Neurology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
Spinal cord
The extracranial part of the CNS
2
New cards
Spinal column
Encases + protects the spinal cord
3
New cards
Neurolocalisation
Identification of what part of the spinal cord is being affected
4
New cards
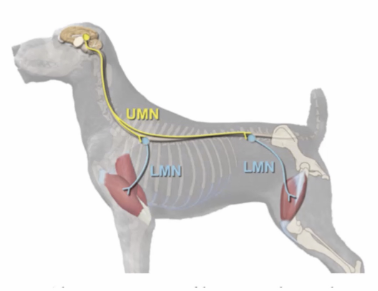
Upper motor neurons
Neurons between the cerebral cortex + spinal cord
* Loss of motor function
* Paresis
* Increased reflexes
* Increased extensor muscle tone
* Chronic atrophy
* Loss of motor function
* Paresis
* Increased reflexes
* Increased extensor muscle tone
* Chronic atrophy
5
New cards
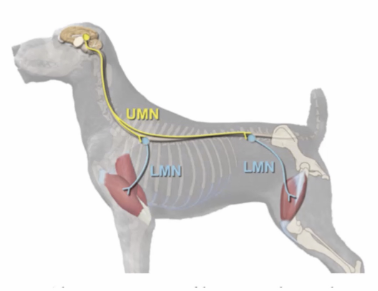
Lower motor neurons
Neurons connecting the CNS to the effector organ
* Flaccid paralysis
* Reduced reflexes
* Loss of muscle tone
* Muscle atrophy
* Flaccid paralysis
* Reduced reflexes
* Loss of muscle tone
* Muscle atrophy
6
New cards
Ataxia
Uncoordinated gait
7
New cards
Paresis
Weakness, with decreased voluntary movement
8
New cards
Paralysis
No voluntary movement
9
New cards
Mono-
One side affected
10
New cards
Hemi-
Both limbs on one side affected
11
New cards
Para-
Both pelvic limbs affected
12
New cards
Quadra/tetra-
All 4 limbs affected
(very rare as this also compromises respiratory function!)
(very rare as this also compromises respiratory function!)
13
New cards
Head tilt
One ear below the other
14
New cards
Head turn
Nose turned towards the body
15
New cards
Ventroflexion of the neck
Low head carriage
16
New cards
Scoliosis
Lateral spine curvature
17
New cards
Lordosis
Ventral deviation of the spine
18
New cards
Kyphotic
Spine arching dorsally
19
New cards
Decerebrate rigidity
Extension of the limbs, head, and neck
20
New cards
Decerebellate rigidity
Extension of thoracic limbs, head, and neck
21
New cards
Wide based stance
Feet and legs wider apart than normal when standing
22
New cards
Proprioceptive positioning
Reaction to moving their paw
23
New cards
Hopping
Lifting one limb, and getting them to hop
24
New cards
Visual placing
Getting them to put their paw on a table. They should reach out when moving towards a table
25
New cards
Tactile placing
Covering their eyes and moving their paw to touch a table. They should replace their paw to its natural position
26
New cards
Hemi-walking
Supporting their limbs on one side and getting them to walk
27
New cards
Wheelbarrowing
Lifting their hind limbs and getting them to walk
28
New cards
Withdrawal reflex
Pinching between the toes. They should withdraw
29
New cards
Extensor carpi radialis reflex
Tapping the extensor carpi radialis and checking for a response
30
New cards
Perineal reflex
Stroke or pinch skin in the anal region to check for contraction
31
New cards
Panniculus reflex
Pinching skin either side of the spinal column. The skin should twitch
32
New cards
Deep pain negative
Inability to feel any pain in the toes.
We check for this by pinching the nail bed on digits of each limb, checking for any turning, vocalising, or biting
We check for this by pinching the nail bed on digits of each limb, checking for any turning, vocalising, or biting
33
New cards
Upper motor neuron bladder
* Increased urethral resistance
* Detrusor + urethral sphincter muscle contraction at the same time
* Urinary retention
* Kidney damage
* Difficult to manually express - Requires catheterisation
* Detrusor + urethral sphincter muscle contraction at the same time
* Urinary retention
* Kidney damage
* Difficult to manually express - Requires catheterisation
34
New cards
Lower motor neuron bladder
* Flaccid bladder than doesn’t contract spontaneously
* Continues to fill = Overflow leakage
* Overstretched bladder muscle
* Easy to express manually
* Continues to fill = Overflow leakage
* Overstretched bladder muscle
* Easy to express manually
35
New cards
Neuromuscular disease
Disease particularly affecting lower motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscle.
This causes a reduction in muscle function
This causes a reduction in muscle function
36
New cards
Polyradiculoneuritis
Immune mediated neuromuscular disease affecting the myelin of axons.
* Short-strided gate (tetraparesis)
* Autonomic function remains
Once stabilised, recovery is within 1-4 months
* Short-strided gate (tetraparesis)
* Autonomic function remains
Once stabilised, recovery is within 1-4 months
37
New cards
Myasthenia gravis
Disease of neuromuscular transmission, affecting the neuromuscular junction.
