Pulmonary Diagnostics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Pulse Oximetry
estimates O2 saturation (SpO2) of capillary blood based on the absorption of light from light-emitting diodes positioned in a finger clip or adhesive strip probe
oxyhemoglobin, arterial, none, 95, 93
Transcutaneous Pulse Oximetry
-Able to detect only _________, not able to detect other types like carboxyhemoglobin or methemoglobin
-Very accurate
-Indication: to monitor _______ O2 saturation
-Contraindication: none after exclusion of accuracy interferences
-Advantage: easy and quick, noninvasive
-Cost: low
-Normal: __-100%, long-term smokers may be __-95% at baseline
polish, cold, systemic, carboxyhemoglobin, O2
Limitations of Pulse Oximetry
Results may be less accurate in patients with:
-Highly pigmented skin
-Wearing nail ________
-Arrhythmias
-Hypotension
-_____ temperature
-Profound ________ vasoconstriction
-Edema
-Unable to differentiate ______________ sat from __ sat
Carbon monoxide, 5, headache, cherry-red, oxygen
Carboxyhemoglobin (COHB)
-______ _________ (CO) is an odorless, colorless, poisonous gas
-Normal range: 0-_%, anything higher can be deadly
-The most common and earliest symptoms of CO poisoning are nonspecific: ___________, confusion, dizziness, weakness, N/V, chest pain, _______-___ skin coloring and cutaneous bullae
-Initial therapy: 100% _______ via mask or endotracheal tube
CBC, BMP, ABG
Pulmonary Labs
-___: shows WBC count and anemia of chronic disease
-___: shows CO2 and electrolytes
-Arterial blood gas (___)
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)
done to obtain accurate measures of PaO2, PaCO2, and blood pH
-allows for the calculation of HCO3 level
-accurately measures carboxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin
-from artery and can show how well someone is ventilating/perfusing
acid-base, oxygen, carbon dioxide, interventions, hemoglobin, venous
Indications of Arterial Blood Gas
-Identification and monitoring of _____-____ disturbances, determine respiratory vs metabolic
-Measurement of the partial pressures of ________ (PaO2) and _______ _______ (PaCO2)
-Assessment of the response to therapeutic __________ (eg insulin in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis)
-Detection and quantification of the levels of abnormal ____________
-Procurement of a blood sample in an acute emergency setting when _______ sampling is not feasible (most tests can be performed from an arterial sample)
circulation, Allen’s, puncture, peripheral, Raynaud’s
Arterial Blood Gas Contraindications:
-Poor collateral __________ (abnormal ______’_ test)
-Local infection, thrombus, or distorted anatomy at the _______ site (previous surgical interventions, congenital or acquired malformations, burns, aneurysm, stent, AV fistula, vascular graft)
-Severe _________ vascular disease of the artery selected for sampling
-Active _________’_ syndrome (particularly sampling at the radial site)
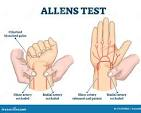
Allen’s Test
used to assess the patency and adequacy of the radial and ulnar arteries in the hand, specifically to evaluate collateral circulation
-the ability of the ulnar artery to supply blood to the hand if the radial artery is compromised
arterial, needle, radial, ischemia
Arterial Blood Gas
-Procedure: _________ blood is obtained by percutaneous ______ puncture or from an indwelling arterial catheter. Common sites are the ______ artery, brachial artery, femoral artery, axillary artery, and dorsalis pedis artery
-Risks: _________ distal to the puncture site, hemorrhage, hematoma
Sputum, hospitalization, nosocomial, lavage
______ Smear, Culture, and Sensitivity
-Indication: community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) needing ____________ or _________ pneumonia, especially ventilator-associated pneumonia
-Alternative procedure: bronchoalveolar ______. Bronchoscopy acquires samples of lower respiratory tract secretions.
