Lecture 6 - Electric Potential and Currents
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Electric Potential Energy
When a charge, q, moves from point a to point b in an electric field, the change in its PE is equal to the work down on it by the electric force
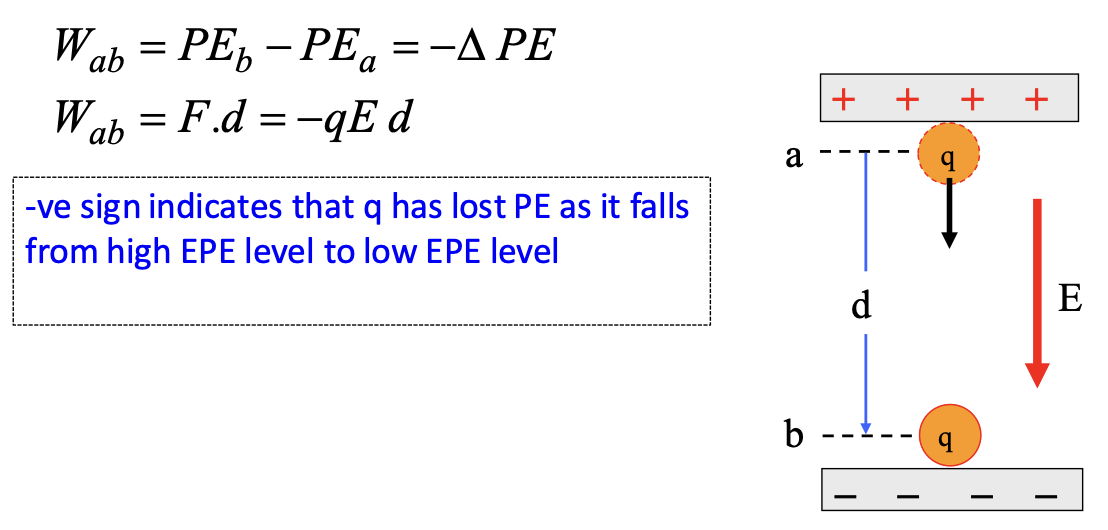
The larger the charge the larger the…
electric potential energy
Electric Potential V Equation
V(a) = PE(a)/q
Unit = Volts
relationship between V and E
V = W/q → W = -qV
E = F/q AND W = Fd
W = qEd
therefore: E =-V/d
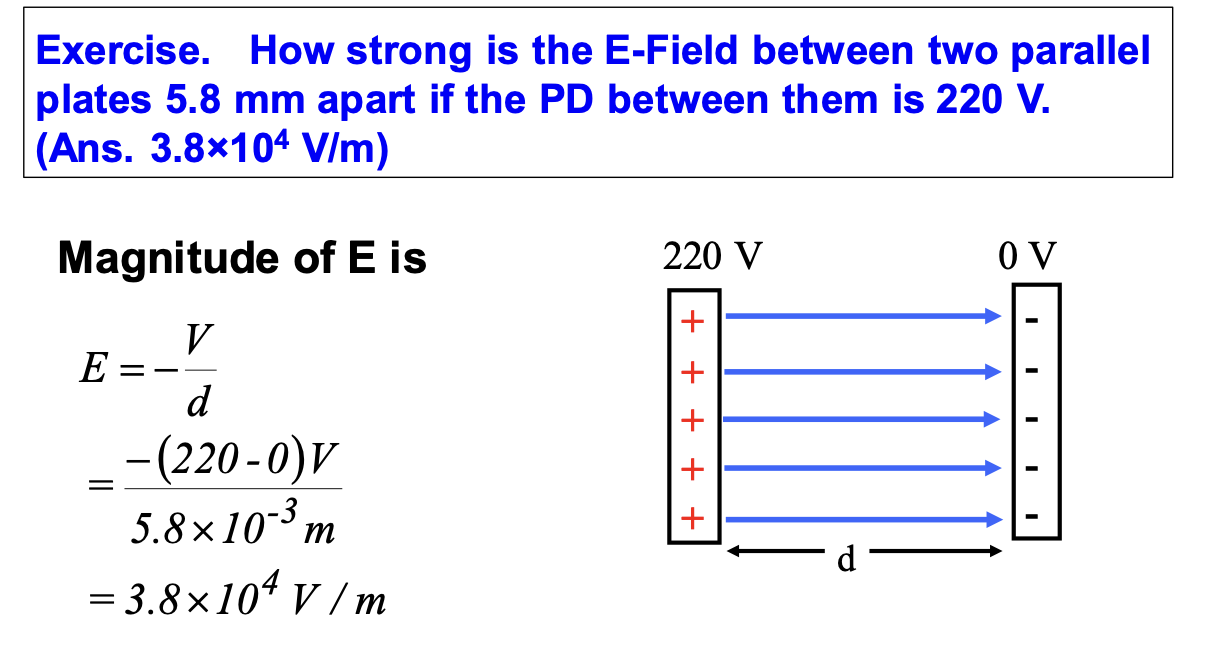
Battery in car is rated as 12V, what does this mean
12V terminal is at higher potential and the other is at 0 potential, potential difference between the terminal is 12V
when you switch on your headlights, what does the battery do?
the battery does 12V of work in pushing each coulomb of charge through the filament of the headlight
electric cell
a cell transforms chemical energy into electrical energy
chemical reactions within the cell create potential difference between the terminals
this potential difference can be maintained even if a current is kept flowing, until one or the other terminal is completely dissolved
many cells connected = battery
Electric Current
the amount of charge flowing per unit time at any point in the circuit
battery in circuit charges
long side = positive
short side = negative
electrons flow from the negative to positive terminal
Ohm’s Law
V = IR
Why are resistors used in circuits
used to limit the amount of current flowing through the circuit
symbol on circuit is a jagged line
resistivity
resistivity of any material is directly proportional to its length L and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area A
NOTE: p = the resistivity of the material in ohm metres
R = p * L/A
If a wire is stretched to twice its original length, what will be its new resistance
new resistivity = 4x the previous resistance
Temperature and resistivity
Electric Power
Electric energy can be transformed into other forms of energy such as mechanical, heat and light energy
POWER is the energy transformed by a device by unit time
P = IV = I²R = V²/R
Electron Volt
1 eV is the energy an electron gains or loses when acceleration through a potential difference of 1 Volt
1 eV = 1.60 × 10^(-19) J
Capacitor
a device used to store electric charge, consisting of two conductors separated by an insulator
unit = farad (F)
Capacitance equation
C =ε₀ A/d
A = area
d = distance
ε₀ = permittivity of free space
Dielectric material in capacitor
C = k(ε₀ A/d)
when inserted between the plates of an empty capacitor, it increases the capacitance by a factor k
EXAMPLES:
vacuum = 1
teflon = 2.1
water = 80.4
charge and capacitance equation
Q = CV
Storage of electric energy
in charging up capacitor the battery does work in transferring the charge from one plate to the other This energy is stored in the capacitor as electric potential energy
W = 0.5 Q/V
W = 0.5 CV²
Q = CV
W = 0.5 x Q²/C
use of capacitors
electronic circuits
RAM chaos
electronic flash camera
mobile x-ray unit
defibrillators