Carbonyl compounds as nucleophiles
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
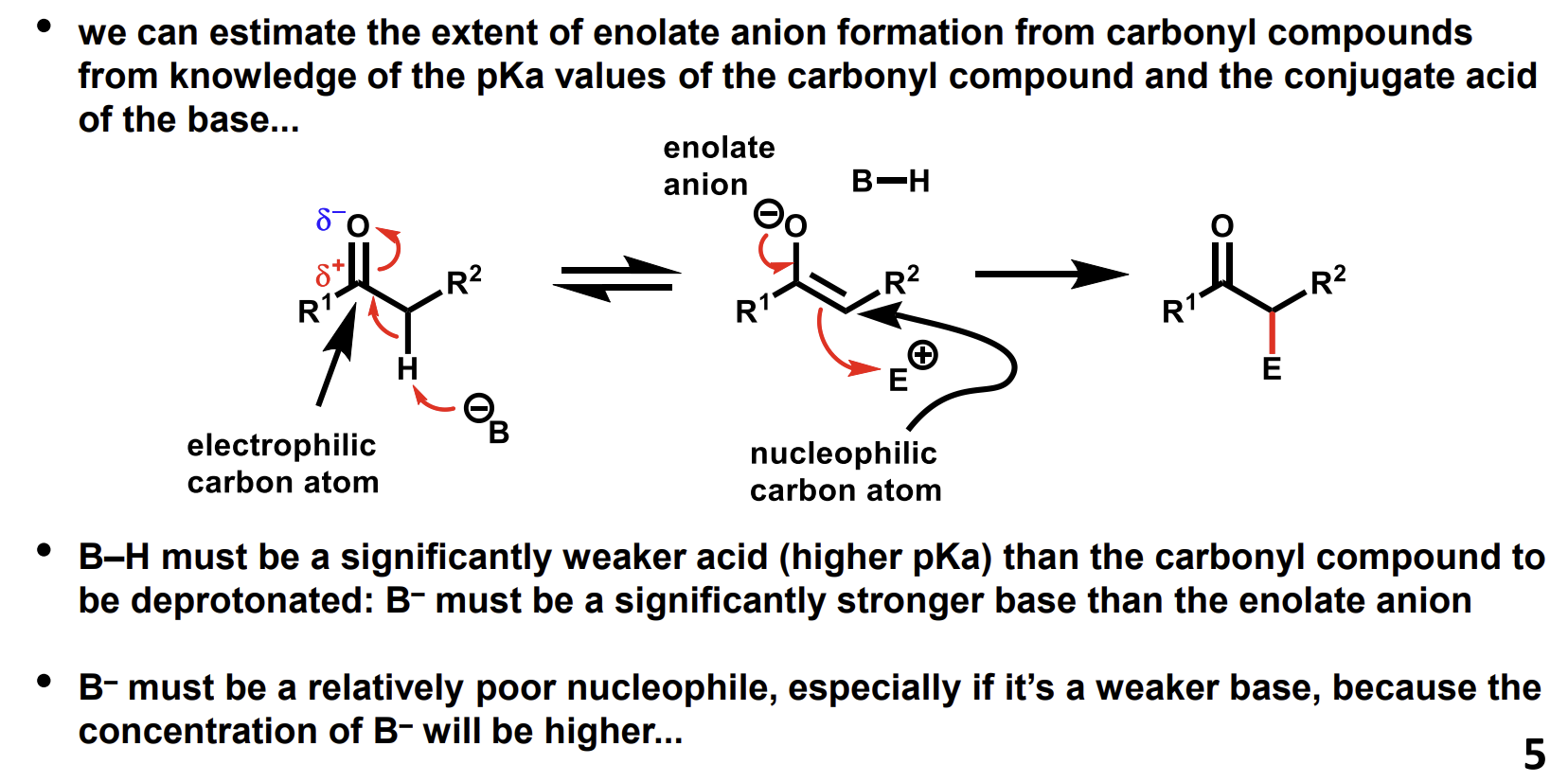
How do we choose the correct base to use to form enolates from electrophilic carbonyl compounds
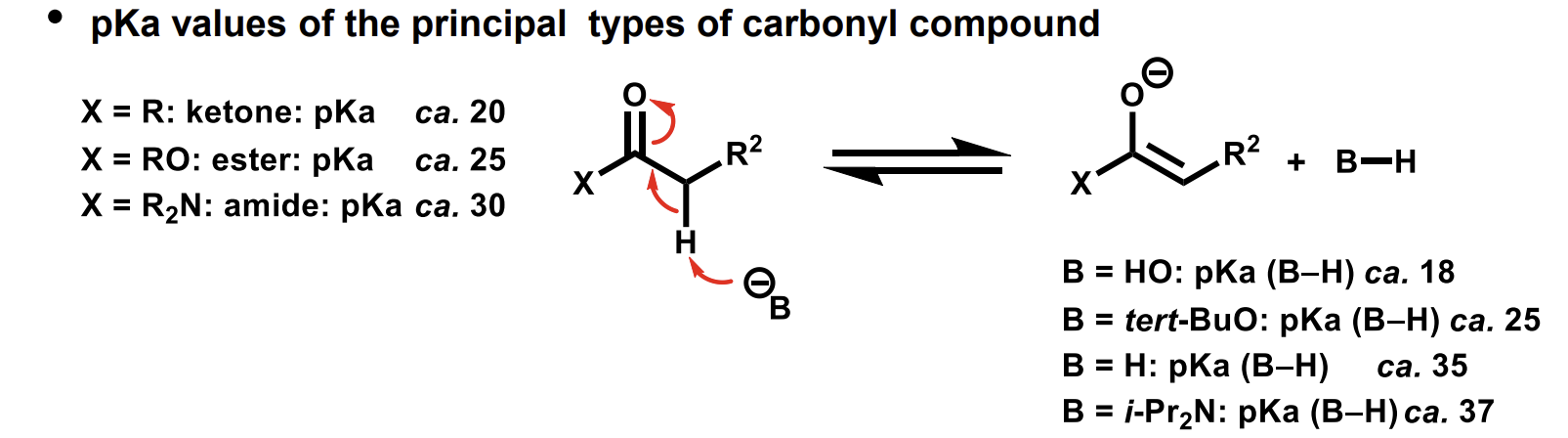
Different pKa values of ketones, esters and amides
The amide conjugate base (enolate) is less stable so is more reactive.