25, 10, induction, increase
Determining Quality of a Sputum Sample
-Good quality = > __ leukocytes and < __ epithelial cells per low-power field
-If you have a poor sample, you can do sputum ___________ via inhaled nonbacteriostatic saline mist + chest percussion. This may _________ the yield for Pneumocystis, mycobacteria, and malignancy
pathogen, pharmacologic, morning, sterile
Culture and Sensitivity
-Indication: _________ identification and guidance for ___________ therapy
-Procedure: cough up sputum first thing in the ________, collect in a ______ container, and incubate in the lab
culture, 3+, inhalatory, slow, treatment
Culture and Sensitivity
-________ results are reported in a semi quantitative manner, on a scale of 1+ to 4+. Most true pathogens are present in at least __ (moderate)
-Contraindication: organism that is an ___________ pathogen like Chlamydia psittaci
-Limitations: ________ results
-Advantage: specific ________ and antibiotic stewardship
-Cost: moderate
PPD
tuberculosis skin test
-purified protein derivative of tuberculin is injected intradermally via a 27-gauge needle to evoke a memory T cell response to mycobacterial antigens
-delayed hypersensitivity
transverse, induration, 15, 10, 5
PPD Test
-Measure the ________ width of _________ in millimeters after 48-72 hrs
-A positive result for an average person is > __ mm, someone with high-risk exposure is > __ mm, and immunosuppressed patients is > _ mm
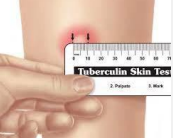
negatives, immunosuppression, improper, differentiate, vaccine, blood, hypersensitivity, burns
Limitations and Contraindications
-False ________ may occur due to biologic or technical limitations: biologic limitations include _____________ and very recent infection, and technical limitations include _________ tuberculin handling and interpretation
-Does not _________ well between M. tuberculosis and other non-tuberculosis mycobacteria.
-BCG _______ can cause some degree of cross-reactivity, so order a ______ test
-____________ to tuberculin purified protein derivative (PPD) or any component of the formulation, previous severe reaction to PPD skin test, documented active TB or clear history of TB treatment, and extensive _____ or eczema
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFT)
series of tests which provide objective measures of lung function, can be done in all patient populations
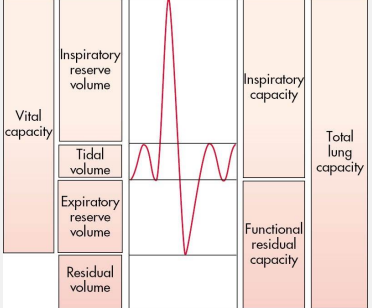
asthma, symptoms, progression, assessment
PFT Indications
-Diagnostics, especially for ________
-Signs/_______ (SOB, wheezing, exertional dyspnea, cough)
-Measure of treatment effect and/or disease __________
-Staging: asthma, COPD, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
-Prognosis
-Preoperative or disability ____________
Special Pulmonary Tests
exercise pulmonary stress, gas diffusion, and bronchial provocation
Spirometry
measures the volume of air exhaled at specific time points during a forceful and complete exhalation after a maximal inhalation
-total exhaled volume = forced vital capacity (FVC)
-procedure: breathe calmly at tidal volume, draw a maximal inhalation, and perform a forced exhalation
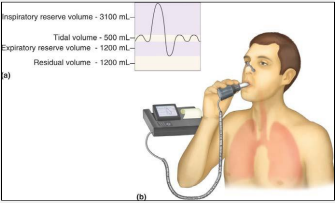
FVC, FEV1, obstructive
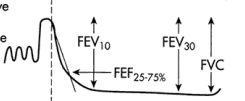
Spirometry Terminology
-Forced vital capacity: ___, total volume of air exhaled after maximal inspiration
-Forced expiratory volume in one second: ____, total volume exhaled in 1 sec
-FEV1/FVC ratio is typically expressed as a percent and helps differentiate between __________ and restrictive disease
obstructive
What type of pulmonary disorder is being described?
-FEV1/FVC = decreased
-FEV1 = decreased
-FVC = decreased or normal
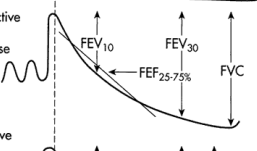
Restrictive
What type of lung disease is being described here?
