Nucleotide Metabolism Part 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
purines
Bases with a double-ring structure.
Adenine and Guanine
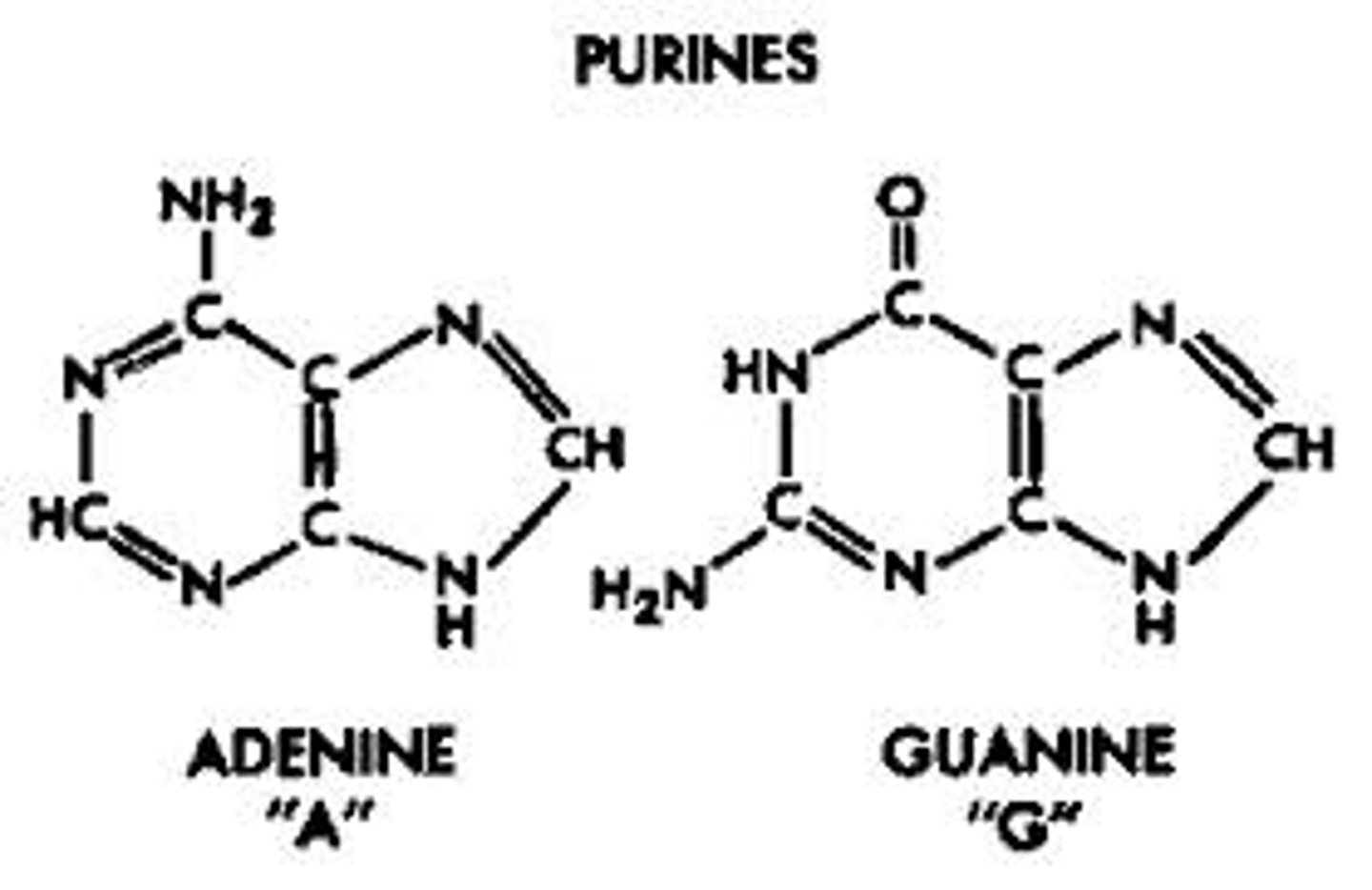
pyrimidine
Cytosine, Thymine, uracil
Made up of one ring
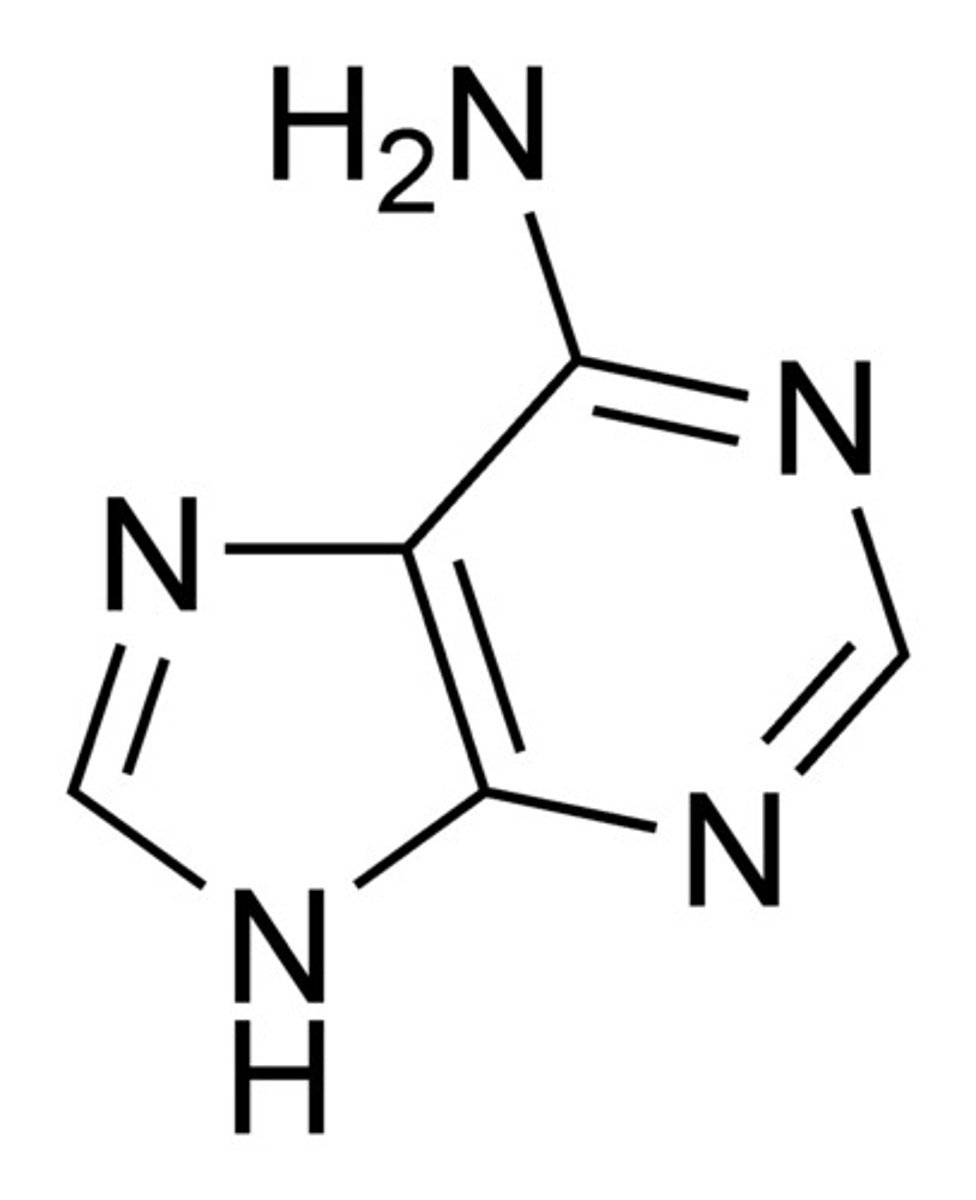
adenine
A component of nucleic acids, energy-carrying molecules such as ATP, and certain coenzymes. Chemically, it is a purine base.
Has NH2 off carbon 6
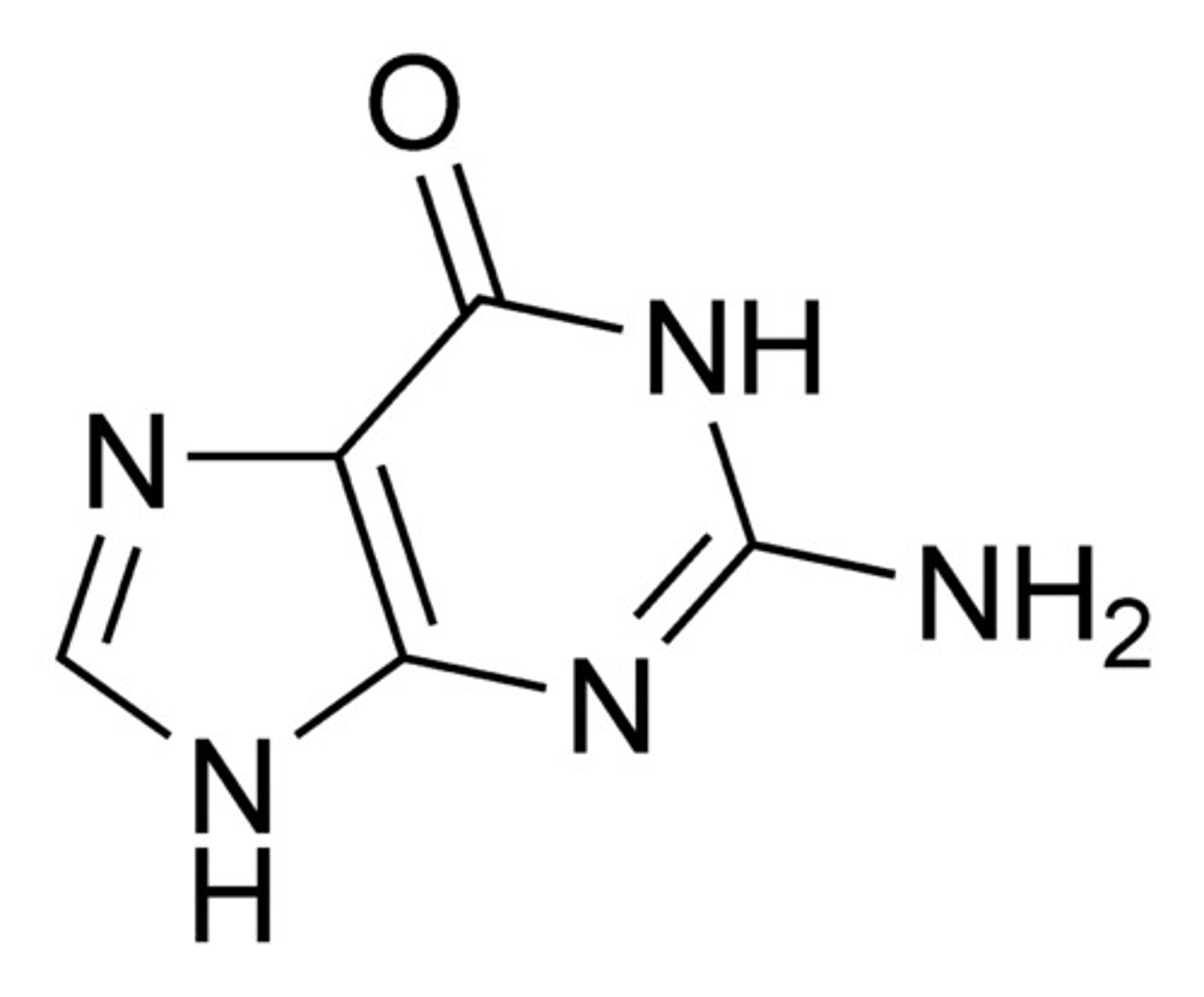
Guanine
A component of nucleic acids that carries hereditary information in DNA and RNA in cells. Chemically, it is a purine base.
Has a C=O off Carbon 6 and NH2 off carbon 2
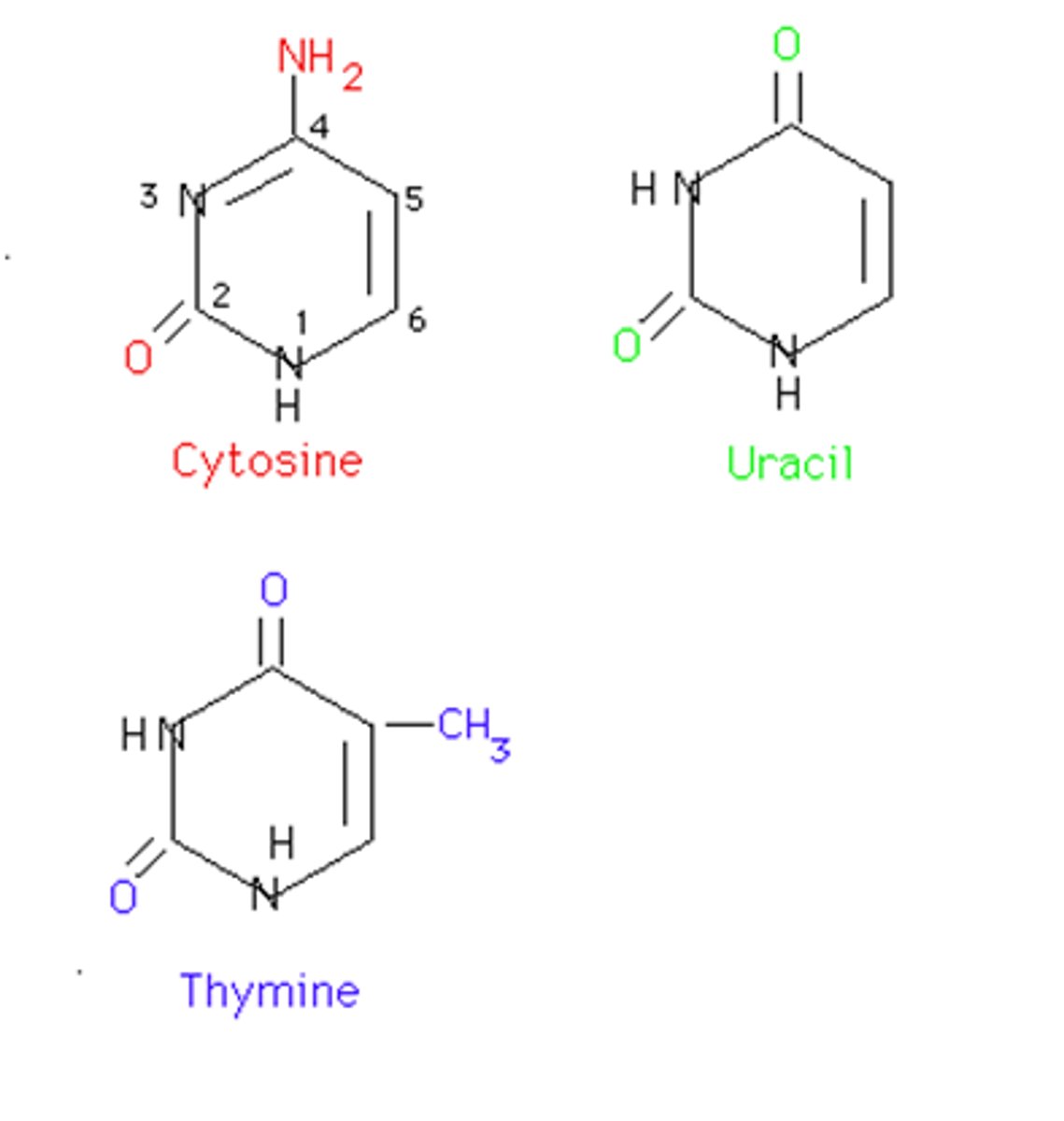
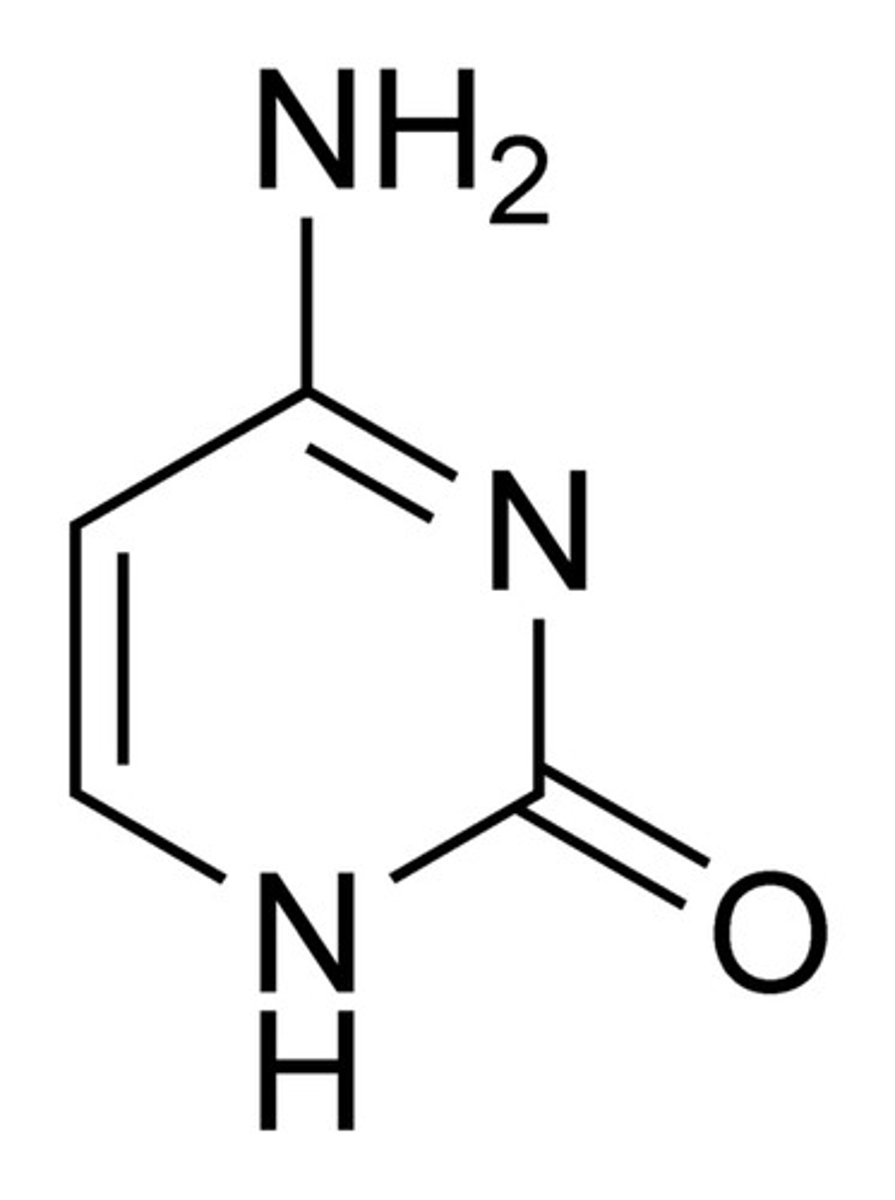
Cytosine
A component of nucleic acids that carries hereditary information in DNA and RNA in cells. Chemically, it is a pyrimidine base.
