AP Biology: Meiosis
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Oogenesis
Eggs in ovaries halted before anaphase I meiosis I completed during maturation meiosis 2 completed after fertilization
Nondisjunction
problems with meitotic spindle fibers cause Incorrect # of chromosomes because chromosomes don't separate properly
Nondisjunction in meiosis I
Homologous chromosomes do not separate properly (all cells abnormal)
Nondisjunction in meiosis 2
Half cells abnormal, sister chromatids fail to separate in meiosis 2
Trisomy disorder
2n+1, cells have 3 copies of one chromosome
Monosomy disorder
Cells have only one copy of a chromosome
Syndrome
A survivable chromosomal mutation
Down syndrome
3 copies of chromosome 21, the smallest chromosome, not least amount of genes, frequency correlates with age of mother
Prophase II
Spindle apparatus forms, chromatids still held at centromere
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
Cell has haploid set of chromosomes, cytokinesis creates cleavage furrow creating 2 cells, no replication between m I and m II
Metaphase II
Chromosomes position on metaphase plate, chromatids not genetically identical cuz of m I crossing over, kinetochores attach to spindle fibers
Anaphase II
Breakdown of proteins holding sister chromatids together, chromatids separate moving to opposite poles of cells,
Telephase II and cytokinesis
Nuclei form with haploid number of chromosomes, each 4 new cells genetically distinct
Heredity
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next
Variation
Differences between members of the same species
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity and hereditary variation
Gametes
A haploid reproductive cell, such as an egg or sperm. Gametes unite during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote
Somatic Cell
Any cell in a multicellular organism except a sperm or egg
Locus
A specific place along the length of a chromosome where a given gene is located
Asexual Reproduction
The generation of offspring from a single parent that occurs w/o fusion of gametes. In most cases, the offspring are genetically identical to the parent
Clone
A lineage of genetically identical individuals or cells
Sexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction in which two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the gametes of the parents
Life Cycle
The generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape
Homologous Chromosomes
A pair of chromosomes of the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern that possesses genes for the same characters at corresponding loci
