Lecture 22: Benign vs Malignant vs Metastatic Tumors
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
How are benign tumors ultimately distinguished?
based on their invasiveness (do not go to distant sites and usually have well-defined margins)
What are characteristics of benign tumros?
similar to tissue of origin (little to no anaplasia)
slow growth (rare but normal mitotic figures), little necrosis
no invasion, capsule often present
no metastasis
Why do benign tumors have little necrosis?
they grow slow, so they have no problem with vascular supply
What are the unique characteristics of malignant tumors?
highly infiltrative and invasive
usually have little resemblance to the cell or tissue of origin
uncontrolled growth (large amounts of abnormal mitotic figures)
necrosis if poor blood supply
capsule often absent or breached
Why is it often difficult to find clean margins on a malignant tumor?
they often lack a capsule or breach their capsule, so they are not well contained
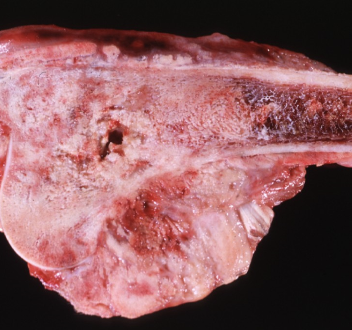
How can you tell this is a malignant tumor?
is has breached the bone (invasive)
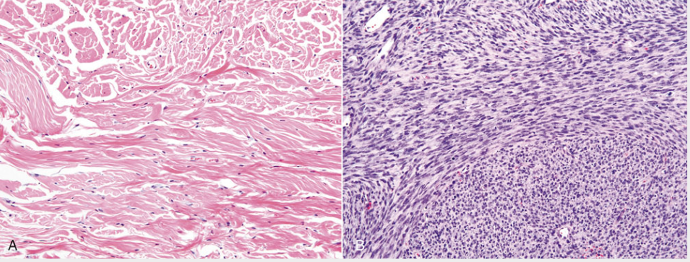
How could you tell A is from a benign tumor and B is from a malignant tumor?
B is densely cellular with little collagen and elongated nuclei can be seen
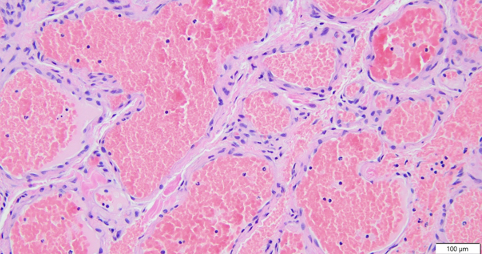
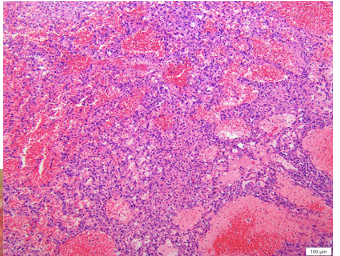
Both of these histologies come from a dark red vascular mass. How can you differentiate histologically which is a hemangioma and which is a hemangiosarcoma?
top is hemangioma bc their are well defined vascular channels, where as the bottom picture, a hemangiosarcoma, does not have as well distinguished vascular channels because the neoplastic cells are lining the channels and interddispersed
What is the cellular criteria to determine malignancy?
well/poorly differentiated (anaplasia)
cellular pleomorphism (shape)
cytomegaly & karyomegaly
anisocytosis (cell size)
anisokaryosis (nuclei size)
mitotic figures
multinucleation
What is a metastatic tumor?
neoplasm that has spread to distant sites
What is the most common area of metastatsis?
lungs
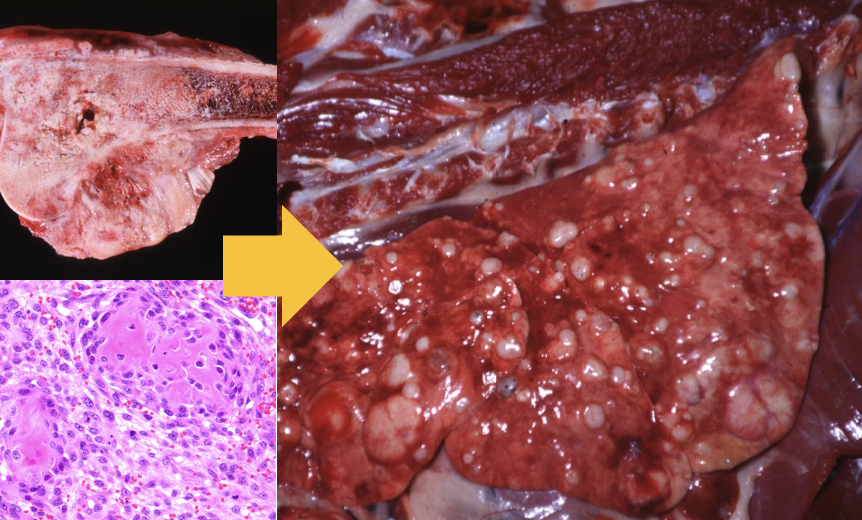
Postmortem, you find a firm white mass attached to a bone. You also notice the lungs have multifocal white masses as well. What has occurred here?
osteosarcoma has metastasized to the lungs
What are the steps to metastases
tumor cells detach from main mass
tumor cells breach the basement membrane using matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and enter ECM
tumor cells migrate through stroma and secrete autocrine growth factors that promote cell migration
formation of emboli
extra
What vessels is metastatic spread more commonly seen in and why?
veins and capillaries because they have thinner walls than arteries
What does the invasion step of metastasis trigger?
a schirrous response
True or false: the metastasis process is highly inefficient.
true
What are the routes of metastasis?
lymphatic
hematogenous (vascular)
transcoelomic (seeding of a cavitary space by neoplastic cells)
What is metastatic dormancy?
metastatic cells migrate to a new area but can lie dormant until the right signals or set of environmental conditions occurs
What type of tumor is more commonly associated with lymphatic metastasis?
carcinomas
Where do metastatic tumors spreading through the lymphatic system often metastasize to first, before distant sites?
the draining lymphatics (ex. lymph node)
What type of tumor is commonly associated with hematogenous metastasis?
sarcomas
Where do tumors that invade portal vessels, such as pheochromocytomas, tend to metastasize first?
the liver
What types of cancers is most often associated with transcoelomic metastasis?
mesotheliomas or carcinomas
What are the two most common tumors that spread using transcoelomic metastasis?
ovarian adenocarcinomas and pancreatic adenocarcinomas
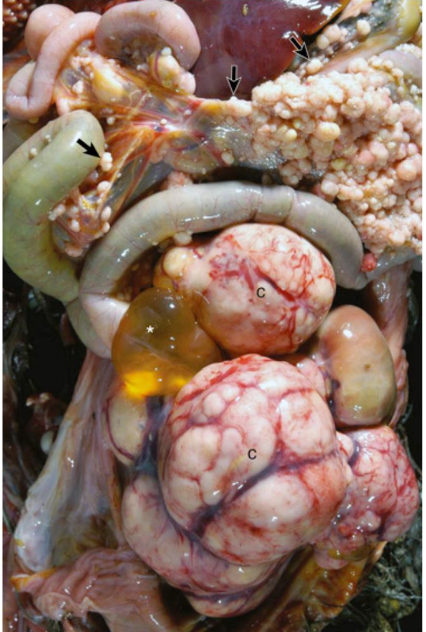
This chicken was suffering from a reproductive tract carcinoma. What type of metastasis occurred? note where the white nodules are.
transcoelomic metastasis (nodules in the mesentery