astro 3
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
interstellar medium
interstellar medium is the thin gas laced with microscopic dust particles between the space of stars
nebula
nebula is any interstellar cloud of light and dust
emission nebula
emission nebula is a glowing gassy nebula whose spectrum has bright emission lines and is composed of ionized hydrogen atoms. Has a red apperance
Dark nebula
Dark nebula is a cloud of interstellar gas that blocks visible light coming from stars that lay behind it.
reflection nebula
reflection nebula is a comparatively dense cloud of dust in interstellar space that is illuminated by a star. Has a blue apperance
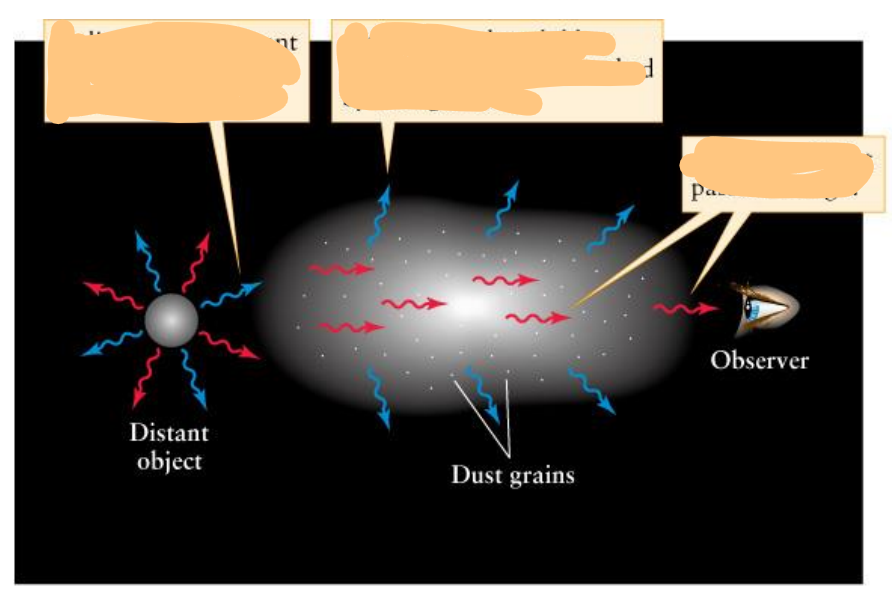
What is going on in this picture?
Star from space emits blue and red light
The short blue wavelength is scattered or absorbed by dust grains
while red lights pass through to the human eye
Where is the only place stars can form?
dark nebula
how is a star formed?
The pressure inside the protostar is too low to support all the cool gas against gravity, so the protostar collapses. As this happens, the gravitational energy is converted into thermal energy, making the gases heat up and star glowing
core hydrogen fusion
core hydrogen fusion is when a main-sequence star convert hydrogen into helium by thermonuclear reactions in their core
Main -sequence lifetime
Main -sequence lifetime is the total time that a star spends fusing hydrogen in its core, and hence the total time that it will spend as a main-sequence star
Why is the sun getting brighter?
The sun is getting brighter because the sun is gradually converting hydrogen into helium
to maintain pressure and balance gravity the core must expand and get hotter
How does a main-sequence star form into a red giant?
After the main-sequence star runs out of hydrogen to react with it, it will create more hydrogen fusion with hydrogen rich materials outside the core
this creates an increase in the core’s temperature
the increase in temperature causes more hydrogen fusions leading it to expand and “eat” more outside material
this leads to more limounsity and creates a red giant
zero-age main-sequence star
zero-age main-sequence star is the main sequence of young stars that have just started burning hydrogen in their cores
breakdown life cycle of sun
protostar
main-sequence star
red giant
open clusters
open clusters are a loose association of young stars in the disks of our galaxy

Which cluster is an open cluster and globular cluster
Cluster with the bright blue stars is younger
cluster with white dim stars is older
planetary nebula
planetary nebula is a luminous shell of gas ejected from an old, low mass star
how do planetary nebula glow?
as a dying star ejects its outer layers, the star’s hot core becomes exposed
the exposed core emits UV radiation intense enough to ionize atoms that expand the shell’s of ejected gases
these gasses therefore glow and emit visible light
What happens after low mass stars consume all the hydrogen in its core?
after low mass stars consume all the hydrogen in its core, it is able to ignite nuclear reactions that covert hilum to carbon and oxygen
white dwarf
white dwarf is a low mass star that has exhausted all its thermonuclear fuel, strips to its core, cools down and contracted to a size roughly equal to earth
white dwarf is made of ionized carbon and oxygen atoms in a sea of degenerate electrons
Chandrasekhar limit
Chandrasekhar limit is the maximum mass of a white dwarf