COMPTIA NETWORK + (100, but should have been 130)
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Imported from Quizlet without modification
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What is the OSI model?
Open System Interconnection: A model used to conceptualize the many parts of a network.
What is the TCP/IP model?
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol: a model used to conceptualize the many parts of a network.
What is ISO (the creators of the OSI model)?
The International Organization for Standardization.
What are the 7 levels of the OSI Model?
From Top to Bottom:
7)Application
6)Presentation
5) Session
4) Transport
3) Network
2) Data Link
1) Physical
What is the First Layer of the OSI Model?
The Physical Layer:
This layer is comprised of the Physical Components used to transport data from one place to another. This can be anything from copper cabling to Radio Waves from a WAP.
What is UTP?
Unshielded Twisted pair.
What is a NIC?
Network Interface Card - a communication controller that is required by a computer to connect to a network.
• Translates the computer data to the protocol used by the network.
What is a MAC Address?
Media Access Control Address: a 48 bit address unique to each NIC.
What is the IEEE?
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
What is OUI?
Organizationally Unique Identifier: the first six digits of a MAC Address, these are the parts of MAC addresses assigned to organizations.
What is ipconfig?
Ipconfig is a utility program that is commonly used to identify the addresses information of a computer on a network. It can show the physical address as well as the IP address.
What is ipconfig/ all?
A more detailed version of ipconfig.
What is ifonfig?
The ipconfig command but for users of Mac Os.
What is ip a?
Ipconfig for Linux users.
What is EUI-48?
Extended Unique Identifier: the name for the address space that MAC addresses occupy.
What is MAC-48?
The original name for the numbering space MAC addresses occupy.
What is a Frame?
A container for a chunk of data moving across a network. This is a "wrapper" placed on data by a NIC. These are sent, received, and read by NICs.
What is a PDU?
Protocol Data Unit: The unit of data specified by a protocol at each layer of the OSI Model.
Describe an Ethernet Frame from beginning to End.
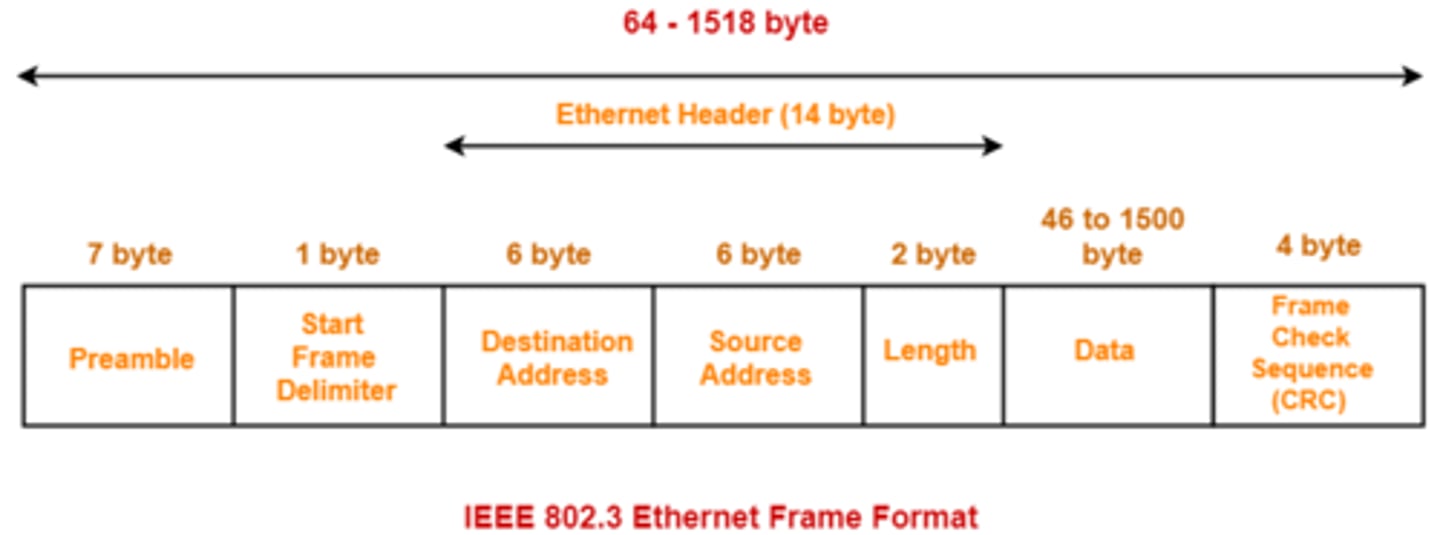
What is FCS?