Enolate anions are ambident - what are the 2 alkylation reactions that can take place
Which 2 factors influence the proportions
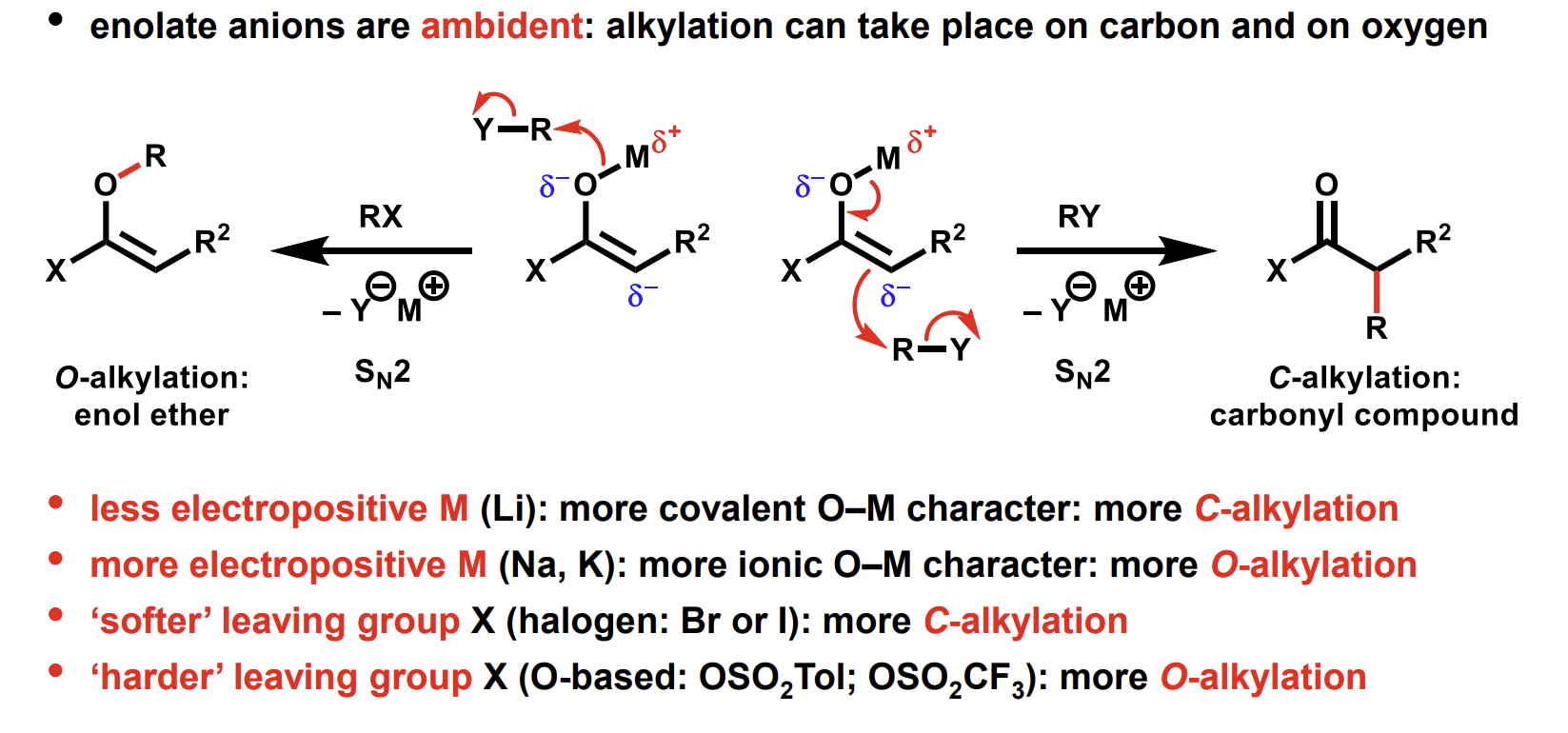
C-alkylation of enolate anions
What is a good base and solvent combination to use