NH2 off 4 and a C=O off 6
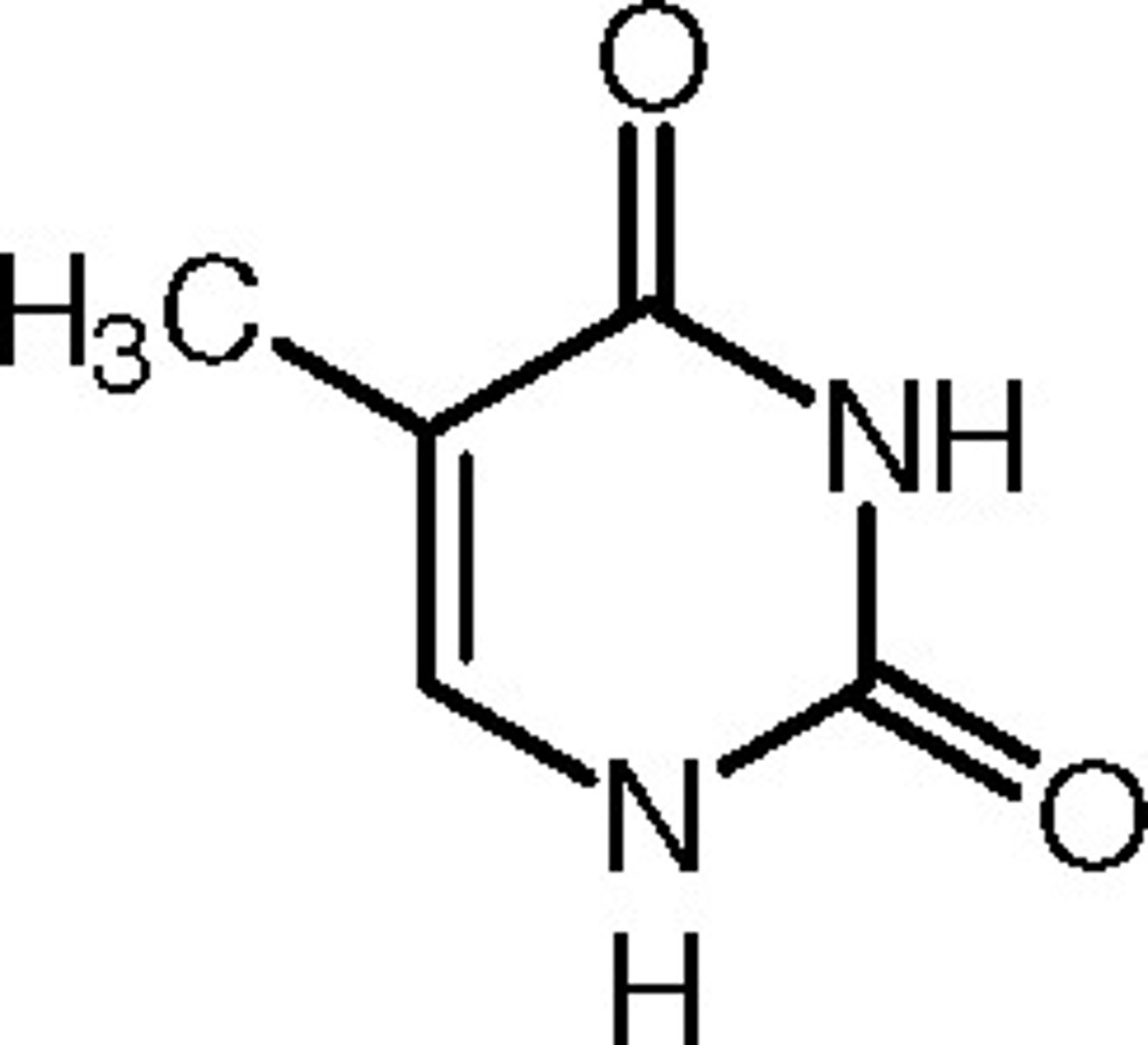
thymine
A component of nucleic acid that carries hereditary information in DNA in cells. Chemically, it is a pyrimidine base.
Has methyl off 5, C=O off 2 and 3
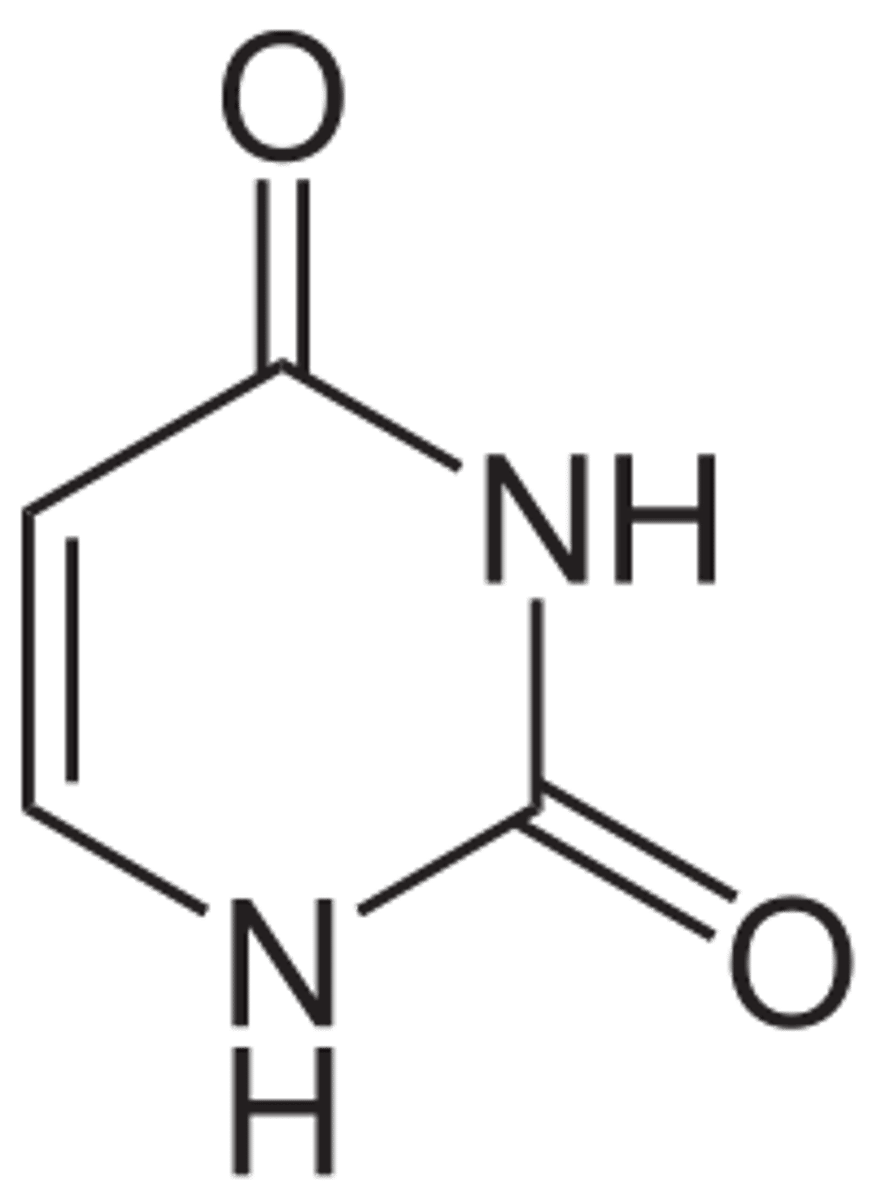
uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA) and derived from pyrimidine
Thymine but no methyl off 5
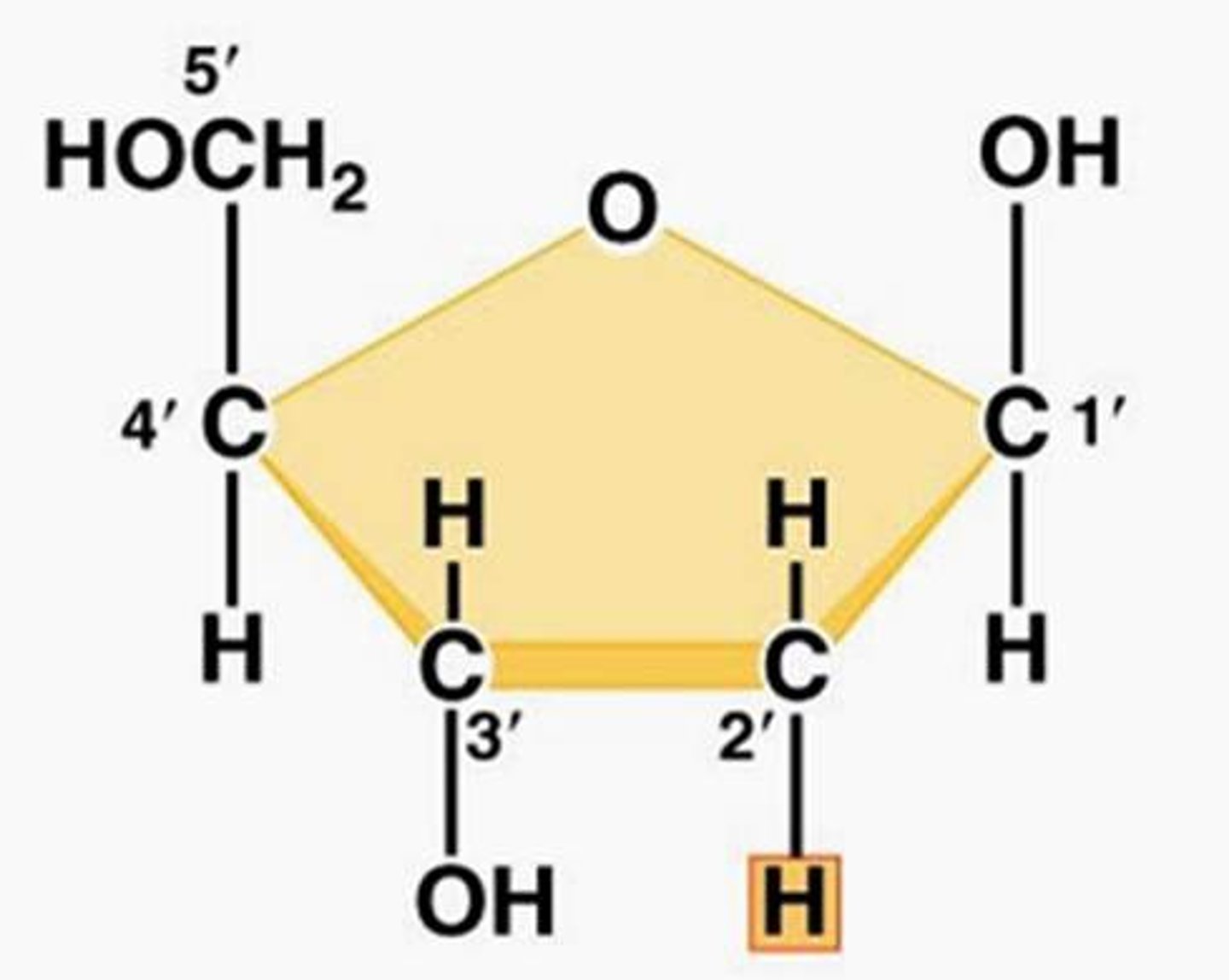
1'
nucleotides always attach to this carbon in the sugar when forming the glycosidic bonds
De Novo and Salvage Pathways
biosynthesis from PRPP has one of these two pathways
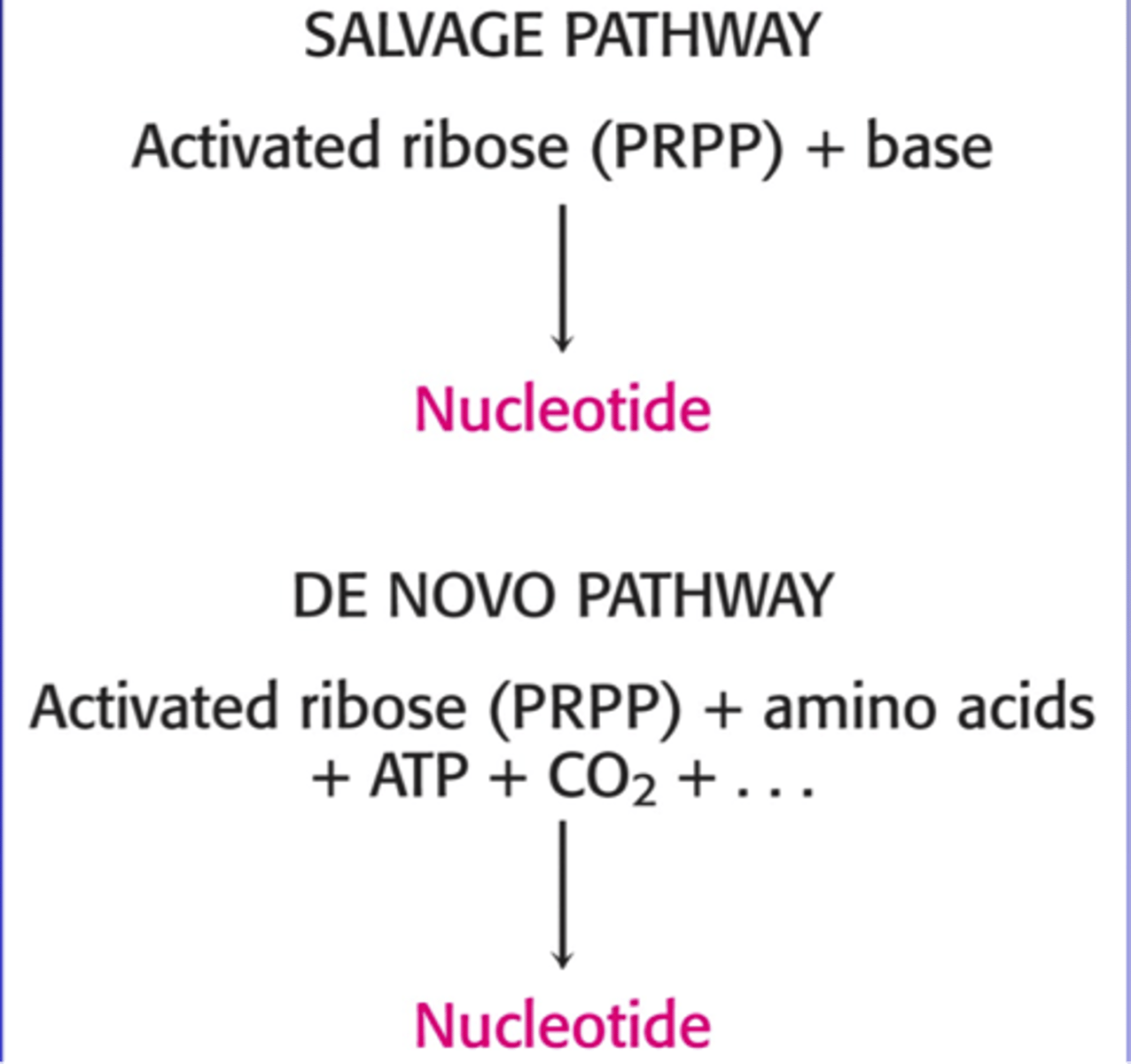
Beta-alanine
degredative product of pyrimidine degredation - useful metabolite
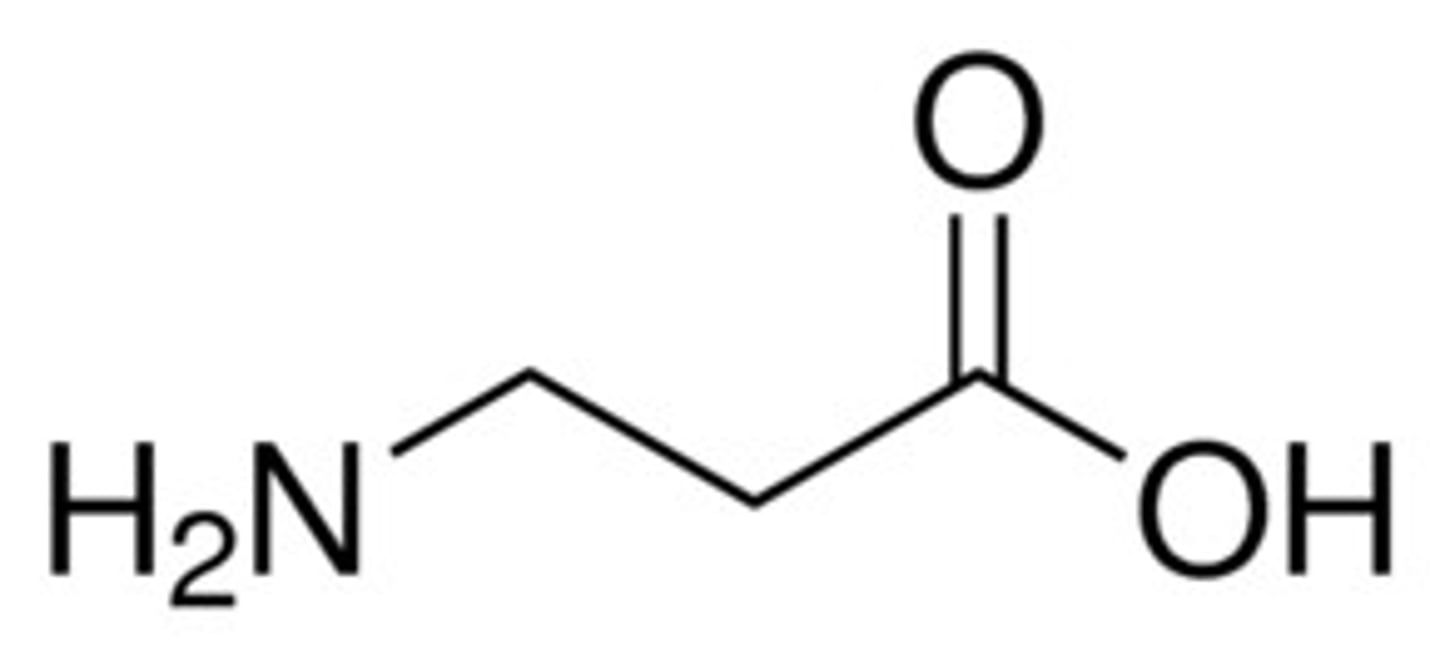
