BIO 202 Lab: Section 1.1-1.2: Endocrine System
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Endocrine System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What hormones does the parathyroid glands produce and its function
Parathyroid hormone (PTH): the main hormone that maintains calcium ion homeostasis. It increases calcium levels and triggers osteoclast activity, bone resorption, increase calcium ion absorption from intestines, increased calcium ion reabsorption from kidneys
What are hormones like PTH and calcitonin considered to be
Antagoinsts
Where is the thymus gland located
Sits in the superior mediastinum
When is the thymus gland most active and what hormones does it secrete
It is large and active during infancy and early childhood, during which it secretes thymosin and thymopoietin
What does the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin stimulate in the thymus gland
Stimulate the development of T lymphocytes within the thymus gland
What happens to the thymic tissue in the thymus gland in adults
It gradually is replaced by fat and other connective tissue
Where is the adrenal gland located
Sits atop the superior pole of each kidney (ad: next to, renal: kidney)
What are the two structures of the adrenal gland
Outer adrenal cortex and inner adrenal medulla
What are the adrenal glands surrounded by
A thin layer of connective tissue called adrenal capsule
What type of hormones does the adrenal cortex secrete and derived from what
They secrete steroid hormones derived from cholestrol in response to stimulation by adrenocorticotropic hormone
What are the three zones of the adrenal cortex
Zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis (Zona GFR)
What type of steroid hormone does zona glomerulosa secrete and an example
Secretes mineralocorticoids. An example is aldosterone, which regulates fluid, electrolyte, and acid-based homeostasis (GMA)
What type of steroid hormone does zona fasciculata secrete and an example
Secretes glucocorticoids. An example is cortisol, which regulates stress response, blood glucose, fluid homeostasis, and inflammation
What type of steroid hormone does zona reticularis secrete and an example
Secrete gonadocorticoids and glucocorticoids. An example is androgens and estrogens, which affect the gonads and other tissues
What does the adrenal medulla consist of and what hormone does it secrete and derived from
Consist of modified postsynaptic sympathetic neurons that secrete the hormone adrenal catecholamines, which are derived from amino acids
What are examples of adrenal catecholamines in the adrenal gland
Norepinephrine and epinephrine, which prepares the body for stressful situations (sympathetic nervous system)
What effects does adrenal catecholamines have the same effect on target cells as and what are they
Neuronal catecholamines: dilation of bronchioles, increase rate and force of heart contraction, constriction of blood vessels serving skin and abdominal viscera, dilation of pupils
What does adrenal catecholamines do that neuronal catecholamines do not
Prolongs sympathetic response (neuronal catecholamines are terminated after a few seconds) and acts on target cells not innervated by sympathetic neurons
Where is the pancreas located and what type of functions does it do
Behind and below the stomach. It has both endocrine and exocrine functions
What carries out the exocrine functions in the pancreas and its function
Pancreatic acini or acinar cells that release pancreatic juices into pancreatic ducts. The pancreatic juices neutralize hydrochloric acid, digesting protein, fat, and starches
What carries out endocrine functions in the pancreas and its function
Pancreatic islets that is embedded into the pancreatic acini. Cells within pancreatic islet secrete insulin and glucagon which regulate blood glucose levels
What cells produce insulin and glucagon and its function
Insulin in secreted by beta (β) cells which helps lower glucose levels and glucagon is secreted by alpha (α) cells which helps increase glucose levels
Where is the testes located and what does it produce
Male reproductive organ located in the scrotum that produce sperm cells (male gametes)
What are the cells in the testes called and what steroid hormone does it produce and its function
Interstitial cells that produce testosterone, which promotes production of sperm cells and the development of male secondary sex characteristics (deep voice, greater bone, muscle mass, facial hair)
Where is the ovaries located and what does it produce
Female reproductive organs located in pelvic cavity that produce oocytes (female gametes)
What hormones does the ovaries produce and its function
Estrogen: plays a role in development of oocytes and female secondary sex characteristics (breast, subcutaneous fat stores) Progesterone: prepares the body for pregnancy
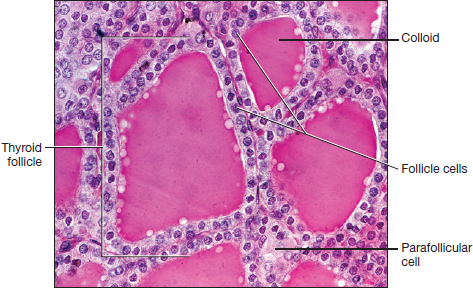
What type of histology slide is this showing and how do you know
Thyroid gland: simple cuboidal epithelium and colloid in middle