Li is solvated effectively due to its charge density
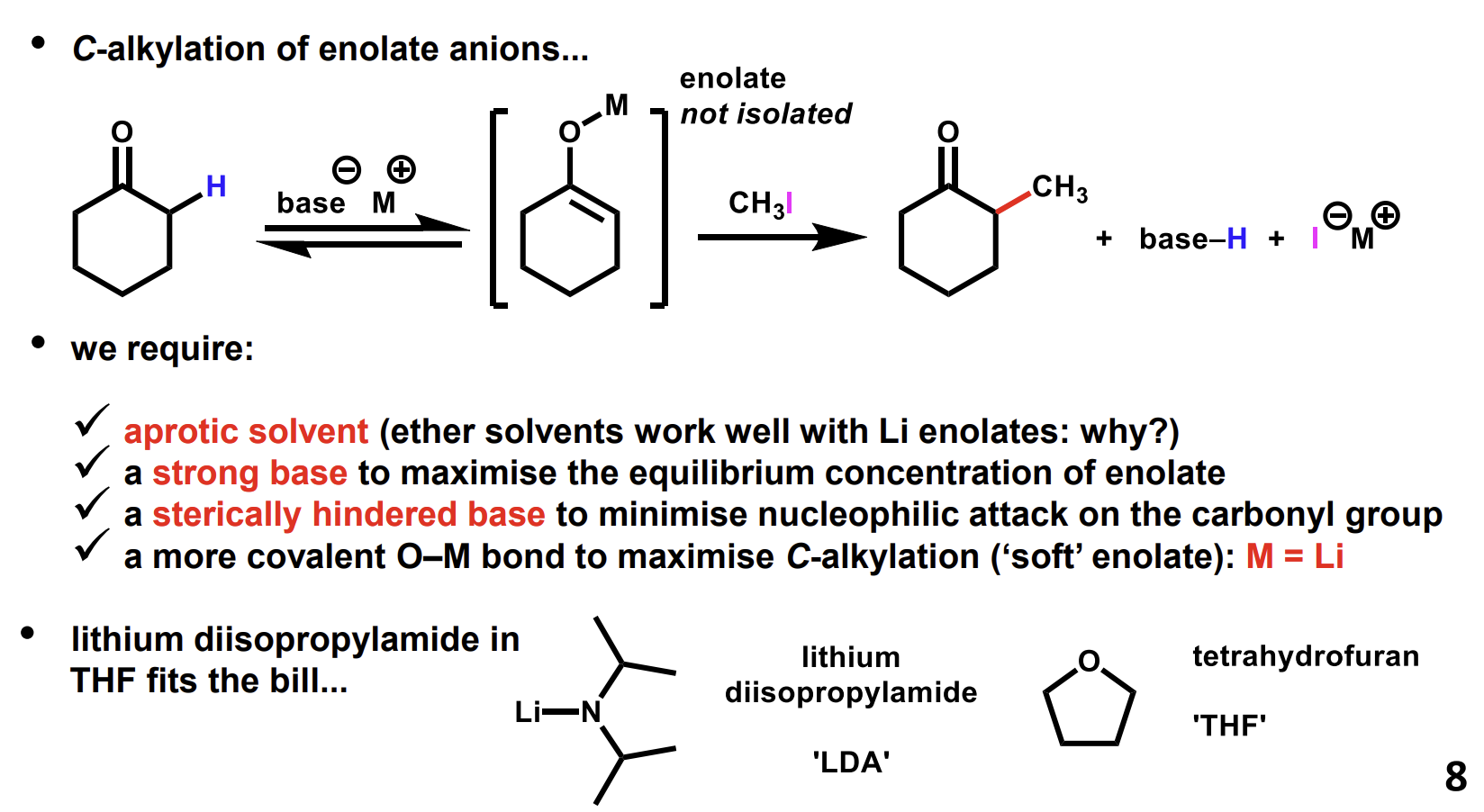
Nitrile alkylation
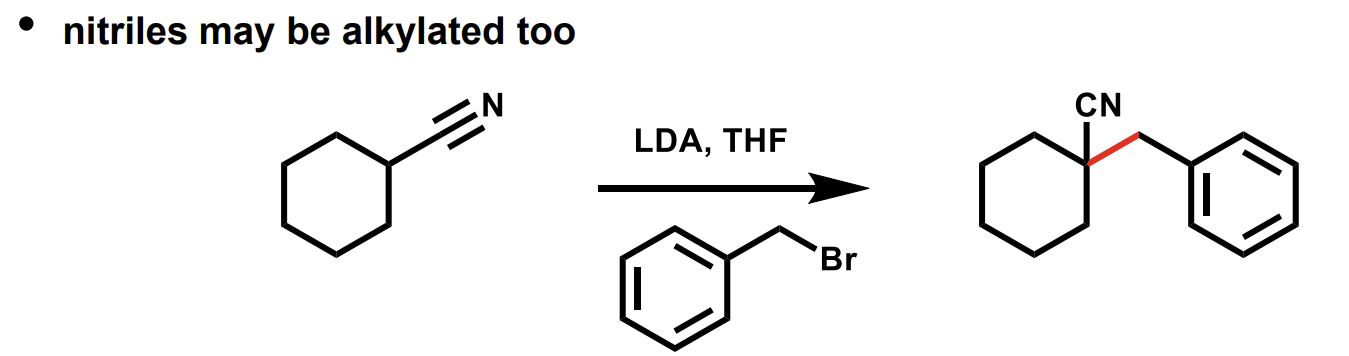
aldol reaction - enolate reaction with carbonyl compounds
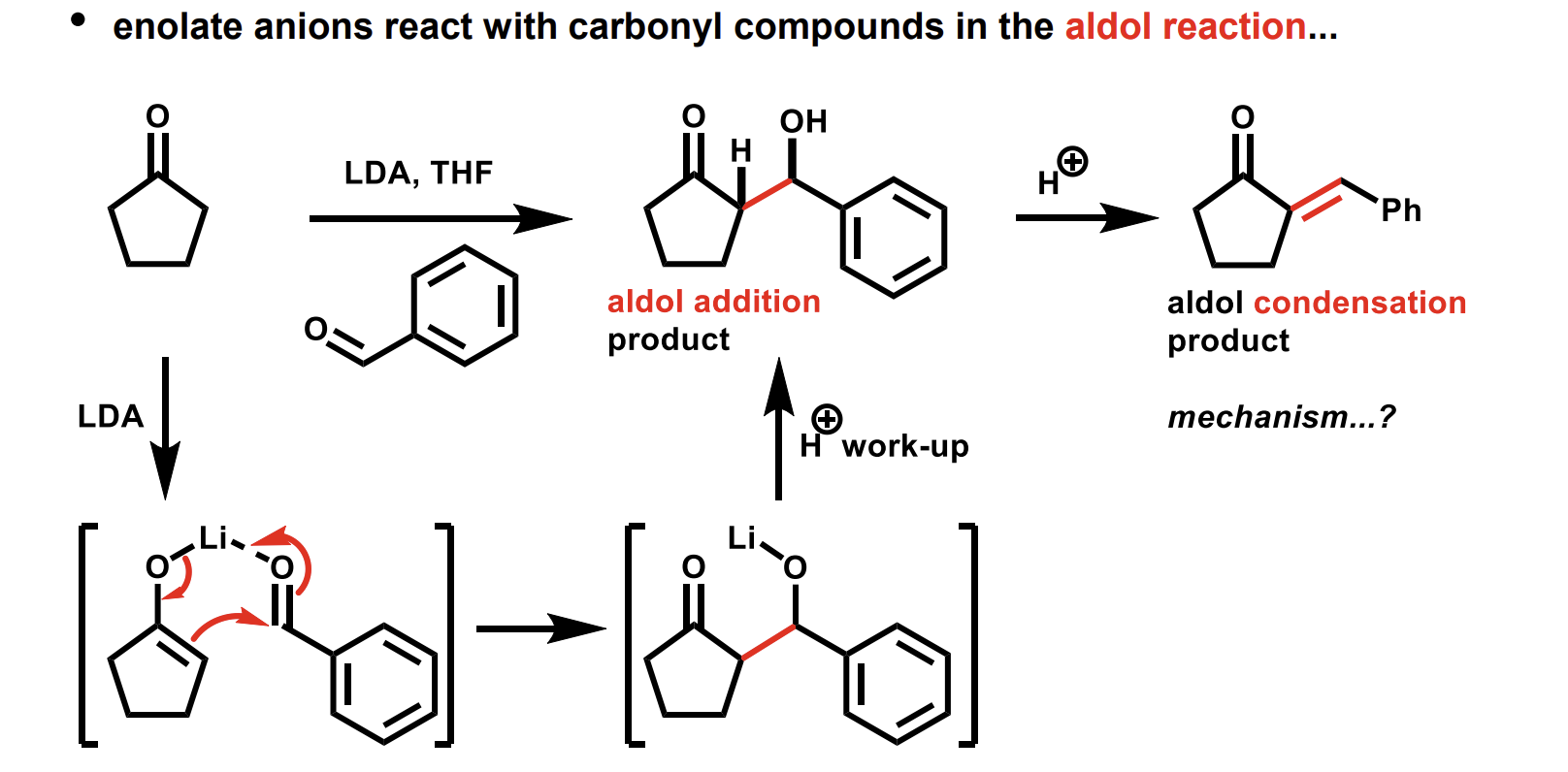
aldol reaction catalysed by a weak base or by an acid