uric acid
product of the purine degredation: nitrogenous waste excreted in the urine
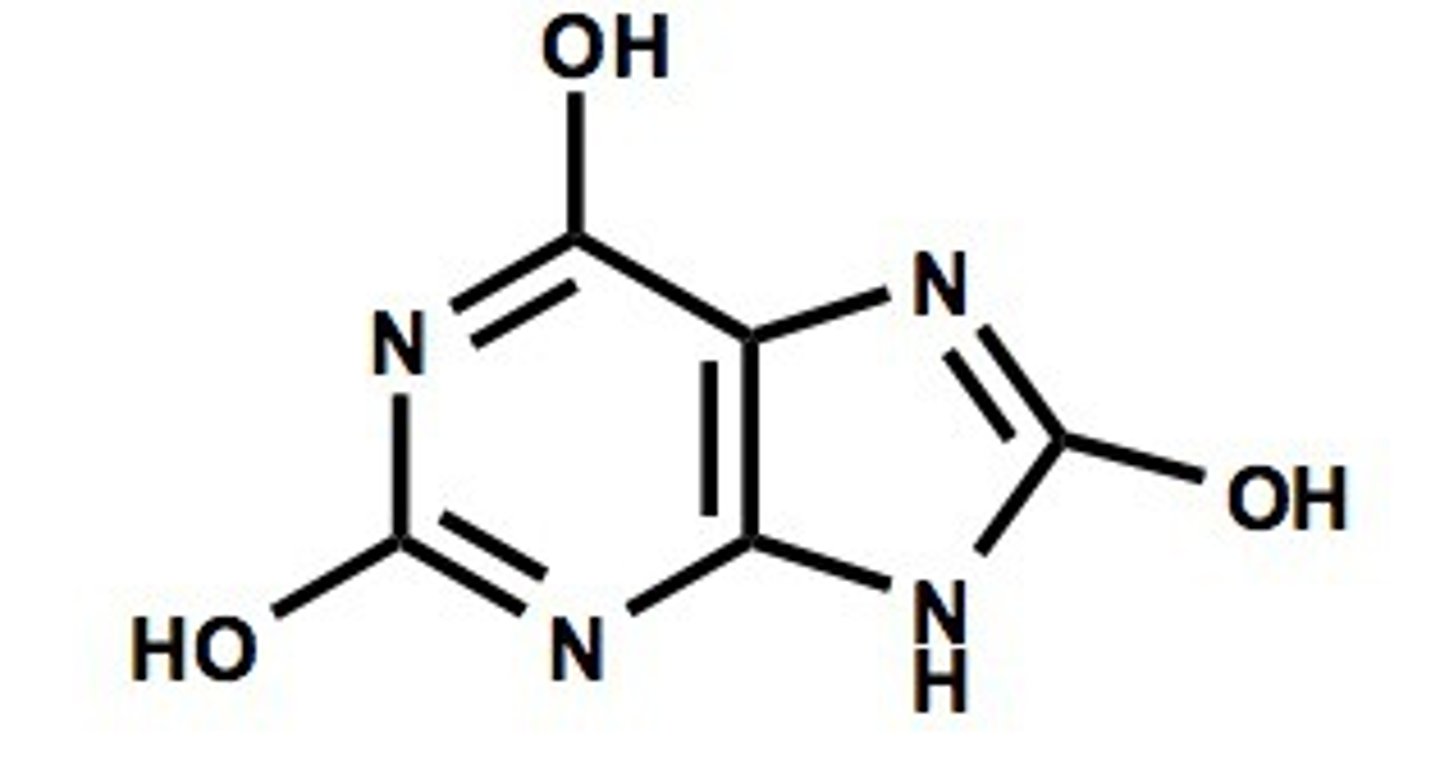
D-ribose
main form of ribose that is present
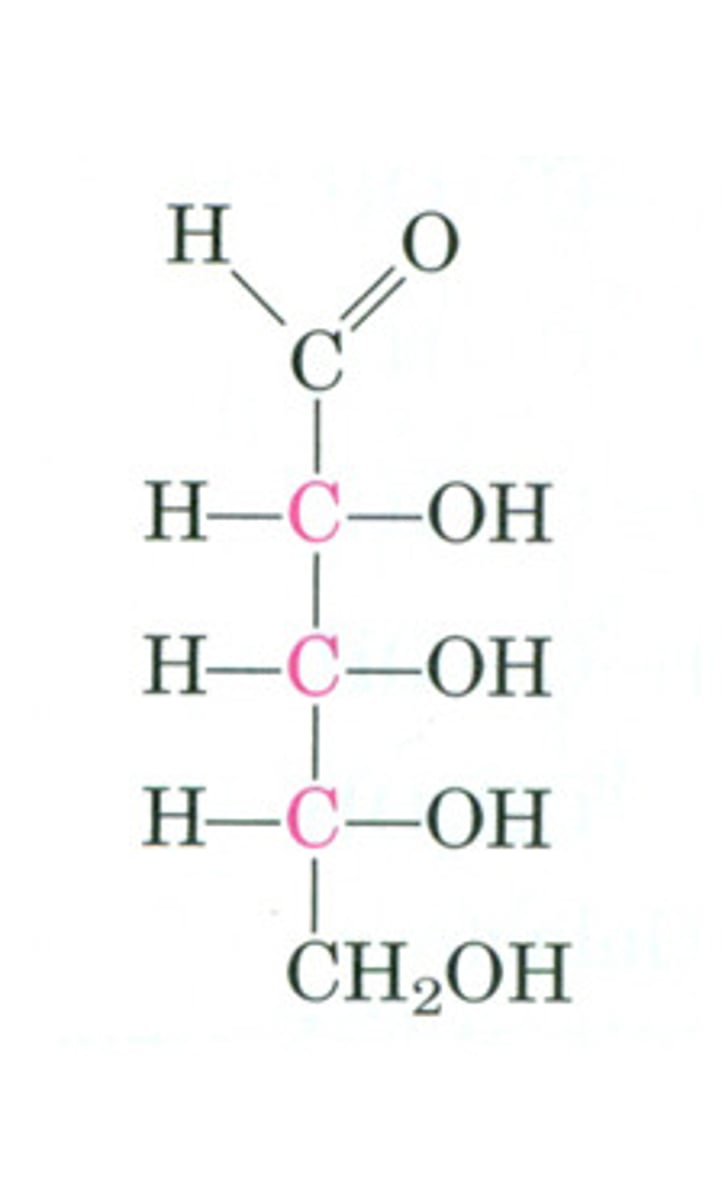
glyceraldehyde
the simplest aldose
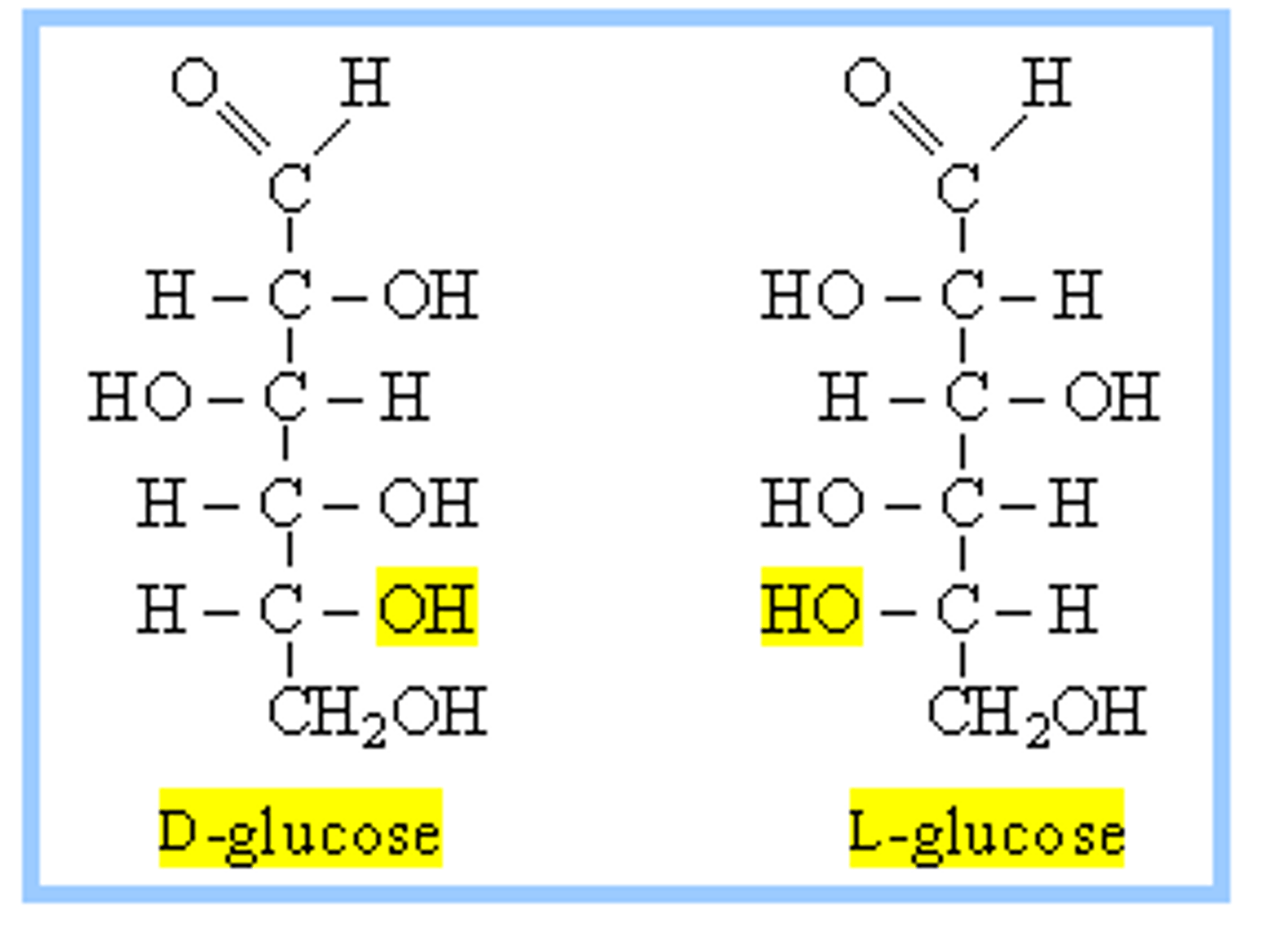
used as template to assign L or D
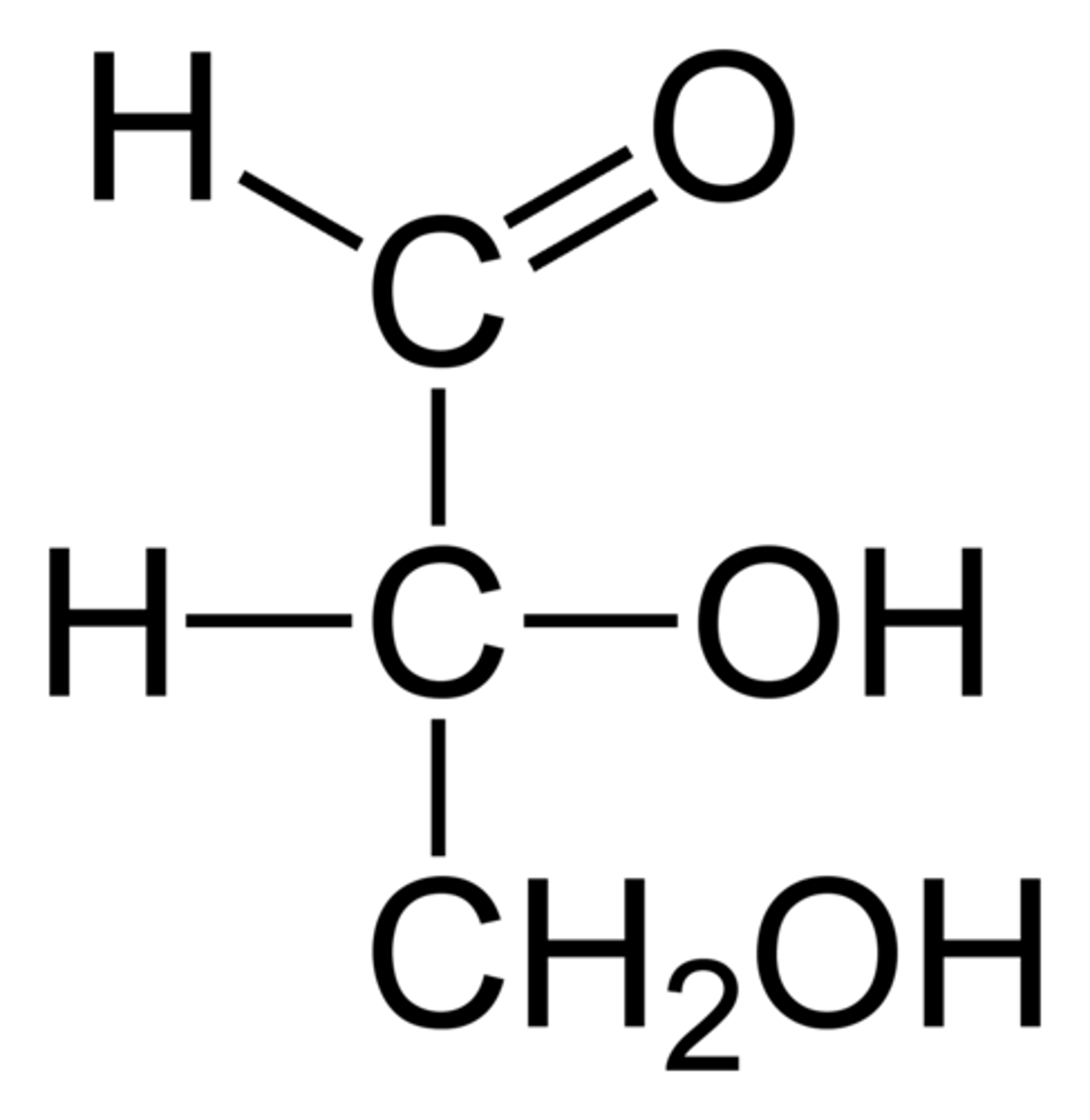
furthest chiral center
this determines if D or L for a carbohydrate
L have OH on the left
PPP
main synthetic source of D-ribose
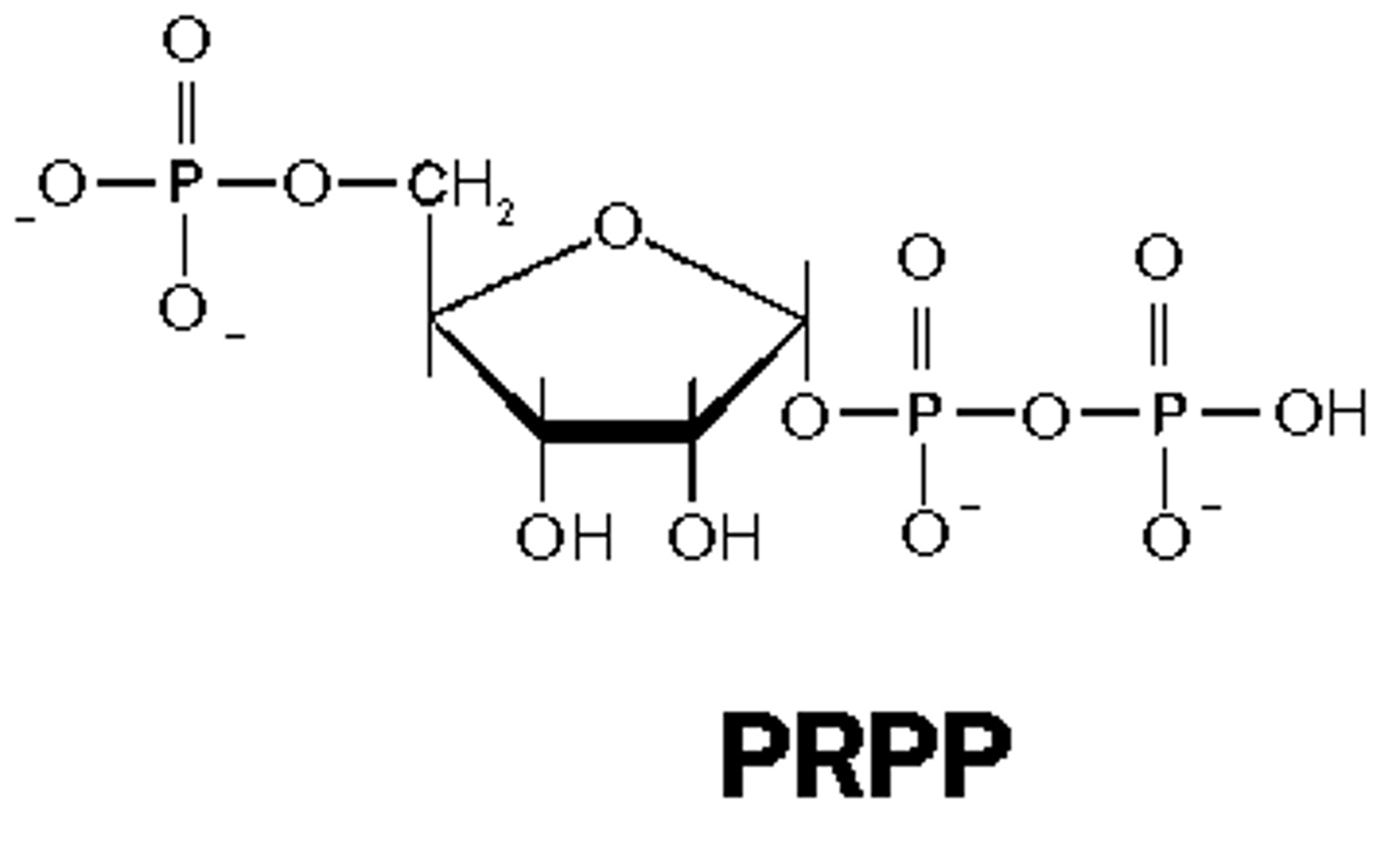
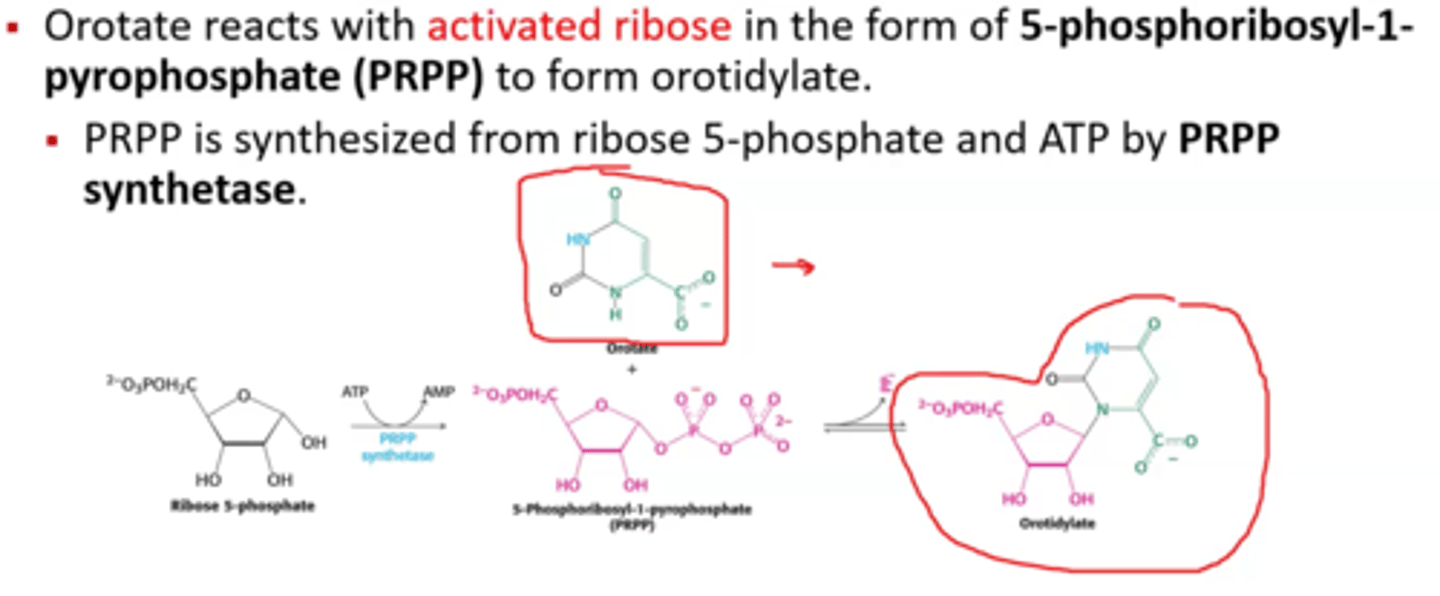
PRPP
5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate
the basic sugar for nucleotide metabolism that is for both purine and pyrimidine synthesis
