Avian Anatomy and Physiology Vocabulary
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering essential terms related to avian anatomy, physiology, and unique adaptations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Aves
The taxonomic class comprising all birds.
Psittaciformes
Order of birds that includes parrots, budgerigars, cockatiels, cockatoos, macaws, conures, lovebirds, and lorikeets.
Passeriformes
Order of perching birds such as canaries and finches; also called passerines.
Columbiformes
Order that includes pigeons and doves.
Anseriformes
Order containing ducks, geese, and swans.
Galliformes
Order that includes chickens, turkeys, and grouse.
Integument
The skin and its derivatives (feathers, beak, claws) forming the external covering of birds.
Patagium
Web of skin stretching from shoulder to wrist that assists avian aerodynamics.
Beak
Keratin-covered upper and lower mandibles that continuously grow and vary in shape with feeding style.
Talons
Horny sheaths at the ends of toes; large and curved in birds of prey, short in scavengers and ground birds.
Uropygial Gland
Also called the preen gland; bi-lobed gland at the tail base that secretes oil for cleaning and waterproofing feathers.
Feather
Keratinous structure unique to birds; provides flight, insulation, protection, camouflage, and communication.
Contour Feather
Outer feathers that shape the body and include flight feathers of wings (remiges) and tail (rectrices).
Semiplume Feather
Feather type under contour feathers that provides insulation, flexibility, and buoyancy.
Down Feather
Soft, fluffy feather next to the skin that provides insulation and may generate powder down.
Filoplume Feather
Hair-like feather with nerve endings that monitors movement of adjacent contour feathers.
Bristle Feather
Stiff feather aiding tactile sensation, often around nostrils, eyes, beak, or toes.
Powder Down
Special feathers that grow continuously and disintegrate at the tips to produce a waxy powder for waterproofing.
Primaries
Large flight feathers originating from the carpus, metacarpus, and phalanges; provide thrust.
Secondaries
Flight feathers attached to the radius and ulna; provide lift.
Blood Feather
An immature, growing feather containing a blood supply within its shaft.
Molting
Periodic replacement of feathers, generally symmetrical and hormonally controlled.
White Muscle Fibers
Avian muscle fibers adapted for short, rapid bursts of flight; low blood supply, high glucose.
Red Muscle Fibers
Muscle fibers specialized for sustained flight; rich blood supply, many mitochondria, high fat.
avian body temp
104-109 deg F
Pectoralis
Largest flight muscle, responsible for the powerful downstroke; origin on sternum, inserts on humerus. –Make up 20% of bird’s weight

Supracoracoideus
Muscle inserting dorsally on humerus that produces the upstroke by abducting the wing.
Perching Reflex
Automatic digital flexion triggered when tendons of pelvic limb are tensioned, allowing birds to grip perches.
Pneumatic Bone
Hollow bone containing air spaces connected to the respiratory tract; e.g., humerus, femur.

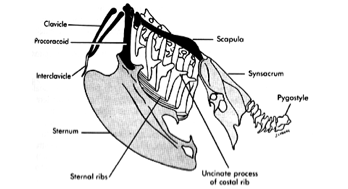
Coracoid
Strong pectoral girdle bone that acts as a strut between sternum and shoulder, unique to birds.
Furcula
Fused clavicles (wishbone) forming part of the pectoral girdle and acting as a spring during flight.
Keel
Prominent ridge on the avian sternum where major flight muscles attach; absent in flightless birds.
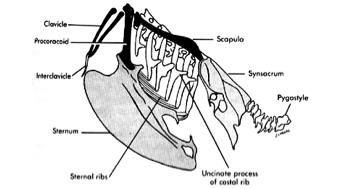
Synsacrum
Fusion of caudal thoracic, lumbar, and proximal coccygeal vertebrae with pelvic bones to support legs.
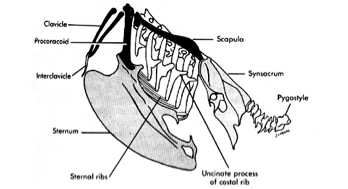
Pygostyle
Fused terminal caudal vertebrae supporting tail feathers and muscles.
Sclerotic Ring
Circle of small bones surrounding each eye globe for reinforcement.
Choana
slitlike opening in roof of mouth, leads to glottis and trachea (birds have NO epiglottis)
Pecten (Eye)
Pigmented, pleated vascular structure projecting into the vitreous that nourishes the avian retina.
Rhodopsin
Light-absorbing pigment in rod cells; present in higher amounts in nocturnal birds for night vision.
Operculum (Ear)
Fleshy flap covering the external ear opening in some birds, aiding sound funneling.
Crop
Expandable pouch of the esophagus that stores and softens food before digestion.
Proventriculus
Glandular stomach where enzymatic digestion begins in birds.
Ventriculus (Gizzard)
Muscular stomach that mechanically grinds food, often with grit.
Ceca
Paired blind sacs at the small-large intestine junction involved in water absorption and fermentation in some species.
Cloaca
Common chamber for digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts, divided into coprodeum, urodeum, and proctodeum.
Cere
Fleshy, often colored area at the upper beak base surrounding the nares.
Syrinx
Avian voice box located at the tracheal bifurcation; responsible for sound production.
Air Sacs
Nine thin-walled sacs that store, warm, and move air through lungs; aid in thermoregulation and buoyancy.
Unidirectional Airflow
Respiratory pattern where air passes through lungs in one direction, enabling gas exchange on both inspiration and expiration.
Renal Portal System
Vascular arrangement allowing blood from caudal body to pass through kidneys before returning to the heart.
Urates
White, pasty excretion of uric acid produced by avian kidneys and eliminated with feces.
Phallus (Avian)
Rudimentary male reproductive organ located inside the cloaca in many bird species.
Infundibulum
First section of the oviduct that captures the ovulated ovum.
Magnum
Oviduct section that deposits the thick layer of albumin around the egg.
Isthmus
Oviduct region where the inner and outer shell membranes (keratin layers) are added.
Shell Gland (Uterus)
Section of oviduct that applies watery albumin, hard calcified shell, and pigment to the egg.
Egg Tooth
Temporary keratinized tip on a hatchling's beak used to break the eggshell during hatching.
Alula
Small projection from the wrist carrying steering feathers that aid low-speed maneuvering.
Avian Chlamydiosis

Polyomavirus

Proventricular Dilation Disease

Psittacine Beak and Feather Disease (PBFD)

Papillomatosis

West Nile Virus