Enolate reactions with acylating agents (like esters)
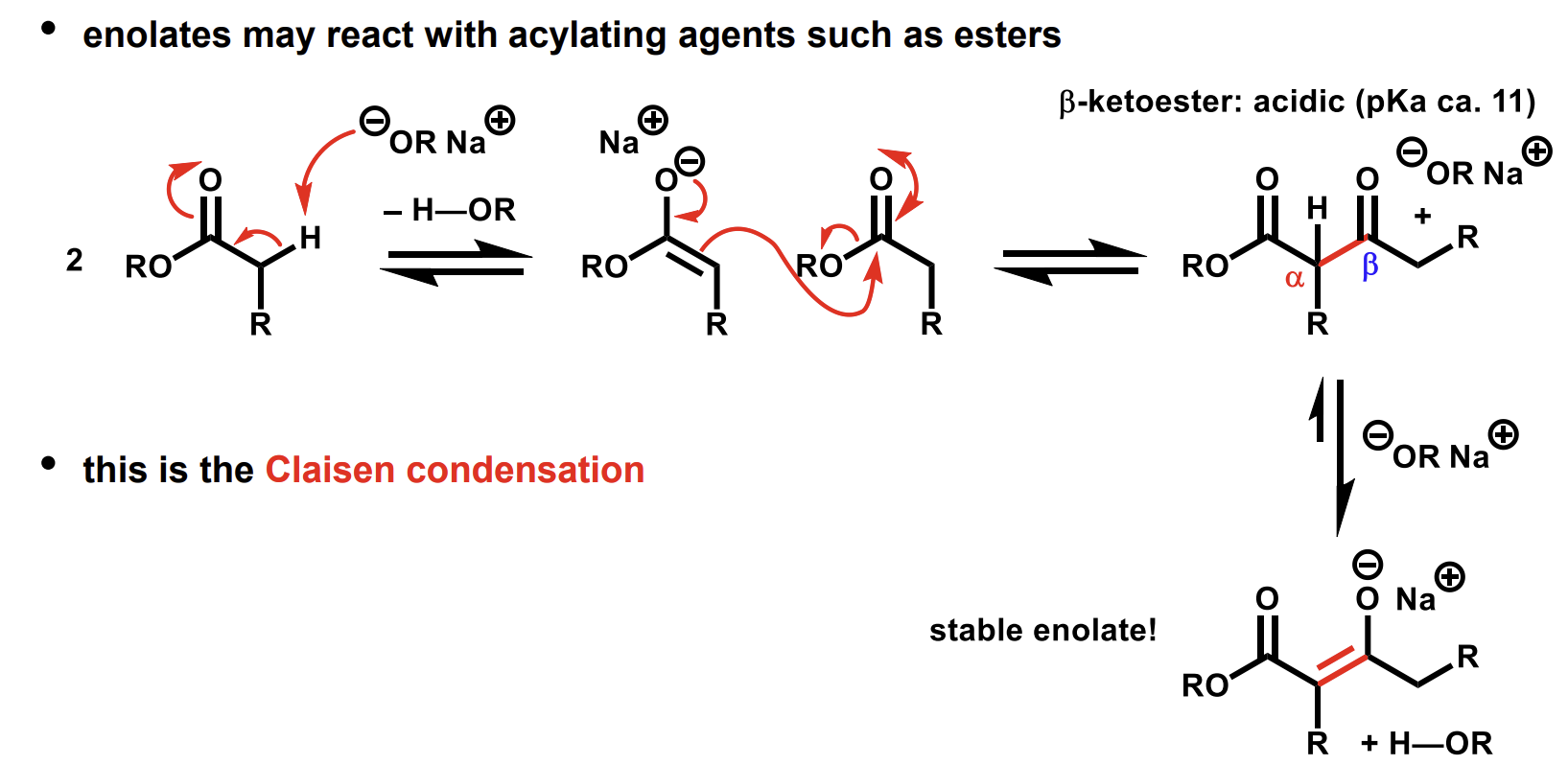
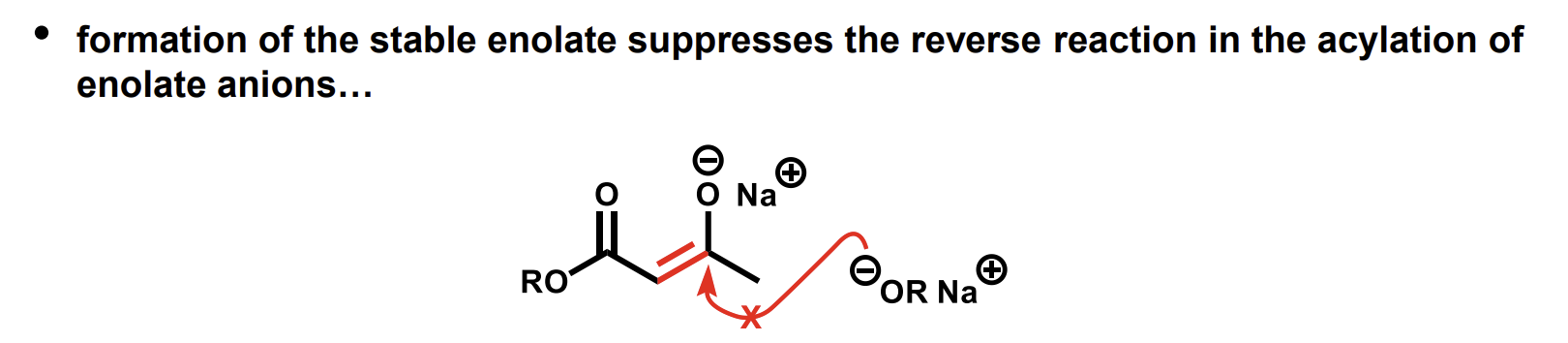
Why is the equilibrium far towards the stable enolate
The nucleophile alkoxide is not going to attack the negatively charged enolate