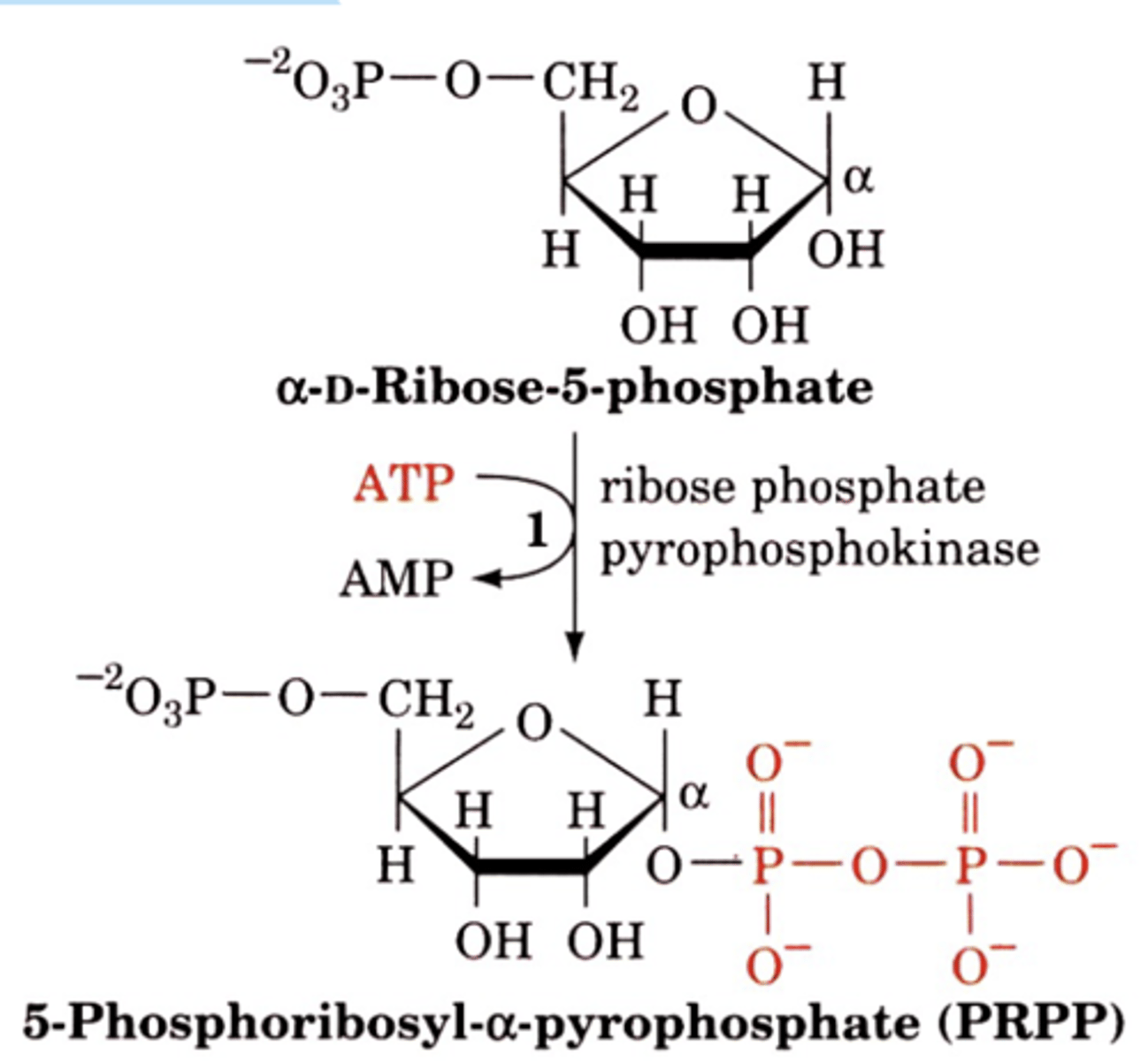
R5P pyrophosphokinase
1st step of Purine syn.
converts R5P->PRPP
adds PPi to 1'OH
enzyme that converts R5P to PRPP
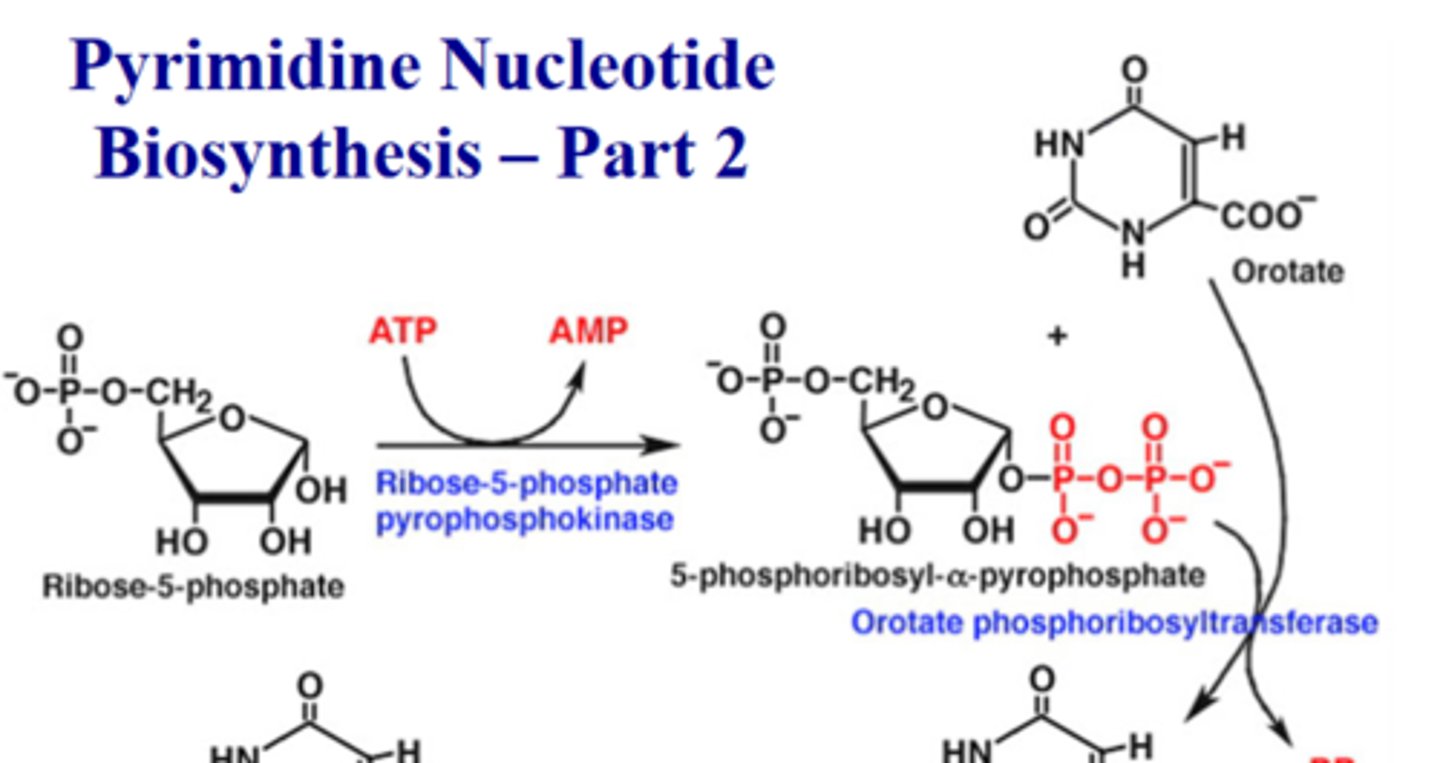
R5P + ATP --> AMP + PRPP
net reaction of the ribose 5 phosphate pyrokinase reaction
make ribose-1-phosphate to favor purine salvage pathway
phosphoribosyl transferase favors formation of this substance and why, when pyrimidine concentration is high
1) Uridine monophosphate (UMP)
2) Cytidine Triphosphate (CTP)
first two steps of the pyrimidine biosynthesis
apsartate, bicarbonate, Gln amide
3 sources of the 2N and 4C that make a 6 atom pyrimidine ring
N1, C4-6
what in a pyrimidine comes from aspartate?
N3
what in a pyrimidine comes from Gln amide?