A Frame Check Sequence(FCS) is error detection method used by PPP encapsulation. If the FCS key does not match the receiving NIC's answer, the data was not received properly, and the frame is dropped.
What is PPP?
Point-to-Point Protocol
What is CRC?
Cyclical Redundancy Check: the section at the end of an Ethernet Frame that is used to ensure that the data was received intact.
What is a HUB?
A precursor to modern switches, this network device would receive data from a host and then would forward this data to every host on the network.
Describe layer 2 of the OSI Model
Data Link Layer:
This layer deals with the forwarding of information based on MAC addresses. Switches and NICs operate at this level. PDU= Frames.
Routers function at this layer
What is LLC?
Logical Link Control:
the aspect of a NIC that talks to the systems operating system
What is TCP?
Transmission Control Protocol
Describe layer 3 of the OSI Model.
The Network Layer:
This layer deals with logical addressing and routing. PDU= Packets
Describe an IP packet from beginning to end.

Describe Layer 4 of the OSI Model.
The Transport Layer:
This Layer handles the segmentation and reassembly of data to be sent and received as IP packets.
Data is broken up as segments or datagrams, each of which receive a sequence number to allow for the reassembly of the data at the other end of the connection.
Describe Layer 5 of the OSI Model.
The Session Layer:
This layer manages a systems sessions. It initiates sessions, accepts incoming sessions, and opens and closes existing sessions.
Describe Layer 6 of the OSI Model.
The Presentation Layer:
This layer translates data from the lower levels for use by the application layer and vice versa.
Describe Layer 7 of the OSI Model.
The Application Layer:
This is perhaps the most visible layer of the OSI Model. It does not refer directly to the applications that one may use, but instead refers to the coding that enables network aware applications.
What is API?
Application Programming Interface:
Coding that can be used to make applications network aware.
What is encapsulation?
The entire process of preparing data to go onto a network.
What are the 4 layers of the TCP/IP Model?
4) Application Layer
3) Transport Layer
2) Internet Layer
1) Link/Network Interface
Describe the first layer of the TCP/IP Model.
The Link/Network Interface Layer:
A combination of layers 1and 2 of the OSI model, this layer deals with the physical aspects of networking.
PDU= Frames
Describe the second layer of the TCP/IP Model.
The Internet Layer:
IP addressing takes place at this layer; IP packets are created at this layer; any devices/protocols that deal purely with IP packets sit at this layer.
This layer is the "IP Packet layer".
Describe the fourth layer of the TCP/IP Model.
The Transport Layer:
This layer combines features of the OSI Transport and session layers, and some of the application layer.
Which layer of the TCP/IP model controls the segmentation and reassembly of data?
The Transport Layer
Which Layer of the OSI Model keeps track of a system's connections to send the right response to the right computer?
The Session Layer
Describe the coaxial cable.
A cable that contains a central conductor wire surrounded by an insulating material, surrounded by a braided metal shield. Coax because the tire and shield share a common axis.
The metal shield helps to protect from EMI.
What is EMI?
Electromagnetic Interference:
Extra electrical current generated by electrical other machines.
What is a BNC connector?
Either British Naval Connector, or Bayonet Neillconcelman: this stick and twist style is commonly seen with coaxial cables.