Sex Chromosomes
A chromosome responsible for determining the sex of an individual
Autosome
A chromosome that is not directly involved in determining sex; not a sex chromosome
Diploid Cell
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each parent
Haploid Cell
A cell containing only one set of chromosomes
Fertilization
The union of haploid gametes to produce a diploid zygote
Zygote
The diploid product of the union of haploid gametes during fertilization; a fertilized egg
Meiosis
A modified type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms consisting of two rounds of cell division but only one round of DNA replication. It results in cells w/ half the number of chromosome sets as the original cell
Meiosis I
The first division of a two-stage process of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that results in cells with 1/2 the number of chromosome sets as the original cell
Meiosis II
The second division of a two-stage process of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that results in cells w/ half the number of chromosome sets as the original cell
Prophase I
Chromosomes condense, crossing over, Synapsis, centrosome, movement, chiasmata, micro tubules attach to centromeres
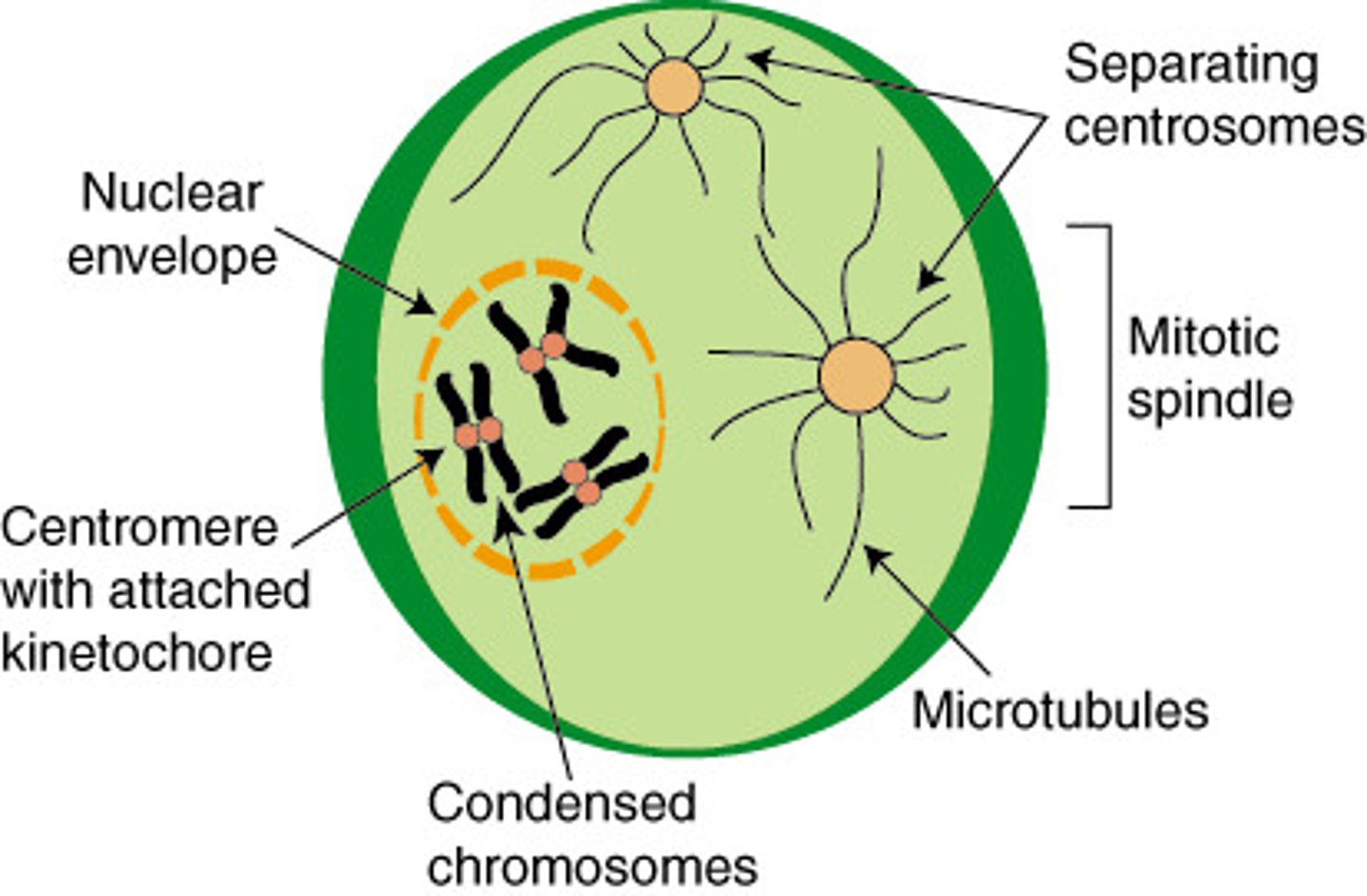
Synapsis
The pairing and physical connection of replicated homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis
Tetrad
A set of 4 chromatids
Crossing Over
The reciprocal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis
Metaphase I
Chromosomes line up on plate crossed over with independent assortment, chromosomes attached to micro tubule,
Anaphase I
Proteins holding chromatids together break down, chromosomes move to opposite poles of cell,
Recombinant Chromosomes
A chromosome created when crossing over combines the DNA from two parents into a single chromosome
Independent Assortment
The process of random segregation and assortment of chromosomes during anaphase I of meiosis resulting in the production of genetically unique gametes
Random Fertilization
Any possible egg can be fertilized by any possible sperm
How are karyotypes prepared?
By pairing up chromosomes based on size centromere location and staining patterns on a computer
What are the 3 steps of crossing over?
Breakage of DNA
Crossing over
Refusal of DNA
What happens to to most chromosomal mutations?
The baby will be aborted with high frequency, too disastrous, developmental problems result from biochemical imbalance, certain conditions tolerated