C2
what in a pyrimidine comes from HCO3-
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
catalyzes the first step in pyrimidine synthesis:
1) glutamine + HCO3- + 2 ATP --> 2 ADP + Pi + Carbamoyl Phosphate
only step that requires ATP
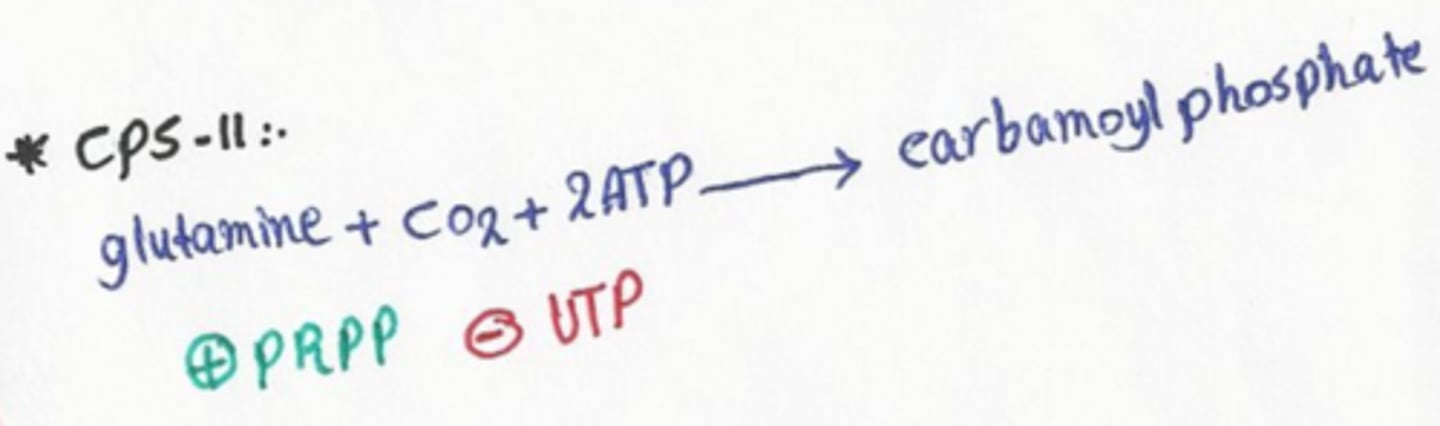
glutamine + HCO3- + 2 ATP --> 2 ADP + Pi + Carbamoyl Phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II net reaction
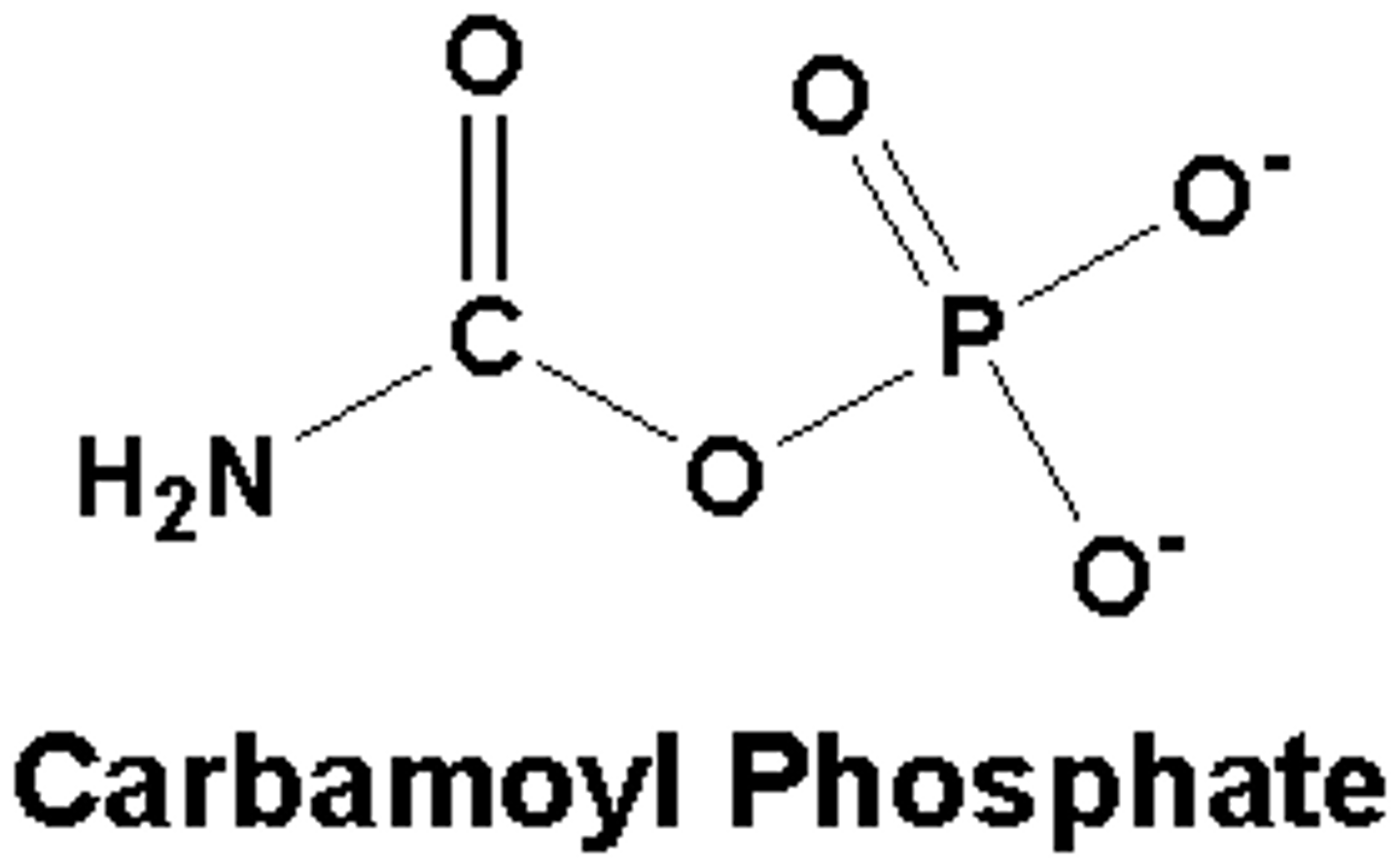
carbamoyl phosphate
product of the carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II reaction - same product in the urea cycle
aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase)
This enzyme adds aspartate to Carbamoyl Phosphate to produce carbamoyl aspartate.
Carbamoyl phosphate + Aspartate --> Pi + Carbamoyl Aspartate
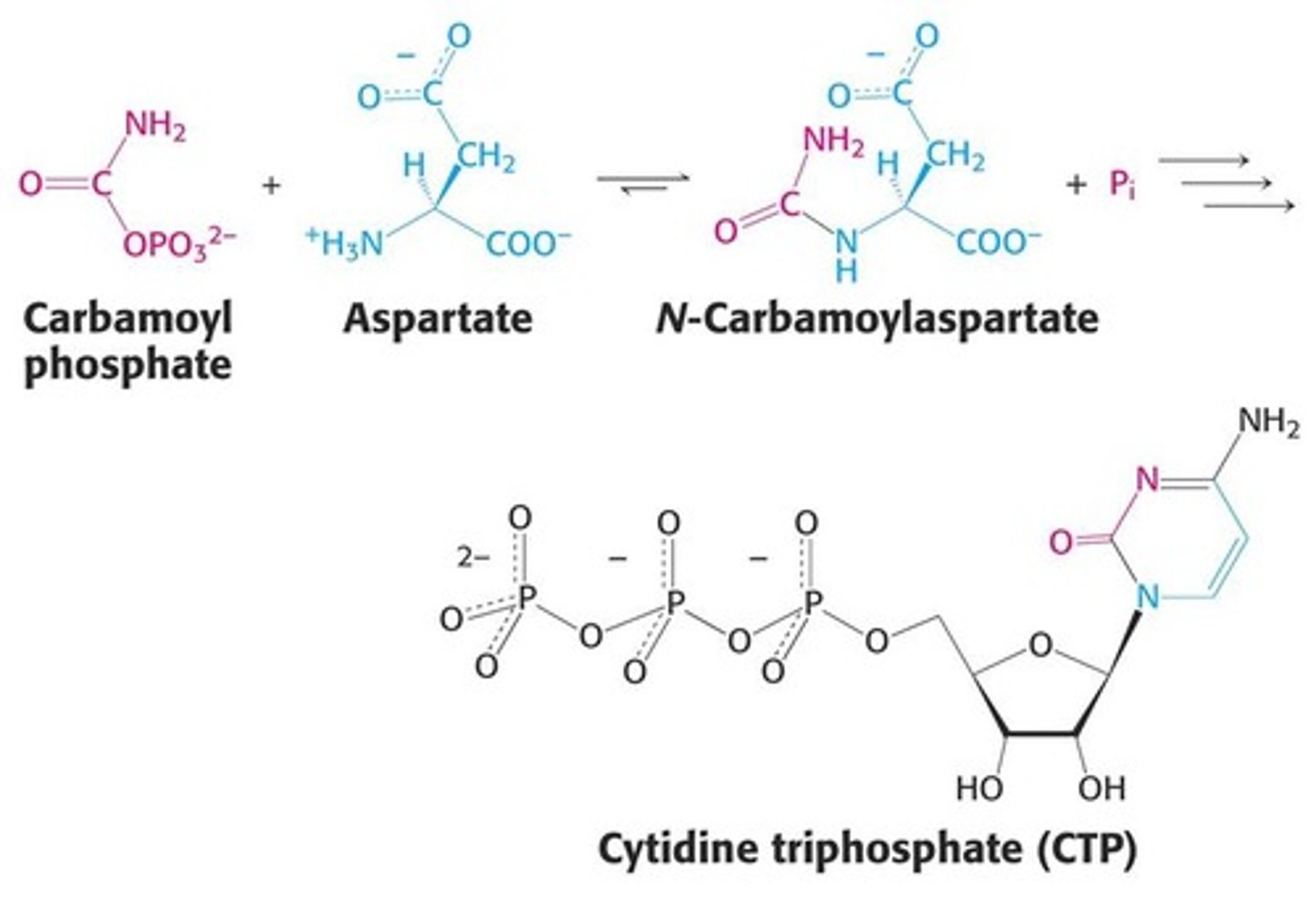
Carbamoyl phosphate + Aspartate --> Pi + Carbamoyl Aspartate
aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) net reaction
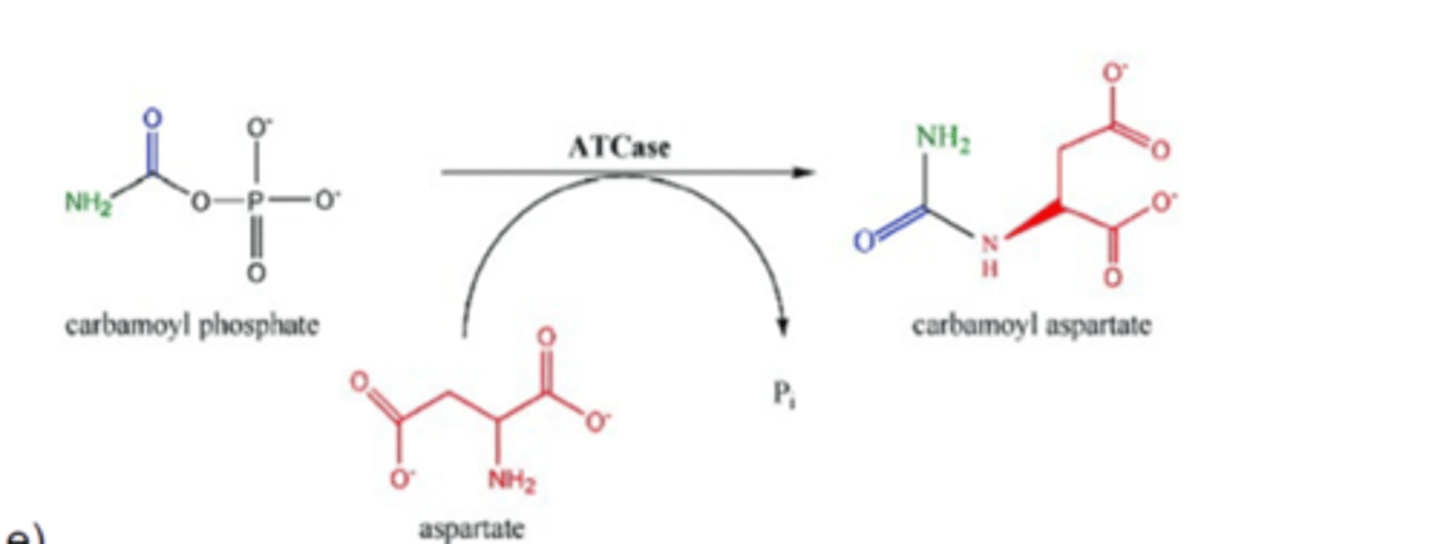
carbamoyl aspartate
product of the aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) reaction
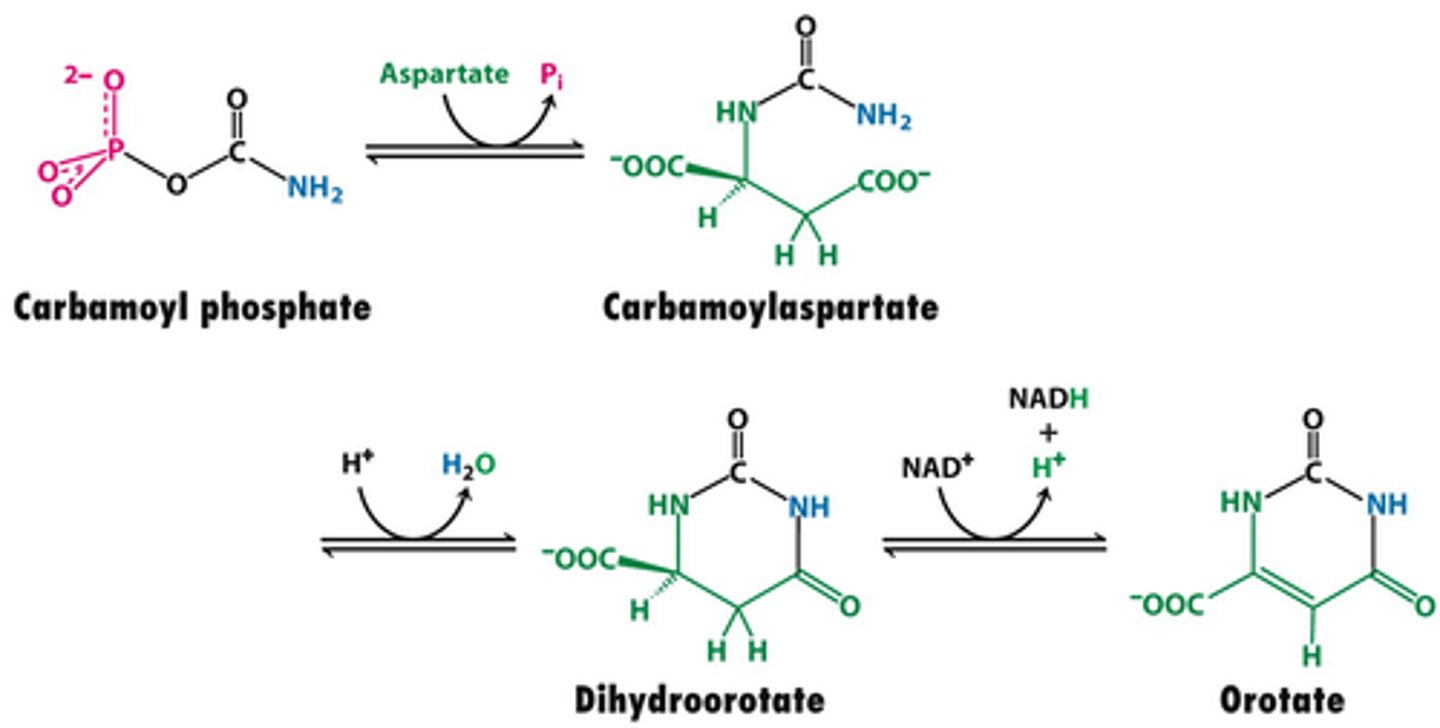
Dihydroorotase
catalyzes the removal of water from N-carbamoylaspartate to close the pyrimidine ring
carbamoyl phosphate --> H2O + Dihydrorotate
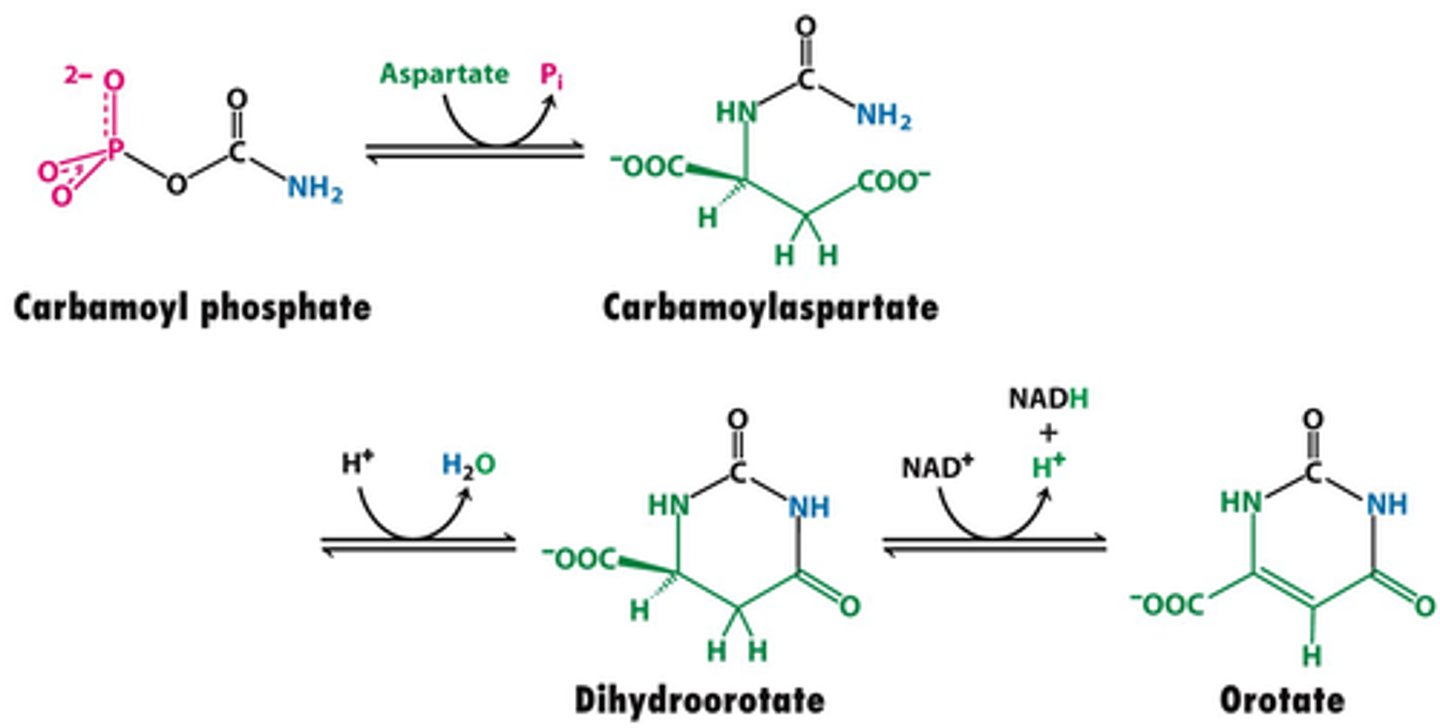
carbamoyl phosphate --> H2O + Dihydrorotate
Dihydroorotase net reaction
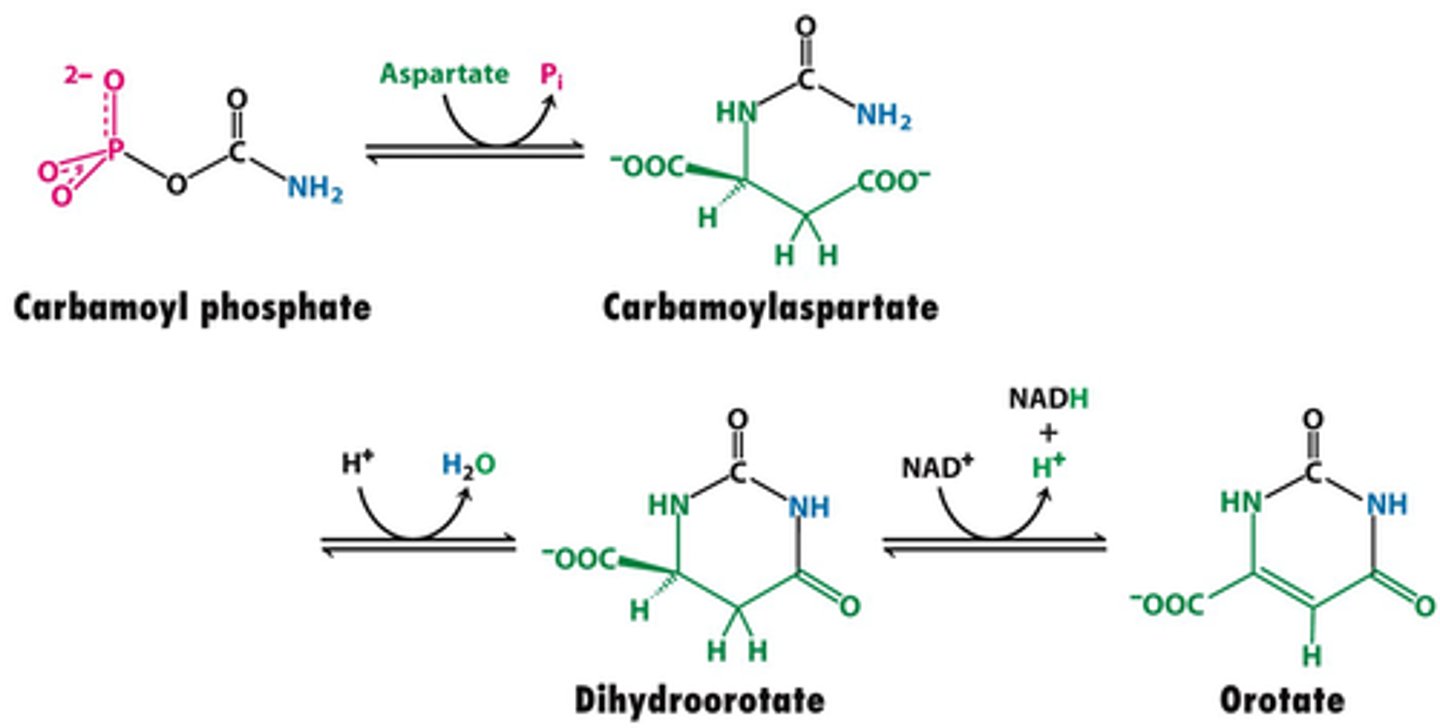
dihydroorotate
product of the Dihydroorotase net reaction
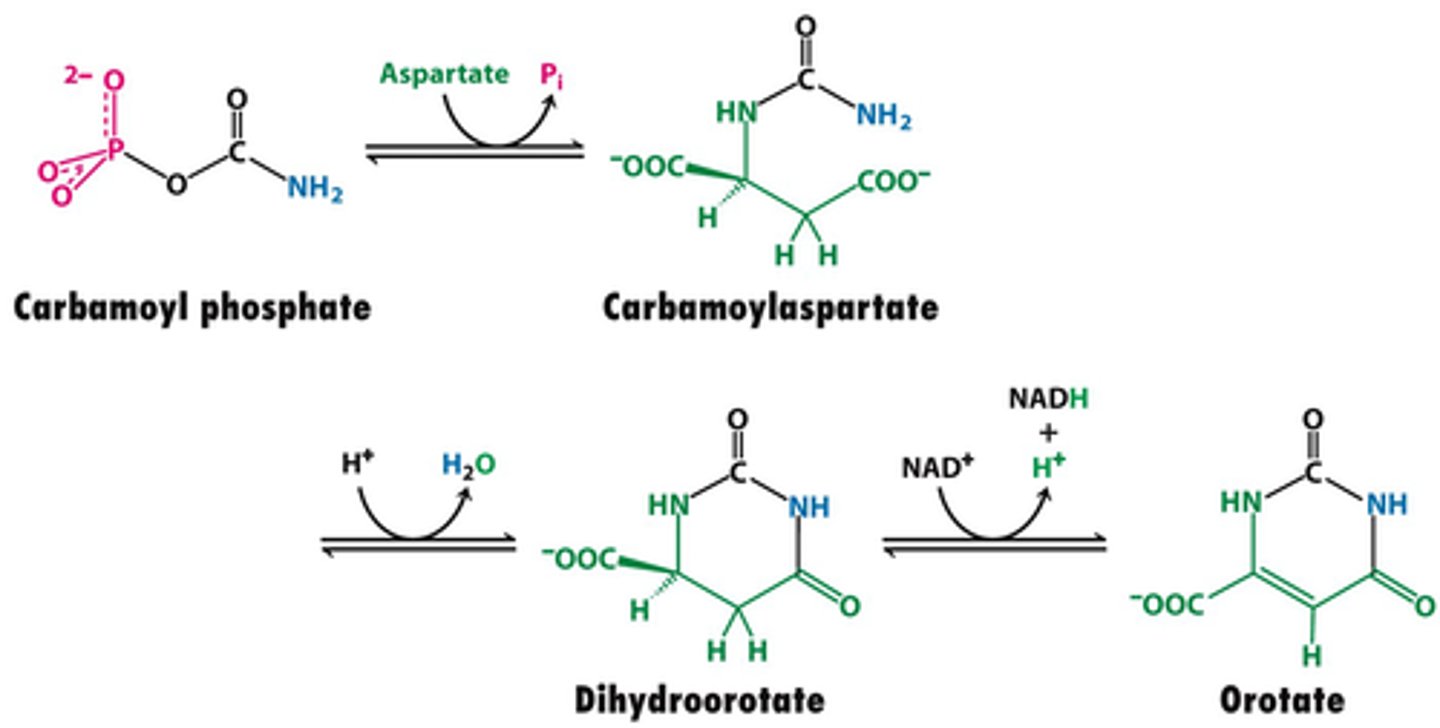
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
