The Brain and Neuropsychology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Brain diagram
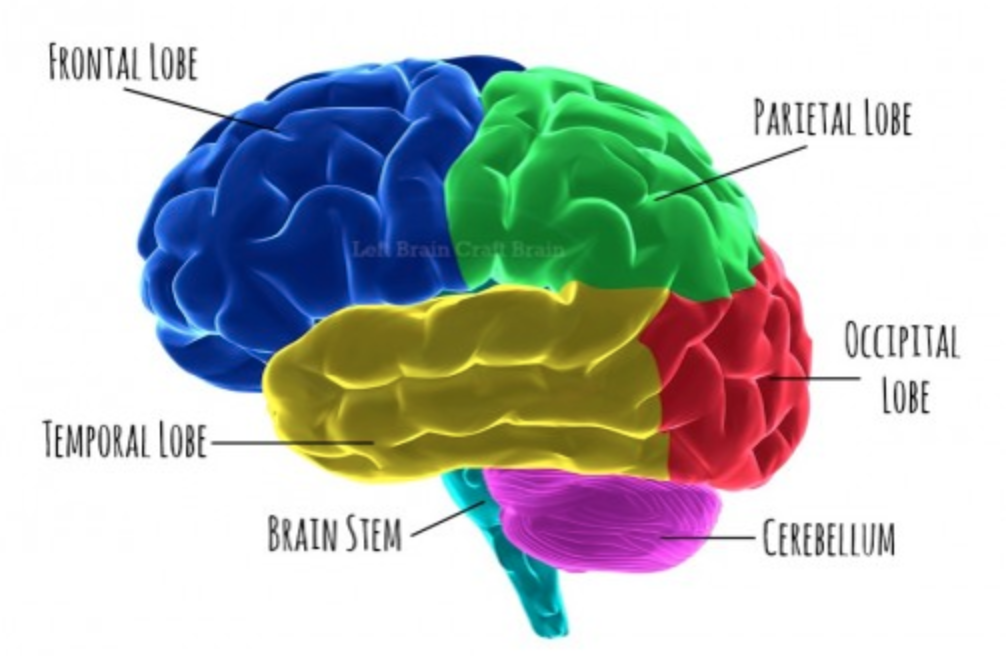
Temporal lobe function
Hear and understand speech
Create speech
Damage: Understand and process speech
Occipital lobe function
Processes visual information
Our ability to see
Damage: Vision. Understanding surroundings
Frontal lobe function
Decision making
Impulse control
Problem solving
Concentration
Damage: Memory and problem solving
Parietal lobe function
Facial recognition
Sense of touch
Damage: Facial recognition
Cerebellum function
Movement and coordination
Balance
Information from senses
Damage: Balance, coordination
Broca and Wernicke’s area
Broca: Responsible for speech
Wernicke: Responsible for comprehension
Hemisphere dominates
Left: Language, logic and math skills
Right: Dominates emotion, creativity and music
Sex differences in brain
Size: Male brain is 10% larger than female brain
Hemisphere: Men are left dominant, woman are equally balanced
Language: Women process in both hemispheres. Men only process in one
Emotion: Women have larger limbic so are more emotional. They are more likely to experience depression and other disorders
Sex differences strengths
Haresty et al found language part is bigger in females than in males
Rilea et al found males are better at spacial tasks than females
Sex differences weaknesses
Sommar et al found no strong evidence that women use both sides for language
Most tasks focused on the left brain so can’t explain spacial tasks
Central Nervous System
Made of brain and spinal cord
Brain sends messages to the body
Messages are carried through the spinal cord
The spinal cord can activate the Peripheral Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
Connects the CNS to the muscle, skin and organs
Carries out the action required by the message sent from the brain
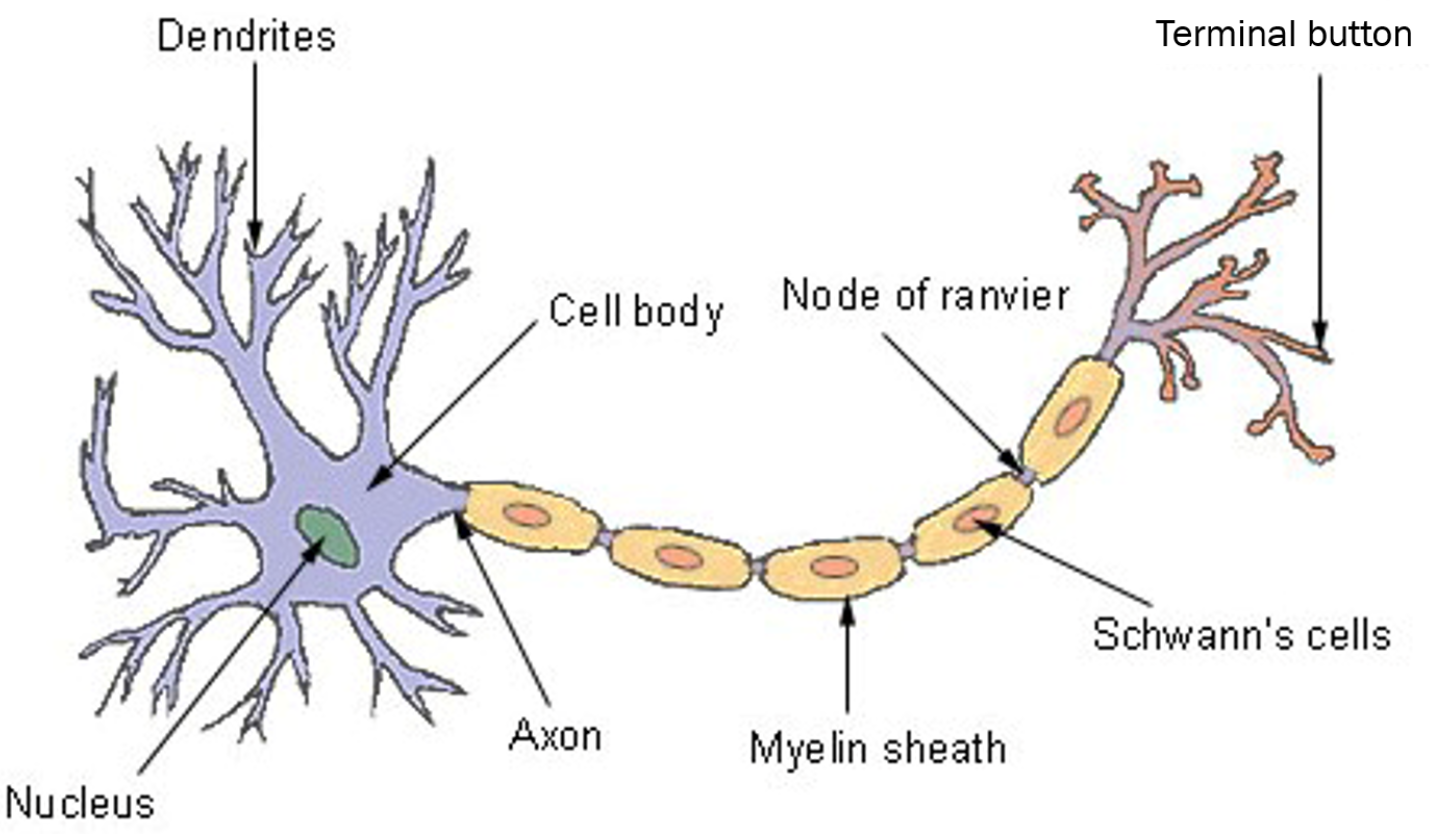
Neurone
Synapse
Dendrite
Receives messages through receptors from other cells
Axon
