Radioisotopes
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Gravitational Force
Weakest force, acts over long ranges, depends on mass and distance, reponsible for planetary orbit
Weak Nuclear Force
Second weakest force, very short range, holds quarks inside protons and neutrons together, can cause some types of particle decay
Electromagnetic Force
Second strongest force, infinite range, responsible for attraction and repulsion of magnets, attraction of protons and electrons
Strong Nuclear Force
Strongest force, very short range, holds nuclei atoms (protons and neutrons) together
Nuclides
Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons, also known as isotopes
Stable isotopes
Isotopes that do not decay. The forces in their nuclei keep them form breaking apart unless a great force disturbs them
Radioactive/Unstable Isotopes
Isotopes that randomly emit smaller subatomic particles and electromagnetic radiation from their nuclei called radioactivity
What causes an atom to be stable or unstable?
The interaction between the strong nuclear and electromagnetic forces within the atom. Generally speaking, the more protons an atom has, the more neutrons it needs to have for it to be stable
All elements with an atomic number larger than 83 are…
Unstable and radioactive
Alpha Decay
When the nucleus of a heavy, unstable isotope breaks down into an alpha particle and a smaller nucleus.
Alpha Particle
Two neutrons and two protons (helium nucleus), alpha particle movement can be stopped with a sheet of paper
Where do energy transformations take place during beta particle production?
Nucleus
Net Effect of Beta Particle Production
An electron is produced and a neutron is changed into a proton (electron anti-neutrino), mass stays the same but atomic number increases by one
Aluminum Foil
Can stop beta particle movement
Gamma Ray Production
Gamma rays are high energy photons that are often emitted when the nucleus of an unstable isotope goes through alpha or beta decay.
Lead
Can block gamma rays
Beta particle symbol

Alpha particle symbol

Gamma ray symbol
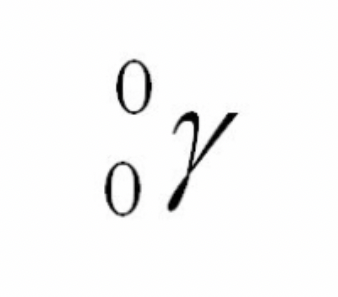
Positron symbol
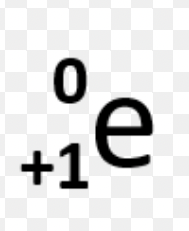
What are the five types of decay?
Alpha decay, beta particle production, gamma ray reduction, positron emission, and electron capture
What do scientists use nuclear equations to express?
Radioactive decay, nuclear fission and fusion
Positron
An electron with positive charge
What does gamma ray production release?
Electromagnetic energy
Neutrino
Subatomic particle similar to an electron except no charge

What are the three types of neutrinos?
Electron, muon, and tau
Positron decay creates…
An electron neutrino
Anti-matter
Particles with opposite electrical charge of the normal particles
Anti-proton
Proton with negative charge