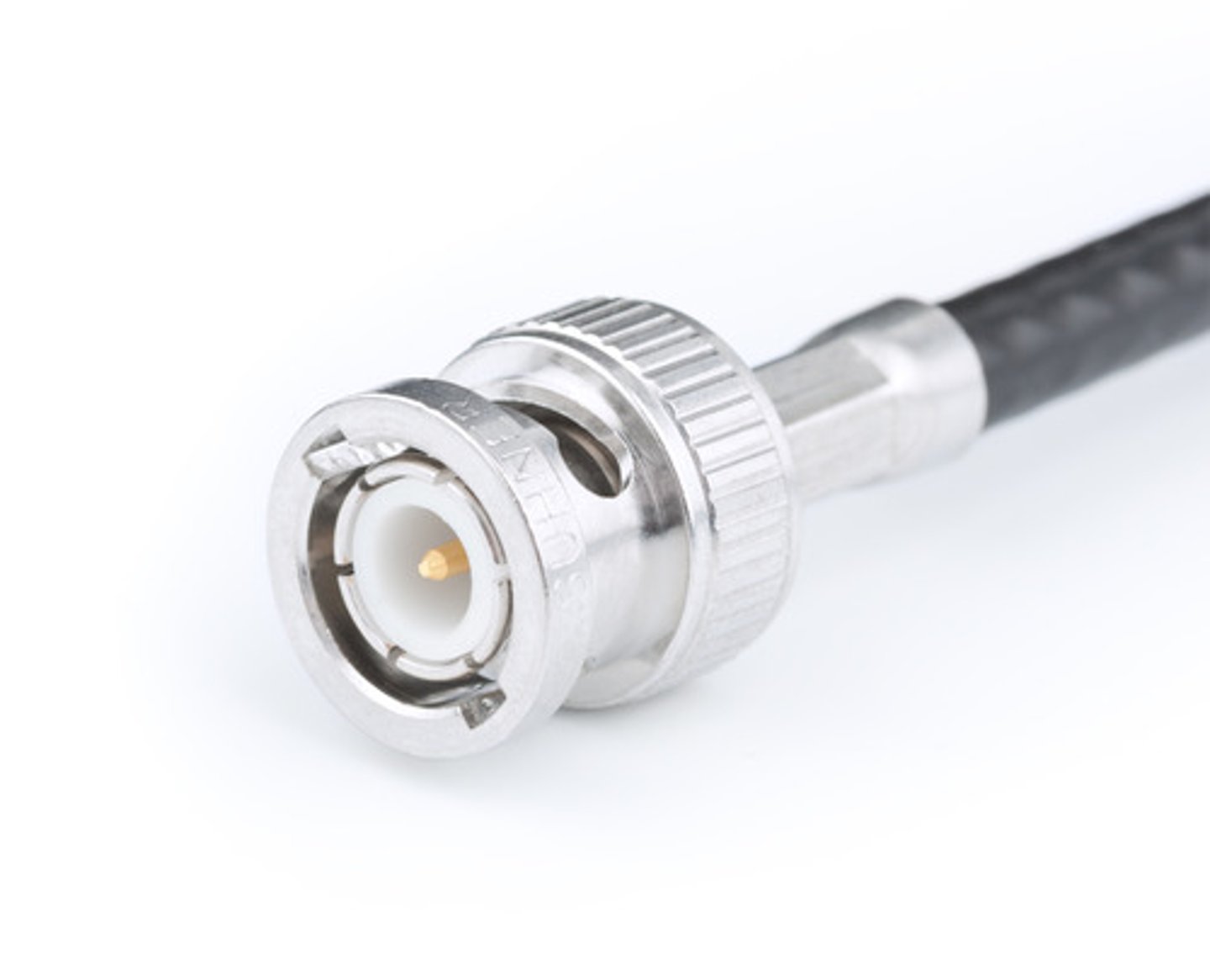

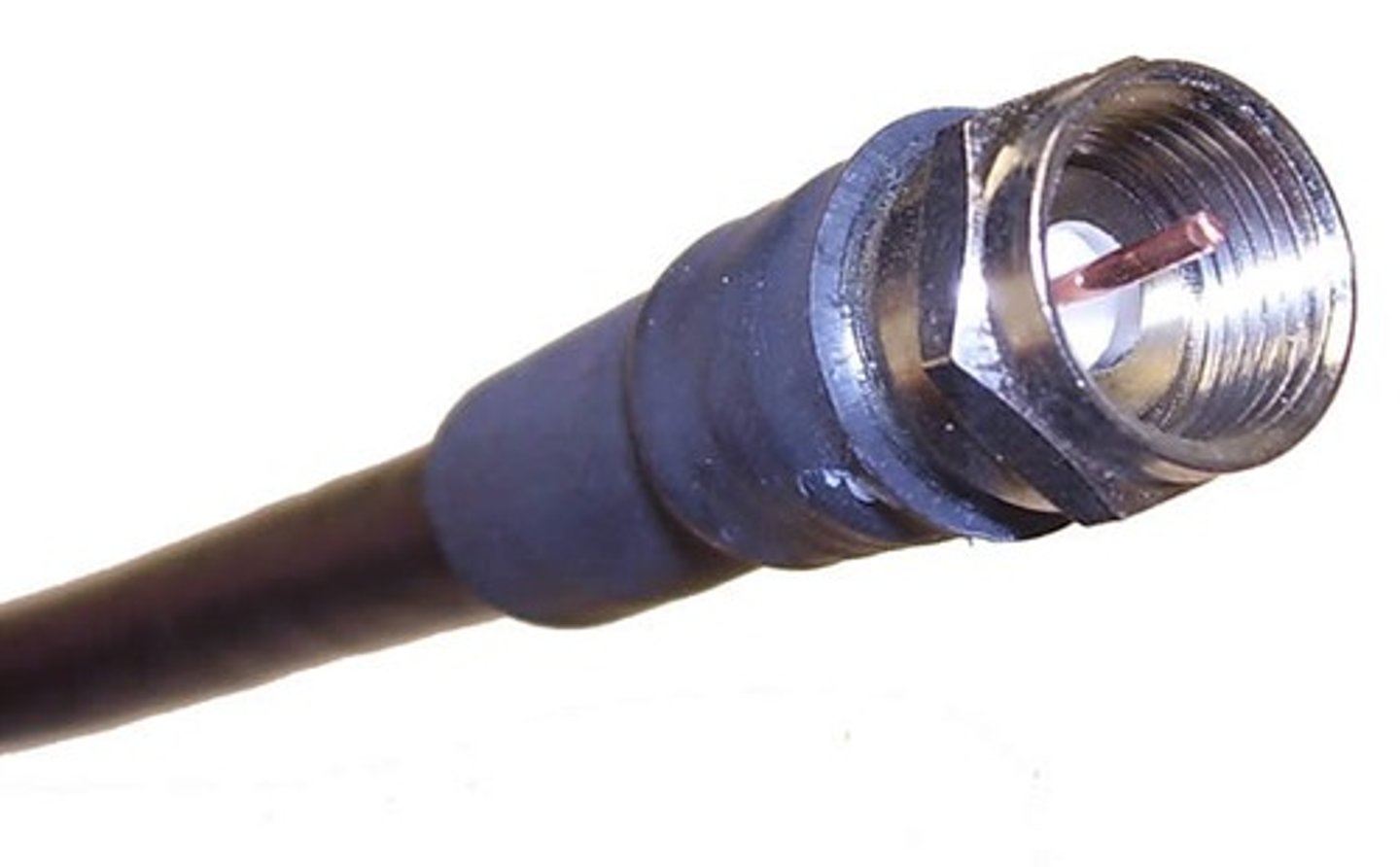
Describe an F Connector.
An F Connector is typically seen with the coaxial cables used by cable companies and their modems. These screw on to their connecting locations to secure the connection.

What is RG-59?
A common coaxial cable type used primarily for cable television. Its thinness and the intro of digital cable caused this type of cable to become outdated.
What is RG-6?
A common coaxial cable type used for digital cable television.
What is RG-58?
A type of Coaxial cabling that is used in networking. These use the BNC connector.
What is STP?
Shielded Twisted Pair
What is UTP?
Unshielded Twisted Pair
What is the maximum bandwidth of a Cat 3 cable?
16 Mbps
What is the maximum bandwidth of a Cat 4 cable?
20 Mbps
What is the maximum bandwidth of a Cat 5 cable?
100 Mbps
What is the maximum bandwidth of a Cat 5e cable?
1 Gbps
What is the maximum bandwidth of a Cat 6 cable?
10 Gbps
What is the difference between a Cat 6 and Cat 6a cable?
Cat 6 can operate at 10 Gbps only at lengths of 55 meters or less. Cat 6a can operate at 10 Gbps at the full 100 meters.
What is ANSI?
American National Standards Institute
What is the maximum bandwidth of a Cat 7 cable?
10 Gbps+
What is the maximum bandwidth of a Cat 7a cable?
40-100 Gbps
40 Gbps at 50 meters
100 Gbps at 15 meters
What is 8p8c?
8 position 8 contact connectors (RJ-45)
What is MMF?