Passes messages from the cell body to other neurones, muscles or glands via terminal buttons that hold neurotransmitters
Nerve impulse
An electrical signal that travels down the axon from the cell body to the terminal buttons so it releases a neurotransmitters
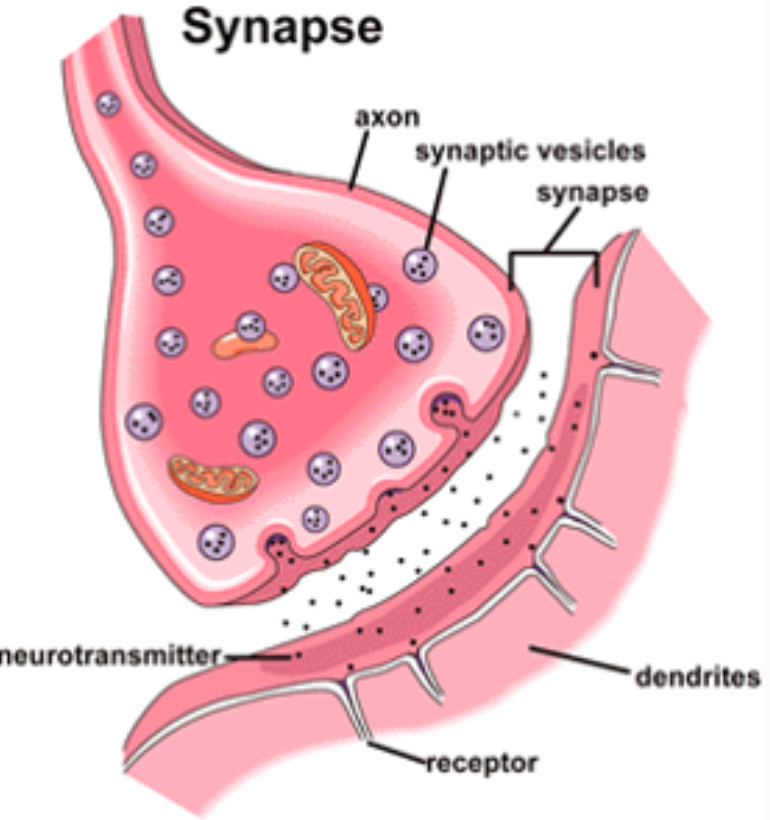
Synaptic transmission
An electrical impulse is triggered inside the neurone
A small impulse is passed along the axon towards the end of the nerve
It arrives at the terminal buttons which are filled with vesicles
These contain neurotransmitters
When the impulse reaches here, the vesicles release their chemical into the synaptic gap
These chemicals are grabbed by the receptors on the next nerve cell, which passes the message on.
Dopamine
Plays a role in attention and learning
Not enough dopamine makes it difficult to concentrate
Seratonin
Plays a role in our mood
Too little serotonin can make people depressed
GABA
Plays a role in calming us down
Not enough BAGA causes us to feel stressed
Neurological damage
Damage to the body’s central and peripheral nervous system
Messages can be interrupted
Neurons might not be working
Normal functions of the brain not possible
Behaviour can be affected
Visual agnosia
The inability to recognise things that can be seen
Affected by parietal lobe
Prosopagnosia
Patient is unable to recognise faces of people
Affected by temporal lobe
What happened to Gage
1848 – railway line worker
Explosion forced iron rod through his head
Before: calm and well liked
After: irresponsible and rude
Died 12 years later – epilepsy
Demasio 1994 Aim
To investigate the brain damage to Phineas Gage using his skull
Determine functions of the frontal lobe
Demasio 1994 Procedure
Took photos and measurements of Gage’s skull
Built a 3D replica of skull
Measured iron rod and compared it to damaged areas of skull
Mapped 20 entry and 16 exit points
Narrowed this to 5 paths
Demasio 1994 Results
Damage to both the left and right hemisphere.
Extreme damage to the frontal lobe