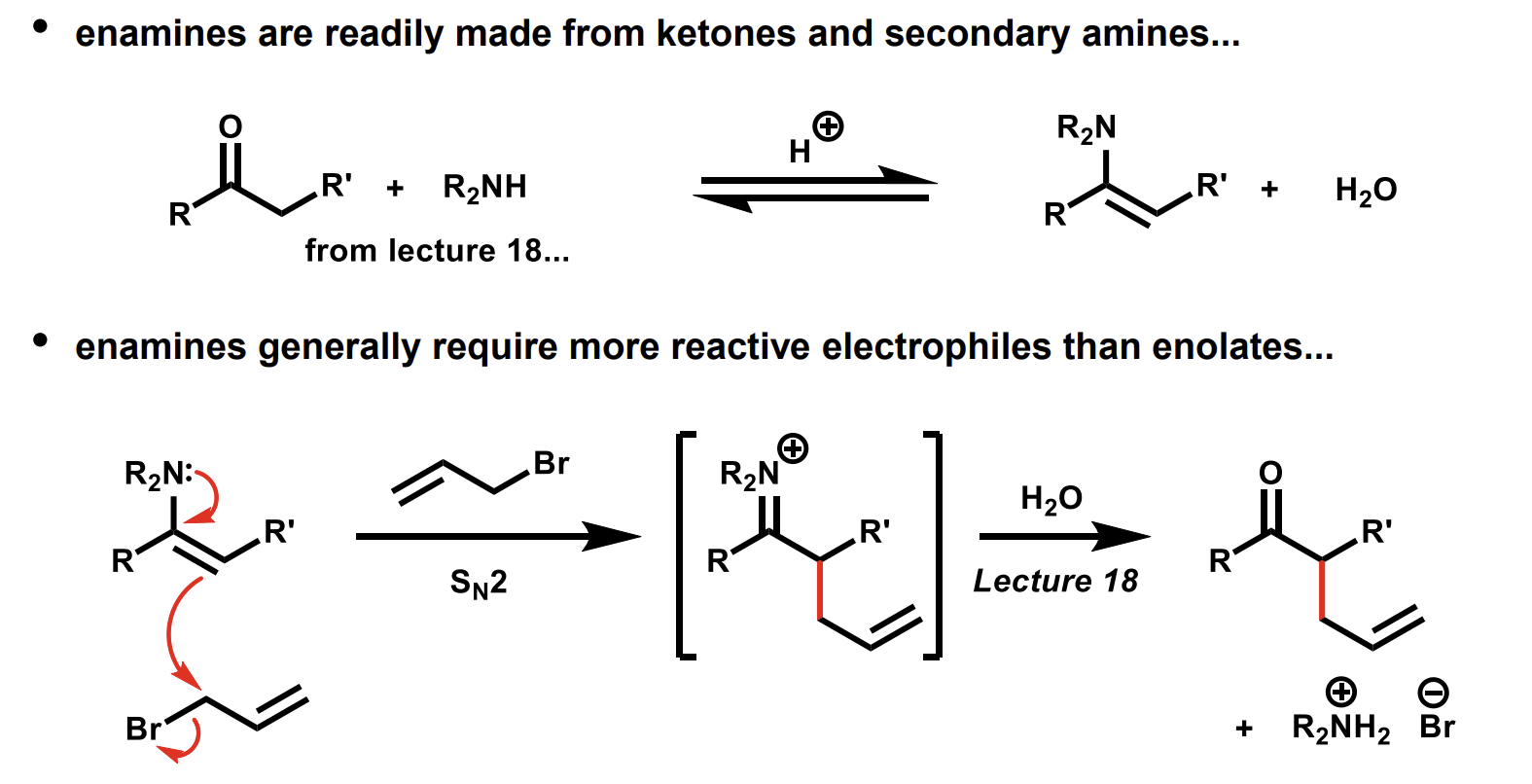
enamine reactivity compared to enolates
They are rather similar to enolates but are less reactive(the N has fewer lone pairs than O-)
Enamines can form the same products as enolates with a little workup.