Multimode Fiber:
A type of fiber optic that uses LED's to send light signals.
What is SMF?
Single-mode Fiber:
A type of fiber optic that uses laser light to send light signals
What wavelength do multimode cables typically use?
850-nm
What wavelength is typically used by single-mode fiber?
Either 1310 nm or 1550 nm
Why would you want to use Plenum rated cabling?
Plenum rated cabling creates fewer toxic fumes when burned. You would use these in higher Fire risk areas to lower the risk of poisonous gas.
IEEE subcommittee 802.3 oversees what aspect of networking?
Wired networks that share the same basic frame type and network access method.
What segment of a frame begins the transmission?
Preabmble (which may also include some extra filler called a pad)
What is a preamble?
a 7 byte series of info followed by a 1 byte start frame delimiter.
Describe 10baseT.
10 Mbps, baseband, Unshielded twisted pair.
From 1-8, describe the order of the TIA/EIA 568a standard.
1) Green/White
2) Green
3) Orange/White
4) Blue
5) Blue/White
6) Orange
7) Brown/White
8) Brown
From 1-8, describe the order of the TIA/EIA 568b standard.
1) Orange/White
2) Orange
3) Green/White
4) Blue
5) Blue/White
6) Green
7) Brown/White
8) Brown
Describe 10BaseF.
10 Mbps, Baseband, Fiber Optic
In switching, what is an SAT?
Source address table:
A table that a switch will construct that contains the MAC addresses of the devices connected to it.
What is STP?
Spanning Tree Protocol:
Allows for multiple redundant paths while breaking loops.
How does Spanning Tree Protocol prevent loops?
It uses and Configuration BRDU to establish the topology of a network and then elects one switch as the Root Bridge. It uses this root bridge as a reference to maintain a loop free topology.
What is a BPDU?
Bridge Protocol Data Unit
What is a "blocking" port?
A port that has received a BPDU, and has begun to listen rather than forward information in order to prevent loops.
What is PortFast
PortFast is a STP feature that enables the interface of a client to come up right away, without the normal latency introduced by STP.
What is BPDU Guard?
A feature of STP that will move a port configured with PortFast into an errdisable state should that port receive a BPDU.
What is Root Guard?
a mechanism that will move a port into a root-inconsistent stated if the BPDUs coming in from a certain direction indicate another switch is trying to become the root bridge.
What is 802.1D?
The Original Spanning Tree Protocol
What is 802.1w?
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
What is RSTP?
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol:
a successor to STP that offers considerably faster convergence time following some kind of network changed.
(50 seconds vs 6 seconds)
What is 100BaseT4?
100 Mbps, Baseband, Twisted Pair Cabling:
Typically won't see this in modern networks, these used Cat 3 cabling
What is 100BaseTx?
100 Mbps, Baseband, Twisted Pair Cabling:
Common in modern networks but moving to the "on the way out" phase. These 100 Mbps cables utilize Cat5/5e cabling.
T4 is outdated and not used anymore, so techs will refer to 100BaseTx as 100BaseT
What is 100BaseFX?
A fiber-optic cabling standard for ethernet over fiber at 100 Mbps
This uses Multimode Fiber, ST or SC connectors, and supports cable lengths of up to 2Kilometers.
What is 10BaseFL?
A fiber-optic cabling standard for ethernet over fiber at 10Mbps
Describe HalfDuplex.
Devices configured to run half-duplex can only send OR receive at any given moment
Describe Full Duplex.
Devices configured to run Full duplex can send and receive at the same time.
What is 1000BaseSX?
A fiber-optic cabling standard for ethernet over fiber using MMF at 1000 Mbps
Supports lengths of 220-500 meters
uses 850nm wavelength
typically uses LC Connector
What is 1000BaseLX?
A fiber-optic cabling standard for ethernet over fiber using SMF at 1000 Mbps
Supports lengths of up to 5Kilometers
uses 1300nm wavelength
What is SFF?
Small Form Factor Pluggable
What is MT-RJ
Mechanical Transfer Registered Jack
What is LC?