Can be congenital, or immune mediated
* Muscle weakness (esp. during exercise)
* Regurgitation (oesophageal dilation)
Can be focal, generalised, or acute fulminating
Can be congenital, or immune mediated
* Muscle weakness (esp. during exercise)
* Regurgitation (oesophageal dilation)
Can be focal, generalised, or acute fulminating
38
New cards
Focal myasthenia gravis
Localised myasthenia gravis, affecting just 1 muscle group
39
New cards
Generalised myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis affecting 2 or more muscle groups
40
New cards
Acute fulminating myasthenia gravis
Most severe myasthenia gravis type
41
New cards
Polymyostitis
Immune-mediated inflammatory myopathy (neuromuscular disease) where there is an infiltration of inflammatory cells into skeletal muscle
* Exercise intollerance
* Stiff gait
* Muscle weakness + atrophy
* Dysphonia, dysphagia, regurgitation
* Exercise intollerance
* Stiff gait
* Muscle weakness + atrophy
* Dysphonia, dysphagia, regurgitation
42
New cards
Focal polymyostitis
Polymyostitis affecting just 1 muscle
43
New cards
Diffuse polymyostitis
Polymyostitis affecting a large group of muscles
44
New cards
Muscle contracture
The adaptive shortening of soft tissue + muscle as a result of recumbency + immobilisation.
Treated with intensive physiotherapy
Treated with intensive physiotherapy
45
New cards
Intracranial disease
Disease or injury affecting the brain
46
New cards
Skull vault
A closed, inelastic compartment that doesn’t allow room for inflammation + swelling.
This contains:
* Parenchymal tissue (brain)
* Blood
* Cerebrospinal fluid
This contains:
* Parenchymal tissue (brain)
* Blood
* Cerebrospinal fluid
47
New cards
Cushings reflex
A reflex triggered by severe, acute increase in ICP.
* Hypertension
* Reflex bradycardia
This is an emergency - Treat ASAP
* Hypertension
* Reflex bradycardia
This is an emergency - Treat ASAP
48
New cards
Anisocoria
Asymmetric pupils
49
New cards
Mydriasis
Dilated pupils
This indicates neurological deterioration (likely brain dead) if no pupillary light reflex!
This indicates neurological deterioration (likely brain dead) if no pupillary light reflex!
50
New cards
Glasgow coma score
Assessment of:
* Motor activity
* Brainstem reflexes
* Level of consciousness
Lower score = More severe neurological deficit
* Motor activity
* Brainstem reflexes
* Level of consciousness
Lower score = More severe neurological deficit
51
New cards
Mannitol
First line medication infusion for raised ICP
52
New cards
Hydrocephalicus
Excessive accumulation of CSF within the ventricular system
53
New cards
Meningoencephalitits
Non-infectious inflammatory disorder of the CNS causing brain and spinal cord changes
* Seizures
* Muscle tremors
* Blindness
* Head tilt
* Altered balance/posture
* Circline
* Seizures
* Muscle tremors
* Blindness
* Head tilt
* Altered balance/posture
* Circline
54
New cards
Decubital ulcer
An open skin wound caused by continued pressure of skin on a firm surface, which eventually causes tissue ischemia.
Most common on bony prominences + can develop rapidly
Most common on bony prominences + can develop rapidly
55
New cards
Effleurage
Physio technique: Gentle contact w/ the palm of the hand. Like a warm up before exercise.
Stroke towards the heart if oedema present
Stroke towards the heart if oedema present
56
New cards
Petrissage
Physio technique: Roll, squeeze, compress + kneed the skin + muscles to inc circulation
57
New cards
Percussion
Physio technique: Gentle tapping of the skin with the palm or side of hand.
This increases blood supply to aid muscle relaxation
This increases blood supply to aid muscle relaxation
58
New cards
Vibration
Physio technique: Gently shaking limbs to stimulate the whole limb.
Can be good at the end of a massage
Can be good at the end of a massage
59
New cards
Coupage
Respiratory physio technique for recumbent animals, or those with pulmonary disease.
This loosens secretions + assists coughing for airway clearance
* **Never use with fractured ribs/throacic trauma!**
* **Never use with those lacking a gag or cough reflex**
This loosens secretions + assists coughing for airway clearance
* **Never use with fractured ribs/throacic trauma!**
* **Never use with those lacking a gag or cough reflex**
60
New cards
Passive range of motion
Physio technique: Stretching and mobilising the joint within its normal capacity, with no active muscle contraction.
Start with the toes (flex + extend 10 times) then move up joint by joint
Start with the toes (flex + extend 10 times) then move up joint by joint
61
New cards
Three-legged standing
Assisted exercise technique: Lift 1 leg to build strength in other limbs
62
New cards
Weight-shifting
Assisted exercise technique: Gently shift weight back and forth
63
New cards
E stim
Electrical stimulation using a neuromuscular electrical nerve stimulation device.
This:
* Stimulates muscle contraction
* Increases tissue perfusion
* Minimises muscle atrophy
This:
* Stimulates muscle contraction
* Increases tissue perfusion
* Minimises muscle atrophy