Biology Master
1/269
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
270 Terms
What are the components of both plant and animal cells? (4)
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Mitochondria
What are the functions of the nucleus?
Stores genetic information.
Controls cellular activities.
Describe the structure of the cytoplasm.
Fluid component of the cell.
Contains organelles, enzymes, and dissolved ions and nutrients.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Site of cellular reactions, e.g., the first stage of respiration.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Controls the entry and exit of materials into and out of the cell.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Site of later stages of aerobic respiration in which ATP is produced.
What organelles are found only in plant cells? (3)
Cell wall
Large, permanent vacuole
Chloroplasts
What is the cell wall made of?
Cellulose.
What is the function of the cell wall?
Provides strength.
Prevents the cell from bursting when water enters by osmosis.
What does the permanent vacuole contain?
Cell sap (a solution of salts, sugars, and organic acids).
What is the function of the permanent vacuole?
Supports the cell, maintaining its turgidity.
What is the function of the chloroplasts?
Site of photosynthesis.
What piece of equipment is used to observe plant and animal cells?
Light microscope.
How does a light microscope work?
Passes a beam of light through a specimen, which travels through the eyepiece lens, allowing the specimen to be observed.
Describe the pathway of light through a light microscope.
Lamp → Condenser → Specimen → Objective lens → Eyepiece lens → Eye.
What is the function of the eyepiece lens?
Magnifies the image.
Fixed magnification, usually ×10.
What is the function of the objective lens?
Magnifies the image.
Interchangeable magnifications: ×4, ×10, ×40.
What is the function of the iris diaphragm?
Adjusts the amount of light that passes through the specimen and enters the objective lens.
What is the function of the condenser?
Focuses light onto the objective lens.
How is a light microscope manually focused?
Using the coarse focus control and fine focus control.
What is the function of the coarse focus control?
Used to focus the image under the low-power objective lens.
What is the function of the fine focus control?
Used to finely adjust the focus of an image.
What is cell differentiation?
Process in which unspecialised cells (stem cells) become specialised to have a specific function.
Why is cell differentiation important?
Enables the formation of specialised cells with specific functions, e.g., sperm cells, red blood cells.
What is a tissue?
A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function, e.g., muscle tissue, xylem tissue.
What is an organ?
A group of tissues that work together to perform a specific function, e.g., brain, heart, kidney.
What is an organ system?
A group of organs that work together to perform a particular function, e.g., nervous system, digestive system.
What is an organism?
A living thing that is able to function independently, e.g., human, sunflower.
Why can substances pass through cell membranes?
Cell membranes are partially permeable, enabling some molecules to pass through.
By what three methods can different substances pass through cell membranes?
Diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
What is diffusion?
The net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration down a concentration gradient.
Why is diffusion described as a passive process?
It does not require energy.
What substances can pass through cell membranes by diffusion?
Small molecules, e.g., carbon dioxide, oxygen.
What two factors affect the rate of diffusion?
Temperature
Concentration gradient
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
The higher the temperature, the more energy possessed by molecules, and the faster the rate of diffusion.
How does concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
The steeper the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion.
What is osmosis?
The net movement of water molecules from an area of high water (low solute) concentration to an area of low water (high solute) concentration across a partially permeable membrane.
Describe what happens to an animal cell if it is placed into a more dilute solution.
Higher concentration of water in the surrounding solution.
Water enters the cell by osmosis.
Pressure inside the cell increases, causing the cell to burst.
Describe what happens to a plant cell if it is placed into a more dilute solution.
Higher concentration of water in the surrounding solution.
Water enters the cell by osmosis.
The cell wall resists the increase in pressure, causing the cell to become turgid.
Describe what happens to an animal cell if it is placed into a more concentrated solution.
Lower concentration of water in the surrounding solution.
Water leaves the cell by osmosis.
Pressure inside the cell decreases, causing the cell to shrink.
Describe what happens to a plant cell if it is placed into a more concentrated solution.
Lower concentration of water in the surrounding solution.
Water leaves the cell by osmosis.
Pressure inside the cell decreases, causing the cytoplasm to shrink.
The cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall (plasmolysis).
Describe what happens to a cell if it is placed into a solution of equal water concentration.
No net movement of water molecules into or out of the cell.
What is active transport? (Higher)
The movement of molecules across a cell membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, against the concentration gradient, using energy.
What are enzymes?
They are biological catalysts. These biological catalysts increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being permanently changed themselves.
What is an advantage of enzymes in the body?
They enable cellular reactions to take place at lower temperatures.
What group of chemicals do enzymes belong to?
Proteins.
Describe how DNA controls the production of a specific enzyme (Higher).
DNA codes for a specific sequence of amino acids.
The order of amino acids determines how the enzyme folds and its structure.
The shape of the enzyme determines its function.
What is the chemical that an enzyme works on called?
Substrate.
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The region of an enzyme to which a substrate molecule binds, and the reaction takes place.
Why are enzymes described as having a ‘high specificity’ for their substrate?
Only substrates with a specific, complementary shape can fit into an enzyme’s active site.
What must happen between an enzyme and its substrate for a reaction to occur?
Enzyme and substrate must collide.
Describe the ‘lock and key’ model (Higher).
Substrate collides with the active site of an enzyme.
Substrate binds, enzyme-substrate complex forms.
Substrate is converted to products.
Products are released from the active site, which is now free to bind to another substrate.