Enzyme involved in converting carbamoyl phosphate to orotic acid (with addition of aspartate)
Inhibited by leflunomide
Dihydroorotate + Quinone --> Reduced Quinone + Orotate
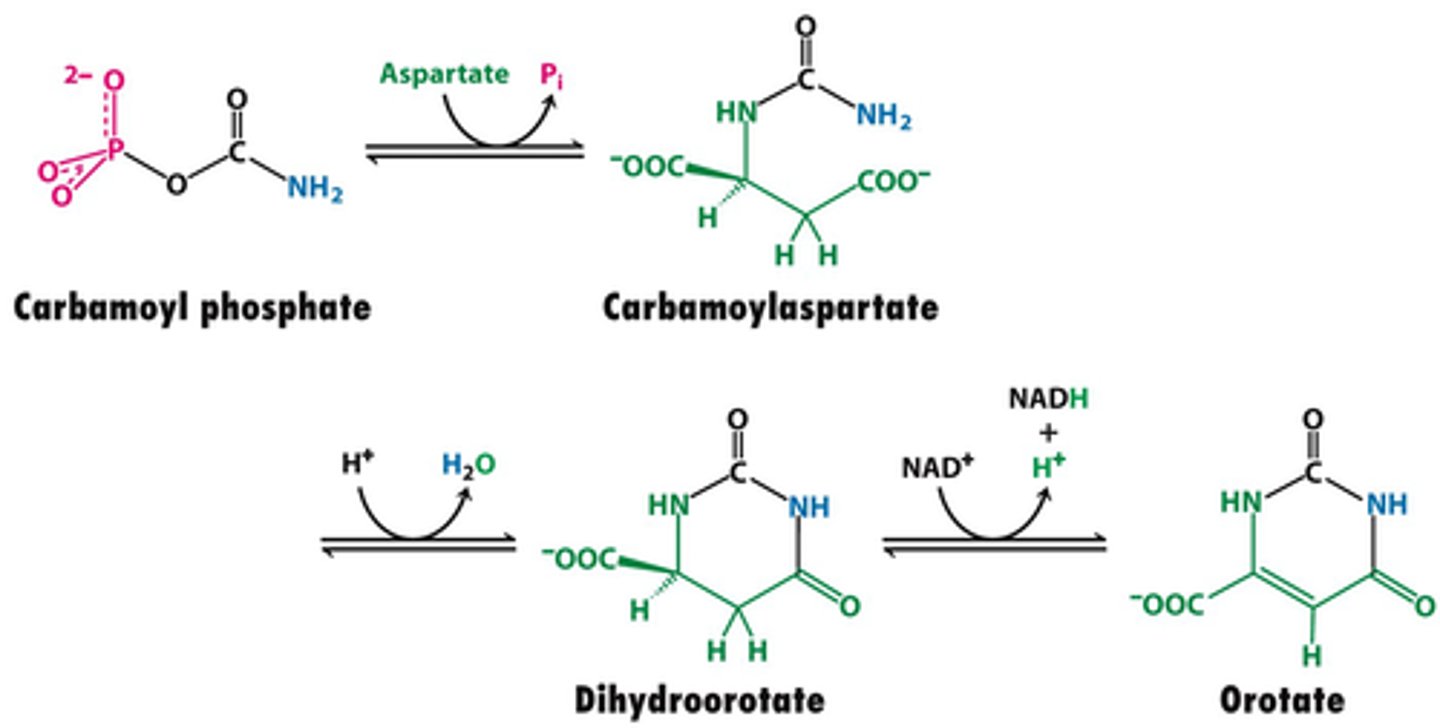
Dihydroorotate + Quinone --> Reduced Quinone + Orotate
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase net reaction
Quinone could be NADH
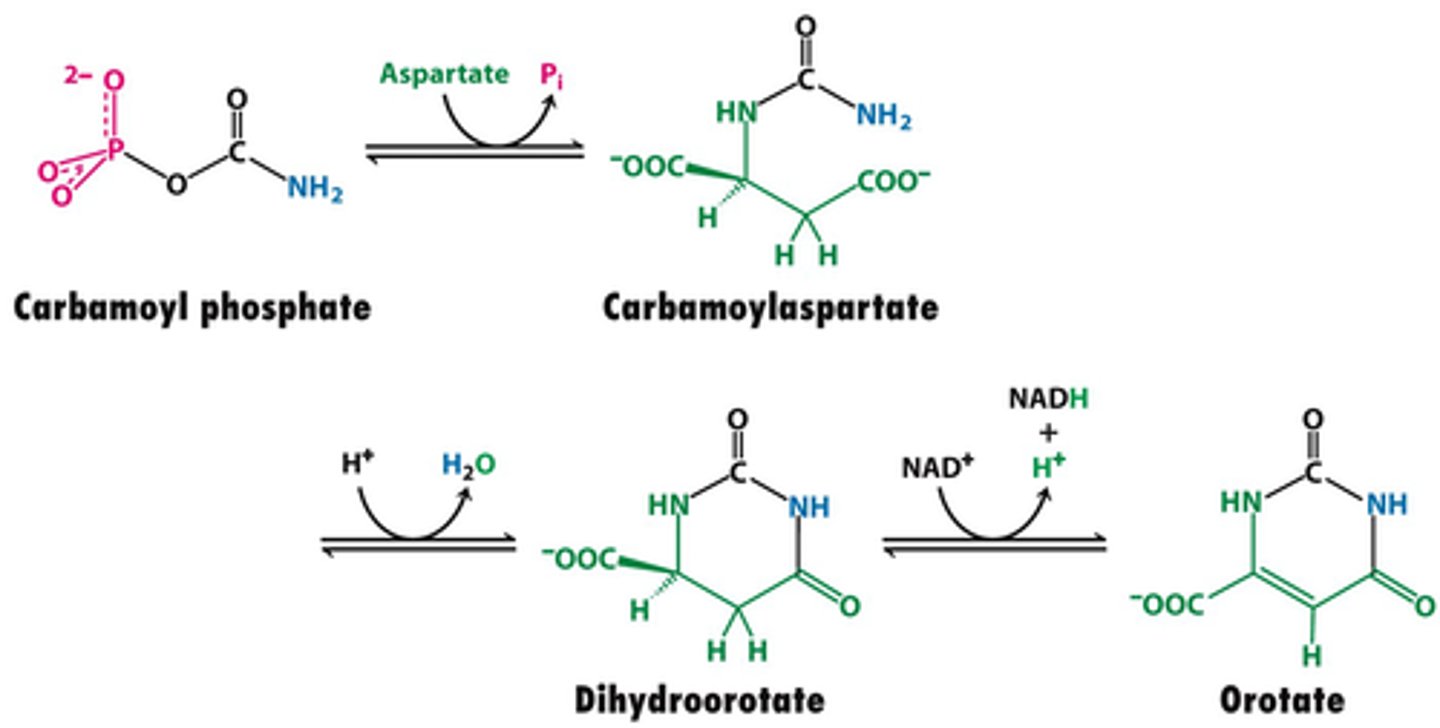
orotate
product of the Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase net reaction
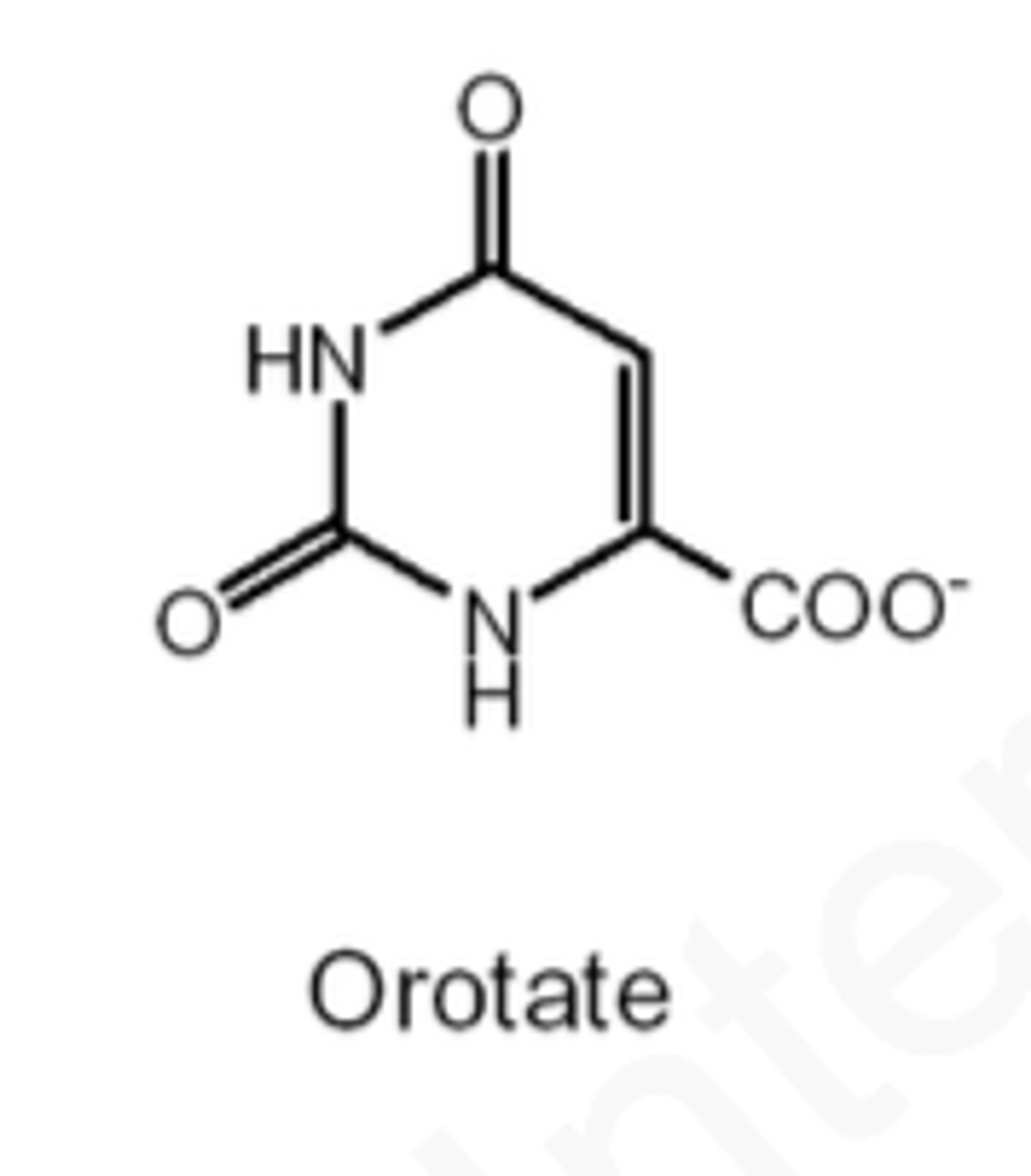
orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
catalyzes:
orotate + PRPP --> PPi + Orotidine 5' Monosphosphate (OMP)
this is the irreversible step
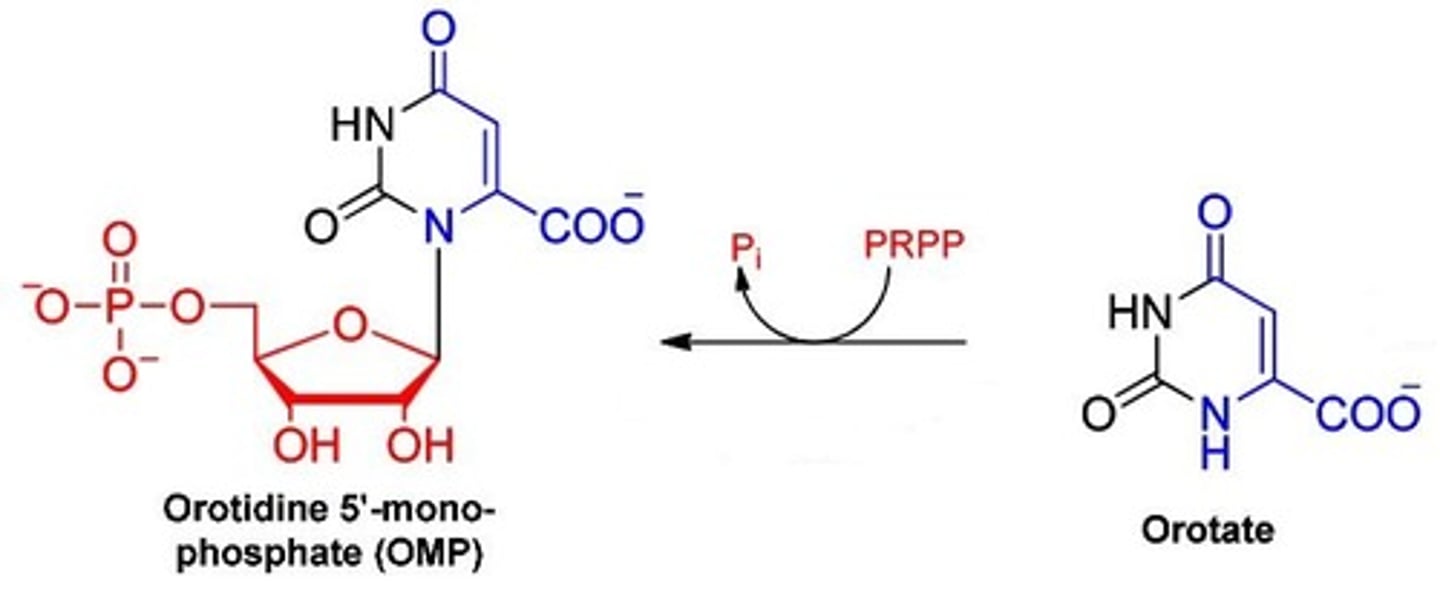
orotate + PRPP --> PPi + Orotidine 5' Monosphosphate (OMP)
orotate phosphoribosyl transferase net reaction
Orotidine 5' Monosphosphate (OMP)
product of the orotate phosphoribosyl transferase net reaction
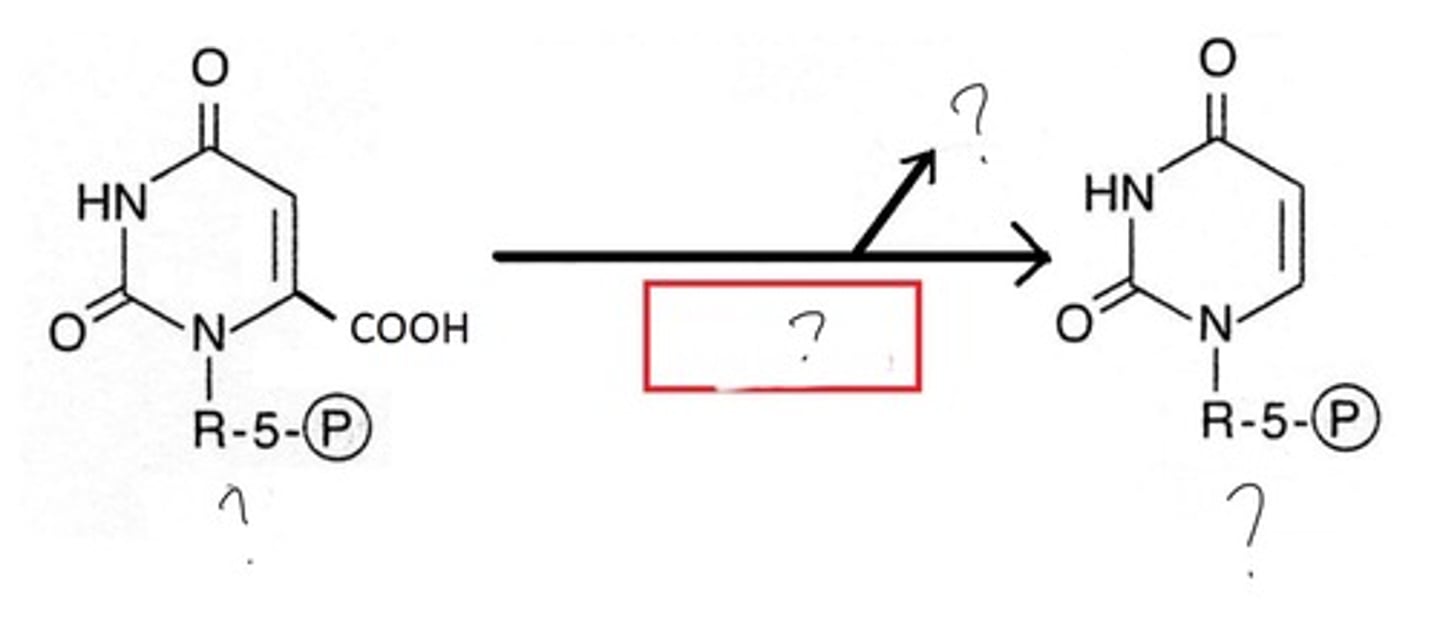
OMP decarboxylase
last enzyme used in pyrimidine synthesis
- makes 1st pyrimidine ring= UMP
-OMP--> UMP + CO2
Very efficient enzyme that does not require any cofactors for decarboxylation as it does not have a high energy intermediate
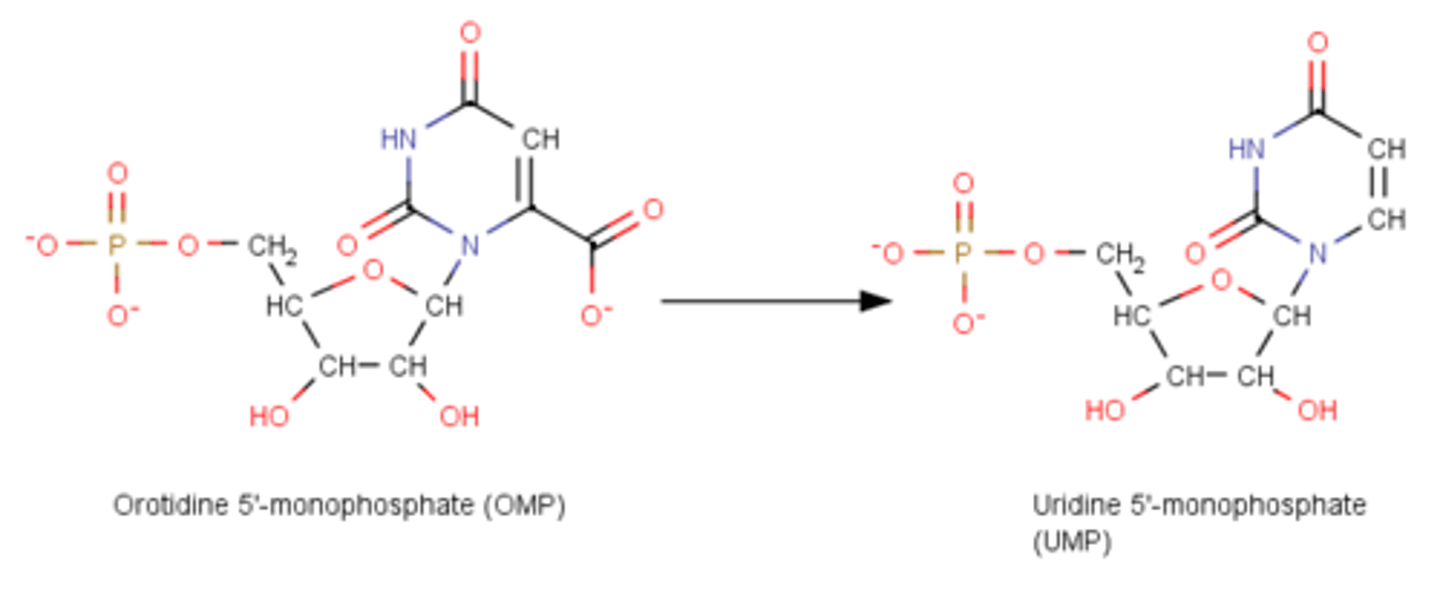
OMP--> UMP + CO2
OMP decarboxylase net reaction
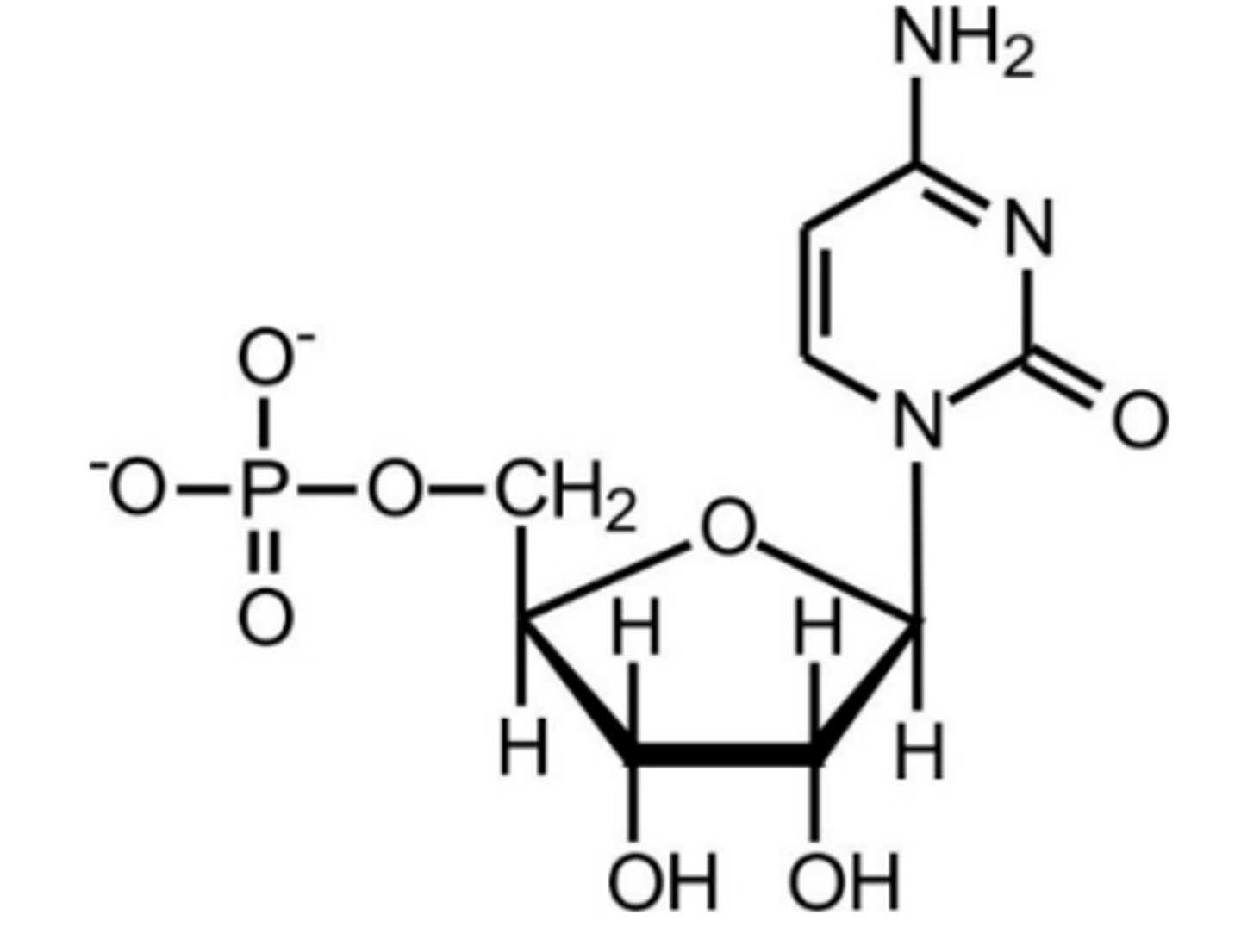
Uridine Monophosphate (UMP)
STEP 6: DECARBOXYLATION OF OMP PRODUCT:
ATCase and Dihydrootase
2 reactions in UMP formation that have a hydration rxn
intramitochondrial enzyme
dihydrotate dehyrogenase is this type of enzyme that gets power from quinone reduction