Lucent Connector:
A common connector for fiber cabling
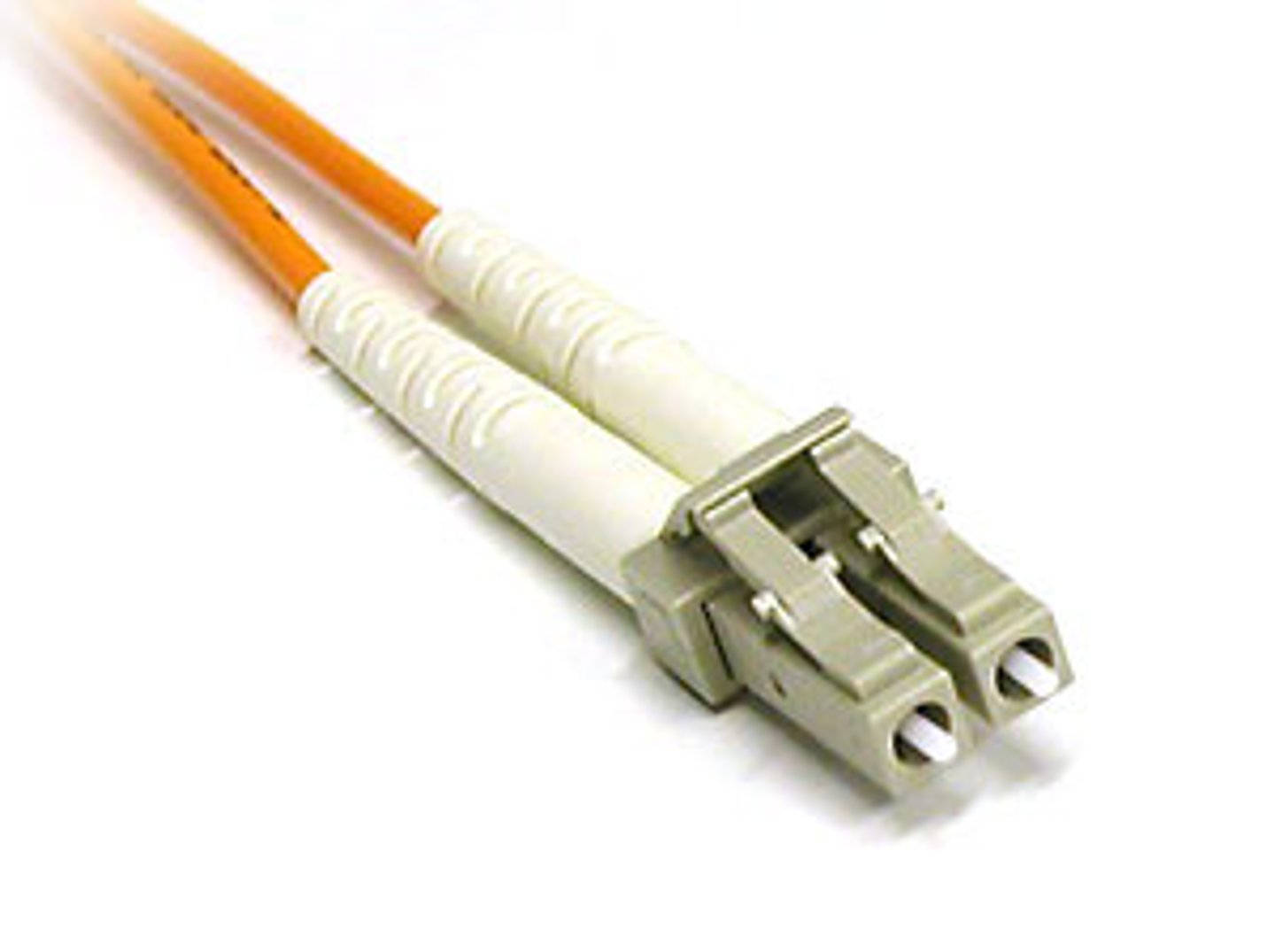

What is UPC?
Ultra Physical Contact connectors
a connector in fiber cabling with a super polished tip to reduce signal loss
What is APC?
Angled Physical Contact connectors
A connector in fiber cabling with angled ends that help reduce reflection of signal, helping to lower overall signal loss
What are Media Converters?
In networking, these allow for various types of data transfer mediums to communicate with one another (Copper to Fiber)
What is GBIC?
Gigabit interface converter:
Modular port that supports a standardized, wide variety of gigabit interface modules.
What is SFP?