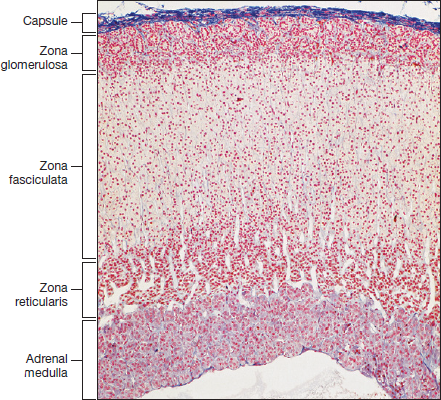
What type of histology slide is this showing and how do you know
Adrenal gland: the layers and capsule
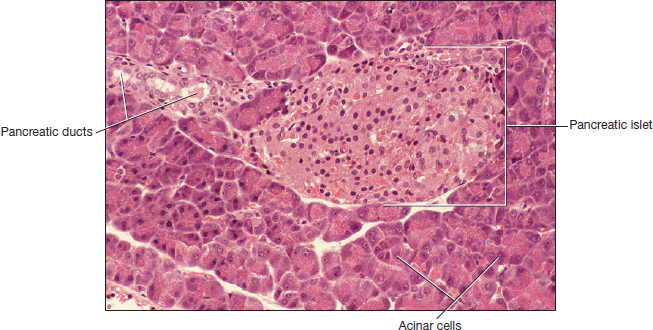
What type of histology slide is this showing and how do you know
Pancreas: the pancreatic islets
What are exocrine glands and some examples
Glands that rely on ducts to release their substance. For example: sweat, salivary, lacrimal, digestive, mammary glands
What is the endocrine system
Diverse group of ductless glands that play a major role in maintaining homeostasis of multiple physiological variables
How does the endocrine and nervous system differ
The nervous system functions by action potentials and releases neurotransmitters that directly affect target cells. Effects are immediate but short in duration. Endocrine system secretes hormones that act on distant targets. Effects are not immediate but longer-lasting
Which endocrine glands secrete hormones as their primary functions
Thyroid and anterior pituitary glands
Which endocrine glands secrete hormones as their secondary function
The heart (atrial natriuretic peptide), adipose tissue (leptin), the kidneys (erythropoietin), and stomach (gastrin)
What type of system is the nervous and endocrine also referred to as
Nervous is referred to as our fast response system and endocrine system is our slow response system
Where is the hypothalamus located and what is it also known as
The inferior part of the diencephalon and is known as a neuroendocrine organ and the CEO of endocrine system
What is the endocrine system primary means of travel
Blood
What does the hypothalamus working closely with and how is it attached
Works closely with pituitary gland, which is attached by a stalk called infundibulum
What hormones does the hypothalamus produce that works with the anterior pituitary
Releasing and inhibiting hormones
How does the hypothalamus communicate with the anterior pituitary gland
Through the hypothalamic - hypophyseal portal system
What is another name for the 2 regions of the pituitary gland and what are they composed of
Anterior pituitary gland or adenohypophysis: composed of glandular epithelium Posterior pituitary gland or neurohypophysis: composed of nervous tissue
What is the pathway of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system
The inhibiting and releasing hormones are synthesized by hypothalamic neurons -> then they enter hypothalamic capillary bed -> then they travel through the portal veins in infundibulum -> then they enter anterior pituitary capillary bed -> then they exit the blood
What hormones does the hypothalamus produce that works with the posterior pituitary and its functions
Oxytocin: uterine contraction and milk ejection from mammary glands Antidiuretic (ADH): causes water retention from kidneys and controls blood pressure
What hormones does the anterior pituitary gland produce (mostly tropic)
Follicle stimulating hormone: stimulates follicles in ovary & sustentacular cells in testes
Luteinizing hormone: stimulates oocytes in ovary & interstitial cells in testes Adrenocorticotropic hormone: stimulates secretion from adrenal cortex
Thyroid stimulating hormone: stimulates growth/secretion of thyroid gland Prolactin: stimulates milk production from mammary glands
Growth hormone: increases rate of cell division & protein synthesis; has both tropic/non-tropic effects (FLAT-PG)
What hormones does the posterior pituitary gland produce
They do not produce hormones, it stores oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone produced by hypothalamus
Where is the pineal gland located and what type of organ is it
In the posterior and superior diencephalon and is a neuroendocrine organ
What hormones does the pineal gland secrete and based on what
Melatonin in response to decreased light levels. This hormone acts on the reticular formation part of the brainstem to trigger sleep
How does follicle cells respond to TSH from anterior pituitary in thyroid gland
By secreting a chemical into the colloid that reacts with iodine to produce 2 hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
Where is the thyroid gland located
Anterior-inferior neck, superficial to the larynx or voicebox
What does the thyroid gland consist of and how are they connected
Consist of left and right lobes connected by a thin band of tissue called isthmus
Describe what the thyroid gland is composed of
Composed of thyroid follicles that are lined with simple cuboidal follicle cells and encapsulates a colloid
What is between the follicle cells in the thyroid gland and its function
Parafollicular cells - it produces calcitonin which decreases blood calcium levels and triggers osteoblast activity and bone deposition
What is the function of triiodothyronine (T3) of the thyroid gland
It is the most active of the two hormones. It increases metabolic rate, protein synthesis, regulate heart rate and blood pressure. When T3 levels are low, T4 gets converted to T3