irreversible
orotate phosphoribosyl transferase's reaction step is this - enzyme also abbreviated as OPRT
substrate channeling between 1-3 on same peptide and 5-6 on same peptide, enzymes
this helps increase efficiency of UMP synthesis
preferential transition state binding
Binding to the transition state with greater affinity to either the product or reactants
OMP and active site of OMP decarboxylase bind and release energy to stabilize the transition state:
therefore can form UMP with no high energy intermediates and. cofactors
Lysine and Aspratate
amino acids used by OMP decarboxylase - in decarboxylation rxn
Orotic aciduria
Caused by OMPT and/or OMP decarboxylase deficiencies - the last two steps of the UMP formation
Orotic acid in urine, megaloblastic anemia that is not corrected with B12 or folic acid and no hyperammonemia
only inherited affect in pyrimidine formation
inherited
orotic aciduria is the only this type of defect in pyrimidine formation
uridine and cytidine
two ways to treat orotic aciduria
nucleoside monophosphate kinase
Catalyzes this:
UMP + ATP --> ADP + UDP
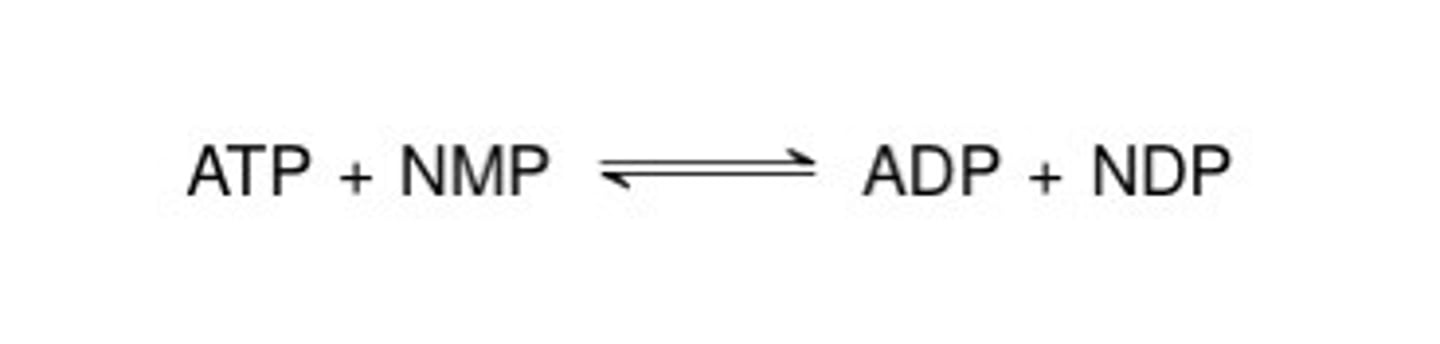
nucleoside diphosphate kinase
catalyzes this:
UDP + ATP --> ADP + UTP
CTP synthetase
enzyme that converts UTP to CTP
UTP + ATP + Glutamine + H2O --> CTP + ADP + Pi + Glutamate
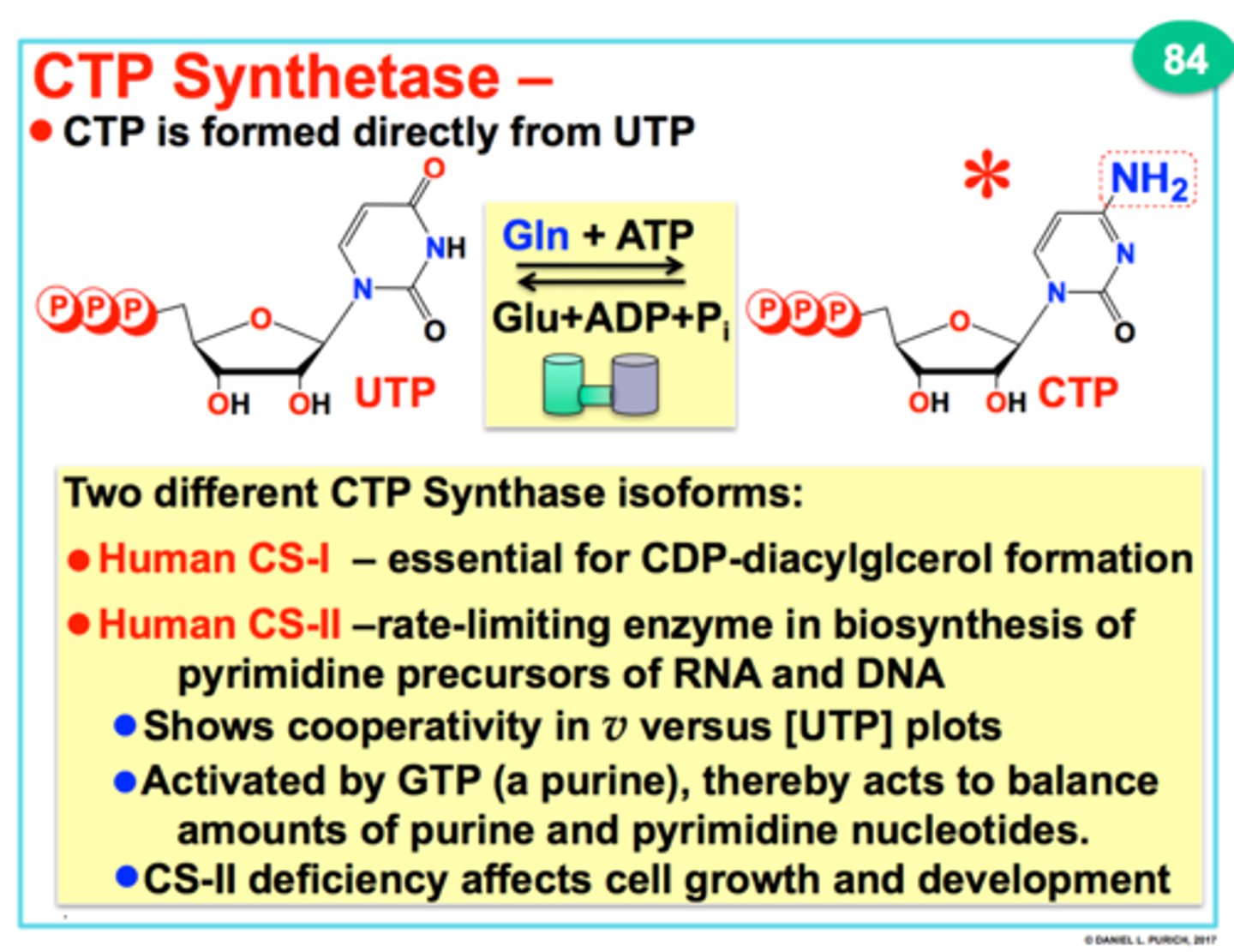
UTP + ATP + Glutamine + H2O --> CTP + ADP + Pi + Glutamate
ctp synthetase net reaction
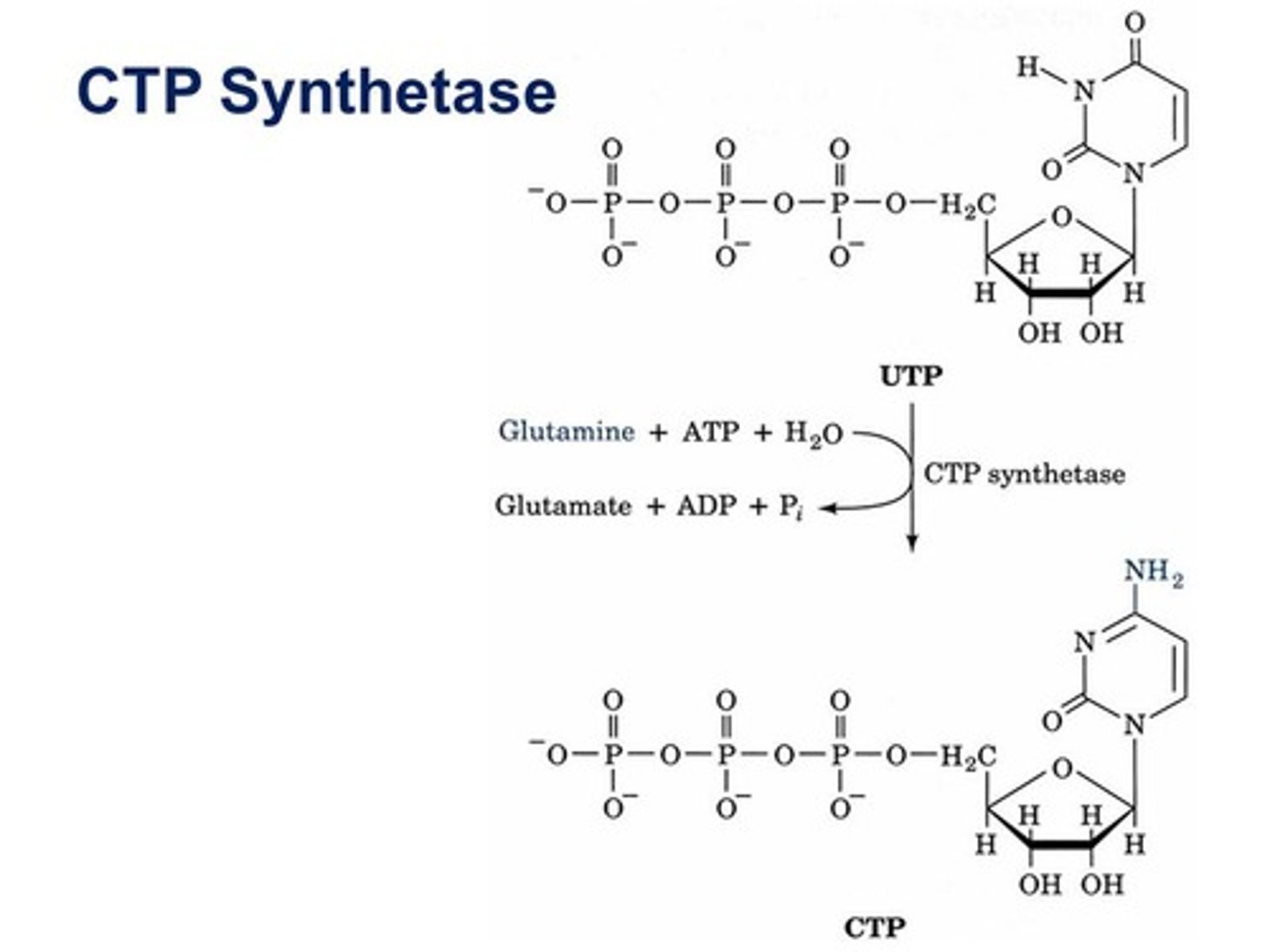
CTP and Glutamate
two major products from the CTP synthetase net reaction
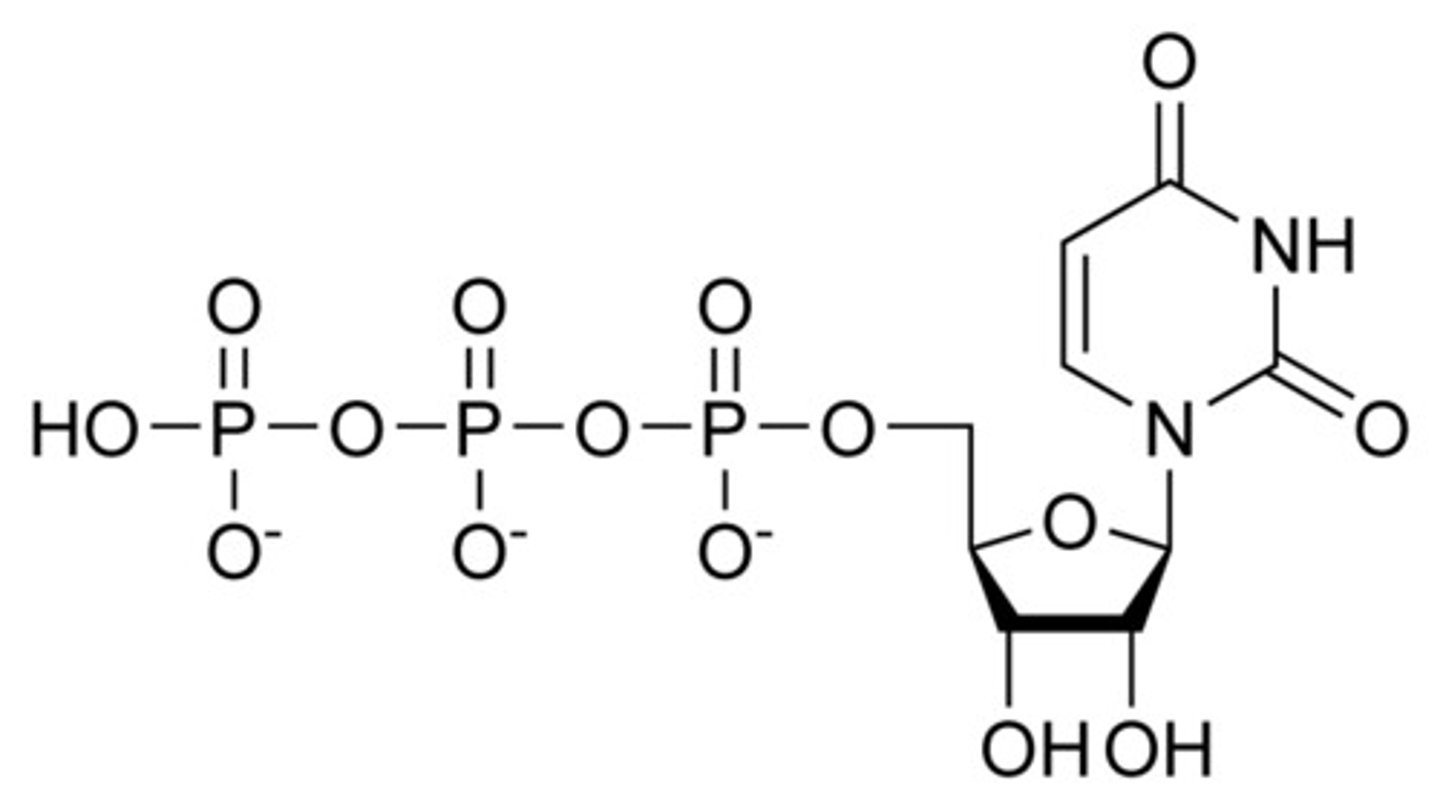