Small form factor pluggable:
Similar to GBIC's in that it offers hotswappable ports: these come in much smaller sizes, allowing for more to be connected to interfaces
What is SFP+?
Enhanced Small Form Factor Pluggable
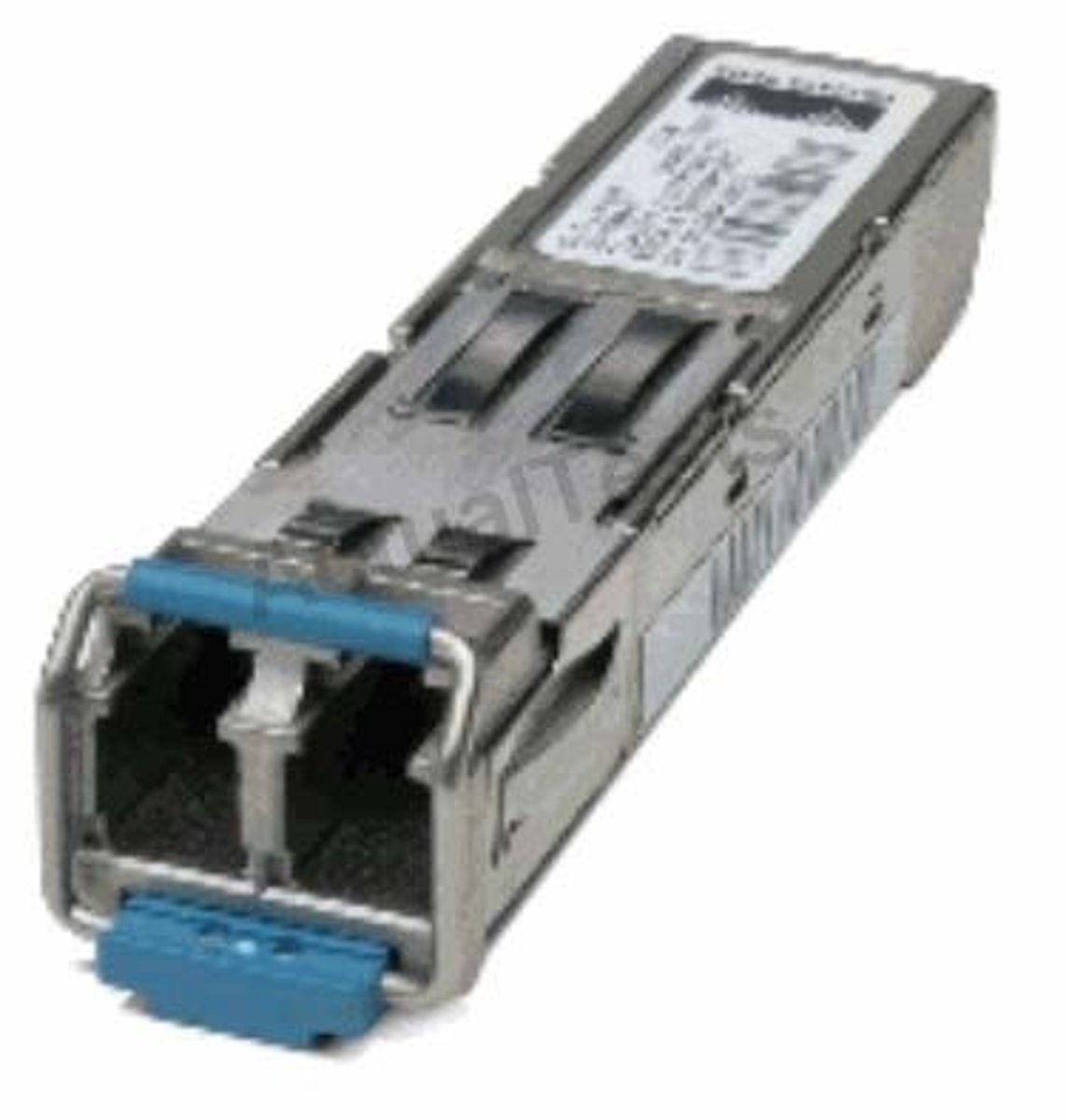

What are BiDi Transcievers?
Bidirectional Transcievers:
These allow for simultaneous transmission and reception across a fiber cable, where the transmission and reception occur at differing wavelengths