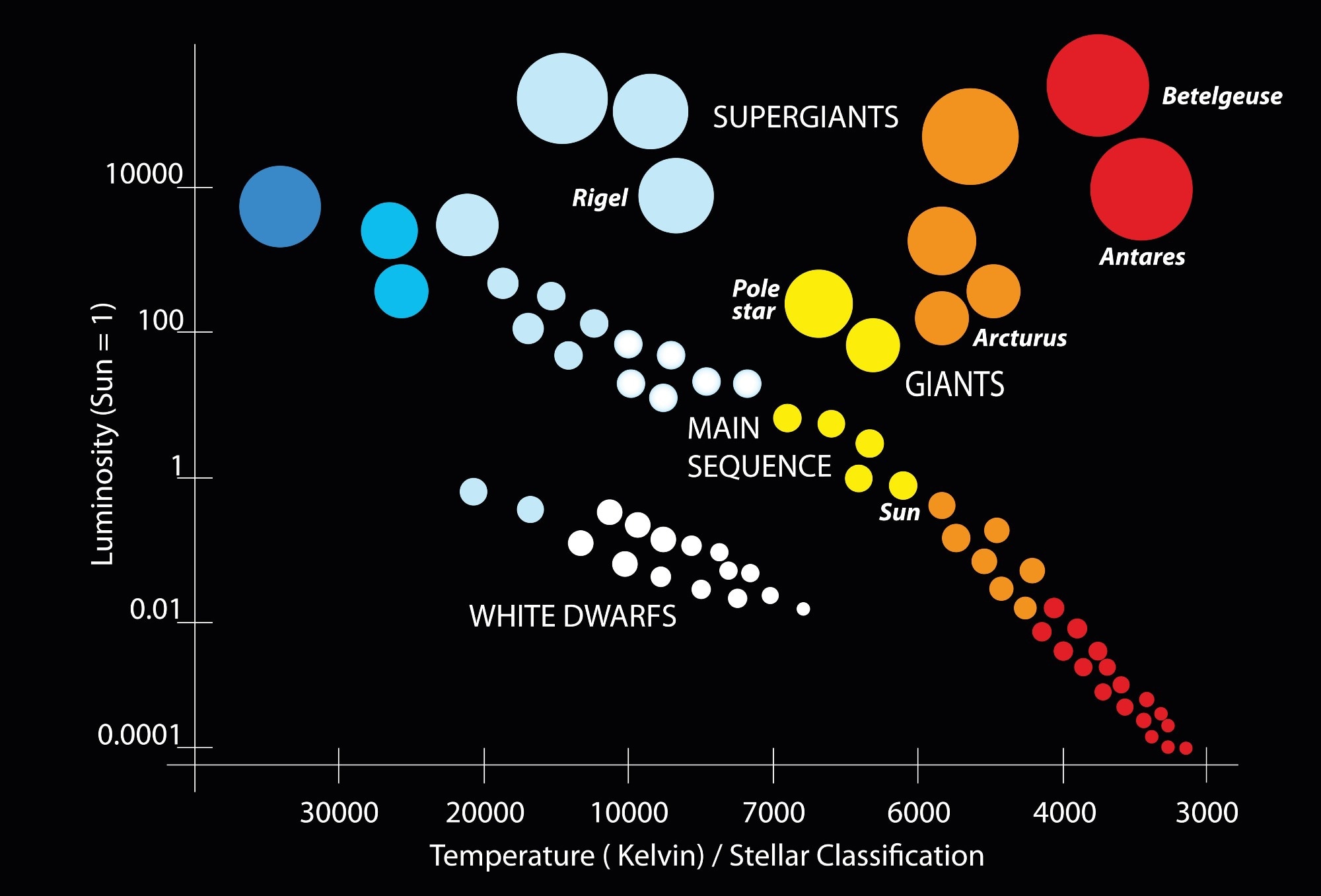
wiens law
the product of the maximum wavelength and temperature is constant
stefans law
The total energy emitted by a black body per unit area per second is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature of the body
Stefan's Law equation is given by:
L = 4πr2σT4
AU
Mean distance from the centre of the earth to the centre of the sun
stellar parallax=
p=1/d d is distance in parsecs
Hubbles law
the recessional velocity of a galaxy is proportional to its distance from the earth
the cosmological principle
on a large scale the universe is both homogenous and isotropic
The big bag theory
states that the universe was created from a singularity where all of the universes current mass was situated. It was much smaller, hotter and denser then it is now
isotropic
the same in all direction
homogeneous
of uniform density
timeline of the universe
10^-35 - rapid expansion, high energy gamma photons and em waves
10^-6 - 1st fundamental particles gain mass
10^-3 - 1st hadrons come from quarks
1s - production of mass halted
100s - pprotons and neutrons fuse to become light nuclei
380,000 years - first atoms form
30mil years - 1st stars form, fusion of heavier elements
200mil - our galaxy forms
13.7bill years - current life as we know it
dark matter
matter which can not be seen and that does not emit or absorb e.m. radiation
Dark energy
A type of energy that permeates the whole universe and opposes the attractive force of gravitation between galaxies
three possible outcomes of the universe
open universe - keeps expanding forever
flat universe - stops expanding at a certain size and stays in equilibrium
closed universe - ‘Big crunch’, the universe will eventually collapse in on itself