glutamine
source of amide nitrogen to make CTP from UTP on the C4 in plants
ATCase reaction
major flux point for pyrimidine synthesis in bacteria
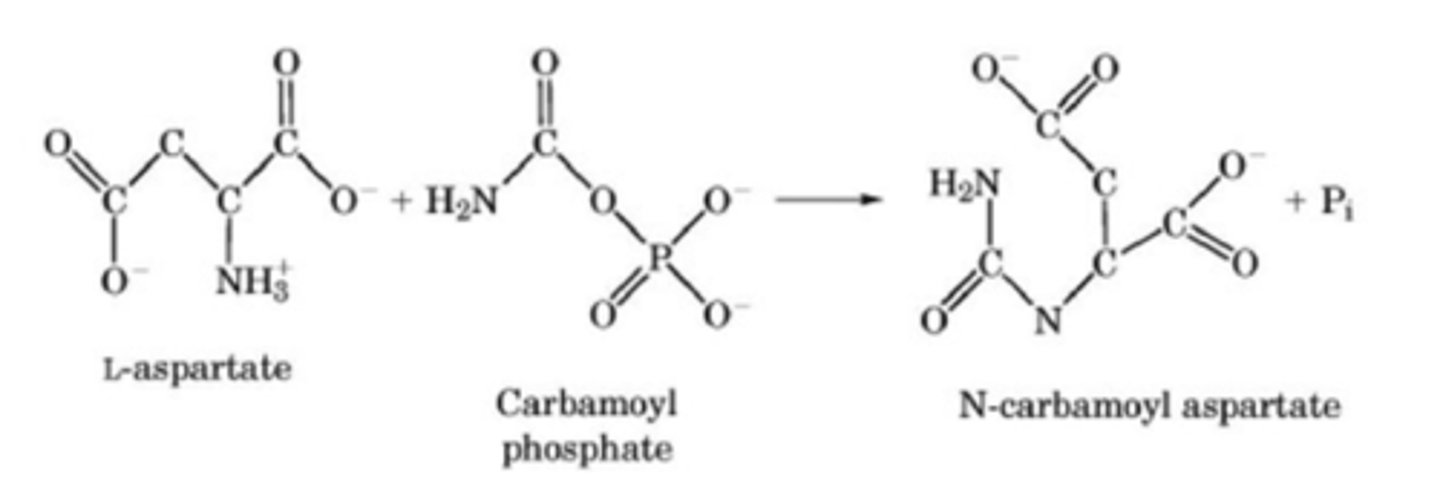
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
major flux point for pyrimidine synthesis in animals
UDP and UTP
inhibitors of Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II in animals
ATP and PRPP
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II positive regulators (metabolism)
UMP and CMP
two inhibit OMP decarboxylase - minor level of control
ADP and GDP
two compounds that inhibit purine synthesis at the ribose phosphate pyrophosphate kinase step
control level of PRPP; therefore inhibit pyrimidine synthesis too
purines (A,G) activate, pyrimidines (C,T) inhibit
in prokaryotes describe ATCase activity in terms of purines and pyrimidines
T-state
this state of ATCase is favored by the binding of CTP to it at an allosteric site
2 substrate binding sites movement to one another is inhibited and cannot react with substrate
c3 dimers close
R-state
this state of ATCase is favored by the binding of by the binding of ATP to it to the r2 site
c3 dimers further apart
have proximity of substrate binding sites and can react
c3 dimers
distance of these between each others affects atcase activity
too close in T
far enough for reactivity in R - immediate proximity
aspartate and carbamoyl phosphate
these are in the two homotropic binding sites of ATCase, the two substrates of the reaction
have possible reaction in R-state
affected by hetertropic states/regulatory dimers of CTP and ATP