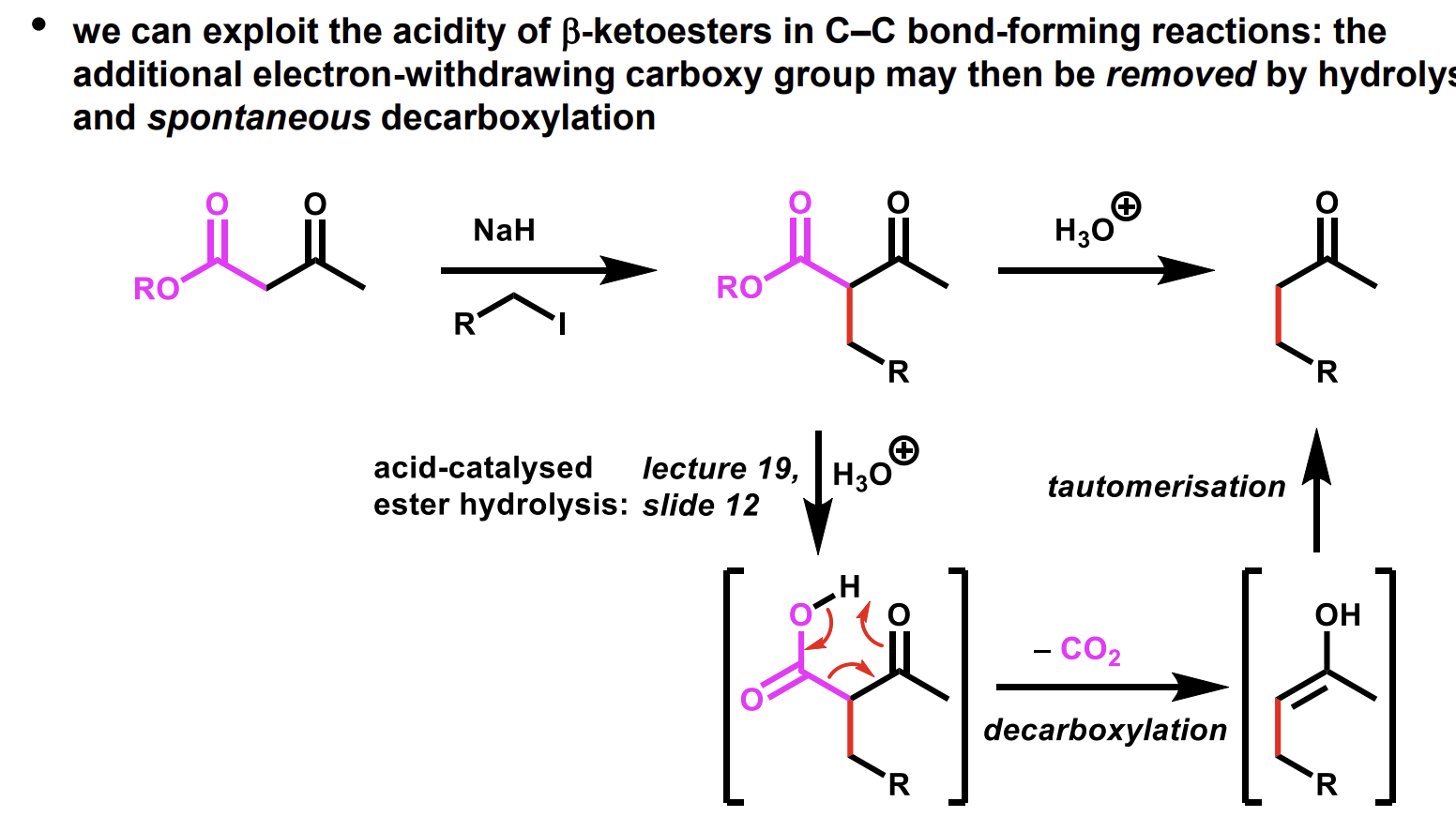
How can the relatively high acidity of beta-ketoesters be used
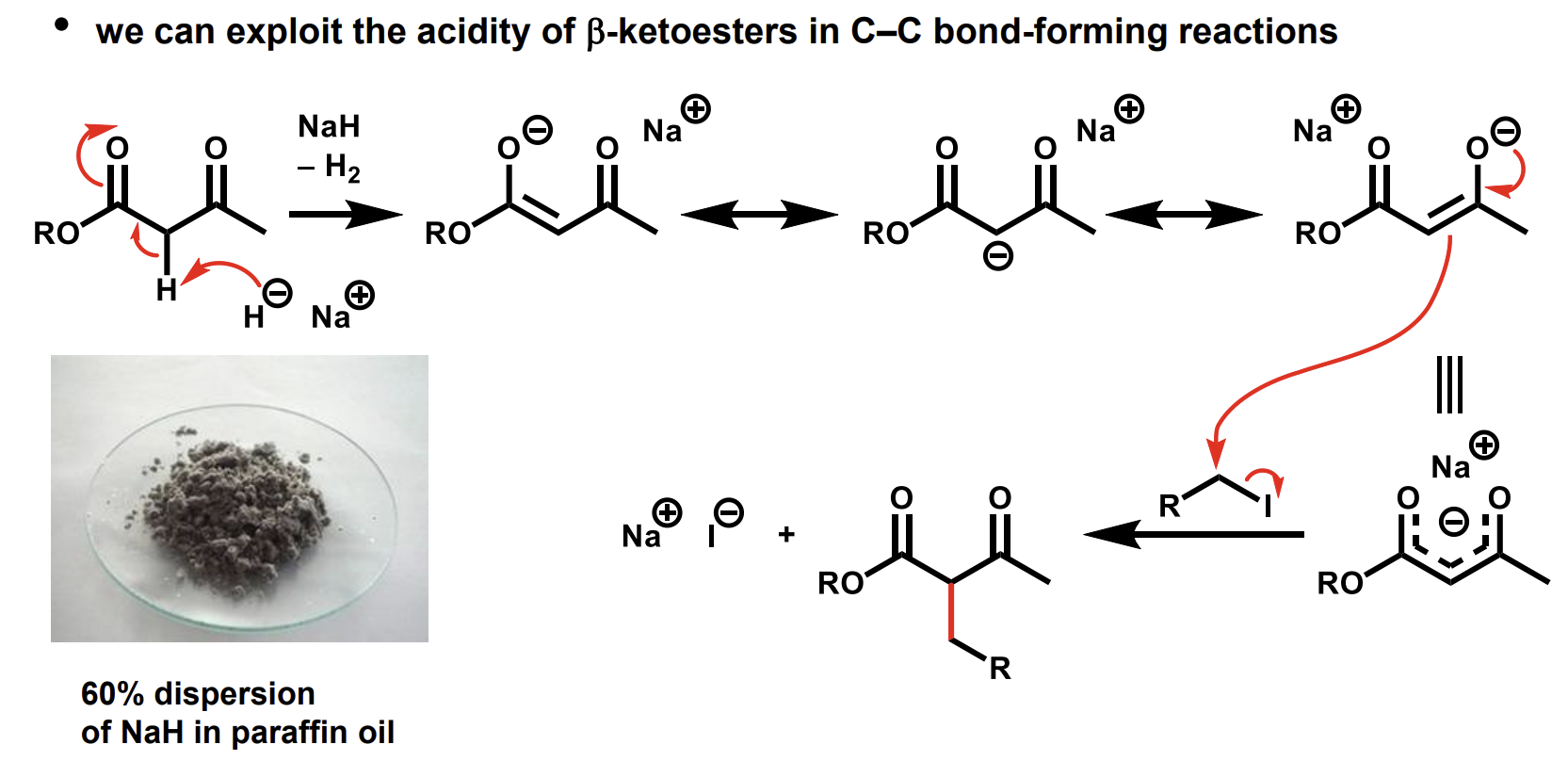
How can we remove the additional carboxyl group