Damage to white matter (where neurones pass their message along)
Damage was worse in the ventro medial region
Broca’s area was undamaged
Demasio 1994 Conclusion
Ventromedial region of the frontal lobe responsible for sensible decisions
Evaluating Demasio
Generalisable: No, brain damage is unique to Gage.
Reliable: No, the reports of the damage are over 150 years old
Validity: The study is based on a real life case
Used modern day technology making the study scientific.
We can make predictions about damage to the frontal lobes.
We can now treat people who have similar brain damage based on what happened to Gage.
Sperry 1968 Aim
How the split brain works
Examine the extent of which the 2 hemispheres are specialised
Sperry 1969 Procedure
Studied 11 patients who had their corpus callosum cut
Had them complete 2 tasks
Visual: Word or picture was shown for 1/10th of a second. They had to recall the picture
Tactile: Had to close eyes and name the object that was placed in their left or right hand
Sperry 1968 Results
Information sent to the right field could be described in speech
Objects placed in the right hand could be named
Sperry 1968 Conclusion
Hemispheres can function without each other but the information can’t be shared
The left hemisphere= language abilities
The right hemisphere = spatial abilities
Sperry Strengths
Reliability: Sperry gathered a lot of consistent information
Reliability: The procedure was kept the same for each participant, keeping it standardised.
Real world application: The study tells us a lot about the lateralisation of the brain so strategies can be put in place to support individuals with damage to one side of their brain.
Sperry Weaknesses
Generalisability: It is hard to generalise findings from the study because the sample size is small and so specific.
Validity: The study was a lab experiment which is an artificial setting which means it lacks ecological validity
Validity: The task is not something we would naturally do and so it lacks mundane realism.