-FEV1/FVC = normal or increased
-FEV1 = decreased, normal, increased
-FVC = decreased
Mixed
What type of pulmonary disorder is being described here?
-FEV1/FVC = decreased
-FEV1 = decreased
-FVC = decreased or normal
Peak Flow Meter
handheld devices designed as personal monitoring tools, used to see progress and exacerbation
-not diagnostic
maximal, exhale, maximal, inspiration, FEV1, asthma, multiple, highest, 80, 80, 40
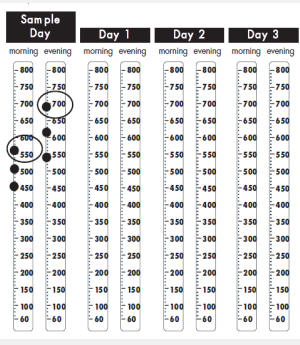
Peak Flow Meter
-Measures peak expiratory flow rate, which is the ________ rate that a person can ______ during a short _______ expiratory effort after a full ____________.
-The PEF percent predicted correlates reasonably well with the percent predicted value for the forced expiratory volume in one second (____) in patients with ______
-Inexpensive and easy to use
-_______ readings in the morning and evening are taken, circle the _______ value
-”Normal” is __-100% of personal best
-Exacerbation is < __%
-Severe exacerbation is < __%
effort, PEF, limitation, current
Peak Flow Meter
-Limitations: very ______ dependent, restrictive processes that limit full inspiration can lead to reduced ___ in the absence of airflow ________, i.e. chest wall disease and obesity
-Benefit: simple and readily available
-Comparison with the patient’s own baseline demonstrates ________ function, comparison with reference values is less helpful
chronic, distance, recovery
Six-Minute Walk Test
-Indication: measures physical function and therapeutic response in patients with ______ lung disease like COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, and PAH
-Measures total _________ walked, magnitude of desaturation, and timing of heart rate _________
Thoracocentesis
percutaneous procedure where pleural fluid is drained
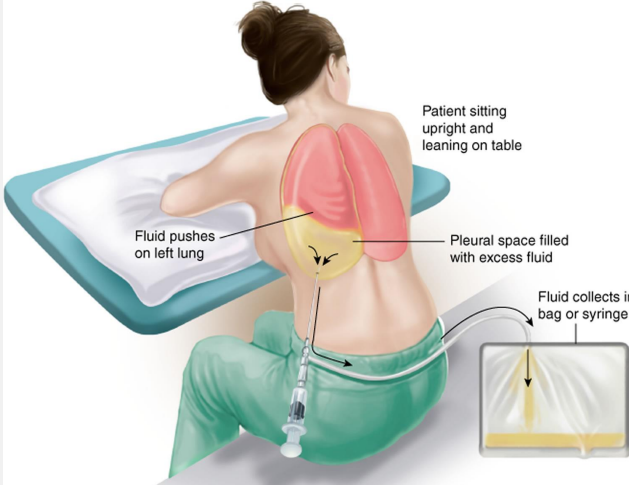
effusion, relief, 8th, 9th, insufficient, insertion, anticoagulation
Indications and Contraindications of Thoracentesis
-Indication: determine the cause of unexplained pleural _________ and symptom _______, for it allows the lungs to better expand
-Needle insertion directly superior to the ___ or ___ rib
-Contraindications: __________ pleural fluid, cellulitis/herpes zoster/wound at needle ________ site, or severe thrombocytopenia / over-____________