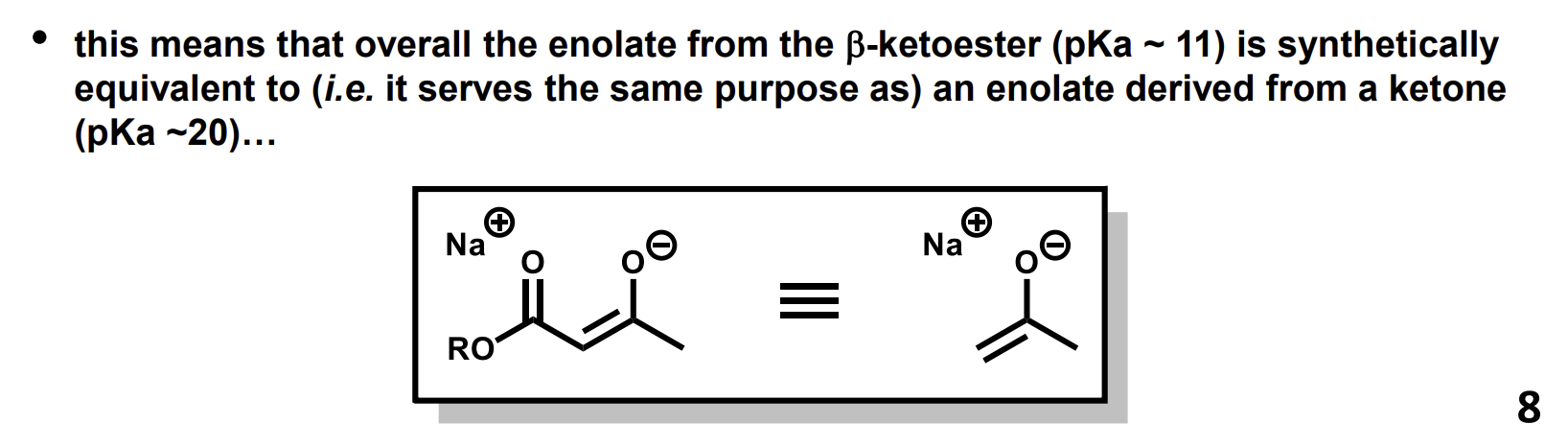
What are beta-ketoesters synthetically equivalent to
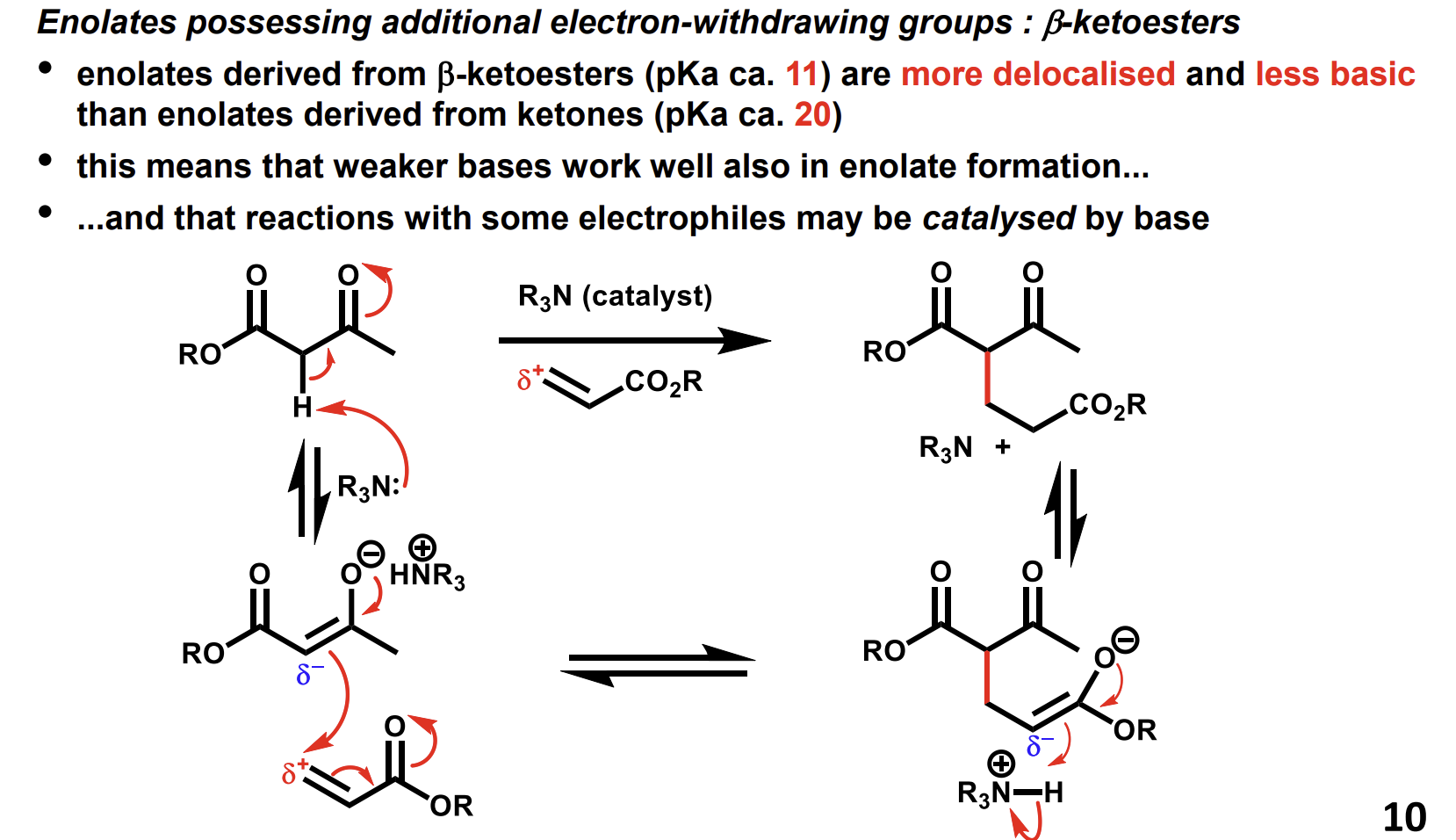
What is the benefit of