What factors affect the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction?
Temperature
pH
Explain how increasing temperature initially affects the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction.
As temperature increases, molecules have more kinetic energy.
Movement of molecules increases.
Probability of a successful collision increases.
More enzyme-substrate complexes form.
Rate of reaction increases.
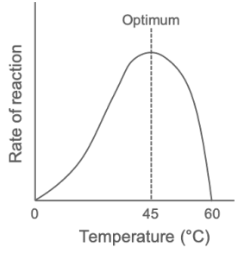
Explain how increasing temperature above the optimum affects the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction.
Temperature increases above the optimum.
Increased vibrations break bonds in the enzyme’s structure.
The active site changes shape, and the enzyme is denatured.
No more enzyme-substrate complexes can form.
Rate of reaction decreases.
Draw a graph to show the effect of increasing temperature on the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
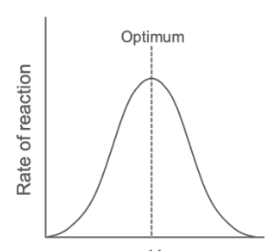
Explain how pH affects the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction.
Enzymes have an optimum pH.
pH shifts from the optimum.
Bonds in the enzyme’s structure are altered.
The active site changes shape, and the enzyme is denatured.
Rate of reaction decreases.
Draw a graph to show the effect of increasing pH on the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
pH
What is respiration?
A process that releases energy (in the form of ATP) from the breakdown of organic compounds (e.g., glucose).
What is ATP? (Higher)
Short-term energy store in all cells. Universal energy carrier.
What does ATP stand for? (Higher)
Adenosine triphosphate.
Why must respiration occur continuously in living cells?
Energy is required for many essential processes in living cells, e.g., movement, homeostasis, and active transport.
What is aerobic respiration?
A series of enzyme-controlled reactions that form ATP from the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen.
Write the word equation for aerobic respiration.
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy.
What does aerobic respiration require?
Glucose (or another respiratory substance, e.g., lipids, proteins). Oxygen.
What does aerobic respiration produce?
Carbon dioxide. Water. Energy (ATP).
What is anaerobic respiration?
Respiration that takes place without oxygen and forms ATP from the breakdown of glucose.
When may anaerobic respiration take place in muscle cells?
During vigorous exercise.
Write the word equation for anaerobic respiration in muscle cells.
Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy.
Why may anaerobic respiration in muscle cells eventually stop?
Lactic acid build-up inhibits anaerobic respiration.
What are the symptoms of lactic acid build-up?
Cramp and fatigue.
What is oxygen debt?
The extra volume of oxygen that must be taken in after anaerobic respiration to break down lactic acid.
Is aerobic or anaerobic respiration more efficient? Explain why (Higher).
Aerobic respiration is more efficient as it produces more molecules of ATP than anaerobic respiration.
Why does anaerobic respiration release less energy than aerobic respiration? (Higher).
Glucose is only partially broken down in anaerobic respiration./
What molecules are required by the body for a balanced diet?
Carbohydrates. Proteins. Lipids. Minerals. Vitamins. Fibre. Water.
What is the function of glucose in the body?
Used in respiration to release energy. Converted to glycogen and stored.
Where is glycogen stored?
In the liver.
What is the function of fatty acids and glycerol in the body?
Energy store.
What is the function of amino acids in the body?
Amino acids join together in long chains to form proteins, which are used for growth.
Why are minerals required by the body?
Required for a range of different functions, e.g., iron is required for the synthesis of haemoglobin in red blood cells.
Why are vitamins required by the body?
Required for a range of different functions, e.g., vitamin C is involved in the formation of collagen and the functioning of the immune system.
What happens when the body doesn’t receive enough vitamins or minerals?
Deficiency diseases develop, e.g., iron deficiency causes anaemia, and vitamin C deficiency leads to scurvy.
Why is water required by the body?
Main component of cells. Enables chemical reactions to take place within cells. Transport medium for glucose, minerals, etc.
What is the function of fibre in the body?
Provides bulk, which aids the movement of food via peristalsis.
What type of food releases the greatest amount of energy per gram?
Lipids.
What happens to excess carbohydrates in the body?
Stored as glycogen in the liver. When stores become full, glycogen is converted to fats. Fats are stored beneath the skin and surrounding organs.
Outline the health risks associated with obesity.
Cardiovascular disease. Cancer. Type 2 diabetes.
Outline the health risks associated with a diet high in sugar.
Type 2 diabetes. Obesity. Tooth decay.
Outline the health risks associated with a diet high in salt.
High blood pressure. Cardiovascular disease.
What is digestion?
The breakdown of large insoluble molecules of food into smaller soluble molecules.
Why is digestion important?
Large molecules are too big to be absorbed across the surface of the gut wall so must be broken down. Ensures food molecules are soluble so that they can be transported to cells in the bloodstream.
What type of molecules are proteins and carbohydrates?
Polymers.
During digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into __________
Simple sugars.
Which group of enzymes catalyses the breakdown of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrases.
Where are carbohydrases produced?
Mouth, pancreas, small intestine.
During digestion, proteins are broken down into __________
Amino acids.
Which type of enzyme catalyses the breakdown of proteins?
Proteases.
Where are proteases produced?
Stomach, small intestine.
During digestion, lipids are broken down into _______ and _______
Fatty acids and glycerol.
Which type of enzyme catalyses the breakdown of lipids?
Lipases.