pneumothorax, tumor, diagnostic
Complications and Advantages of Thoracentesis
-Complications: _______________, intrapleural bleeding, hemoptysis, reflex bradycardia and hypotension, seeding of _______, and empyema delivered by aspirating needle
-Advantage: ___________ and therapeutic
Thoracostomy
procedure where a thoracostomy tube or catheter is placed through the chest wall into the pleural cavity to either drain an indication (pneumothorax, hemothorax, effusion, or empyema) or instill medication
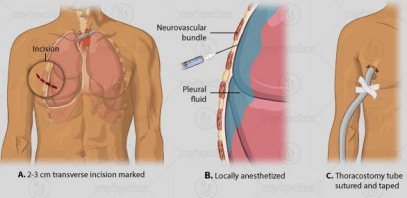
pneumothorax, effusion, infection, liver
Indications and Contraindications of Thoracostomy
-Indications: _____________, hemothorax, pleural ________ or empyema, or pleurodesis
-Contraindications: coagulopathy, skin ___________, and transudative pleural effusions due to ______ failure
fourth, fifth, axillary, infection, injury, edema
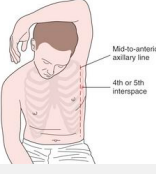
Thoracostomy
-Insertion site: ________ or ______ intercostal space in the anterior ______ or midaxillary line
-Advantage: diagnostic and therapeutic
-Disadvantage: dangerous
-Risks/complications: malposition, _________, intercostal nerve or artery injury, organ _______, pulmonary ______, pulmonary laceration, intercostal artery aneurysm, cardiac compression leading to cardiogenic shock
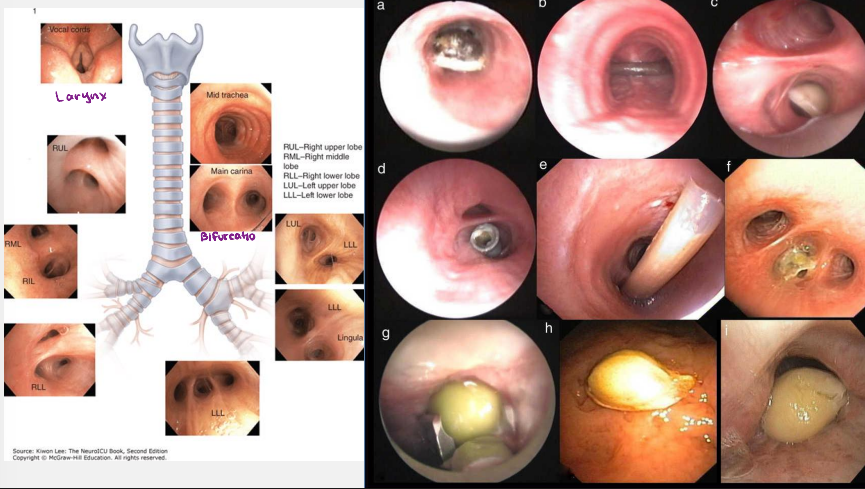
Bronchoscopy
endoscopic procedure that visualizes the tracheobronchial tree by placing an optical instrument inside the airways
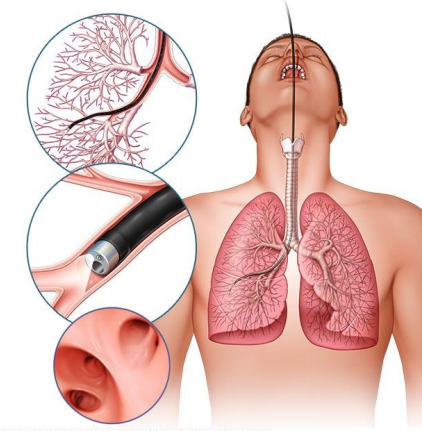
hypoxemia, hypertension, cardiac, bleeding, sedation, fever
Bronchoscopy Contraindications and Complications
-Contraindications: severe _______ with inability to maintain adequate oxygenation during the procedure, severe pulmonary ____________, unstable or severe obstructive airway disease, hemodynamically unstable, myocardial ischemia, poorly controlled heart failure, life-threatening _______ arrhythmias, uncooperative patient, and risk of ____________
-Complications: mild transient hypotension and hypoxia related to _________, bleeding, pneumothorax, nasal discomfort, sore throat, mild hemoptysis, bronchospasm, hypoxemia, epistaxis, _____, and pneumonia