beta-ketoester enolates being less basic than ketone enolates
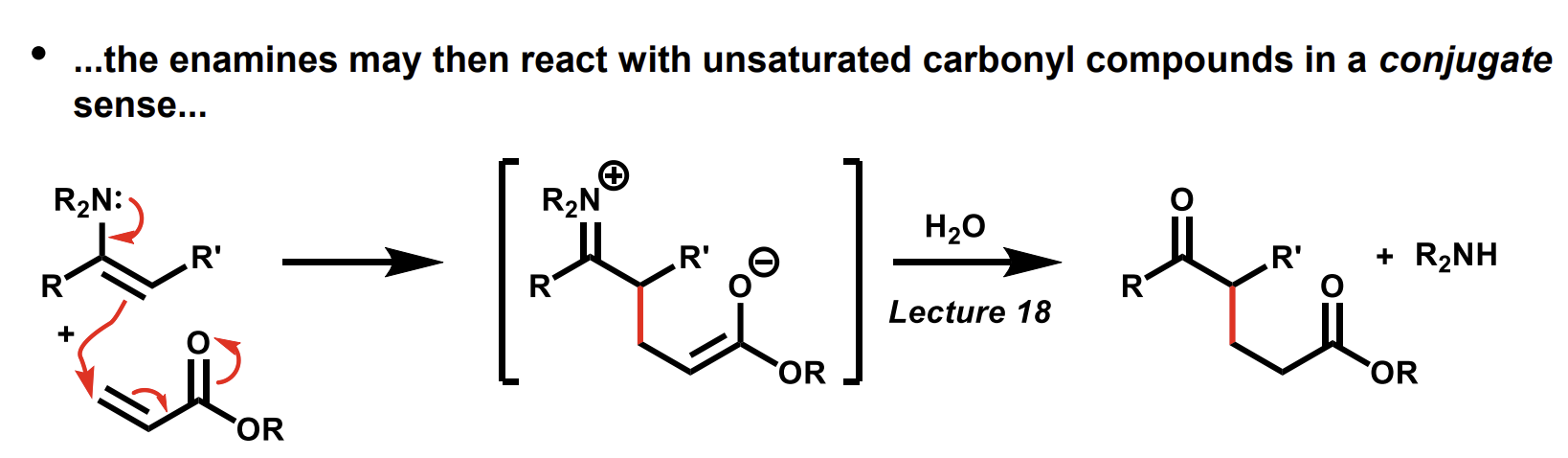
How do enamines react with unsaturated carbonyl compounds
Forms a new C-C bond